Alzheimer's Disease Market Summary
- The Alzheimer’s disease market in the 7MM is valued at approximately USD 5,048 million in 2025.
- The Alzheimer’s disease market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 23.7% by 2034 in leading countries like US, EU4, UK and Japan
Alzheimer’s Disease Market and Epidemiology Analysis
- The current Alzheimer’s disease market includes approved therapies such as LEQEMBI (lecanemab), along with off-label therapies like galantamine, memantine, and others, contributing to a Alzheimer’s disease market size of USD 3,610 million in the 7MM in 2023. The Alzheimer's Disease market size is expected to increase with the projected launch of emerging therapies during the forecast period (2024–2034).
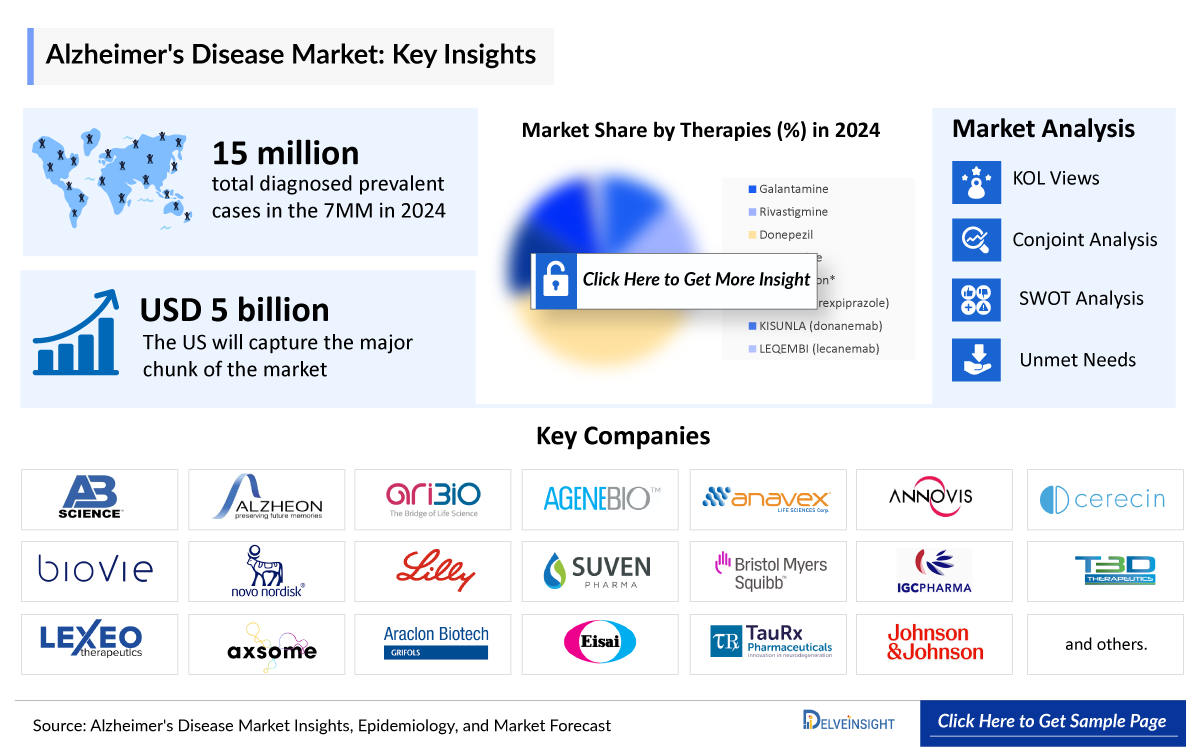
- In 2023, the 7MM reported approximately 15,840 thousand diagnosed prevalent cases of Alzheimer’s disease, reflecting a significant disease burden. This high prevalence underscores the need for innovative treatments to address the rising impact on healthcare systems and patient care.
- In 2023, among the EU4 and the UK, Germany accounted for the highest diagnosed prevalent cases of Alzheimer’s disease, representing 30% of the total cases, followed by France (24%). Analysis by DelveInsight’s experts indicates that the overall diagnosed prevalent cases of Alzheimer’s disease are expected to rise in the coming years.
- According to DelveInsight analysis, nearly 2,325 thousand males and 4,650 thousand females were affected with Alzheimer’s disease in the US in 2023. DelveInsight estimates that these numbers will increase by 2034.
- DelveInsight’s epidemiological model estimates that in 2023, the 75–84 age group in the EU4 and the UK had the highest Alzheimer’s disease cases, totaling 2,300 thousand. In contrast, the under 65 age group had the fewest cases, with nearly 125 thousand recorded.
- DelveInsight’s estimates indicate that in 2023, Japan had approximately 2,470 thousand diagnosed prevalent cases of agitation associated with Alzheimer’s disease, a figure expected to grow by 2034. This behavioral symptom, marked by restlessness, irritability, aggression, and anxiety, significantly diminishes patient quality of life and heightens caregiver strain.
