Epstein–Barr Virus Market
Key Highlights:
- The market for Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) is poised for growth during the forecast period (2024-2034), due to heightened research and development efforts, increasing investments in healthcare infrastructure, and a growing focus on infectious disease management globally.
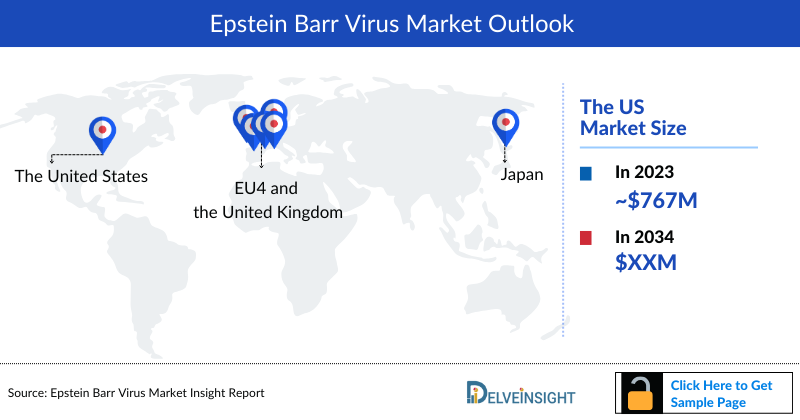
- The United States showed the diagnosed incident cases of EBV-IM compared to other 7MM countries. As per DelveInsight’s estimates, in 2023, the country alone accounted for ~37% of total diagnosed incident cases of EBV-IM, in the 7MM countries.
- In 2023, the market size of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) was highest in the US among the 7MM accounting for approximately USD 767 million that is further expected to increase by 2034.
- In December 2022, Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc. and Pierre Fabre received marketing authorization for EBVALLO (tabelecleucel) from the European Commission (EC) as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients two years of age and older with relapsed or refractory Epstein‑Barr virus-positive post‑transplant lymphoproliferative disease (EBV+ PTLD) who have received at least one prior therapy.
- Potential launch of emerging therapies have the potential to create a significant positive shift in the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market size.
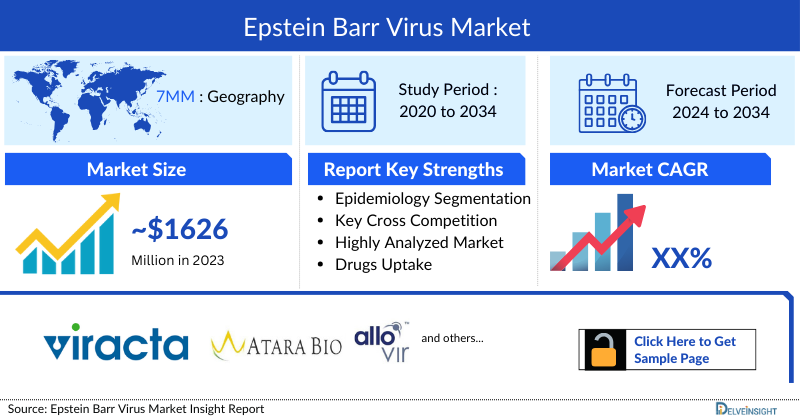
DelveInsight's “Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)- Market Insights, Epidemiology and Market Forecast– 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV), historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, and France) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best of the opportunities and assesses the underlying potential of the market.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
Study Period: 2020-2034
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Disease Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Overview
EBV is a double-stranded DNA virus that infects B lymphocyte cells. EBV is the causative agent of many diseases, including infectious mononucleosis (IM), and it is associated with different subtypes of lymphoma, sarcoma, and carcinomas such as Hodgkin’s lymphoma, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and gastric carcinoma.
Epstein-Barr Virus is known for causing infectious mononucleosis and linked to various malignancies such as Burkitt lymphoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and gastric carcinoma. EBV infects B lymphocyte cells and can lead to severe illnesses, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Diagnosis
The appropriate laboratory tests can diagnose primary EBV infection with certainty. Patients with mild illness are unlikely to be identified because they do not seek medical attention, or EBV infection is not considered in the differential diagnosis. Patients with a typical infectious mononucleosis syndrome are still a diagnostic challenge because their signs and symptoms are not very sensitive or specific for EBV infection.
