Fecal Incontinence Market
Key Highlights
- Fecal Incontinence is present in 7% to 15% of the general Western population and is associated with a considerable impact on quality of life, which, in turn, is compounded by social stigma, leading to isolation and confinement to home.
- More than 5.5 million Americans have fecal incontinence. It is more common in older people and in women. However, many people do not like to talk about fecal incontinence, and it may not be apparent that fecal incontinence is relatively common.
- It is involuntary defecation. Diagnosis is clinical. Treatment is a bowel management program and perineal exercises, but sometimes colostomy is needed.
- Major risk factors include age, gender (female), obesity, diabetes, neurological conditions (e.g., stroke, multiple sclerosis), and previous surgeries like hysterectomy or prostatectomy.
- Chronic conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) also contribute to the risk of fecal incontinence.
- The global market for fecal incontinence treatments is driven by the aging population, increasing awareness, and advancements in therapeutic options.
- Key market segments include pharmaceuticals (e.g., anti-diarrheals, bulking agents), surgical interventions (e.g., sphincteroplasty, sacral nerve stimulation), and non-invasive treatments like biofeedback therapy.
- Key challenges include underdiagnosis due to social stigma, limited treatment adherence, and the high cost of advanced therapies.
- Opportunities exist in the development of cost-effective and accessible treatments, as well as in raising awareness and education to reduce the stigma associated with the condition.
DelveInsight’s "Fecal Incontinence – Market Insight, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034" report delivers an in-depth understanding of the fecal incontinence historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the fecal incontinence market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The fecal incontinence market report offers an in-depth analysis of current treatment practices, market share of individual therapies, and the projected market size from 2020 to 2034, segmented across seven major markets. Additionally, the report examines treatment algorithms and unmet medical needs, identifying key opportunities and assessing the market's underlying potential.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the UK, and Japan |
|
Fecal Incontinence |
Segmented by: ● Total Prevalent Cases of Fecal Incontinence ● Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Fecal Incontinence ● Gender-based Cases of Fecal Incontinence ● Cases of Fecal Incontinence based on Risk Factors ● Cases of Fecal Incontinence based on Frequency ● Total Treated Cases of Fecal Incontinence |
|
Fecal Incontinence key companies |
● Cook MyoSite ● Innovacell |
|
Fecal Incontinence key therapies/drug |
● Iltamiocel ● aSMDC |
|
Fecal Incontinence Market |
Segmented by: ● Region ● Therapies |
|
Analysis |
● KOL Views ● SWOT Analysis ● Reimbursement ● Unmet needs |
Fecal Incontinence: Disease Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Fecal Incontinence Overview
Fecal incontinence is the inability to control your bowel movements, causing stool (feces) to leak unexpectedly from your rectum. Also called bowel or anal incontinence, fecal incontinence can range from occasional leakage of a small quantity of stool while passing gas to a complete loss of bowel control.
The ability to hold stool (called continence) requires the rectum, anus and nervous system to be working normally. Two groups of muscles in the wall of the anus and rectum are responsible for holding the stool in the rectum, the outer muscle group (external anal sphincter) and the inner muscle group (internal anal sphincter). Normal continence also requires the ability to sense the presence of stool in the rectum (called rectal sensation), and the ability to relax and store stool (called rectal compliance) when having a bowel movement is not convenient. In addition, you need the physical and mental capabilities to recognize the urge to defecate, and go to the toilet.
Fecal Incontinence Diagnosis
Fecal incontinence diagnosis involves a thorough evaluation by your doctor, who will discuss your symptoms and perform a physical exam, including a rectal examination. Diagnostic tests may include anal manometry to measure sphincter strength and rectal sensation, anorectal ultrasonography or MRI to visualize the anal muscles, and defecography to assess rectal function during defecation. Additional tests like proctosigmoidoscopy can detect inflammation or tumors, and anal electromyography (EMG) may identify nerve damage around the anus. These tests help determine the underlying cause of incontinence and guide appropriate treatment.
Further details related to diagnosis will be provided in the report…
Fecal Incontinence Treatment
Effective treatments for fecal incontinence aim to improve or restore bowel control through various approaches depending on the underlying cause. Dietary adjustments, such as avoiding spicy and fatty foods, alongside medications like anti-diarrheal agents, can help manage symptoms. For cases involving weakened anal sphincter muscles or reduced rectal sensation, bowel retraining and biofeedback therapy may strengthen muscle control and improve rectal sensation. Moisture-barrier creams and proper hygiene practices are essential for managing frequent leakage. In more severe cases, surgical interventions, such as sacral nerve stimulation or sphincteroplasty, may be considered, with colostomy reserved as a last resort.
