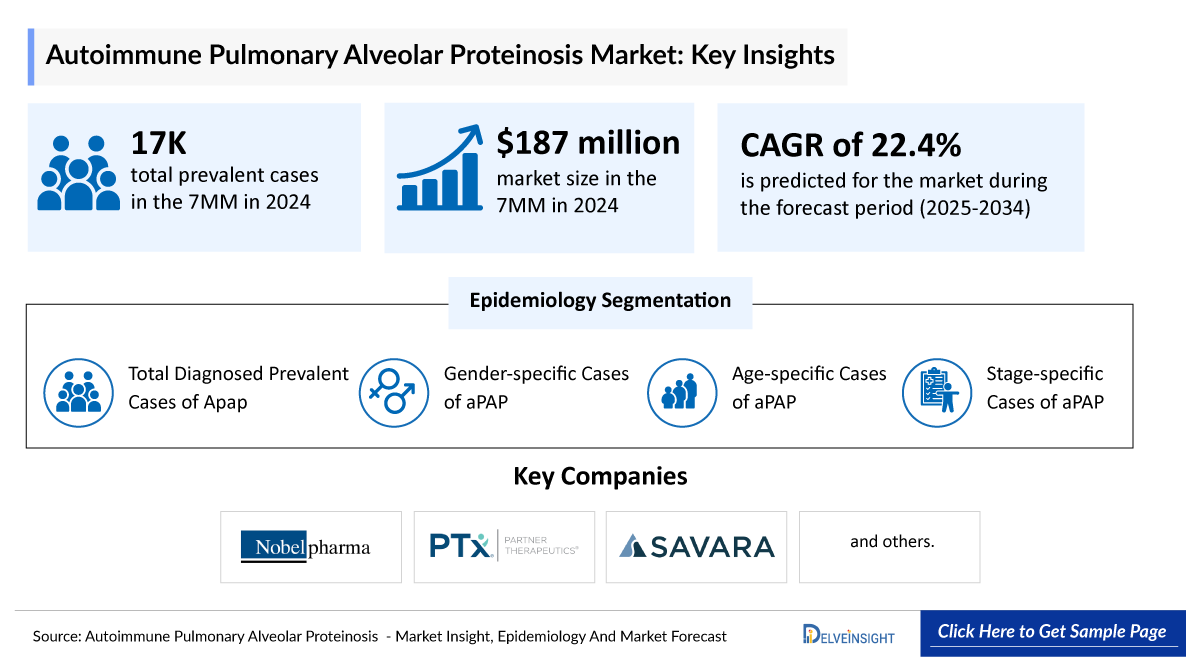
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Market
Key Highlights
- aPAP is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the accumulation of surfactant-derived lipoproteins and immune cells within the alveoli of the lungs. This condition leads to impaired gas exchange and respiratory distress.
- WLL performed under general anesthesia remains the standard therapeutic intervention for patients with severe aPAP. Despite its widespread use, standardized criteria for determining when to discontinue or complete a WLL session have not been established.
- Sargramostim is not approved in the US or Europe for aPAP or any other acute or chronic lung disease, though it is occasionally used in the US off-label as a pharmacy-compounded injectable formulated for inhalation.
- The diagnosis of aPAP relies on integrating clinical assessment with radiographic and laboratory findings. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) typically demonstrates the characteristic “crazy-paving” pattern. Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid often appears milky and may show elevated surfactant protein D (SP-D). Confirmation is achieved by detecting anti–GM-CSF antibodies in serum or BAL.
- Japan leads globally in disease awareness following the 2024 approval of LEUKINE, the only approved treatment of its kind worldwide. In most other countries, lack of comparable regulatory approval and recognition results in delayed diagnoses and less effective treatment decisions.
- The US and EU markets remain essentially unpenetrated for this rare indication, creating a sizable addressable market for Savara. With limited existing therapeutic options and sustained unmet need, Savara could secure a leading market position and potentially the majority share, assuming favorable regulatory and commercial execution.
- The competitive landscape is led by Partner Therapeutics and Nobelpharma with Sargramostim (Japan approved), alongside Savara with Molgramostim (pending approval).