- In September 2024, Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare approved KISUNLA (donanemab-azbt, 350 mg/20 mL) for intravenous infusion every four weeks. Developed by Eli Lilly, the drug targets adults with early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease, including mild dementia, both with confirmed amyloid pathology.
Alzheimer’s Disease Market size and forecast
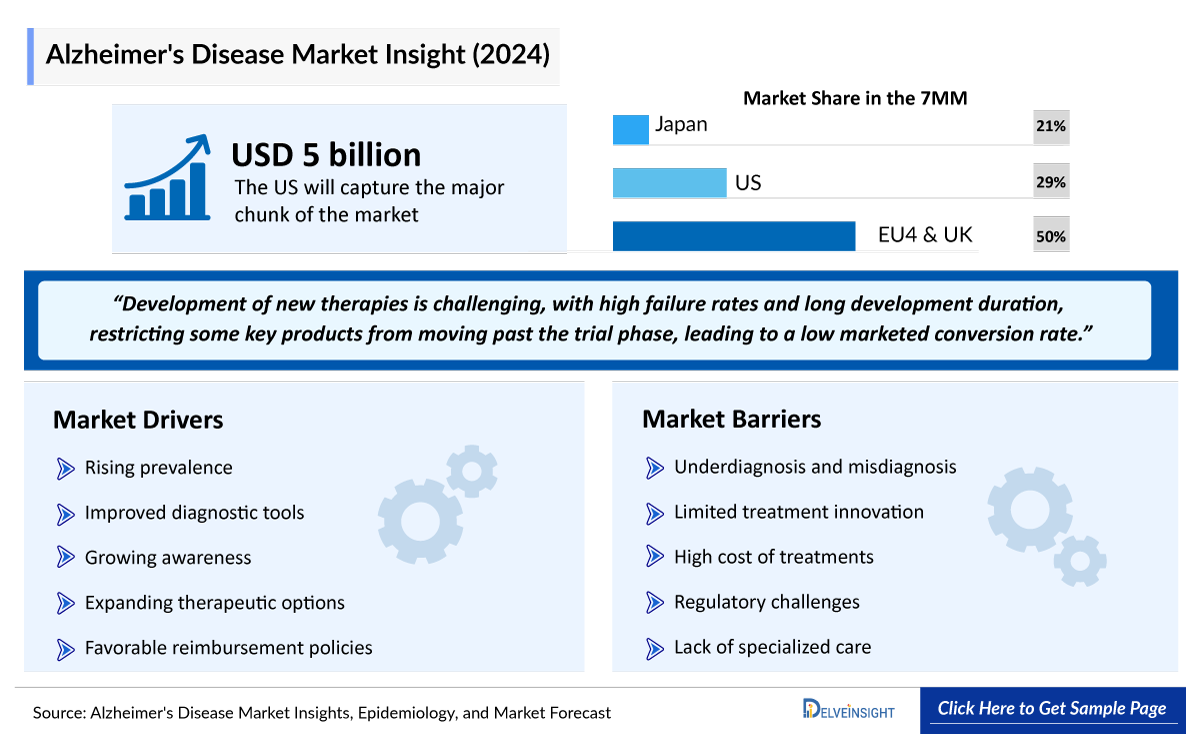
- 2025 Market Size: USD 5,048 million in 2025
- 2034 Projected Market Size: USD 34,335 million in 2034
- Growth Rate (2025-2032): 23.7% CAGR
- Largest Market: United States
Request for Sample Report @ Alzheimer’s Disease Drugs Market
Key Factors Driving the Growth of the Alzheimer’s Disease Market
Rising Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence
DelveInsight’s analysis indicates that in 2024, there were around 15 million diagnosed prevalent cases of Alzheimer's disease across the 7MM. These numbers are expected to grow steadily and are projected to reach 21.5 million by 2034, reflecting the increasing aging population and advancements in diagnostic capabilities.
Strong Alzheimer’s Disease Clinical Trial Activity
Over 25 molecules are in late-stage clinical trials, targeting a broad spectrum of Alzheimer’s disease, from early-stage to the most severe cases. Some of the promising therapies in clinical trials include BioVie's Bezisterim (NE3107), AB Science's Masitinib (AB1010), Annovis Bio’s Buntanetap, Cassava Sciences' Simufilam (PTI-125), TauRx Therapeutics' Hydromethylthionine mesylate (TRx0237), Novo Nordisk's semaglutide (NN6535), Eli Lilly's Remternetug (LY3372993), Alzheon's ALZ-801 (valiltramiprosate), Eisai's E2814, UCB Pharma's Bepranemab, and GemVax & KAEL’s GV1001, among others.
Strategic Pricing for Regional Adoption
With strong regulatory momentum in the US and Japan, and market access challenges in Europe, developers must optimize global trial designs and pricing to boost regional adoption and payer support.
DelveInsight’s “Alzheimer’s Disease Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of the Alzheimer’s disease, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the Alzheimer’s disease market trends in the United States, EU4 and the UK (Germany, France, Italy, Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The Alzheimer’s Disease market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, and market share of the individual therapies, current and forecasted 7MM Alzheimer’s disease market size from 2020 to 2034. The Alzheimer’s disease treatment market report also covers current Alzheimer’s disease treatment practice, market drivers, market barriers, SWOT analysis, reimbursement and market access, and unmet medical needs to curate the best of the opportunities and assess the underlying potential of the Alzheimer’s disease market.
