Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Summary
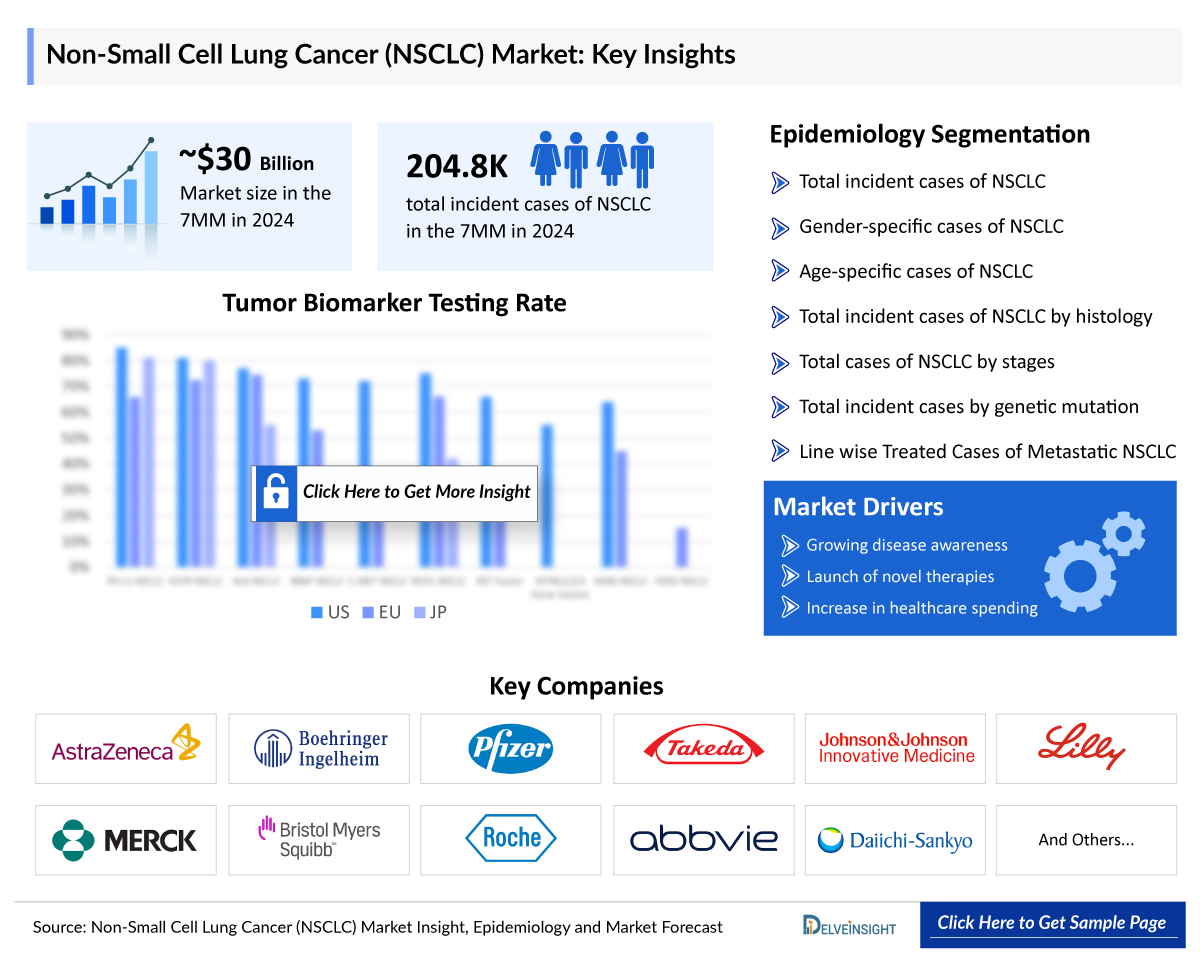
- The NSCLC Market Size in the 7MM is expected to grow from USD 32,442 million in 2025 to USD 64,819 million in 2034.
- The NSCLC Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8% by 2034 in leading countries like the US, EU4, UK, and Japan.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market and Epidemiology Analysis
- The leading Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer companies include Novartis, AstraZeneca, Roche, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, and and others, advancing innovative therapies and treatments.
- NSCLC market size has seen a revolutionary change in the last decade owing to the increase in incident cases, continuous uptake of approved therapies, mainly immune checkpoint inhibitors, expected entry of potential premium price emerging therapies, and increasing awareness of mutations like KRAS, BRAF, c-Met, and others.
- The real-world treatment trend depicts a drastic shift toward targeted and immunotherapies (from only systemic therapies in the past), which is expected to contribute the most now.
