Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market
- According to DelveInsight’s analysis, the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market in the 7MM was valued at approximately USD 3,615.6 million in 2023. Over the forecast period from 2024 to 2034, this market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5%. This expansion in the 7MM is driven by the introduction of innovative therapies such as CYR-064, and others.
- Given the high unmet needs, key players in the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market include Cyrano Therapeutics, among others, who are actively advancing therapeutic and preventive solutions to address the growing prevalence and management of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss.
- According to DelveInsight’s estimates, in 2023, there were approximately 257 million total prevalent cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM. Of these, the United States accounted for approximately 34% of the cases, while Germany and Spain represented approximately 15% and 7% of the cases, respectively. These cases are expected to rise driven by factors such as the aging population, chronic diseases, medications and treatments, and improved lifestyle factors.
- The absence of FDA-approved therapies for Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss highlights a critical unmet need, driving ongoing research and development in emerging pipelines to address this sensory dysfunction, particularly post-viral sequelae such as COVID-19-induced anosmia.

DelveInsight’s “Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of chronic smell and flavor loss, historical and forecasted epidemiology, as well as the chronic smell and flavor loss market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The chronic smell and flavor loss market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM chronic smell and flavor loss market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers chronic smell and flavor loss treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
|
Study Period
|
2020–2034
|
|
Forecast Period
|
2024–2034
|
|
Geographies Covered
|
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the UK, and Japan
|
|
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Epidemiology
|
- Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
- Total Diagnosed Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
- Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
- Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
- Etiology-specific Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
|
|
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market
|
- Total Market Size
- Market Size by Therapies
|
|
Market Analysis
|
- KOL Views
- Conjoint Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Unmet Needs
|
|
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market players
|
- Cyrano Therapeutics
- Others
|
|
Future opportunity
|
A promising future opportunity for pharmaceutical companies in the area of chronic smell and flavor loss lies in developing targeted therapies that address the underlying neurobiological mechanisms. With a growing understanding of olfactory and gustatory disorders, companies can innovate novel treatments, such as regenerative therapies or neuromodulation techniques, to restore these senses. Additionally, leveraging digital health tools to enhance diagnosis and monitoring, combined with personalized treatment approaches, could significantly improve patient outcomes and meet the rising demand for effective interventions in this underserved area.
|
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Market
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Overview
Olfactory dysfunction (OD) and gustatory dysfunctions encompass a spectrum of sensory impairments characterized by reduced or distorted abilities to smell and taste, respectively. With the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic, these disorders have gained prominence, particularly as anosmia and hyposmia became prevalent symptoms among infected individuals, especially in Europe. Gustatory disturbances, including hypogeusia, dysgeusia, phantogeusia, and ageusia, are often associated with various etiologies such as viral infections, neurological damage, autoimmune conditions, and environmental exposures. The American Academy of Otolaryngology and the British Association of Otorhinolaryngology advocate for recognizing chemosensitive disorders as primary indicators of COVID-19. Given the overlapping neural pathways between taste and olfactory systems, inflammatory damage in these areas may lead to concurrent sensory dysfunctions, manifesting as a wide range of symptoms from complete loss to altered perception of taste and smell, underscoring the need for targeted research and therapeutic interventions in this evolving field.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Diagnosis
Diagnosis of smell and taste disorders typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) to identify the underlying etiology. The process begins with a thorough physical examination, complemented by self-assessment questionnaires and psychophysical assessments to gauge the extent of sensory impairment. Advanced imaging techniques may be employed to visualize anatomical abnormalities or inflammatory changes in the nasal and oral cavities. This multifaceted diagnostic approach ensures accurate identification of potential causes, allowing for targeted interventions to address the specific dysfunctions impacting the patient’s olfactory and gustatory abilities.
Further details related to country-based variations are provided in the report…
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment
Treatment options for smell disorders remain limited, primarily effective in cases where nasal pathologies are the underlying cause. Surgical interventions and corticosteroid therapy are the mainstays for addressing these conditions. In contrast, therapeutic strategies for taste disorders, including corticosteroids and vitamin A, lack robust clinical validation, as do acupuncture approaches. However, zinc gluconate has shown promise in treating idiopathic dysgeusia when administered at a dosage of 140 mg/day for three months. For patients experiencing burning mouth syndrome (BMS), tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline and imipramine have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating abnormal sensations, with additional successful outcomes reported using benzodiazepines like clonazepam or diazepam. This highlights the necessity for further clinical research to establish effective treatments for both olfactory and gustatory disorders.