Download Our In-Depth Research Report Now! @ LEQEMBI Market
Scope of the Alzheimer’s Disease Market Report | |
|
Study Period |
2020 to 2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
The US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and UK, Japan |
|
Alzheimer’s Disease Market |
|
|
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Size | |
|
Alzheimer’s Disease Companies |
BioVie, AB Science, Cassava Sciences, Eli Lilly, TauRx Therapeutics, Novo Nordisk, KeifeRx, Eli Lilly, AriBio, Cerecin, Alzheon, Neurim Pharmaceuticals/Syneos Health, Athira Pharma, Annovis Bio, Anavex Life Sciences, AgeneBio, Eisai, and others. |
|
Alzheimer’s Disease Epidemiology Segmentation |
|
Alzheimer’s Disease Understanding
Alzheimer’s Disease Overview
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive, irreversible neurological disorder, primarily impacting memory, reasoning, and cognitive abilities. It is the leading cause of dementia, responsible for roughly 60–80% of all cases. Though often emerging in the mid-60s, early-onset Alzheimer’s can affect individuals as young as their 40s or 50s, albeit rarely. Initial symptoms commonly include memory loss that significantly interferes with daily life, followed by confusion, language difficulties, impaired judgment, and behavioral changes. The disease’s exact cause remains unknown, but it is associated with abnormal accumulations of Amyloid Beta protein plaques and tau protein tangles in the brain, which disrupt cellular communication and lead to cell death. Increasing age and family history are recognized as key risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease remains challenging due to its gradual onset and overlapping symptoms with other cognitive disorders. The diagnosis primarily relies on clinical assessments, including a detailed medical history, cognitive tests, and evaluations of memory, reasoning, and language skills. Neuroimaging techniques, like MRI and PET scans, help detect structural brain changes, while biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid can reveal amyloid and tau protein abnormalities. However, definitive diagnosis often occurs post-mortem through brain tissue examination.
The complexity of Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis is compounded by variability in symptom progression and the absence of a single diagnostic test. Additionally, the need for specialized tools and resources makes early diagnosis difficult, especially in low-resource settings. Misdiagnosis risks are high, which can delay appropriate interventions and add stress for patients and caregivers. Improved diagnostic accuracy through advancements in biomarker research and neuroimaging is critical to enabling timely, targeted treatments and addressing these diagnostic challenges in Alzheimer’s disease.
Further details related to diagnosis are provided in the report…
Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
The treatment landscape for Alzheimer’s disease centers around managing symptoms rather than halting disease progression. Current FDA-approved treatments, including cholinesterase inhibitors and the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine, temporarily aid cognitive functions but do not reverse the underlying pathology. Recently, anti-amyloid monoclonal antibodies, like aducanumab, have targeted amyloid plaques to potentially slow cognitive decline, though these options have faced scrutiny regarding efficacy and safety. Additionally, non-pharmacological interventions—such as cognitive therapy, physical exercise, and lifestyle modifications—are vital components of patient care to support mental and physical health.
However, treatment challenges persist. The progressive nature of Alzheimer’s disease, coupled with an incomplete understanding of its causes, limits therapeutic advancements. Effective treatment is further hindered by high costs, potential adverse effects, and the variability of patient responses. Consequently, addressing these challenges requires ongoing research to develop therapies that effectively target Alzheimer’s disease’s complex pathology and enhance patients' quality of life.
Further details related to treatment are provided in the report…
Alzheimer’s Disease Epidemiology
As the market is derived using a patient-based model, the Alzheimer’s disease epidemiology chapter in the Alzheimer's Disease market report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by, Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease, Gender-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease, Age-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease, Severity-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease, Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Agitation in Alzheimer’s Disease, and Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Psychosis in Alzheimer’s Disease in the 7MM covering, the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
Key Findings from Alzheimer’s Disease Epidemiological Analyses and Forecast
- In the assessment done by DelveInsight, the estimated total diagnosed prevalent cases of Alzheimer’s disease in Japan were nearly 3,920 thousand in 2023.
- In 2023, the United States represented approximately 44% of diagnosed Alzheimer’s disease cases across the 7MM, with 6,980 thousand cases, a figure anticipated to increase by 2034, as per DelveInsight’s estimates.
- In Japan, there were nearly 1,390 thousand diagnosed males and 2,530 thousand cases of females with Alzheimer’s disease in 2023, highlighting gender distribution among the population.
- Age-specific cases in the US are categorized into four groups: under 65, 65–74, 75–84, and 85+ years. In 2023, the 75–84 age group held the highest prevalence with nearly 2,790 thousand cases, whereas the under-65 group recorded the lowest with nearly 175 thousand cases.