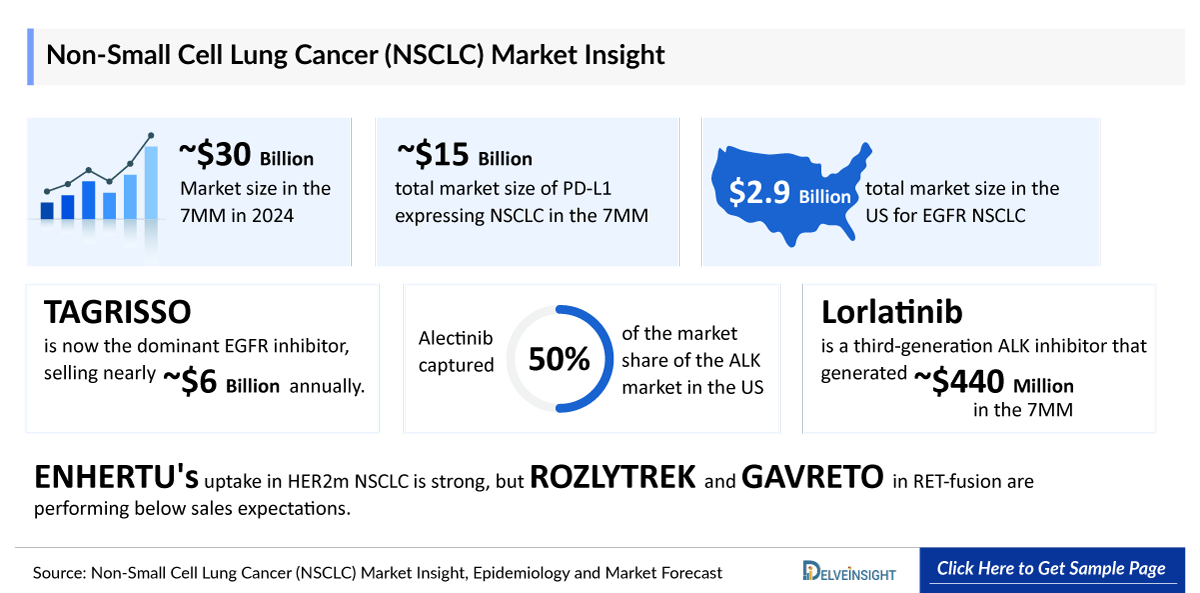
- NSCLC is increasingly becoming a biomarker-driven market. EGFR is one of the profitable biomarker segment, with blockbuster therapies such as TAGRISSO. TAGRISSO is now the dominant EGFR inhibitor selling nearly USD 6 billion annually. The prevalence of patients with this resistance mutation has increased since TAGRISSO was authorized for use in the first line. The post-TAGRISSO setting is one of the highest areas of unmet need.
- At present, ALECENSA and ALUNBRIG are the preferred first-line ALK TKIs. ALECENSA is much more widely used compared to ALUNBRIG and dominate the ALK market. Prior to entry of ALECENSA and ALUNBRIG, XALKORI was the first-line treatment choice in ALK patients.
- ADCs are a class of oncology medications that are among the most rapidly expanding. Despite the outstanding patient responses that conventional ADCs have produced, they have only been tested on patients with the highest target expression levels and a narrow number of targets. Although only one ADC is approved for NSCLC, and it is only for a limited subgroup (HER2m NSCLC), companies are attempting to target a larger NSCLC population, particularly in areas where KEYTRUDA is the market leader. Among the upcoming therapies in the 7MM, Dato-DXd is expected to capture a significant market size of patients expressing PD-L1.
- As per DelveInsight’s analysis, the total incident cases of NSCLC in the 7MM were approximately 537,700 in 2024; these cases are estimated to increase by 2034.
- Various types of mutations are commonly observed in NSCLC. There is mounting evidence that substantial molecular and clinical heterogeneity exists within oncogenic driver-defined subgroups of NSCLC. The most frequent biomarkers are EGFR in Japan and KRAS in the US and Europe.
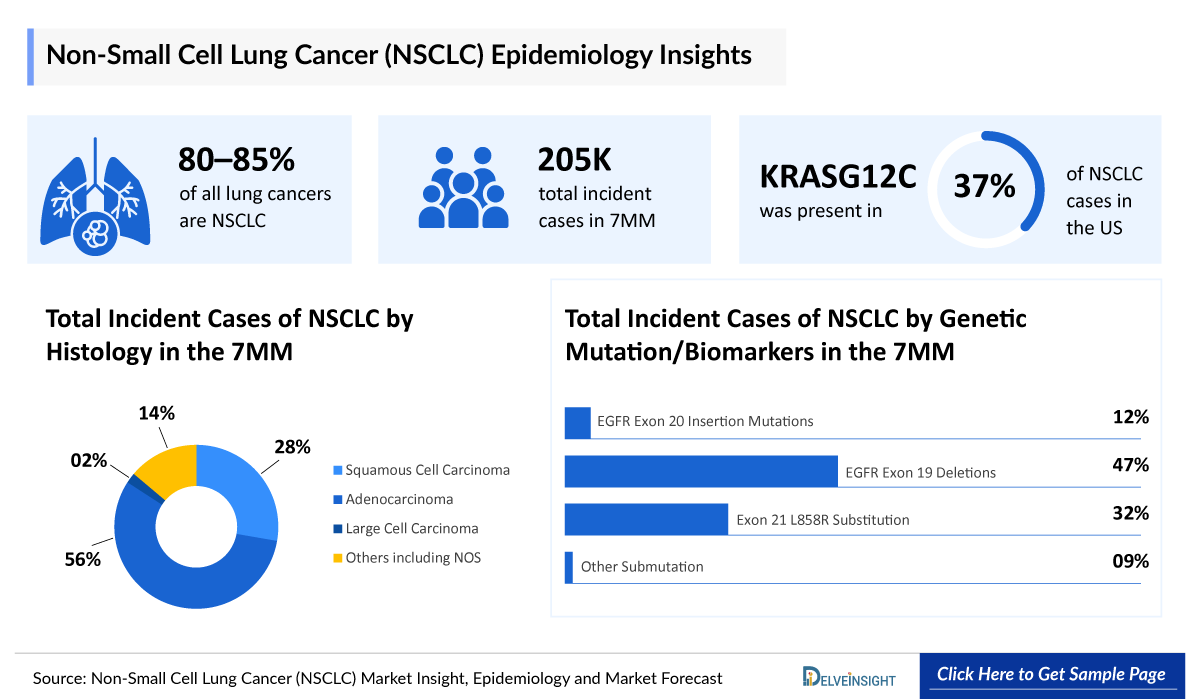
- EGFR exon 19 deletions and Exon 21 L858R substitution (sensitizing mutations) account for approximately 80% of EGFR mutations in NSCLC.