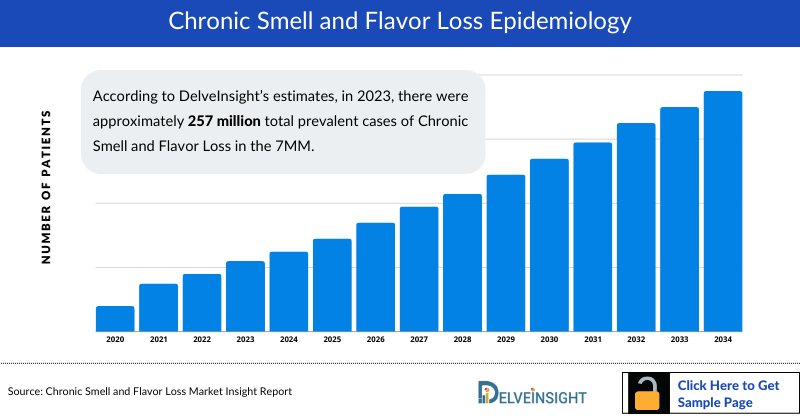
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Epidemiology
- As the market is derived using a patient-based model, the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, Total Diagnosed Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, and Etiology-specific Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
- According to DelveInsight’s epidemiology model, in the US, the total prevalent cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss were approximately 86 million in 2023. This number is anticipated to rise during the forecast period (2024-2034), driven by increased awareness and screening, along with advancements in testing.
- Among the diagnosed prevalent cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK in 2023, the highest cases were observed in Germany which was approximately 11 million cases and the least number of diagnosed cases were in Spain with approximately 5 million.
- In 2023, gender-specific instances (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss were seen to be more in females with around 2.2 million cases as compared to males which were around 1.8 million in the UK.
- According to DelveInsight's epidemiology model, age-specific cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the US for 2023 were segmented into the age groups of 40-49 years, 50-59 years, 60-69 years, 70-79 years, and 80 years and older. The highest prevalence was observed in the 70-79 years age group.
- In 2023, Japan reported 1.6 million cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss due to post-influenza hyposmia and hypogeusia, alongside 1.7 million cases attributed to other causes.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Drug Chapters
Emerging Drugs
CYR-064: Cyrano Therapeutics
CYR-064, developed by Cyrano Therapeutics, is an innovative nasal spray designed to restore olfactory and gustatory function in individuals with chronic sensory loss. This formulation utilizes phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors for intranasal delivery, targeting the mechanisms underlying smell and flavor loss. These conditions typically inhibit stem cell activation mediated by adenylyl cyclase III through cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), reducing growth factor secretion from nasal mucus and impairing stem cell activity in the olfactory epithelium. By delivering PDE inhibitors directly to this region, cAMP and cGMP levels can be increased, potentially restoring olfactory function. Clinical experience has shown that various PDE inhibitors can correct smell loss and, in some cases, restore olfactory function to near-normal levels. CYR-064 is currently in Phase II clinical trials specifically targeting hyposmia, with promising implications for improving outcomes in affected patients.
|
Drug
|
MoA
|
RoA
|
Company
|
Phase
|
|
CYR-064
|
PDE inhibitors
|
Intranasal
|
Cyrano Therapeutics
|
II
|
|
XX
|
XX
|
XX
|
XXX
|
X
|
Note: Further emerging therapies and their detailed assessment will be provided in the final report.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Drug Class Insights
The treatment of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss involves several classes of interventions aimed at addressing the underlying causes and alleviating symptoms. Corticosteroids are commonly used to reduce inflammation in cases related to nasal pathology, enhancing olfactory function. Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline and imipramine, are employed to manage abnormal sensations associated with taste disorders, particularly in conditions like burning mouth syndrome (BMS). Zinc supplements, specifically zinc gluconate, have shown therapeutic potential in idiopathic dysgeusia, offering a targeted approach for taste disturbances. Additionally, benzodiazepines like clonazepam and diazepam are utilized to address anxiety and discomfort associated with sensory dysfunctions. Emerging therapies and further research into neuroprotective agents may also contribute to a more comprehensive treatment landscape for these disorders.