Further details related to treatment will be provided in the report…
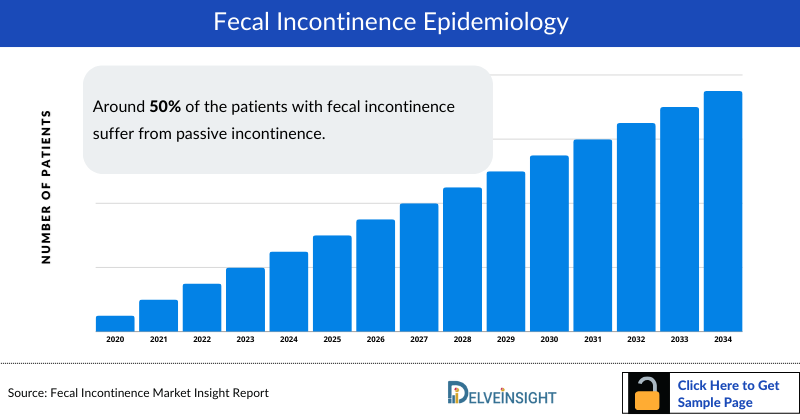
Fecal Incontinence Epidemiology
The fecal incontinence epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by the Total Prevalent Cases of Fecal Incontinence, Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Fecal Incontinence, Gender-based Cases of Fecal Incontinence, Cases of Fecal Incontinence based on Risk Factors, Cases of Fecal Incontinence based on Frequency, and Total Treated Cases of Fecal Incontinence in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
- The condition is more common in women, particularly those who have had multiple vaginal deliveries. The prevalence increases with age, with a significant rise in individuals over 65 years.
- Around 50% of the patients with fecal incontinence suffer from passive incontinence. In contrast to urge incontinence, those affected by passive incontinence do not feel an urge to defecate, which can lead to involuntary stool loss.
- The condition significantly impacts the quality of life, leading to social isolation, anxiety, and depression. It is a major reason for the institutionalization of elderly individuals.
- Fecal incontinence results in increased healthcare utilization, including frequent visits to healthcare providers and the use of incontinence products. The economic burden on the healthcare system is substantial due to the costs associated with management and care.
Fecal Incontinence Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the fecal incontinence report encloses a detailed analysis of the emerging drugs. The drug chapter also helps understand the fecal incontinence clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, and the latest news and press releases.
Emerging Drugs
Iltamiocel: Cook MyoSite
Iltamiocel is an emerging cell-based therapy being investigated for the treatment of fecal incontinence (FI). It involves the use of autologous muscle-derived cells that are injected into the anal sphincter muscle to improve muscle tone and function. Early studies have shown promise in enhancing sphincter contractility, leading to improved continence in patients with FI. As a regenerative therapy, Iltamiocel represents a novel approach to addressing the underlying muscle weakness in FI, offering potential long-term benefits over traditional pharmacological treatments.
aSMDC: Innovacell
aSMDC (autologous skeletal muscle derived cells) is an innovative investigational therapy designed to treat fecal incontinence by targeting the anal sphincter muscles. This therapy involves the administration of specialized muscle-derived cells that are activated and engineered to enhance the strength and functionality of the sphincter. The approach focuses on regenerating and restoring muscle tissue that has weakened due to aging, injury, or other factors contributing to FI. If successful, aSMDC could offer a new, minimally invasive treatment option that directly addresses the root cause of fecal incontinence, potentially reducing the need for surgical interventions.
|
Emerging Drug |
Company |
Phase |
Mechanism of Action |
Route of Administration |
Condition |
|
Iltamiocel |
Cook MyoSite |
III |
Cell replacements |
Intramuscular Injection |
Fecal incontinence |
|
aSMDC |
Innovacell |
III |
Cell replacements |
Intramuscular Injection |
Fecal incontinence |
Detailed therapy assessment will be provided in the final report.
Drug Class Insight
Antidiarrheals
Antidiarrheals work by slowing down intestinal transit, which reduces the frequency and urgency of bowel movements. They are primarily used for diarrhea, which can be a contributing factor to fecal incontinence. These are standard treatments for managing fecal incontinence when diarrhea is the underlying issue. They do not address the sphincter muscle dysfunction but can help in controlling stool consistency.