- The most frequent KRAS variant observed in NSCLC is G12C. In the US, KRASG12C is present in ~37% of NSCLC cases.
- HAIYITAN’s recent approval by the PMDA positions it as a significant player in Japan’s growing c-MET inhibitor market. Its regulatory success enhances credibility and sets the stage for rapid adoption in treating cancers with c-MET alterations, particularly in a market where precision oncology is expanding.
- In BRAF mutation, TAFINLAR + MEKINIST combination has led the market since its 2021 launch, driven by its strong clinical performance
- Due to their rarity and the lack of late-stage clinical studies, the treatment paradigm for rare NSCLC mutations is less clear. Rare biomarkers like ROS-1, HER2, RET Fusion, and NTRK1/2/3 Gene fusion have seen a lot of progress in past few years.
- Among EU4, Germany accounted for the highest number of NSCLC cases in 2024, whereas Spain accounted for the lowest cases in 2024.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size and Forecasts
- 2025 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size: USD 32,442 million in 2025
- 2034 Projected Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size: USD 64,819 million in 2034
- Growth Rate (2025-2034): 8% CAGR
- Largest Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market: United States
Key factors driving Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer market
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patient Pool
There were around 537.7K incident cases of NSCLC across the 7MM in 2024, a number expected to rise further by 2034. Biomarker prevalence varies significantly, with EGFR mutations more frequent in Japan and KRAS mutations dominant in the US and Europe. EGFR exon 19 deletions and exon 21 L858R substitutions account for most EGFR-positive cases, while KRASG12C mutations are present in nearly 37% of US cases.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market
The NSCLC market in the 7MM is projected to reach ~USD 65 billion by 2034 at a CAGR of 8%. The treatment paradigm has shifted from chemotherapy toward immunotherapy and targeted therapies, with drugs like KEYTRUDA, OPDIVO + YERVOY, TECENTRIQ, TAGRISSO, ALECENSA, ALUNBRIG, LORLATINIB, and ENHERTU playing central roles. KEYTRUDA dominates the PD-1/PD-L1 segment, while TAGRISSO is the leading EGFR inhibitor, generating multi-billion-dollar sales annually.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is evolving with several late- and mid-stage pipeline candidates targeting diverse mechanisms such as antibody–drug conjugates, checkpoint inhibitors, bispecific antibodies, targeted kinase inhibitors, and cancer vaccines. Key emerging therapies include Telisotuzumab vedotin (AbbVie), Datopotamab deruxtecan (Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca), Eftilagimod alpha (Immutep), Serplulimab (Shanghai Henlius Biotech), V940 (Moderna Therapeutics/Merck), Plinabulin (BeyondSpring), Zipalertinib (Cullinan Oncology/Taiho Pharma), Sigvotatug vedotin (Pfizer), Trodelvy (Gilead Sciences), Opdualag (Bristol-Myers Squibb), and others. These therapies in the NSCLC clinical trials are poised to expand treatment options and improve outcomes for NSCLC patients.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Dynamics
ADCs, currently limited to HER2m NSCLC, are expected to capture broader subsets in the coming years, competing directly with IOs. Unmet needs remain in post-TAGRISSO progression, KRAS-driven resistance, and rare mutations, creating opportunities for next-generation targeted and cell-based therapies.
Factors Impacting the NSCLC Market Growth
-
Increase in incident cases
Biomarker testing, approval of high cost combination therapies, launch of novel therapies
DelveInsight's “Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of top oncogenic drivers/biomarkers in NSCLC (such as EGFR, c-MET, ROS1, KRAS, ALK, HER2, BRAF, RET fusion, NRG1 Fusion, NTRK1/2/3 gene fusion, PD-L1, etc.), historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the NSCLC market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan. The NSCLC therapeutics market is driven by advancements in targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and personalized medicine, improving patient outcomes globally.
NSCLC Market Teport provides real-world prescription pattern analysis, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and historical and forecasted 7MM Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current NSCLC treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
|
Study Period |
2020 to 2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025-2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
|
|
NSCLC Market |
|
|
NSCLC Market Size | |
|
NSCLC Companies |
AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Takeda, Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine, Eli Lilly and Company, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, Shanghai Henlius Biotech, AbbVie, Daiichi Sankyo, Nuvation Bio, PDC*line Pharma, Moderna Therapeutics, Pfizer, GSK, Gilead Sciences, BieGene, Nuvalent, and others. |
|
NSCLC Epidemiology Segmentation |
|
NSCLC Disease Understanding
NSCLC Overview and Diagnosis
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for 81% of all lung cancer diagnoses. Early diagnosis offers the best prognosis for NSCLC. However, NSCLC and other lung cancers can be difficult to diagnose because these cancers often have symptoms mistaken for common illnesses or the effects of long-term smoking. Because of this, 80% of people diagnosed with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer have already progressed to advanced stages, making it more difficult to treat. If lung cancer is suspected, the physician will recommend imaging tests (CT, PET, or MRI scans) to identify abnormalities in and around the lungs. The physician may also examine a sample of mucus under the microscope.