Continued in report…

Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Outlook
Current treatment options for olfactory and gustatory disorders are limited, primarily focusing on corticosteroids and surgical interventions for nasal pathologies, such as polypectomy and pan sinus procedures. For taste disorders, while corticosteroids and vitamin A are often considered, they lack robust clinical evidence. Zinc gluconate has shown some therapeutic effectiveness in idiopathic dysgeusia, and tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline and imipramine are utilized for managing burning mouth syndrome (BMS). Cyrano Therapeutics is a major player in this market with its lead product, CYR-064, which comprises phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors formulated for intranasal administration. This candidate is designed to address the common mechanisms underlying smell and flavor loss by inhibiting stem cell activation. Following successful fundraising and patent approvals, Cyrano is advancing toward a Phase II clinical trial in the US. Despite the absence of other pharmaceutical companies actively developing novel treatments, ongoing trials led by universities and research organizations are exploring potential alternatives, driven by increased awareness and the pressing need for effective therapies in the context of rising cases linked to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Continued in report…
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2020–2034. For example, CYR-064 is expected to enter the US market in 2025 and is projected to have a medium uptake during the forecast period.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Pipeline Development Activities
The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline development activities
The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for emerging therapies for Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss KOL Views
To keep up with current Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including Medical/scientific writers, Medical Professionals, Professors, Directors, and Others.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 50+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers like the King’s College in London, the University of Washington in Seattle, and European Hospital Georges-Pompidou among others, were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Physician’s View
“As per the KOLs from the UK, there are now millions of people around the world that still have persistent olfactory loss” after COVID-19. It is still very much a neglected area, both in terms of research funding and support from healthcare systems, and it is dismissed in terms of the impact it has on people.”
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple emerging Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
To analyze the effectiveness of these therapies, have calculated their attributed analysis by giving them scores based on their ability to improve atrial and ventricular dimension/function and ability to regulate heart rate.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials, which directly affects the safety of the molecule in the upcoming trials. It sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Access and Reimbursement
The high cost of therapies for the treatment is a major factor restraining the growth of the global drug market. Because of the high cost, the economic burden is increasing, leading the patient to escape from proper treatment.
The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Further details will be provided in the report.
The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenarios, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Report
- The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines have been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market, historical and forecasted market size, and market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market.
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market report insights
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Pipeline Analysis
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Trends
- Existing and Future Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Opportunity
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market report key strengths
- 11 years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Attribute analysis
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Drugs Uptake
- Key Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Forecast Assumptions
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market report assessment
- Current Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Practices
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Unmet Needs
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Pipeline Product Profiles
- Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Attribute Analysis)
Key Questions
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Insights
- What was the total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market size, the market size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by therapies, and market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- How will CYR-064 affect the treatment paradigm of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss?
- Which drug is going to be the largest contributor by 2034?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and marketed therapies?
- How would future opportunities affect the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Epidemiology Insights
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM with respect to the patient population pertaining to Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss?
- What is the historical and forecasted Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- Out of the countries mentioned above, which country would have the highest diagnosed prevalent Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss population during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- What factors are contributing to the growth of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss cases?
Current Treatment Scenario, Marketed Drugs, and Emerging Therapies
- What are the current options for the treatment of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss? What are the current clinical and treatment guidelines for treating Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss?
- How many companies are developing therapies for the treatment of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss?
- How many emerging therapies are in the mid-stage and late stage of development for treating Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- What is the cost burden of current treatment on the patient?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the accessibility issues of approved therapy in the US?
- What is the 7MM historical and forecasted Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market?