- Alzheimer’s disease is also classified by severity: mild cognitive impairment (MCI), mild, moderate, and severe dementia. Within EU4 and the UK, the MCI stage had the highest prevalence with around 2,560 thousand cases in 2023, while severe dementia showed the lowest with 645 thousand cases.
- The US reported nearly 5,233 thousand diagnosed cases of agitation associated with Alzheimer’s disease in 2023, which is expected to grow by 2034.
- In Japan, approximately 2030 thousand cases of psychosis in Alzheimer’s disease were documented in 2023, a number forecasted to increase over time.
Alzheimer’s Disease epidemiology segmentation
- Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Gender-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Age-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Severity-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Alzheimer’s Disease
- Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Agitation in Alzheimer’s Disease
- Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Psychosis in Alzheimer’s Disease
Unlock comprehensive insights! Click Here to Purchase the Full Report @ Alzheimer’s Disease Prevalence
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Recent Developments and Breakthroughs
- In September 2025, Eisai’s investigational anti-MTBR tau antibody, etalanetug (E2814), received FDA Fast Track designation for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease.
- In September 2025, Actinogen Medical Limited (ASX: ACW) announced the successful completion of its scheduled Type C meeting (written response) with the U.S. FDA regarding Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
- In September 2025, Alzinova AB announced that the U.S. FDA approved its Investigational New Drug (IND) application for a planned Phase II clinical trial of ALZ-101, a vaccine candidate targeting Alzheimer’s disease.
- In August 2025, Eisai and Biogen announced FDA approval of the BLA for LEQEMBI® IQLIK™, a once-weekly subcutaneous autoinjector (360 mg/1.8 mL) for maintenance dosing of lecanemab-irmb. The injection can be administered in about 15 seconds.
- In August 2025, Cognition Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: CGTX) announced that it received final minutes from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) following its end-of-Phase 2 meeting held on July 9, 2025. The FDA confirmed that the proposed Phase 3 program design for zervimesine (CT1812), an investigational therapy for Alzheimer’s disease, may be sufficient to support a future New Drug Application (NDA) filing.
- In July 2025, Eisai and Biogen presented new data at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference showing the benefits of continuous treatment with lecanemab-irmb (LEQEMBI®), an anti-amyloid beta protofibril antibody for early Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Lecanemab uniquely targets both amyloid plaques and protofibrils, potentially affecting tau protein downstream.
- In July 2025, ProMIS Neurosciences received FDA Fast Track designation for PMN310, its lead antibody therapy targeting toxic misfolded proteins in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), aiming to accelerate development and regulatory review.
- In July 2025, NKGen Biotech received FDA authorization for an Expanded Access Program (EAP) to use its NK cell therapy, troculeucel, in multiple neurodegenerative diseases—including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, ALS, MSA, PSP, FTD, CBD, MS, and Lewy Body Dementia—beyond its current Phase 2a trial in moderate-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
- In July 2025, Cognition Therapeutics held an end-of-Phase 2 meeting with the FDA to review results of zervimesine (CT1812) for Alzheimer’s disease and to discuss plans for a Phase 3 program to support a new drug application.
- In July 2025, the FDA cleared the new Magstim Rapid TMS system for research, clinical use, and treatment of pain. This next-generation non-invasive neuromodulation device supports studies and therapy for conditions including depression, OCD, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, autism, and stroke, featuring upgraded touchscreen, user-friendly software, and improved data management.
- In July 2025, Quest Diagnostics announced plans to offer the FDA-cleared Lumipulse® G pTau 217/β-Amyloid 1-42 Plasma Ratio test, the first blood-based diagnostic to aid in identifying amyloid pathology linked to Alzheimer's disease in adults aged 50 and older with cognitive decline.
- In July 2025, Eli Lilly announced FDA approval of a new dosing schedule for Kisunla (donanemab-azbt), a once-monthly amyloid-targeting therapy for early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease, including mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia stages. The updated schedule reduces amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA-E) while maintaining effectiveness in amyloid plaque removal.
- In June 2025, Eli Lilly and Company (NYSE: LLY) announced that the U.S. FDA approved a label update for Amyvid (florbetapir F 18 injection), used for brain imaging to estimate amyloid plaque density in patients with cognitive impairment being evaluated for Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive decline causes.
- In June 2025, GE HealthCare (Nasdaq: GEHC) announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved an updated label for its PET imaging agent Vizamyl™ (flutemetamol F 18 injection) for beta-amyloid detection. The revised label expands indications, enables quantitative analysis of scans, and removes prior limitations such as restrictions on monitoring patient response to anti-amyloid therapy.
- In June 2025, Cognition Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: CGTX) announced it will hold an end-of-Phase 2 meeting with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on June 9 to review results from the Phase 2 ‘SHINE’ study of zervimesine (CT1812) in mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease, and to discuss plans for a Phase 3 program aimed at regulatory approval.
- In May 2025, the FDA granted Breakthrough Device designation to Fujirebio Diagnostics’ Lumipulse G pTau217/ß-Amyloid 1-42 Plasma Ratio, an in vitro blood test for detecting amyloid plaques in adults aged 55+ showing signs of Alzheimer’s disease.