If these initial tests identify cancer, a lung biopsy can be conducted. A bronchoscopy can also be recommended, allowing the physician to visualize and remove tissue. If lung cancer is confirmed, genetic testing can be done on the lung tissue to identify details about the cancer that can help inform treatment.
NSCLC Treatment
Ongoing NSCLC clinical trials are advancing innovative therapies, improving survival rates, and exploring targeted treatments for better patient outcomes worldwide. Treatment options and recommendations depend on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, possible side effects, and the patient’s preferences and overall health. The most common treatments for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer are:
- Surgery
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy with radiotherapy (chemoradiotherapy)
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted cancer drugs
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Epidemiology
The Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total NSCLC Incidence Cases, gender-specific cases of NSCLC, age-specific cases of NSCLC, total incident cases of NSCLC by histology, total cases of NSCLC by stages, total incident cases of NSCLC by genetic mutation/biomarkers, Line wise Treated Cases of Metastatic NSCLC in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034. The prevalence of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) varies, with higher incidence rates in smokers and older adults.
Key Findings from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Epidemiological Analyses and Forecast
- About 10–15% of all lung cancers are SCLC, and about 80–85% are Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- In the US, in 2024, there were approximately 204,800 new cases of NSCLC cancer (~115,500 in men and ~89,300 in women.
- The three main histological subtypes of NSCLC are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma. In the US, approximately 59% of all lung cancers are adenocarcinomas. About 25% of all lung cancers are squamous cell carcinoma. Large cell (undifferentiated) carcinoma makes up around 6% of all lung cancers.
- Among the age-specific contribution, age =65 years are affected more by NSCLC than age <65 years. In 2024, there were ~140,000 of NSCLC in age =65 years in the US.
- In 2024, the total incident cases of NTRK1/2/3 gene fusion NSCLC in the US was around 450.
- In biomarker specific specific cases, most number of cases is from PD-L1 followed by KRAS, EGFR. On the other hand, NTRK accounted for least number of cases whereas, BRAF accounted for approximately 5% cases.
- The two main subtypes of KRAS NSCLC are KRAS G12C, and KRAS non-G12C (G12V, G12D, G13D, G12R, and others). In Japan, ~4,900 comprised of KRAS G12C, and ~13,300 comprised of KRAS non-G12C in 2024.
NSCLC Epidemiology Segmentation
- Total NSCLC Incidence Cases
- Gender-specific cases of NSCLC
- Age-specific cases of NSCLC
- Total incident cases of NSCLC by histology
- Total cases of NSCLC by stages
- Total incident cases of NSCLC by genetic mutation/biomarkers
- Line wise Treated Cases of Metastatic NSCLC
NSCLC Market Recent Developments and Breakthroughs
- In September 2025, Merck (NYSE: MRK) announced U.S. FDA approval of KEYTRUDA QLEX™—a subcutaneous formulation of pembrolizumab combined with berahyaluronidase alfa—for use in adults across most solid tumor indications for KEYTRUDA®. Developed with Alteogen Inc.'s hyaluronidase technology, KEYTRUDA QLEX must be administered by a healthcare provider and is expected to be available in the U.S. by late September.
- In August 2025, TOLREMO Therapeutics announced that its lead candidate, TT125-802, received two FDA Fast Track designations for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- In August 2025, Innovent Biologics received FDA clearance to begin a global Phase 3 trial (MarsLight-11) of IBI363, a novel PD-1/IL-2α-bias bispecific antibody, for IO-resistant squamous NSCLC—marking its first global pivotal study.
- In August 2025, SystImmune and Bristol Myers Squibb announced that the FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation to izalontamab brengitecan (iza-bren) for the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R mutations after progression on EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor and platinum-based chemotherapy.
- In July 2025, Thermo Fisher Scientific announced FDA approval of the Oncomine™ Dx Express Test on the Ion Torrent™ Genexus™ Dx Sequencer as a companion diagnostic for Dizal’s ZEGFROVY® (sunvozertinib) to detect EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The test also supports tumor profiling of 46 genes, delivering rapid genomic insights in about 24 hours to enhance precision oncology in clinical settings.
- In June 2025, Nuvalent, Inc. (Nasdaq: NUVL) announced it will host a webcast and conference call on June 24 at 8:00 a.m. ET to discuss pivotal data for zidesamtinib, a ROS1-selective inhibitor, in TKI pre-treated advanced ROS1-positive non-small cell lung cancer from the ARROS-1 Phase 1/2 trial.
- In June 2025, Guardant Health, Inc. (Nasdaq: GH) announced that its Shield multi-cancer detection (MCD) test received Breakthrough Device designation from the FDA. The methylation-based blood test is designed to screen for multiple cancers—including bladder, colorectal, esophageal, gastric, liver, lung, ovarian, and pancreatic—in adults aged 45+ at average risk.
- In May 2025, Bayer announced FDA granted Priority Review to sevabertinib (BAY 2927088), an oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor for advanced NSCLC patients with HER2 mutations who have had prior systemic therapy.
- In May 2025, Roche announced FDA approval of the VENTANA® MET (SP44) RxDx Assay—the first companion diagnostic to assess MET protein expression in NSQ-NSCLC patients eligible for AbbVie’s MET-targeted therapy, Emrelis™ (telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv).