Additionally, there are several diagnostic methods for EBV detection, including serological and molecular diagnostic methods, although each has its limitations. For instance, the heterophile antibody (Hab) test is associated with high false negative results in children. Apart from this, it has other disadvantages, including non-specificity to malignancies and autoimmune disorders. It could generate false positive results in non-EBV infections, malignancies, and autoimmune disorders.
For accurate detection of EBV, it is paramount to standardize the processes; further evidence and consensus are needed, like sample type, preparation, primer/probe designs, equipment, protocols, reporting unit, and intervention threshold. Nevertheless, the innovations in proteomics assays and gene expression profiling will reveal unique viral and human gene expression patterns corresponding to EBV diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment outcomes.
Further details related to country-based variations are provided in the report
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Treatment
There remains a significant unmet medical need for effective and well-tolerated therapies in the EBV + PTLD population and other cancers. Nevertheless, adoptive T-cell therapy, T-cell receptor (TCR) engineered T-cell therapy, and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy has demonstrated promising approaches to prevent EBV-associated cancer and PTLD. Hence, continued investigation for innovative therapies is necessary to address this unmet need for effective therapy.
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epidemiology
As the market is derived using the patient-based model, the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by, Diagnosed Incident Cases of EBV-IM, Incident Cases of EBV + Cancers, and Incident Cases of EBV + PTLD in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
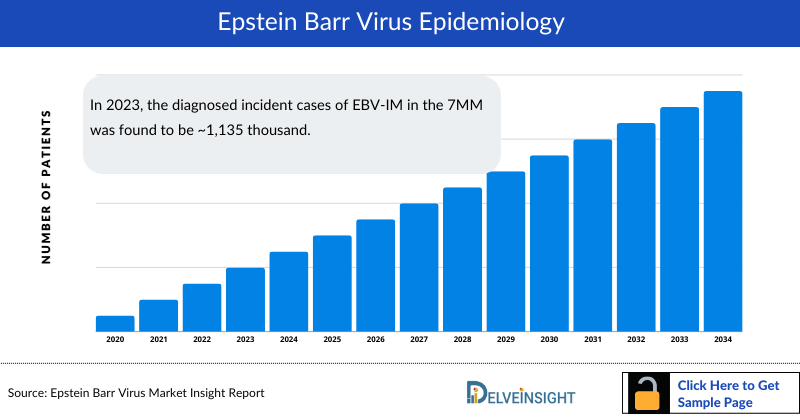
- In 2023, the diagnosed incident cases of EBV-IM in the 7MM was found to be ~1,135 thousand.
- The total diagnosed incident cases of EBV-IM in the US are expected to increase with a significant CAGR by 2034, from around 422 thousand cases in 2023 in the US.
- Among the European countries, Germany (26%) had the highest incident population of EBV-IM, followed by France in 2023. On the other hand, Spain had the least incident population around 14% of EBV-IM in the same year.
- However, the incident cases of EBV-IM are expected to decrease in Germany, Italy and Japan attributed to decrease in country population and other factors.
- In Japan, among incident cases of EBV + Cancers most cases were of Gastric carcinoma (GC) (~4.8 thousand) in 2023. While least were in Burkitt lymphoma (BL) around ~0.8 thousand in the same year.
- Assessments as per DelveInsight’s analysts show that the majority of cases of EBV + PTLD are occupied by EBV-associated PTLD in HSCT in comparison to EBV-associated PTLD in SOT. There were ~590 cases of EBV-associated PTLD in HSCT and ~347 cases of EBV-associated PTLD in SOT in 2023 in Japan.
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) report encloses a detailed analysis of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) marketed drugs and late-stage (Phase-III and Phase-II) pipeline drugs. It also helps to understand the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug, and the latest news and press releases.
Marketed Drugs
EBVALLO (tabelecleucel): Atara Biotherapeutics, Inc./ Pierre Fabre
EBVALLO (tabelecleucel) is a monotherapy for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients two years of age and older with relapsed or refractory Epstein‑Barr virus positive post‑transplant lymphoproliferative disease (EBV+ PTLD) who have received at least one prior therapy. For solid organ transplant patients, prior therapy includes chemotherapy unless chemotherapy is inappropriate. EBVALLO’s approval represents a significant moment in the cell therapy space and a breakthrough for European patients with EBV+ PTLD. EBVALLO has orphan designation in Europe.