Reasons to Buy
- The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- The distribution of historical and current patient share is based on real-world prescription data in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying upcoming Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss companies in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of Access and Reimbursement policies for Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, barriers to accessibility of approved therapy, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss companies can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
1 Key Insights
2 Report Introduction
3 Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Overview at a Glance
3.1 Market Share (%) Distribution of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in 2020
3.2 Market Share (%) Distribution of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in 2034
4 Executive Summary of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
5 Disease Background and Overview
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Classification
5.2.1 Smell disorders
5.2.2 Taste disorders
5.3 Signs and Symptoms
5.3.1 Anosmia or hyposmia
5.3.2 Dysgeusia
5.3.3 Ageusia
5.4 Etiology and Risk Factors
5.4.1 Etiology of taste disorders
5.4.2 Etiology of OD
5.5 Physiology and Pathogenesis
5.5.1 Sense of olfaction and pathophysiology of olfactory disorders
5.5.2 Sense of gustation and pathophysiology of gustatory disorders
5.6 Smell and Taste Disorders in COVID-19
5.7 Diagnosis of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
5.7.1 Physical examination and self-assessment tools
5.7.2 Psychophysical assessment
5.7.3 Imaging tests
5.7.4 Other tests
5.8 Differential Diagnosis
5.8.1 Ageusia
5.8.2 Anosmia
5.9 Treatment
5.9.1 Treatment of olfactory disorders
5.9.2 Treatment of taste disorders
5.10 Clinical Practice Guidelines
5.10.1 Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of OD by the Japanese Rhinologic Society
5.10.2 Management of New-Onset Loss of Sense of Smell during the COVID-19 Pandemic – BRS Consensus Guidelines
5.10.2.1 ENT referral
5.10.2.2 Investigations
5.10.2.3 Management
6 Epidemiology and Patient Population
6.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM
6.2 Key Findings
6.3 Assumptions and Rationale: 7MM
6.4 The United States
6.4.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
6.4.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.4.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.4.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.4.2 Total Diagnosed Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
6.4.2.1 Diagnosed prevalent cases
6.4.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19)
6.4.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
6.4.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
6.4.5 Etiology-specific (excluding COVID-19 patients) Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
6.5 The EU4 and the UK
6.5.1 Germany
6.5.1.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
6.5.1.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.5.1.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.5.1.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.5.1.2 Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
6.5.1.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.5.1.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.5.1.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
6.5.1.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
6.5.1.5 Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
6.5.2 France
6.5.2.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
6.5.2.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.5.2.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.5.2.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.5.2.2 Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
6.5.2.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.5.2.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.5.2.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
6.5.2.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
6.5.2.5 Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
6.5.3 Italy
6.5.3.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
6.5.3.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.5.3.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.5.3.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.5.3.2 Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
6.5.3.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.5.3.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.5.3.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
6.5.3.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
6.5.3.5 Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
6.5.4 Spain
6.5.4.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
6.5.4.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.5.4.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.5.4.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.5.4.2 Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
6.5.4.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.5.4.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.5.4.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
6.5.4.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
6.5.4.5 Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
6.5.5 The UK
6.5.5.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
6.5.5.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment
6.5.5.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.5.5.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.5.5.2 Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
6.5.5.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.5.5.2.2 Diagnosed prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.5.5.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
6.5.5.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
6.5.5.5 Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
6.6 Japan
6.6.1 Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
6.6.1.1 Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss
6.6.1.2 Prevalent Cases of Smell Impairment
6.6.1.3 Prevalent Cases of Flavor Impairment
6.6.2 Total Diagnosed Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
6.6.2.1 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
6.6.2.2 Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients)
6.6.3 Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
6.6.4 Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
6.6.5 Etiology-specific Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
7 Patient Journey
8 Emerging Therapies
8.1 Key Cross Competition
8.2 CYR-064: Cyrano Therapeutics
8.2.1 Drug Description
8.2.2 Drug Profile
8.2.3 Other Development Activities
8.2.4 Clinical Trial Information
8.2.5 Safety and Efficacy
8.2.6 Analysts’ Views
9 Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss: The Seven Major Market Analysis
9.1 Key Findings
9.2 Market Outlook
9.3 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM
9.4 The United States Market Size
9.4.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States
9.4.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in the United States
9.5 The EU4 and the UK Market
9.5.1 Germany
9.5.1.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany
9.5.1.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in Germany
9.5.2 France
9.5.2.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France
9.5.2.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in France
9.5.3 Italy
9.5.3.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy
9.5.3.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in Italy
9.5.4 Spain
9.5.4.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain
9.5.4.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in Spain
9.5.5 The UK
9.5.5.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK
9.5.5.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in the UK
9.6 Japan
9.6.1 Total Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan
9.6.2 Market Size of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss by Therapies in Japan
10 SWOT Analysis
11 Unmet Needs
12 Market Access and Reimbursement
12.1 The United States
12.1.1 Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS)
12.2 EU4 and the UK
12.2.1 Germany
12.2.2 France
12.2.3 Italy
12.2.4 Spain
12.2.5 The United Kingdom
12.3 Japan
12.3.1 MHLW
13 KOL Views
14 Acronyms and Abbreviations
15 Appendix
15.1 Bibliography
15.2 Report Methodology
16 DelveInsight Capabilities
17 Disclaimer
18 About DelveInsight
List of Tables:
Table 1: Summary of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss, Market, Epidemiology, and Key Events (2020–2034)
Table 2: Olfactory Dysfunctions (ODs)
Table 3: Causes of Olfactory Disturbance
Table 4: Total Prevalent Population of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 5: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 6: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 7: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 8: Total Diagnosed Prevalent cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 9: Total Diagnosed Prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 10: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 11: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 12: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 13: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in the EU4 and the UK , in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 14: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 15: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 16: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 17: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 18: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 19: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 20: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 21: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 22: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 23: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 24: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 25: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 26: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 27: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 28: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 29: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 30: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 31: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 32: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 33: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 