- In May 2025, Hansoh Pharma (03692.HK) announced that Ameile (almonertinib) has been approved in China for a new indication: adjuvant treatment of adult NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 19 deletion or exon 21 (L858R) mutations post-surgery. This marks its fourth approved indication, reinforcing its leadership among domestic third-generation EGFR-TKIs.
- In April 2025, Roche announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Breakthrough Device Designation for its VENTANA® TROP2 (EPR20043) RxDx Device. This marks the first Breakthrough Device Designation granted for a computational pathology companion diagnostic (CDx) device.
- In May 2025, AbbVie (NYSE: ABBV) announced that the FDA granted accelerated approval to EMRELIS™ (telisotuzumab vedotin-tllv) for treating adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) exhibiting high c-Met protein overexpression (≥50% tumor cells with strong staining) after prior systemic therapy.
- In May 2025, Lantern Pharma Inc. (Nasdaq: LTRN) announced FDA clearance of an IND amendment to start a Phase 1b/2 trial of LP-184 in genomically defined non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients, aiming to improve outcomes.
- In April 2025, Verastem Oncology received FDA clearance for its IND application of VS-7375, an oral KRAS G12D (ON/OFF) inhibitor, and plans to begin a Phase 1/2a study by mid-year targeting advanced solid tumors including pancreatic, colorectal, and non-small cell lung cancers.
- In April 2025, Biocon Biologics received FDA approval for Jobevne™ (bevacizumab-nwgd), a biosimilar to Avastin®, for intravenous use. Jobevne is approved for multiple cancers, including metastatic colorectal cancer, non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer, recurrent glioblastoma, metastatic renal cell carcinoma, advanced cervical cancer, and ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer.
- In April 2025, Halozyme announced that the European Commission approved the subcutaneous formulation of RYBREVANT® (amivantamab) plus LAZCLUZE® (lazertinib) for first-line treatment of advanced EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). RYBREVANT® was also approved as monotherapy for EGFR exon 20 insertion mutation-positive NSCLC after platinum therapy failure.
- In April 2025, AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi (durvalumab) combined with chemotherapy was approved in the EU for adults with resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) at high risk of recurrence, without EGFR mutations or ALK rearrangements. Treatment includes neoadjuvant Imfinzi plus chemotherapy before surgery and adjuvant Imfinzi monotherapy after surgery.
- In March 2025, Boan Biotechnology (06955.HK) announced that its targeted CD228 antibody-drug conjugate, BA1302, received orphan drug designation (ODD) from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for squamous non-small cell lung cancer and pancreatic cancer.
- In March 2025, CERo Therapeutics Holdings, Inc. announced that the FDA has cleared its second Investigational New Drug (IND) application for lead compound CER-1236. This will allow the company to proceed with a Phase 1 clinical trial in advanced solid tumors, including non-small cell lung cancer and ovarian cancer.
- In January 2025, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted priority review to Dizal's new drug application (NDA) for Sunvozertinib, targeting the treatment of locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients.
European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) 2024 Key Updates
- In December 2024, Shanghai Henlius Biotech presented the results of serplulimab trial ASTRUM-004 at the ESMO Asia 2024.
- In December 2024, Daiichi Sankyo announced that the pooled analysis of the TROPION-Lung05 Phase II and the TROPION-Lung01 Phase III trials showed Datopotamab deruxtecan demonstrated clinically meaningful tumor response in patients with previously treated advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
- In December 2024, PDC*line Pharma announced the primary clinical results from the last cohort of patients in its Phase I/II clinical trial with PDC*lung01, in an oral presentation at the ESMO-IO 2024.
- In September 2024, Nuvation Bio presented pooled data from the pivotal Phase II TRUST-I and TRUST-II studies at the ESMO Congress 2024, which will support Nuvation Bio’s NDA in the US.
- In September 2024, Pfizer presented a poster on Be6A Lung-01, a Phase III study of sigvotatug vedotin, an investigational ADC versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated NSCLC at the ESMO Congress 2024.
- In September 2024, Nuvalent presented the updated Phase I dose escalation data of zidesamtinib at the 2024 ESMO Congress.
- In September 2024, Dizal Pharmaceutical presented subgroup analysis findings of its WU-KONG1 Part B (WU-KONG1B) study at the 2024 ESMO Congress.
- In September 2024, Bristol-Myers Squibb presented data from the proof-of-concept Phase II RELATIVITY-104 trial of OPDUALAG at ESMO 2024.
- In September 2024, Apollomics presented efficacy and safety data of vebreltinib showing it is efficacious in both treatment naïve and previously treated patients with NSCLS and confirmed METex14 mutation, with longer treatment follow-ups, at ESMO 2024.