DelveInsight’s “Autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (aPAP) – Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of aPAP, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as aPAP market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The aPAP market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM aPAP market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current aPAP treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
aPAP Epidemiology
|
Segmented by:
|
|
aPAP Key Companies |
|
|
aPAP Key Therapies |
|
|
aPAP Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP): Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
aPAP Overview
aPAP is a rare lung disorder characterized by the accumulation of surfactant within the alveoli, leading to impaired gas exchange and progressive hypoxemia. It accounts for the vast majority of PAP cases and is caused by autoantibodies that neutralize GM-CSF, a cytokine essential for alveolar macrophage function and surfactant clearance. Patients typically present with dyspnea, reduced exercise tolerance, and diffuse ground-glass opacities on imaging. Although the disease can occur at any age, it most often appears in adults in their 30s to 40s. Without effective surfactant removal or restoration of GM-CSF signaling, aPAP can lead to worsening respiratory impairment and increased susceptibility to infections.
aPAP Diagnosis
Diagnosing autoimmune PAP is difficult due to its rarity, nonspecific symptoms, and unremarkable routine tests, leading to frequent misdiagnosis as pneumonia and a median diagnostic delay of 1.5 years. Clinicians should suspect aPAP in afebrile patients with slowly progressive dyspnea, minimal cough, and diffuse bilateral infiltrates; HRCT typically reveals characteristic ground-glass patterns. BAL fluid with a cloudy, proteinaceous appearance supports the diagnosis, while lung biopsy is rarely needed and reserved for complex cases. The most definitive test is the serum GM-CSF autoantibody assay, which is highly sensitive and specific for aPAP; GM-CSF signaling index testing can help clarify borderline results. Differentiation from hereditary, secondary, or congenital forms of PAP relies on GM-CSF autoantibody status, GM-CSF signaling tests, and when indicated, genetic evaluation for GM-CSF receptor or surfactant-related mutations.
Further details related to diagnosis are provided in the report…
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Treatment
aPAP is primarily managed by restoring alveolar macrophage function and improving surfactant clearance. The standard therapy is whole lung lavage (WLL), which mechanically removes accumulated surfactant and can produce substantial symptomatic and physiologic improvement. Inhaled granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) has become an important non-invasive option that targets the GM-CSF autoantibody–mediated pathophysiology; this includes SARGMALIN (inhaled sargramostim), the formulation approved in Japan, administered in cyclic dosing to improve gas exchange and reduce the need for WLL. Subcutaneous GM-CSF may be considered in select cases, although inhaled therapy is generally preferred. For patients with severe or refractory disease, rituximab to reduce autoantibody production or, rarely, plasmapheresis can be used when standard treatments fail. Supportive measures, including smoking cessation, infection prevention, and close monitoring of oxygenation, remain essential across all disease severities.
Further details related to treatment are provided in the report…
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP): Epidemiology
The aPAP epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Total diagnosed prevalent cases of aPAP, gender-specific cases of aPAP, age-specific cases of aPAP, stage-specific cases of aPAP in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
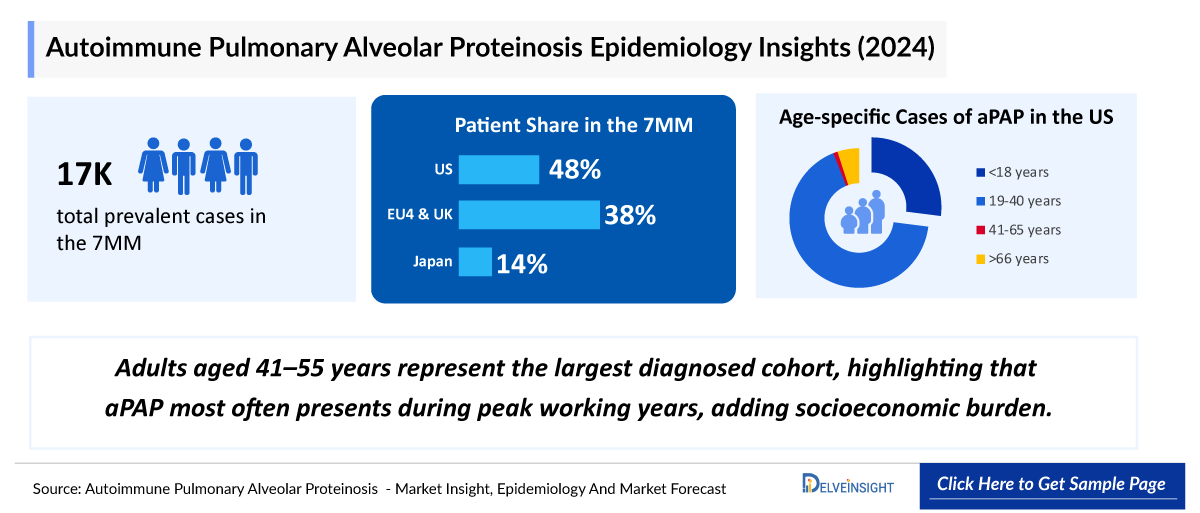
- Throughout the 7MM, US accounted for maximum prevalent cases of aPAP with about 8,300 cases.
- Among EU4 and the UK, males were found to be more affected by aPAP than females.
- Germany accounted for about 580 aPAP diagnosed prevalent cases in 2024.
- Japan accounted for about 780 cases of DSS-3, 4, and 5 (stage-specific cases) of aPAP cases in 2024.
