Sodium Channel Blockers Pipeline
DelveInsight’s, “Sodium Channel Blockers - Pipeline Insight, 2025” report provides comprehensive insights about 50+ companies and 55+ pipeline drugs in Sodium Channel Blockers pipeline landscape. It covers the pipeline drug profiles, including clinical and nonclinical stage products. It also covers the therapeutics assessment by product type, stage, route of administration, and molecule type. It further highlights the inactive pipeline products in this space.
Geography Covered
Global coverage
Sodium Channel Blockers: Understanding
Sodium Channel Blockers: Overview
Sodium Channel Blockers are a class of drugs that inhibit voltage-gated sodium channels (Naᵥ), preventing the influx of sodium ions into cells. This action stabilizes excitable membranes, slows electrical conduction, and reduces abnormal firing in nerve or heart cells. They are widely used as antiarrhythmics (Class I drugs), antiepileptics, local anesthetics, and for neuropathic pain. Their effects are often state-dependent, meaning they work best when sodium channels are frequently active. Examples include lidocaine, phenytoin, and flecainide. Sodium Channel Blockers generally have a lipophilic (fat-soluble) aromatic ring linked to a hydrophilic (water-soluble) amine group through an intermediate chain (often an ester or amide). This amphipathic structure allows the drug to cross cell membranes and access the sodium channel from inside the cell. The aromatic region enables membrane binding, while the amine group interacts with the sodium channel pore. Structural variations determine their affinity, selectivity, and duration of action. Local anesthetics (like lidocaine) and antiarrhythmics (like flecainide) share this basic pharmacophore.
Sodium-channel blockers comprise the Class I antiarrhythmic compounds according to the Vaughan-Williams classification scheme. These drugs bind to and block the fast sodium channels that are responsible for the rapid depolarization (phase 0) of fast-response cardiac action potentials. This type of action potential is found in non-nodal, cardiomyocytes (e.g., atrial and ventricular myocytes; purkinje tissue). Because the slope of phase 0 depends on the activation of fast sodium-channels and the rapid entry of sodium ions into the cell blocking these channels decreases the slope of phase 0, which also leads to a decrease in the amplitude of the action potential.
Sodium channel blockers work by inhibiting voltage-gated sodium (Naᵥ) channels, which are essential for initiating and propagating action potentials in excitable cells like neurons, cardiac myocytes, and muscle fibers. These drugs bind preferentially to the open or inactivated states of the sodium channels, thereby blocking the influx of sodium ions (Na⁺) during depolarization. This reduces the rate of rise (Phase 0) of the action potential and slows conduction velocity across the tissue. In the heart, this helps correct abnormal electrical activity and treat arrhythmias (Class I antiarrhythmics). In the nervous system, it decreases abnormal neuronal firing, helping in conditions like epilepsy or neuropathic pain. Local anesthetics block sodium channels in peripheral nerves, preventing pain signal transmission. Many of these agents exhibit use-dependent blockade, meaning they are more effective when the channel is frequently active. The result is membrane stabilization and reduced excitability of the target cells.
Voltage-gated sodium channels are crucial for the generation and propagation of action potentials in nerve, muscle, and cardiac cells, making them a valuable therapeutic target. Sodium channel blockers modulate these channels to reduce abnormal excitability, offering effective treatment for a range of disorders. In cardiology, they are used as Class I antiarrhythmics to manage life-threatening arrhythmias. In neurology, they help control seizures, neuropathic pain, and bipolar disorder by stabilizing neuronal firing. As local anesthetics, they block pain signals in peripheral nerves. Their tissue-specific targeting and use-dependent action make them highly versatile and clinically valuable. Example: Lidocaine is a commonly used sodium channel blocker that serves as both an antiarrhythmic and a local anesthetic.