- In April 2025, the ApoE4 Alzheimer's Alliance, a new patient advocacy organization, was launched to amplify the voices of individuals with the ApoE4 gene. The Alliance aims to advocate for the unique needs of this community by working with U.S. policymakers and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Its mission includes pushing for accelerated progress toward innovative treatments and supportive policies for those impacted by Alzheimer's disease.
- In April 2025, Biogen Inc. (Nasdaq: BIIB) announced that the FDA granted Fast Track designation to BIIB080, an antisense oligonucleotide therapy targeting tau, for Alzheimer’s disease treatment, aiming to speed up its development and review.
- In February 2025, NKGen Biotech, Inc. received Fast Track designation from the FDA for its investigational drug, troculeucel, aimed at treating moderate Alzheimer's disease (AD).
- In January 2025, Beckman Coulter Diagnostics announced that the FDA granted Breakthrough Device Designation to its Access p‑Tau217/β-Amyloid 1-42 plasma ratio blood test, designed to help healthcare providers identify patients with amyloid pathology linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
- In January 2025, Eisai Co., Ltd. and Biogen Inc. announced that the FDA approved the Supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for lecanemab-irmb (LEQEMBI®) with once every four weeks IV maintenance dosing for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
- In January 2025, the FDA approved Amneal Pharmaceuticals' memantine/donepezil 14-10 mg and 28-10 mg extended-release capsules for the treatment of moderate to severe Alzheimer’s dementia, along with everolimus tablets for oral suspension, and granted tentative approval for rifaximin oral tablets.
- In January 2025, Spear Bio Inc. announced that its pTau 217 blood test received Breakthrough Device Designation from the FDA. This designation highlights the test’s potential to address the critical unmet need for millions of undiagnosed Alzheimer's patients in the U.S.
- In January 2025, BioArctic AB announced that the U.S. FDA has accepted Eisai's Biologics License Application (BLA) for the Leqembi subcutaneous autoinjector (SC-AI) for weekly maintenance dosing. Leqembi is indicated for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease in patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) or mild dementia, referred to as early AD.
- In Jan 2025, the U.S. FDA granted Fast Track designation to posdinemab, a phosphorylated tau-directed monoclonal antibody, being investigated for the treatment of early Alzheimer’s disease in the phase 2b AuTonomy study.
- In January 2025, Axsome Therapeutics announced plans to seek FDA approval for AXS-05 in Alzheimer’s disease agitation, despite mixed results in late-phase studies. AXS-05 is a combination of dextromethorphan and bupropion, already approved for treating major depressive disorder.
- In December 2024, Eli Lilly received regulatory approval in China for Kisunla, its anti-amyloid therapy for Alzheimer's disease, marking a significant milestone in the world's second-largest pharmaceutical market.
- In December 2024, Axsome Therapeutics reported that one Phase 3 trial of Auvelity met its primary goal in treating Alzheimer’s agitation, while another trial showed numerical improvement but lacked statistical significance. The company aims to provide an alternative to Rexulti, the only FDA-approved drug for Alzheimer’s agitation, developed by Lundbeck and Otsuka Pharmaceutical.
- In September 2024, Eli Lilly's Alzheimer's drug KISUNLA (donanemab) received approval in Japan, following its earlier U.S. approval in July. Kisunla is the second amyloid-targeting therapy available in Japan, after Eisai and Biogen's Leqembi (lecanemab). It is indicated for adults with early symptomatic Alzheimer's disease, including those with mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia, who have confirmed amyloid pathology.
Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Analysis
The drug chapter segment of the Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics market report encloses a detailed analysis of Alzheimer’s disease off-label drugs and late-stage (Phase-III and Phase-II) pipeline drugs. It also helps to understand the Alzheimer’s disease clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug, and the latest news and press releases.
Alzheimer’s Disease Marketed Drugs
LEQEMBI (lecanemab): Biogen Inc./Eisai Co., Ltd.
LEQEMBI, an FDA-approved treatment for Alzheimer’s, specifically targets patients in the Alzheimer’s disease or mild dementia stages. Developed as a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, LEQEMBI addresses amyloid ß (Aß) pathology by reducing both soluble and insoluble forms of Aß to slow disease progression.
With ongoing prescription expansion, the focus includes customized facility information on the drug, reimbursement support, and system efficiency enhancements. Approved by regulatory bodies in Great Britain (August 2024) and Japan (September 2023), LEQEMBI marks a significant milestone as the first approved therapy in Europe to target an Alzheimer’s-related pathology directly.
In May 2023, the UK’s Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) granted lecanemab designation under the Innovative Licensing and Access Pathway (ILAP). The MHRA, which oversees the regulation of medicines and medical devices in the UK, recognized lecanemab for this accelerated pathway to enhance patient access.
KISUNLA (Donanemab): Eli Lilly and Company
KISUNLA (donanemab-azbt), developed by Eli Lilly, targets amyloid plaques in patients with Alzheimer’s disease or early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease confirmed by amyloid pathology. This humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody addresses amyloid ß accumulation—a key contributor to Alzheimer’s by focusing on insoluble N-truncated pyroglutamate amyloid beta plaques.