NSCLC Drug Analysis
The drug chapter segment of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer report encloses a detailed analysis of NSCLC drugs market and late-stage (Phase III and Phase II) non-small cell lung caner pipeline drugs. It also deep dives into the pivotal NSCLC clinical trial details, recent and expected market approvals, patent details, the latest news, and recent deals and collaborations. The NSCLC drugs market is expanding due to rising incidence, novel therapies, targeted treatments, and increasing research in lung cancer management.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Marketed Drugs
-
KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab): Merck
KEYTRUDA is a PD-1-blocking antibody. It is mainly used for advanced cancers that have spread to other body parts or are not responding to other treatments. In some cancers, it is only given to patients whose tumors produce high protein levels known as PD-L1. KEYTRUDA was first approved in October 2015 by the US FDA as a monotherapy for metastatic NSCLC. Later, the labels were expanded in 2016, 2017, 2018, and in 2023. In October 2023, the FDA approved KEYTRUDA platinum-containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment, and with continuation of single-agent KEYTRUDA as post-surgical adjuvant treatment for resectable (tumors =4 cm or node positive) NSCLC. The drug has also received approvals in EU4 and the UK (August 2016) and Japan (December 2016), where the labels were expanded as well. Recently in September 2024, Merck announced that the MHLW has approved new indications for KEYTRUDA in combination with chemotherapy as a neoadjuvant treatment. Earlier in March 2024, Merck announced that the EC has approved KEYTRUDA in combination with platinum-containing chemotherapy as neoadjuvant treatment
In December 2024, Merck announced that it is discontinuing the Phase III KeyVibe-003 and KeyVibe-007 trials, which are evaluating the fixed-dose combination of vibostolimab and pembrolizumab in certain patients with NSCLC, based on the recommendation of an independent Data Monitoring Committee (DMC).
-
TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab): Genentech/Roche
TECENTRIQ is a PD-L1-blocking antibody. It is an Fc-engineered, humanized, non-glycosylated IgG1 kappa immunoglobulin with a calculated molecular mass of 145 kDa. According to Roche's recent product development portfolio published in October 2024, the company anticipates submitting a filing for TECENTRIQ in the periadjuvant treatment of NSCLC in 2025.
TECENTRIQ was initially approved by the US FDA for the treatment of people with metastatic NSCLC who have disease progression during or following platinum-containing chemotherapy and have progressed on an appropriate FDA-approved targeted therapy if their tumor has EGFR or ALK gene abnormalities in October 2016. Later, the company expanded the label in 2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, and 2024. The drug was also approved in the EU (September 2017) and in Japan (April 2018) for the treatment of NSCLC. Recently, in September 2024, the US FDA approved TECENTRIQ and HYBREZA (hyaluronidase-tqjs), the first and only PD-(L)1 inhibitor for SC, under the skin injection for patients in the US.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Emerging Drugs
-
Telisotuzumab vedotin: AbbVie
Teliso-V is an investigational antibody–drug conjugate targeting c-Met, a receptor tyrosine kinase overexpressed in tumors, including Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Teliso-V has the potential to become an important new treatment option in non-small cell lung cancer, with an anticipated approval in 2L+ NSCLC in 2024. In January 2022, AbbVie announced that the FDA granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation to investigational telisotuzumab vedotin for the treatment of patients with advanced/metastatic epidermal growth factor receptor wild type, nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer with high levels of c-Met overexpression whose disease has progressed on or after platinum-based therapy. In May 2022, AbbVie initiated a Phase III clinical trial to evaluate Teliso-V versus docetaxel for the treatment of patients with previously treated c-Met overexpressing, epidermal growth factor receptor wild type, and advanced/metastatic non-squamous NSCLC.
-
Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd): AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo
Datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) is an investigational TROP2-directed ADC. Designed using Daiichi Sankyo’s proprietary DXd ADC technology, datopotamab deruxtecan is one of the most advanced programs in AstraZeneca’s ADC scientific platform and one of the three leading ADCs in the oncology pipeline of Daiichi Sankyo. In January 2023, a Phase III clinical trial, combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors for the first-line treatment for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer without actionable genomic alterations, PD-L1 <50% (trial name: TROPION-Lung07), was initiated. No TROP2-directed therapies are currently approved for treating Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer patients. AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo are interrogating Dato-DXd in 1L non-driver mutation patients with TROPION-Lung08 (trying to knock off the Keynote-024 regimen) and with TROPION-Lung07 (trying to dethrone Keynote-189 regimen, the most important indication for Merck’s KEYRTUDA), as well as covering 2L and 3L patients with TROPION-Lung01. In December 2024, Daiichi Sankyo announced Dato-DXd has been granted BTD in the US for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-mutated NSCLC with disease progression on or after treatment with an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) and platinum-based chemotherapy.
NSCLC Drug Class Analysis
The existing NSCLC treatment is mainly dominated by targeted therapies for mutations such as EGFR-sensitizing mutations, EGFR exon 20 insertions, ALK fusions, ROS1 fusions, BRAFV600E mutation, MET exon 14 skipping mutations, RET fusions, and KRASG12C mutation. EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements are well-known genetic abnormalities that drive the development of NSCLC. The use of TKIs as a treatment approach has shown better results in terms of patient outcomes when compared to chemotherapy.
EGFR mutations are frequently observed, EGFR exon 19 deletions and EGFR exon 21 L858R mutations. The FDA has approved various TKIs to treat these mutations, with TAGRISSO considered the standard treatment. GILOTRIF is approved for patients with other EGFR sensitivity mutations like S768I, L861Q, and G719X. However, approximately 8–10% of EGFR mutations involve exon 20 insertions, which do not respond to treatments targeting exon 19 or 21 alterations, including osimertinib. Currently, three targeted therapies, RYBREVANT, TAGRISSO and EXKIVITY, are approved for EGFR. Later EXKIVITY were withdrawn from the market. These mutations represent an area of unmet medical need in NSCLC. While treatment with EGFR TKIs effectively eliminates most cancer cells, a small population of drug-tolerant cells may persist. These cells can remain inactive and undetectable for extended periods but eventually resume growth and spread to other body parts.