- Adults aged 41–55 years represent the largest diagnosed cohort, highlighting that aPAP most often presents during peak working years, adding socioeconomic burden.
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the aPAP report encloses a detailed analysis of aPAP marketed drugs. It also deep dives into aPAP pivotal clinical trial details, recent and expected market approvals, patent details, the latest news, and recent deals and collaborations.
Marketed Drugs
Sargramostim (SARGMALIN): Nobelpharma/Partner Therapeutics
Sargramostim is a glycosylated recombinant human GM-CSF produced by recombinant DNA technology in a yeast (S. cerevisiae) expression system. It functions as a hematopoietic growth factor that stimulates survival, proliferation, and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells into multiple immune cell types, including neutrophils, macrophages, and dendritic cells. It is indicated for the treatment of patients with aPAP and other severe life-threatening indications.
- In July 2024, Nobelpharma launched “SARGMALIN for inhalation 250 µg” for the treatment of aPAP in Japan.
- In March 2024, Nobelpharma received approval from the Japanese PMDA for the inhaled use of sargramostim, branded in Japan as SARGMALIN, to treat aPAP. The approval was based on the Phase II PAGE trial.
Note: Detailed list will be provided in the final report.
Emerging Drugs
Molgramostim Nebulizer Solution (MOLBREEVI): Savara
Molgramostim is a non-glycosylated recombinant human GM-CSF developed for the treatment of aPAP. It is produced using recombinant DNA technology in Escherichia coli. In aPAP, neutralizing autoantibodies against GM-CSF impair alveolar macrophage-mediated surfactant clearance, leading to surfactant accumulation and impaired gas exchange. Inhaled molgramostim is intended to restore GM-CSF signaling, re-establish alveolar macrophage function, facilitate surfactant clearance, and thereby improve pulmonary function.
As per the company’s November 2025 corporate presentation, Savara plans to resubmit the BLA for molgramostim in December 2025, with regulatory approval anticipated in mid-2026, with Fuji as drug substance manufacturer. The company also plans for EU and The UK MAA submission in Q1 2026, with approval anticipated by Q1 2027.
- In October 2025, Savara announced a USD 75 million royalty funding agreement with funds managed by RTW Investments, subject to FDA approval of molgramostim.
Note: Detailed list will be provided in the final report.
Drug Class Insights
The drug class include GM-CSF replacements
GM-CSF replacement therapy offers a mechanism-driven approach to aPAP by counteracting the neutralizing autoantibodies that suppress GM-CSF signaling and disable alveolar macrophages. Restoring this pathway re-establishes macrophage differentiation and surfactant clearance, directly addressing the biological defect rather than its downstream consequences. Sargramostim, administered by inhalation, provides broad GM-CSF exposure but may face variability in achieving optimal lung-targeted activity. Molgramostim, formulated specifically for inhalation, is designed to maximize local bioavailability in the alveolar space and may offer more efficient pathway reactivation. Both agents demonstrate the therapeutic relevance of GM-CSF restoration, but their differing delivery strategies highlight ongoing efforts to fine-tune efficacy, tolerability, and macrophage-target engagement in aPAP management.
Note: Detailed insights will be provided in the final report.
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Market Outlook
Treatment selection in aPAP is driven primarily by disease severity. Most asymptomatic patients remain stable or improve spontaneously, with only a small minority demonstrating progression. WLL remains the gold-standard intervention, providing mechanical removal of accumulated surfactant, though the procedure lacks standardized protocols and is typically reserved for patients whose daily activities are limited by dyspnea or who show physiologic deterioration (e.g., PaO2 <70 mmHg on room air or an A–a gradient >40 mmHg). For patients who are poor candidates for WLL or have disease refractory to it, GM-CSF replacement therapy, via inhaled or systemic administration, serves as a targeted approach addressing the underlying neutralizing GM-CSF autoantibodies. Sargramostim, is used as first-line pharmacologic treatment and reduces reliance on WLL. Immunomodulatory strategies, including rituximab, may be considered for selected refractory cases. Overall, while WLL remains foundational, the emergence of GM-CSF supplementation has expanded treatment options, though high-quality comparative data remain limited.