Emerging Drugs
Nanatinostat in Combination With valganciclovir (Nana-val): Viracta Therapeutics
Viracta’s lead product candidate is an all-oral combination therapy of its proprietary investigational drug, nanatinostat, and the antiviral agent valganciclovir (collectively referred to as Nana-val). Nana-val is currently being evaluated in multiple ongoing clinical trials, including a pivotal, global, multicenter, open-label Phase II basket trial for the treatment of multiple subtypes of relapsed/refractory Epstein-Barr virus-positive (EBV+) lymphoma (NAVAL-1), as well as a multinational, open-label Phase Ib/II trial for the treatment of EBV+ recurrent or metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma and other EBV+ solid tumors. Viracta is also pursuing the application of its “Kick and Kill” approach in other virus-related cancers.
Note: Detailed emerging therapies assessment will be provided in the final report.
Drug Class Insights
Treatment for mononucleosis typically involves supportive care with antipyretics and anti-inflammatory medications to manage symptoms such as fever, sore throat, and fatigue. Antiviral agents, including aciclovir, famciclovir, penciclovir, and ganciclovir, target the lytic phase of EBV replication. They inhibit EBV DNA polymerase and virion production by preferentially incorporating into viral DNA, with ganciclovir exhibiting prolonged antiviral effects. In EBV-associated post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder (EBV-PTLD), therapeutic strategies aim to balance outgrowing EBV-infected B cells and the EBV cytotoxic T lymphocyte response. Options include monoclonal antibodies targeting B cells or chemotherapy. Rituximab, a CD-20 targeted monoclonal antibody, is used alone or in combination with CHOP chemotherapy to control tumor cell proliferation in EBV-PTLD cases. Additionally, reducing immunosuppression may benefit select EBV-PTLD cases.
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Market Outlook
Treatment generally supports mononucleosis; antipyretics and anti-inflammatory medications help treat fever, sore throat, and general fatigue in this illness. Hydration, rest, and good nutritional intake should also be encouraged. Corticosteroids are not generally recommended in the routine treatment of mononucleosis because of concerns with immunosuppression; however, in cases of airway obstruction, corticosteroids are indicated along with appropriate airway management.
Antiviral agents, such as aciclovir, famciclovir, penciclovir, ganciclovir, and other nucleoside analogs, act on the lytic phase of EBV replication. They are preferentially incorporated into viral DNA through the action of EBV thymidine kinase and inhibit EBV DNA polymerase and subsequent virion production. Ganciclovir can inhibit EBV-induced B-lymphocyte immortalization; its antiviral effect after drug withdrawal is more prolonged than that of aciclovir.
When EBV-positive lymphomas arise in the setting of immunosuppression, ameliorating the immune defect can assist in treating these lymphomas. For EBV-related lymphomas in HIV patients, initiation of antiretroviral therapy alone is inadequate for treatment.
In treating EBV-related lymphomas, there are few therapies targeted explicitly against the latent virus within these tumors; in most cases, the treatment approach is not different from EBV-negative lymphomas. Nonetheless, current and emerging therapies focused on exploiting aspects of EBV biology may offer more targeted strategies for EBV-positive lymphomas in the future. Conceptually, EBV-specific approaches include bolstering the antiviral/antitumor immune response with vaccines or EBV-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, activating lytic viral genes to render the tumor cells susceptible to antiviral therapies, and inhibiting the downstream pro-survival or anti-apoptotic pathways that latent EBV proteins may activate.
Treatment options for EBV-PTLD include manipulating the balance between outgrowing EBV-infected B cells and the EBV CTL response and targeting the B cells with monoclonal antibodies or chemotherapy. In EBV-PTLD, select cases may benefit from reducing immunosuppression as the sole intervention or as part of the treatment plan. The current treatment market includes the CD-20 targeted rituximab as monotherapy or rituximab in combination with CHOP to control the cell proliferation in tumors and PTLD. As well as EBVALLO (tabelecleucel).