Moving onto ALK rearrangements, which are present in around 5% of NSCLC cases, primarily in adenocarcinomas, represent a distinct molecular subtype of lung cancer. The first ALK inhibitor approved for treatment was crizotinib, and subsequently, several other ALK inhibitors have received approval, including ceritinib, alectinib, brigatinib, and lorlatinib. A direct comparison among all the ALK TKIs is still lacking, but researchers are actively developing new ALK TKIs to overcome resistance to the currently available ones. This suggests the possibility of a sequential treatment strategy involving different ALK TKIs in this specific disease. There are not many NSCLC companies at present attempting to target this segment. Pipeline of ALK NSCLC is not very robust. Few key player such as Merck and Nuvalent developing there therapies.
While tumors with ROS1 rearrangements, known as ROS1-positive tumors, are not common, the similarities between ROS1 and ALK receptors, as well as the similarities between ROS1-positive and ALK-positive NSCLC, have led to the repurposing of ALK inhibitors for the treatment of ROS1-positive disease. XALKORI, already approved for treating patients with ALK fusions, became the first drug specifically indicated for patients with ROS1-positive NSCLC in 2016. In treating patients with BRAF V600E mutations, TAFINLAR + MEKINIST combination has led the market since its 2021 launch, driven by its strong clinical performance. However, it is worth noting that BRAF mutations are relatively uncommon in NSCLC compared to other cancers such as melanoma.
Even though numerous MET inhibitors with different mechanisms of action have failed to demonstrate significant effectiveness in clinical trials, the FDA has approved MET inhibitors like TABRECTA and TEPMETKO for treating patients with advanced NSCLC that have MET exon 14 skipping mutations. The RET fusion-NSCLC market progressed with RETEVMO and GAVRETO approvals in 2020, but Roche’s decision to end its GAVRETO partnership in February 2023, effective February 2024, led Blueprint to halt global development outside the US and CStone territory.
TRK inhibitors have demonstrated promising effectiveness and good tolerability in patients with solid tumors carrying NTRK fusions, regardless of the tumor's histology. The first-generation TRK inhibitors, such as larotrectinib and entrectinib, are recommended as the initial treatment for patients with locally advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer who have confirmed NTRK fusion. However, resistance to TRK inhibitors can eventually emerge due to various mechanisms, either directly targeting the TRK protein or through other indirect means. Interestingly, NTRK fusion has been identified as a potential resistance mechanism to EGFR-TKIs, suggesting that combining EGFR-TKIs with TRK inhibitors could be a potential treatment option for patients experiencing EGFR-TKI resistance mediated by NTRK fusion.
Considering that HER2 has emerged as a notable targetable oncogenic driver, lung cancer is particularly interesting due to the significant occurrence of mutations in the tyrosine kinase domain of the HER2 gene. In August 2022, ENHERTU (fam-trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki) received approval to treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer patients with an activating HER2 mutation.
Targeting KRAS represents a significant advancement in oncology in recent times. KRAS is the most frequently mutated oncogene in human cancer, with the highest occurrence in non-small-cell lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. In lung cancer, the most prevalent KRAS mutation is G12C. In the past, KRAS was considered "undruggable" due to the absence of conventional drug-binding sites. However, the approval of KRAS G12C inhibitors, such as sotorasib and adagrasib, for treating locally advanced or metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer has revolutionized the approach to treating cancers with KRAS G12C mutations. Numerous other KRAS players such as Gritstone Bio and Elicio Therapeutics, are evaluating their respective Pan-KRAS Vaccines in Phase I/II along with Immuneering Corporation with its KRASG12S in early-stage trial.
Targeted therapies targeting NRG1 alterations have also entered early clinical studies. Currently, there are no approved treatments specifically targeting NRG1-positive cancer. However, zenocutuzumab presents promising potential as a new standard of care. Below is a glimpse of US FDA-approved therapies for NSCLC.
NSCLC Market Outlook
As more targetable mutations are discovered, and new targeted drugs are developed, patients and oncologists will have an expanding array of treatment options. Given the rapid pace of drug approvals, it is important to pause and ensure sufficient data supports the use of specific agents in the appropriate treatment settings, including adjuvant, consolidation, first-line, or subsequent therapy.
Previously, molecular-based treatments were limited to advanced-stage Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. However, recent findings have demonstrated their efficacy in early-stage and locally advanced disease. New studies have explored therapies targeting a wider range of oncogenes, aiming to overcome drug resistance and provide treatment options for patients previously excluded from clinical trials for advanced-stage lung cancer. The emerging data from these ongoing trials are expected to influence future treatment guidelines and foster the adoption of personalized medicine. As a result, a continuous evolution of the treatment landscape is anticipated, ultimately leading to improved survival rates and enhanced quality of life for lung cancer patients.
PD-L1 Expression
With more than 500,000 cases in the 7MM region, lung cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. This condition is often diagnosed when the patient reaches the advanced, inoperable, or metastatic stage, adversely affecting their quality of life.
Till the last decade, chemotherapy was used as the standard of care in the advanced and metastatic stages until the first ICI ‘KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab)’ got approved in 2015 as a second-line treatment option for such advanced patients; a similar path was followed by TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) who entered the market in 2016. These therapies entered the first-line domain after 2016 and expanded their labels by expanding the targetable pool. Recently, in 2020, OPDIVO (nivolumab) + ipilimumab was approved as a 1L treatment for patients with metastatic NSCLC.