Administered intravenously every four weeks, KISUNLA’s structured dosing regimen was informed by Phase III TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 2 trial data, supporting approvals in the US (July 2024) and Japan (September 2024). Unique to KISUNLA is the potential to halt treatment once plaques clear, which may optimize efficacy and lower treatment costs.
In June 2021, Eli Lilly’s donanemab received the US FDA’s breakthrough therapy designation (BTD) for treating Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s Disease Emerging Drugs
Masitinib (AB1010): AB Science
Masitinib, an orally administered tyrosine kinase inhibitor, targets neuro-immune cells such as mast cells and microglia that accumulate in the Central Nervous System (CNS) at effective concentrations. Evidence increasingly links these cells to Alzheimer’s disease pathology. In preclinical studies, masitinib demonstrated synaptic protection by inhibiting mast cells, which contributed to improved spatial learning and recovery of synaptic markers in Alzheimer’s disease models. The drug is currently in Phase III clinical trial and development for the disease.
Clinically, masitinib showed promise in treating mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, with a Phase II trial confirming potential benefits. Additionally, a Phase IIb/III study found that masitinib significantly slowed cognitive decline. A confirmatory Phase III trial is currently underway.
Valiltramiprosate (ALZ-801): Alzheon, Inc.
ALZ-801 is an oral small-molecule prodrug that effectively blocks the formation of neurotoxic amyloid oligomers in the brain. Structurally, it is a valine-conjugated version of tramiprosate, metabolizing into homotaurine in the body, which enhances absorption and extends blood retention compared to tramiprosate. Both ALZ-801 and tramiprosate are metabolized to 3-sulfopropanoic acid (3-SPA), a natural brain compound that prevents Aß42 aggregation.
ALZ-801 was specifically designed to improve tramiprosate's gastrointestinal tolerance and pharmacokinetics, allowing for efficient gut absorption and conversion to active tramiprosate in the bloodstream. Phase I studies indicate improved gastrointestinal tolerance and stable plasma levels.
Currently in Phase III, ALZ-801 is being evaluated as a potential disease-modifying treatment for early-stage Alzheimer’s disease.
Tricaprilin (CER-0001): Cerecin
Cerecin's tricaprilin (CER-0001) (also known as AC-1204) is an innovative oral formulation of caprylic triglyceride, designed to induce a mild state of chronic ketosis that enhances mitochondrial metabolism. Early in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, there is a notable decline in cerebral glucose utilization. Tricaprilin aims to counteract this by providing an alternative energy source for cells, thus boosting metabolic activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Caprylic acid is converted into ketone bodies, including acetoacetic acid and ß-hydroxybutyric acid, which can then be transformed into acetyl-CoA, facilitating energy production through the citric acid cycle.
Clinical studies indicate that CER-0001 is a promising ketogenic agent that demonstrates cognitive improvement in subjects with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease, particularly among those who are APOE4-negative.
Aducanumab (Aduhelm)
Aducanumab (Aduhelm) is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody developed by Biogen and Eisai for early Alzheimer’s disease. It targets aggregated amyloid beta plaques, promoting microglial clearance and reducing plaque burden. Granted accelerated FDA approval in June 2021 for patients with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia with confirmed amyloid pathology, it is administered via monthly intravenous infusions with MRI monitoring for ARIA.
Bezisterim (NE3107): BioVie
NE3107 is an oral small molecule designed to effectively penetrate the blood-brain barrier, serving as both an anti-inflammatory agent and an insulin sensitizer. It selectively targets Extracellular Signal-regulated Kinase (ERK) to inhibit inflammatory pathways by blocking ERK/NF?B activation and decreasing tumor necrosis factor (TNF) production, particularly in response to inflammatory stimuli such as lipopolysaccharides. This mechanism holds promise for reducing pathological inflammatory signaling in peripheral tissues and the Central Nervous System (CNS), potentially alleviating insulin resistance, diminishing inflammatory cell infiltration in the CNS, and modulating microglial activation without impairing their critical functions.
NE3107's dual action may disrupt this detrimental cycle, presenting a novel therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease. Previously known as HE3286, NE3107 is a synthetic analog of the adrenal hormone dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) metabolite and is also being explored for treating conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple myeloma, and prostate cancer. BioVie has completed Phase III trials for NE3107 as a treatment for mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease.
In March 2024, BioVie showcased findings at the International Conference on Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Diseases (AD/PD 2024) held in Lisbon, Portugal. The data presented from a Phase III trial of NE3107 in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease suggest its potential to realign physiological processes, which may lead to a reduction in neurocognitive decline associated with aging.
Gain a Competitive Edge: Explore Our Detailed Market Insights Today! @ NYXOL (PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE) Market
Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Class Analysis
Currently, available therapies for Alzheimer’s disease primarily target symptom management by modulating key neurotransmitters, including acetylcholine, serotonin, and noradrenaline, while aiming to reduce the activity of glutamate and dopamine. However, these approaches often lead to potential side effects, highlighting the necessity for personalized treatment strategies that consider patient comorbidities and potential drug interactions. Recent approvals, such as LEQEMBI (lecanemab) by Biogen and Eisai, Eli Lilly’s KISUNLA (donanemab-azbt), and Brexpiprazole (REXULTI), signify a shift toward more tailored therapeutic options.