Bile Acid Sequestrants
These drugs bind bile acids in the intestine, which can help reduce bile acid-induced diarrhea. They are used off-label for fecal incontinence associated with bile acid diarrhea. They are effective in managing diarrhea related to bile acid malabsorption but not for other types of fecal incontinence.
Detailed drug class insight assessment will be provided in the final report.
Fecal Incontinence Market Outlook
The market outlook for fecal incontinence is shaped by a growing awareness of the condition and the need for effective treatments. With an estimated global prevalence of 2-20%, primarily impacting the elderly and individuals with underlying gastrointestinal or neurological disorders, the demand for management solutions is significant. Current treatment options are largely centered around symptom control, including antidiarrheals, bile acid sequestrants, and anticholinergics. The market is witnessing increased interest in innovative approaches such as regenerative therapies (e.g., Iltamiocel, aSMDC), which aim to address the condition at its root by improving sphincter muscle function. Despite these advances, the market is constrained by the high costs of novel treatments and the need for further clinical validation. Ongoing research and development efforts are likely to drive growth, particularly as new therapies progress through clinical trials and address unmet needs in both symptom management and functional restoration. The increasing emphasis on personalized medicine and patient-centered care is expected to further influence market dynamics, fostering the development of more effective and targeted solutions for managing fecal incontinence.
Detailed market assessment will be provided in the final report.
Key Findings
- Fecal incontinence is increasingly prevalent in the aging population, particularly among those over 65 years old. As the global population ages, the demand for effective treatments and management solutions for FI is expected to rise, driving market growth.
- Despite its prevalence, fecal incontinence remains significantly underreported and undiagnosed due to the stigma associated with the condition. This presents a challenge for market penetration but also an opportunity for awareness campaigns and education to increase diagnosis and treatment rates.
- There is a growing trend towards the development of non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments for fecal incontinence, including biofeedback therapy, electrical stimulation, and advanced pharmacological options. These less invasive treatments are becoming increasingly preferred by patients and healthcare providers.
- Fecal incontinence imposes a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems due to the need for long-term management, including medications, incontinence products, and caregiver support. This is driving interest in cost-effective interventions and reimbursement strategies.
- The market for incontinence products, such as pads, diapers, and skin care products, is experiencing innovation with the introduction of more comfortable, discreet, and absorbent products. This segment is seeing significant growth as patients seek improved quality of life.
- Pharmaceutical companies and medical device manufacturers are investing in R&D to develop new treatments and technologies for fecal incontinence. This includes the exploration of novel drug formulations, regenerative medicine approaches, and advanced surgical techniques. These developments could lead to more effective and accessible treatment options in the near future
KOL- Views
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on the fecal incontinence evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including Gastroenterologists, Geriatricians, Pelvic Floor Physical Therapists, Surgeons and others.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 10+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 5+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS), National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), American Urological Association (AUA), Mount Sinai Health System etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or fecal incontinence market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
|
KOL Views |
|
“A multidisciplinary approach to managing fecal incontinence, combining surgical, medical, and rehabilitative strategies, is essential. Personalized treatment plans that address both symptoms and underlying causes are crucial for achieving optimal outcomes.” |
|
“Regenerative therapies, such as autologous muscle-derived cell injections, show potential in treating fecal incontinence by directly addressing sphincter muscle weakness. These innovative approaches require further clinical validation to establish their long-term efficacy and safety.” |
|
“Pelvic floor rehabilitation plays a significant role in managing fecal incontinence. Physical therapy can effectively improve sphincter function and overall bowel control, particularly when combined with other treatment modalities. Increased integration of pelvic floor exercises and enhanced patient education are important for improving adherence and effectiveness.” |
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of fecal incontinence, explaining its causes, signs, symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently used therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, disease progression, and treatment guidelines has been provided.
- A detailed review of the fecal incontinence market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the fecal incontinence market.
Fecal Incontinence Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Fecal Incontinence Pipeline Analysis
- Fecal Incontinence Market Size and Trends
- Existing and Future Market Opportunity
Fecal Incontinence Report Key Strengths
- Eleven Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Fecal Incontinence Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Fecal Incontinence Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT)
FAQs
- What was the fecal incontinence market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What can be the future treatment paradigm for fecal incontinence?
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of fecal incontinence? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population with fecal incontinence?
- What are the current options for the treatment of fecal incontinence? What are the current guidelines for treating fecal incontinence in the 7MM?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies being developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- What is the patient share in fecal incontinence?
Reasons to Buy
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the fecal incontinence market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Identifying strong players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.