EGFR Mutation
The treatment of EGFR-mutant NSCLC has been transformed by the development of targeted therapies in the last two decades; however, choosing the best therapy after EGFR TKIs fail is still a challenge. There are five EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) approved for first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC with common EGFR-sensitizing mutations (e.g., EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 mutations [L858R]): erlotinib, gefitinib, afatinib, dacomitinib, and osimertinib. These drugs have different efficacy and safety profiles and are classified as first- (e.g., erlotinib, gefitinib), second- (e.g., afatinib, dacomitinib), or third-generation (e.g., osimertinib) TKIs. Afatinib and osimertinib, which are second- and third-generation TKIs, respectively, have shown prolonged activity against some rare EGFR mutations (e.g., T790M [osimertinib], G719X, L861Q, or S768I [afatinib and osimertinib]).
Key players, such as AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, AbbVie, Roche, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Immutep, Sanofi, GlaxoSmithKline, and others, are evaluating their lead candidates in different stages of clinical development, respectively. They aim to investigate their products to treat Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- The total market size of PD-L1 expressing NSCLC is estimated to be ~USD 15,000 million by 2024 in the 7MM, followed by EGFR and KRAS.
- The total market size in the US for EGFR NSCLC was estimated to be nearly USD 2,900 million in 2024, which is expected to increase due to the launch of emerging therapies and label expansion of current therapies.
- Alectinib is a common second ALK TKI used after crizotinib progression in 1st line of treatment. In 2024, Alectinib captured ~50% market share of the ALK market in the US.
- Lorlatinib is a third-generation ALK inhibitor that generated ~USD 440 million in 2024 in the 7MM.
- PD-L1 therapies are mainly utilized in patients without genetic drivers. Merck’s KEYTRUDA is generally considered the ‘gold standard’ of care in 1L NSCLC when combined with platinum-chemotherapy, regardless of PD-1 status.
- ENHERTU's uptake in HER2m NSCLC is strong, but ROZLYTREK and GAVRETO in RET-fusion are performing below sales expectations.
NSCLC Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2025–2034, which depends on the competitive landscape, safety, efficacy data, and order of entry. It is important to understand that the key players evaluating their novel therapies in the pivotal and confirmatory trials should remain vigilant when selecting appropriate comparators to stand the greatest chance of a positive opinion from regulatory bodies, leading to approval, smooth launch, and rapid uptake. The Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer drugs market is expanding due to innovative therapies, rising incidence, and advancements in targeted and immunotherapies.
By overcoming the resistance from first and second-generation EGFR inhibitors and better efficacy in terms of overall response and progression-free survival, TAGRISSO become the market leader in the EGFR NSCLC market with fast uptake. Lorlatinib is a third-generation ALK inhibitor. It showed higher potency and selectivity for ALK mutation, better penetration into the brain, and broader activity against different resistance mutations compared to the previous generation ALK inhibitor. Its uptake is fast compared to alectinib. However, by 2034, the highest market size will be captured by alectinib.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
NSCLC Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer clinical trials within Phase III and II. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Latest KOL Views on NSCLC
To keep up with the real-world scenario in current and emerging market trends, we take opinions from Key Industry leaders working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on the evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient’s therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, including Medical/scientific writers, Medical Oncologists, Pulmonologists and Professors, Chief of the Thoracic Service at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, and Others.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 40+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 18+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as MD Anderson Cancer Center, Texas, UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, Cancer Research UK Barts Centre in London, LUNGevity Foundation, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer market trends.
We perform qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
NSCLC Market Access and Reimbursement
The cost of treating NSCLC has shown significant increases over time, irrespective of the stage of the disease. According to real-world findings, this is particularly true for younger patients treated in the outpatient setting. Although first-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors were reimbursed and available in all countries for other registered therapies—even for ALK inhibitors and checkpoint inhibitors in first-line—there were apparent gaps in availability and/or reimbursement.
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of NSCLC, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies, along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies, will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the NSCLC market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM NSCLC therapeutics market.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Report Insights
- NSCLC Patient Population
- NSCLC Therapeutic Approaches
- NSCLC Pipeline Analysis
- NSCLC Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Report Key Strengths
- Ten Years Forecast
- 7MM Coverage
- NSCLC Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- NSCLC Drugs Uptake
- Key NSCLC Market Forecast Assumptions
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Report Assessment
- Current NSCLC Treatment Practices
- NSCLC Unmet Needs
- NSCLC Pipeline Product Profiles
- NSCLC Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
- NSCLC Market Drivers
- NSCLC Market Barriers
FAQs
- What is the historical and forecasted NSCLC patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- What was the NSCLC total market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- How will different NSCLC target classes affect the treatment paradigm of NSCLC?
- What will be the impact of KEYTRUDA’s expected patent expiry?
- How will KEYTRUDA compete with other therapies in the first- and second lines?
- Which class is going to be the largest contributor in 2034?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
- Although multiple expert guidelines recommend testing for targetable mutations prior to therapy initiation, why do barriers to testing remain high?
- What are the current and emerging options for treating NSCLC?
- How many companies are developing therapies to treat NSCLC?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies?
Reasons to buy Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market Forecast Report:
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the NSCLC Market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Stay updated with us for Recent Articles
- The Next Chapter in NSCLC Treatment Space: Recent Discoveries and Innovations
- Novel mutation-targeting therapies in the horizon to relieve the global healthcare burden NSCLC poses
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market: Treatments and Market Forecast
- Evaluating Key Advancements and Emerging Therapies in EGFR-Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market
- Novel Insights Into The Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market
- Evolving Landscape for Rare Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Latest DelveInsight Blogs
Related Infographics of the Report