Pharmacological treatments, including acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) and the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine, have been in use in the U.S. for over a decade. The US FDA and EMA have approved three AChEIs donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine Administered in over 60 countries for various stages of Alzheimer’s disease. Despite demonstrating modest symptomatic benefits in clinical trials, the effectiveness of these therapies is temporary, necessitating regular re-evaluation.
Additionally, the benefit-risk ratio of these medications remains a topic of debate, influencing reimbursement decisions in some countries, such as France. Memantine, effective as monotherapy or in combination with AChEIs, serves to slow symptom progression in moderate to severe cases, further diversifying treatment options available for this challenging condition.
With a growing focus on advanced treatment options, the market for Alzheimer’s disease is expanding, highlighting opportunities for innovation and investment in new therapies and technologies.
The Alzheimer’s disease market has a rich pipeline and is poised for transformation with the anticipated introduction of therapies like Masitinib, Valiltramiprosate/ ALZ-801, Tricaprilin (CER0001), Bezisterim (NE3107) and others. The approval of these therapies could significantly impact Alzheimer’s disease market dynamics, although their success rates remain uncertain.
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Outlook
- The Alzheimer’s disease market size in the 7MM was ~USD 3,610 million in 2023, which is further anticipated to increase during the forecast period.
- The United States accounted for the highest Alzheimer’s disease market size approximately 54% of the total Alzheimer’s disease market size in 7MM in 2023, in comparison to the other major markets i.e., EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Among the EU countries, Germany had the highest Alzheimer’s disease market size with USD 267 million in 2023, while the UK had the lowest Alzheimer’s disease market size with USD ~104 million in 2023.
- The Alzheimer’s disease market size in Japan was estimated to be about USD 845 million in 2023.
- With the expected launch of upcoming Alzheimer’s disease therapies, such as Masitinib, Valiltramiprosate/ ALZ-801, Tricaprilin (CER0001), Bezisterim (NE3107) among others, the total Alzheimer’s disease market size is expected to show change in the upcoming years.
Alzheimer’s Disease Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential Alzheimer’s disease drugs expected to launch in the Alzheimer’s disease drugs market during 2020–2034. For example, Masitinib in the US is expected to be launched by 2027 with a peak share of 1.20%. Bezisterim is anticipated to take 7 years to peak with a slow medium uptake.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Alzheimer’s Disease Pipeline Development Activities
The Alzheimer’s disease drugs market report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I stage. It also analyzes key Alzheimer's disease companies involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Alzheimer’s disease Clinical Trials Activities
The Alzheimer’s disease treatment market report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for emerging Alzheimer’s disease therapies.
Latest KOL Views on Alzheimer’s disease
To keep up with current Alzheimer’s disease market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate the secondary research. Industry Experts were contacted for insights on Alzheimer’s disease evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, including KOL from Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, US; University of Nevada, US; Hannover Medical School, Germany; Universite Paris Saclay, France; Università di Palermo, Italy; Hospital Virgen De La Salud, Spain; University College London, the UK; and Kyoto University, Japan.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 50+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapies, treatment patterns, or Alzheimer’s disease market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Alzheimer’s Disease Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging Alzheimer’s disease therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Alzheimer’s disease Market Access and Reimbursement
The high cost of therapies for the treatment is a major factor restraining the growth of the global Alzheimer’s disease drug market. Because of the high cost, the economic burden is increasing, leading the patient to escape from proper treatment.
The Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics market report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Alzheimer’s Disease Market Report
- The Alzheimer’s disease treatment market report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview of Alzheimer’s disease, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, and currently available Alzheimer’s disease therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the Alzheimer’s disease market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind the approach is included in the rAlzheimer’s disease market report covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The Alzheimer's disease market report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM Alzheimer’s disease market.
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Report Insights
- Alzheimer's disease Patient Population
- Alzheimer's disease Therapeutic Approaches
- Alzheimer’s Disease Pipeline Analysis
- Alzheimer’s Disease Market Size
- Alzheimer’s disease Market Trends
- Existing and Future Alzheimer’s disease Market Opportunity
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Report Key Strengths
- 11 years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Alzheimer’s Disease Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint Analysis
- Alzheimer’s disease Drugs Uptake
- Key Alzheimer’s disease Market Forecast Assumptions
Alzheimer’s Disease Market Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Alzheimer’s disease Unmet Needs
- Alzheimer’s disease Pipeline Product Profiles
- Alzheimer’s disease Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
Key Questions
Alzheimer’s disease Market Insights
- What was the Alzheimer’s Disease market share (%) distribution in 2020 and how it would look like in 2034?