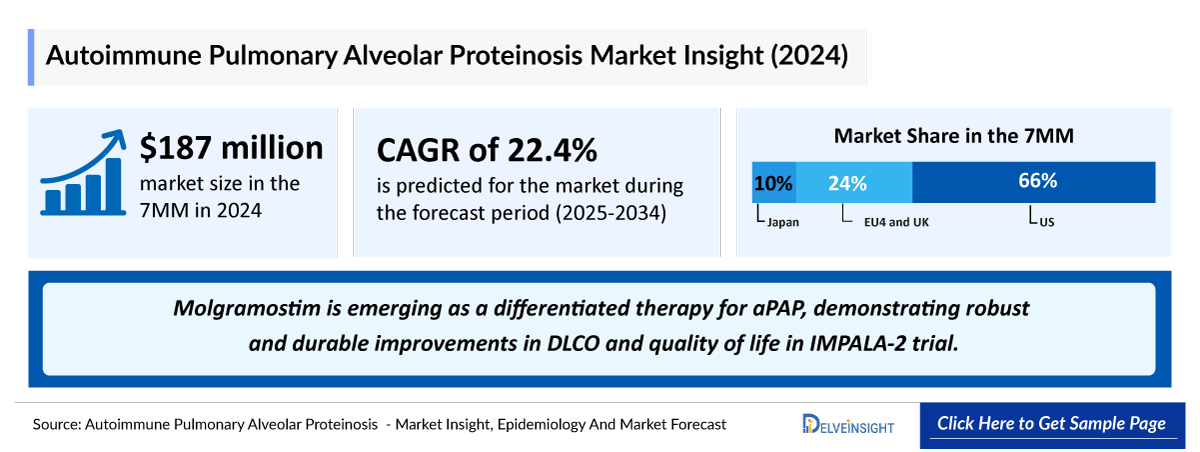
- Throughout the 7MM, the US captured the maximum aPAP market share in 2024 with about USD 120 million.
- Among EU4 and the UK, Germany is expected to capture the maximum market share, followed by Italy and France by 2034.
- Japan remains the only country with an approved therapy for aPAP. The 2024 approval of SARGMALIN established the first regulated treatment option in this space and has increased clinical and public awareness of the disease within Japan. It accounted for sales of 167 million yen in first year of approval.
- Molgramostim is emerging as a differentiated therapy for aPAP, demonstrating robust and durable improvements in DLCO and quality of life in IMPALA-2 trial. Its anticipated sequential launch in the US followed by Europe enables coverage across all 7MM markets, whereas Sargramostim’s approval remains limited to Japan.
- WLL and inhaled GM-CSF supplementation function as complementary first-line therapies, applied sequentially based on clinical need, especially in patients with respiratory impairment. Rituximab and plasmapheresis are reserved for third- and fourth-line use, respectively.
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2025–2034. The landscape of aPAP treatment has experienced a profound transformation with the uptake of novel drugs. These innovative therapies are redefining standards of care. Furthermore, the increased uptake of these transformative drugs is a testament to the unwavering dedication of physicians, professionals, and the entire healthcare community in their tireless pursuit of advancing disease care. This momentous shift in treatment paradigms is a testament to the power of research, collaboration, and human resilience.
Key Highlights
- In September 2025, Savara presented additional analyses from its Phase III IMPALA-2 trial of molgramostim in aPAP as posters at the European Respiratory Society (ERS) Congress 2025.
- In May 2025, Savara received a Refusal to File (RTF) from the FDA for the BLA of molgramostim.
- In September 2024, Savara launched the Early Access Program (EAP) for molgramostim, allowing physicians to request treatment for eligible aPAP patients in regions where the therapy is not yet commercially available.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights into therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I/II. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for aPAP emerging therapy.
KOL Views
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on aPAP evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 15+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 7+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as - University of California, Cinnnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, University of Southern California, IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Hospital Foundation, Foch Hospital, University of Sheffield, NTT Medical Center Tokyo, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or aPAP market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated, wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and this clearly explains the drugs side effects in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement may be referred to as the negotiation of a price between a manufacturer and payer that allows the manufacturer access to the market. It is provided to reduce the high costs and make the essential drugs affordable. Health technology assessment (HTA) plays an important role in reimbursement decision-making and recommending the use of a drug. These recommendations vary widely throughout the seven major markets, even for the same drug. In the US healthcare system, both Public and Private health insurance coverage are included. Also, Medicare and Medicaid are the largest government-funded programs in the US. The major healthcare programs including Medicare, Medicaid, Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and the state and federal health insurance marketplaces are overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Other than these, Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), and third-party organizations that provide services, and educational programs to aid patients are also present.
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of currently used therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of aPAP, explaining its causes, signs, symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently used therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, disease progression, and treatment guidelines has been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the aPAP market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM aPAP market.
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- aPAP Pipeline Analysis
- aPAP Market Size and Trends
- Existing and Future Market Opportunity
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Report Key Strengths
- 10 Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- aPAP Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Autoimmune Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (aPAP) Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT Analysis and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs
- What was the aPAP market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2024, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved therapies?
- What can be the future treatment paradigm of aPAP?
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of aPAP? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population with aPAP?
- What are the current options for the treatment of aPAP? What are the current guidelines for treating aPAP in the US, Europe, and Japan?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies being developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
Reasons to Buy
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the aPAP market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the Analyst view section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of current therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.


-pipeline.png&w=256&q=75)