34: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 35: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 36: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 37: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Italy , in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 38: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 39: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 40: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 41: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 42: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 43: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 44: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 45: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 46: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 47: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 48: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 49: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 50: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 51: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 52: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 53: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 54: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 55: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 56: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 57: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 58: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 59: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 60: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 61: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 62: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 63: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 64: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 65: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 66: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 67: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 68: Etiology-specific Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Table 69: Key Cross Competition, Emerging Drugs
Table 70: CYR-064, Clinical Trial Description, 2024
Table 71: Key Market Forecast Assumptions for CYR-064
Table 72: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the 7MM in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 73: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the United States in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 74: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the United States by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 75: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Germany in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 76: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Germany by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 77: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in France in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 78: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in France by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 79: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Italy in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 80: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Italy by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 81: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Spain in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 82: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Spain by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 83: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the UK in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 84: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the UK by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Table 85: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Japan in USD million (2020–2034)
Table 86: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Japan by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
List of Figures:
Figure 1: Taste Disorders
Figure 2: Signs and Symptoms of Anosmia/hyposmia
Figure 3: Causes of Taste Disorders
Figure 4: Anatomy of Taste and Olfaction
Figure 5: Possible Pathogenesis of Olfactory Disorders in COVID-19
Figure 6: Treatment Algorithm of Post viral OD
Figure 7: Total Prevalent Population of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the 7MM, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 8: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 9: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 10: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 11: Total Diagnosed Prevalent cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 12: Total Diagnosed Prevalent cases (excluding COVID-19) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 13: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 14: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 15: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the United States, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 16: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 17: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 18: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 19: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 20: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 21: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 22: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 23: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in EU4 and the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 24: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 25: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 26: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 27: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 28: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 29: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 30: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 31: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Germany, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 32: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 33: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 34: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 35: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 36: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 37: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 38: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 39: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in France, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 40: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 41: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 42: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 43: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 44: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 45: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 46: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 47: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Italy, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 48: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 49: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 50: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 51: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 52: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 53: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 54: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 55: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Spain, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 56: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Impairment in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 57: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 58: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 59: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 60: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 61: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 62: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 63: Etiology-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in the UK, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 64: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 65: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 66: Total Prevalent Cases of Chronic Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 67: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 68: Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 69: Gender-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 70: Age-specific Diagnosed Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 71: Etiology-specific Cases (excluding COVID-19 patients) of Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss in Japan, in 000’s (2020–2034)
Figure 72: Patient Journey
Figure 73: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the 7MM in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 74: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the United States in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 75: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the United States by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 76: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Germany in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 77: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Germany by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 78: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in France in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 79: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in France by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 80: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Italy in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 81: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Italy by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 82: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Spain in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 83: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Spain by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 84: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the UK in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 85: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in the UK by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)
Figure 86: Total Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Japan in USD million (2020–2034)
Figure 87: Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Market Size in Japan by Therapies in USD Million (2020–2034)