- What would be the Alzheimer’s Disease market size as well as market size by therapies across the 7MM during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- What are the key findings pertaining to the market across the 7MM and which country will have the largest Alzheimer’s Disease market size during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- At what CAGR, the Alzheimer’s Disease market is expected to grow at the 7MM level during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- What would be the Alzheimer’s Disease market outlook across the 7MM during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- What would be the Alzheimer’s Disease market growth till 2034 and what will be the resultant market size in the year 2034?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the Alzheimer’s disease market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
Alzheimer’s disease Epidemiology Insights
- What is the disease risk, burden, and unmet needs of Alzheimer’s Disease?
- What is the historical Alzheimer’s Disease patient population in the United States, EU5 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the UK), and Japan?
- What would be the forecasted patient population of Alzheimer’s disease at the 7MM level?
- What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM with respect to the patient population pertaining to Alzheimer’s Disease?
- Out of the above-mentioned countries, which country would have the highest prevalent population of Alzheimer’s Disease during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- At what CAGR the population is expected to grow across the 7MM during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
Current Treatment Scenario, Marketed Drugs, and Emerging Therapies
- What are the current options for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease along with the approved therapy?
- What are the current treatment guidelines for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease in the US, Europe, And Japan?
- What are the Alzheimer’s Disease marketed drugs and their MOA, regulatory milestones, product development activities, advantages, disadvantages, safety, and efficacy, etc.?
- How many Alzheimer’s disease companies are developing therapies for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease?
- How many emerging Alzheimer’s disease therapies are in the mid-stage and late stages of development for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease?
- What are the key collaborations (Industry–Industry, Industry-Academia), Mergers and acquisitions, licensing activities related to the Alzheimer’s Disease therapies?
- What are the recent therapies, targets, mechanisms of action and technologies developed to overcome the limitation of existing therapies?
- What are the clinical studies going on for Alzheimer’s Disease and their status?
- What are the key designations that have been granted for the emerging therapies for Alzheimer’s Disease?
- What are the 7MM historical and forecasted Alzheimer’s disease market?
Reasons to Buy
- The Alzheimer’s disease treatment market report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Alzheimer’s Disease Market.
- Insights on patient burden/Alzheimer’s disease incidence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- To understand the existing Alzheimer's disease market opportunity in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identification of strong upcoming Alzheimer's disease companies in the Alzheimer’s disease treatment market will help in devising strategies that will help in getting ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and potential of current and emerging Alzheimer's disease therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading emerging Alzheimer's disease drugs.
- Highlights of Access and Reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of off-label expensive therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand the perspective of Key Opinion Leaders around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet need of the existing Alzheimer’s disease market so that the upcoming Alzheimer's disease companies Alzheimer's disease can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Stay Updated with us for New Articles:-
- Semaglutide: Unveiling Hope for Alzheimer's Disease Patients
- Alzheimer's Disease Diagnostic: Market Dynamics, Key Trends, and Growth Potential
- Challenges in the Pursuit of Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment Breakthroughs: Drug Clinical Trial Failures
- Quest Introduced Consumer-Initiated Blood Test for Alzheimer's Disease Risk Assessment; DuPont Acquires Spectrum Plastics; BD Received 510(k) Clearance for Molecular Combination Test; Natera Updates on Phase III ALTAIR Trial of Signatera; Anteris’ DurAVR transcatheter heart valve Trial
- FDA Grants Priority Review for Zolbetuximab BLA; FDA Traditional Approval for LEQEMBI for Alzheimer’s Disease; Iovance Announces Regulatory and Clinical Updates for TIL Therapy in Advanced NSCLC; Biophytis Seeks FDA Approval to Launch Phase 3 Study of Potential Treatment of Sarcopenia; Orphan Drug Designation to Marker Therapeutics’s MT-401 for AML Treatment; Axsome Therapeutics Initiates Phase 3 Trial of Solriamfetol for ADHD
- Leqembi: A New Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease Patients
- GE HealthCare, DePuy Synthes Announced Collaboration; Eko Health Launched CORE 500 Digital Stethoscope; Haemonetics’s NexSys PCS Plasma Collection System; Roche’s Alzheimer's Disease Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) Assays; Medtronic’s MiniMed 780G system; Biodesix’s VeriStrat Blood-Based Host Immune Classifier
- Sarepta Therapeutics’s SRP-9001 Gene Therapy; FDA Approves Astellas’ VEOZAH; FDA Orphan Drug Designation and Rare Pediatric Disease Designation to SiSaf’s siRNA Therapy SIS-101-ADO; FDA Grants Fast Track Designation to IMPT-314; FDA Approves First Drug for Agitation in People With Alzheimer’s Disease; FDA Accepted the CytoAgents’ IND Application for CTO1681
- Ipsen to Acquire Albireo; Chiesi Farmaceutici to Buy Amryt Pharma; Takeda Presents Phase III Results of TAK-755 for cTTP; ACELYRIN Acquires ValenzaBio; FDA Approves LEQEMBI for Alzheimer's Disease; Orphan Drug Designation to Lantern Pharma’s LP-284 for MLL
- Psychosis in Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s Disease Infographics
- Alzheimer's Disease Market: Infographics