“Sodium Channel Blockers - Pipeline Insight, 2025"" report by DelveInsight outlays comprehensive insights of present scenario and growth prospects across the mechanism of action. A detailed picture of the Sodium Channel Blockers pipeline landscape is provided which includes the disease overview and Sodium Channel Blockers treatment guidelines. The assessment part of the report embraces, in depth Sodium Channel Blockers commercial assessment and clinical assessment of the pipeline products under development. In the report, detailed description of the drug is given which includes mechanism of action of the drug, clinical studies, NDA approvals (if any), and product development activities comprising the technology, Sodium Channel Blockers collaborations, licensing, mergers and acquisition, funding, designations and other product related details.
Report Highlights
- The companies and academics are working to assess challenges and seek opportunities that could influence Sodium Channel Blockers R&D. The therapies under development are focused on novel approaches to treat/improve Sodium Channel Blockers.
Sodium Channel Blockers Emerging Drugs Chapters
This segment of the Sodium Channel Blockers report encloses its detailed analysis of various drugs in different stages of clinical development, including phase II, I, preclinical and Discovery. It also helps to understand clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, and the latest news and press releases.
Sodium Channel Blockers Emerging Drugs
- Evenamide: Newron Pharmaceuticals
Evenamide is a novel antipsychotic drug with a unique mechanism of action, distinct from existing treatments. It selectively inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels in hyper-active neurons, leading to normalization of the glutamatergic dysfunction—a key factor in patients who do not respond well to traditional antipsychotic medications. It is a new oral chemical entity being developed by Newron as an add-on therapy to existing antipsychotics for two difficult-to-treat patient populations by reducing hippocampal and cortical hyper-excitability, evenamide directly addresses the root cause of the dysfunction. This action restores neurophysiological balance without interfering with over 150 receptors, enzymes, or transporters involved in CNS activity. Currently, the drug is in the Phase III stage of its development for the treatment of treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS) and chronic schizophrenia with poor response to standard treatment
- Taplucainium: Nocion Therapeutics
Taplucainium (formerly NTX-1175) is a proprietary molecule in the novel class of charged sodium channel blockers that allows for specific silencing of activated/inflamed nociceptors while having minimal local off-target effects or systemic exposure. Unlike other investigative cough therapies, such as P2X3-antagonists, TRPA1-antagonists and TRPM8-agonists, which target a specific large pore channel, taplucainium works downstream by selectively targeting the sodium channels in activated nociceptors which are the target of these large pore channels. Taplucainium is formulated into a dry powder for inhalation and, once inhaled, gains access to the pulmonary nociceptors through any open large pore channel including P2X, TRPV, TRPA and TRPM channels whereupon it inhibits the sodium channels responsible for initiating the pathological cough response. The broader mechanism of taplucainium has shown significant antitussive effects in preclinical models of cough. Combined with good preliminary safety and efficacy data from earlier stage clinical work, this forms the basis for its investigation not just in chronic cough but in other cough indications as well. Currently, the drug is in the Phase III stage of its development for the treatment of Chronic Cough.
- STC-004: Eli Lilly and Company
STC-004 is an investigational therapeutic candidate being developed by Eli Lilly and Company, targeting neurological and psychiatric disorders. Designed as a selective muscarinic M4 receptor positive allosteric modulator (PAM), STC-004 aims to enhance dopaminergic signaling with improved safety and tolerability over traditional dopaminergic agents. The compound is being explored for potential use in schizophrenia and other neuropsychiatric conditions, with a focus on reducing cognitive and negative symptoms. Its mechanism offers a novel, non-dopaminergic approach to restoring functional neural circuits. STC-004, a Phase II ready Nav1.8 inhibitor being studied for the treatment of pain. STC-004 may represent a next-generation, non-opioid treatment for patients suffering from chronic pain.
Further product details are provided in the report……..
Sodium Channel Blockers: Therapeutic Assessment
This segment of the report provides insights about the different Sodium Channel Blockers drugs segregated based on following parameters that define the scope of the report, such as:
- Major Players in Sodium Channel Blockers
There are approx. 50+ key companies which are developing the therapies for Sodium Channel Blockers. The companies which have their Sodium Channel Blockers drug candidates in the most advanced stage, i.e. Phase III include, Newron Pharmaceuticals.