EBV-specific cytotoxic T-cell infusions have proven effective in EBV-PTLD, and expanding such adoptive immunotherapies to other EBV-related malignancies is an active research area. However, other EBV-related lymphomas typically have more restricted, less immunogenic arrays of viral antigens to target with adoptive immunotherapy compared to EBV-PTLD therapeutically. Furthermore, the malignant EBV-positive tumor cells of Hodgkin lymphoma are scattered amid a dense infiltrate of regulatory T cells, macrophages, and other cells that may dampen the antitumor efficacy of adoptive immunotherapy. Strategies to overcome these obstacles are areas of ongoing preclinical and clinical investigations.
Anti-EBV therapy remains a major unmet medical need, particularly for patients with an impaired immune system. Antivirals approved for other herpesviruses evaluated for EBV-associated diseases have delivered disappointing results. A few candidate anti-EBV drugs are available, but more work is needed to show their efficacy. Further research is needed to develop therapeutic strategies for EBV-associated diseases and molecules that could be used in prophylaxis among immunosuppressed patients to avoid complications related to EBV disease.
In the United States, Atara plans to submit a biologics license application (BLA) to the US Food and Drug Administration for tab-cel for the treatment of EBV+ PTLD in the second quarter of 2024.
The emerging pipeline provides hope with various other therapies in the pipeline for the treatment of EBV.
- The total market size of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) in the 7MM was approximately USD 1626 million in 2023 and is projected to increase during the forecast period (2024-2034).
- The market size in the 7MM will increase at a constant CAGR due to increasing awareness of the disease, better diagnosis, and the launch of the emerging target therapy for Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV).
- Among EU4 and the UK, Germany with a share of 25% accounted for the maximum market size in 2023 while Germany occupied the bottom of the ladder with a share of 15% in 2023.
- In 2023, Japan held the second-largest share, approximately 21%, of the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) treatment market among the seven major markets (7MM).
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the rate of uptake of the potential drugs expected to get launched in the market during the study period 2020-2034. For example, for Nana-val, we expect the drug to be launched by 2028 in the US, with a probability-adjusted peak share of around 16%, and years to the peak is expected to be 8 years from the year of launch.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report….
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I stage. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers detailed information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) emerging therapies.
KOL- Views
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs' opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient’s therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, include University of Muenster, Germany; German Cancer Research Center; Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, the US; Boston Children’s Hospital, the US, and others.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 50+ KOLs to gather insights, however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Their opinion helps to understand and validate current and emerging therapies and treatment patterns or Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis, and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
Conjoint Analysis is done to analyze multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement is a crucial point for any drug after its approval. Many drugs or therapies are not properly recognized by the reimbursement body and may fail to get reimbursed or their reimbursement process gets delayed.
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV), explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression along with treatment guidelines
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of both the current and emerging therapies along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will have an impact on the current treatment landscape
- A detailed review of the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market; historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preference that help in shaping and driving the 7MM Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) market
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Pipeline Analysis
- Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Report Key Strengths
- 11 Years Forecast
- 7MM Coverage
- Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Attribute analysis
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
Key Questions
Market Insights:
- What was the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) total market size, the market size by therapies, and market share (%) distribution in 2020, and how it would all look in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the unmet needs are associated with the current treatment market of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
- How is Nanatinostat in Combination With valganciclovir (Nana-val) going to contribute to the market of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) after approval?
- Which drug is going to be the largest contributor in 2034?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
Epidemiology Insights:
- What are the disease risk, burden, and unmet needs of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
- What is the historical and forecasted Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- Why do only limited patients appear for diagnosis? Why is the current year diagnosis rate not high?
- What factors are affecting the diagnosis and treatment of the indication?
Current Treatment Scenario, Marketed Drugs, and Emerging Therapies:
- What are the current options for the treatment of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)? What are the current treatment guidelines for the treatment of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) in the US and Europe?
- How many companies are developing therapies for the treatment of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
- How many emerging therapies are in the mid-stage and late stage of development for the treatment of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitation of existing therapies?
- What are the key designations that have been granted for the emerging therapies for Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies? Focus on reimbursement policies.
- What are the 7MM historical and forecasted market of Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)?
Reasons to buy
- The report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) Market
- Insights on patient burden/disease population, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years
- To understand the existing market opportunity in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identification of strong upcoming players in the market will help in devising strategies that will help in getting ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the Conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes
- Highlights of Access and Reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of off-label expensive therapies, and patient assistance programs
- To understand the perspective of Key Opinion Leaders’ around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in future
- Detailed insights on the unmet need of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy


-pipeline.png&w=256&q=75)