Phases
DelveInsight’s report covers around 55+ products under different phases of clinical development like
- Late stage products (Phase III)
- Mid-stage products (Phase II)
- Early-stage product (Phase I) along with the details of
- Pre-clinical and Discovery stage candidates
- Discontinued & Inactive candidates
Route of Administration
Sodium Channel Blockers pipeline report provides the therapeutic assessment of the pipeline drugs by the Route of Administration. Products have been categorized under various ROAs such as
- Intra-articular
- Intraocular
- Intrathecal
- Intravenous
- Oral
- Parenteral
- Subcutaneous
- Topical
- Transdermal
Molecule Type
Products have been categorized under various Molecule types such as
- Oligonucleotide
- Peptide
- Small molecule
Product Type
Drugs have been categorized under various product types like Mono, Combination and Mono/Combination.
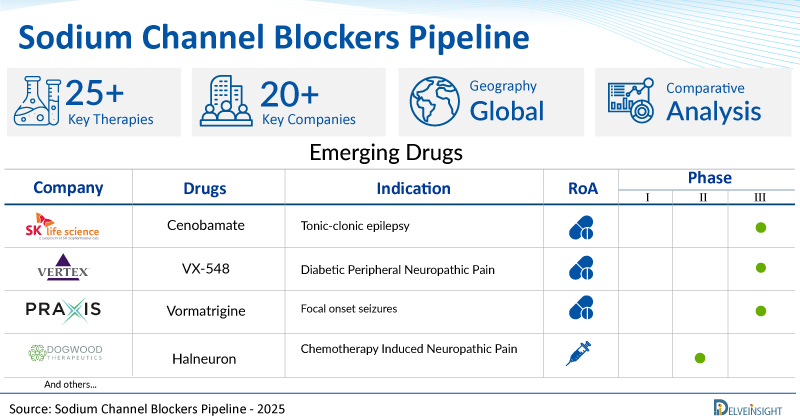
| Drugs | Company | Phase | Indication | RoA |
| Cenobamate | SK Biopharmaceuticals | III | Tonic-clonic epilepsy | Oral |
| VX-548 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals | III | Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain | Oral |
| Vormatrigine | Praxis Precision Medicines | II/III | Focal onset seizures | Oral |
| Halneuron | Dogwood therapeutics | II | Chemotherapy Induced Neuropathic Pain | Subcutaneous |
| LTG-001 | Latigo Biotherapeutics | II | Postoperative pain | Oral |
| NBI-921355 | Neurocrine Biosciences | I | Epilepsy | Unspecified route |
Sodium Channel Blockers: Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in phase II, I, preclinical and discovery stage. It also analyses Sodium Channel Blockers therapeutic drugs key players involved in developing key drugs.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers the detailed information of collaborations, acquisition and merger, licensing along with a thorough therapeutic assessment of emerging Sodium Channel Blockers drugs.
Sodium Channel Blockers Report Insights
- Sodium Channel Blockers Pipeline Analysis
- Therapeutic Assessment
- Unmet Needs
- Impact of Drugs
Sodium Channel Blockers Report Assessment
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Therapeutic Assessment
- Pipeline Assessment
- Inactive drugs assessment
- Unmet Needs
Key Questions
Current Treatment Scenario and Emerging Therapies:
- How many companies are developing Sodium Channel Blockers drugs?
- How many Sodium Channel Blockers drugs are developed by each company?
- How many emerging drugs are in mid-stage, and late-stage of development for the treatment of Sodium Channel Blockers?
- What are the key collaborations (Industry–Industry, Industry–Academia), Mergers and acquisitions, licensing activities related to the Sodium Channel Blockers therapeutics?
- What are the recent trends, drug types and novel technologies developed to overcome the limitation of existing therapies?
- What are the clinical studies going on for Sodium Channel Blockers and their status?
- What are the key designations that have been granted to the emerging drugs?