macrophage activation syndrome market
Key Highlights
- MAS is a rare but life-threatening hyperinflammatory condition that manifests as a secondary form of HLH with high mortality. The total diagnosed pool of MAS is approximately 17,000 in 2024 in the US, and this number is expected to rise over the forecast period due to the rising prevalence/incidence of underlying autoimmune diseases like AOSD, sJIA, SLE, and KD that frequently trigger MAS.
- MAS most commonly emerges as a severe hyperinflammatory complication of rheumatologic diseases, primarily sJIA (13%) and AOSD (9.4%), with Kawasaki Disease contributing a smaller yet clinically important share (1.6%), especially in children. MAS also occurs in other autoimmune conditions, such as SLE, where its prevalence ranges from 1% to 3% and mortality remains high (8–22%) due to delayed recognition and treatment.
- The symptomology of MAS/sHLH is serious and potentially lethal. Mortality has been reported in approximately 20–53% of cases, while sHLH without treatment has a 50–75% mortality rate.
- Management of MAS still depends heavily on high-dose glucocorticoids, typically IV methylprednisolone. Reliance on steroids, off-label biologics, and supportive care underscores the absence of standardized treatment pathways and persistent gaps in timely access to effective therapies.
- The basic principles of treatment are control of triggering factors, supportive care, and relief of hyperinflammation. Systemic steroids and cyclosporine A are frequently used as a first-line treatment. For the treatment of refractory MAS, cytokine-specific biologic agents such as anakinra have recently become preferred over traditional immunosuppressive agents such as etoposide.
- Anakinra is by far the most used biologic treatment for MAS, especially for sJIA-MAS. Even though no (randomized) controlled clinical trial has tested the efficacy of anakinra in MAS, >80% of patients with sJIA-MAS treated with anakinra reported a complete regression of MAS, with a high safety profile.
- Sobi’s GAMIFANT (emapalumab-lzsg) became the first FDA-approved therapy for MAS in June 2025, underscoring the substantial unmet need in a landscape dominated by off-label treatment. The company plans to pursue EU regulatory submission in 2026, indicating continued strategic expansion of its MAS portfolio.
- There are currently no MAS-specific approved therapies, underscoring a major unmet medical need. This gap creates a strong opportunity for emerging targeted candidates such as Tadekinig alfa, ELA026, Plonmarlimab, and MAS825 to shape the clinical and regulatory landscape and potentially become first-in-class solutions for this life-threatening syndrome.
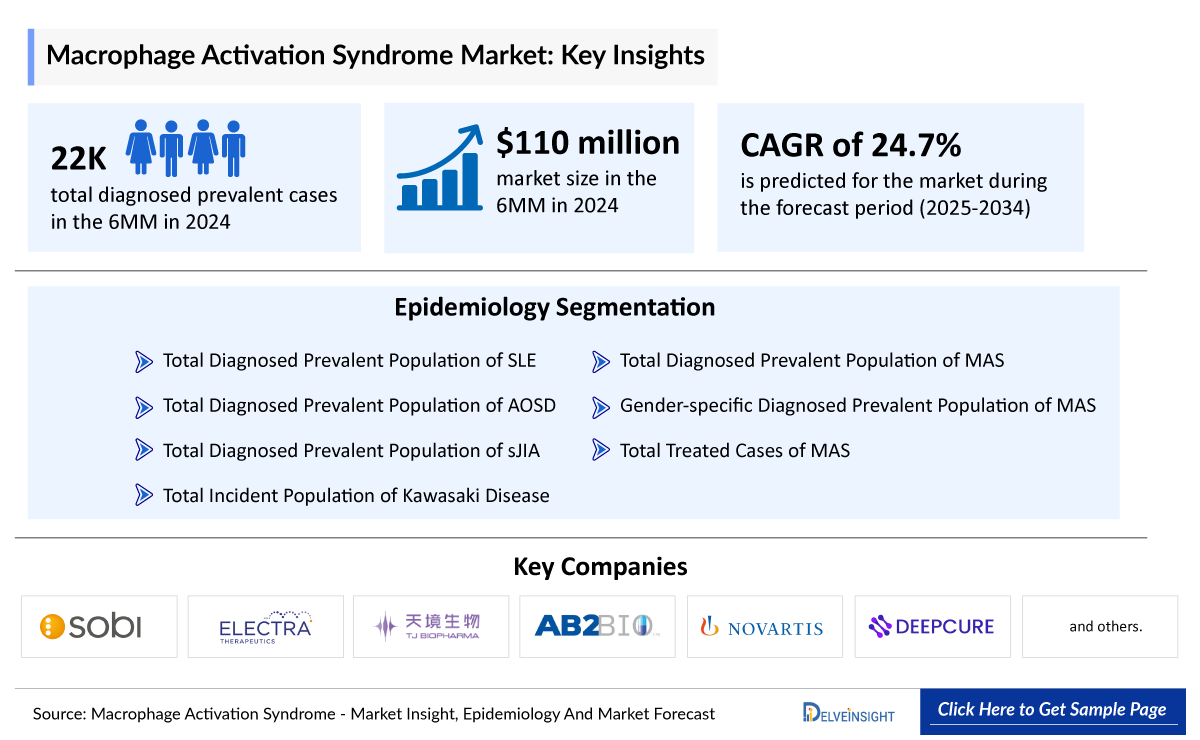
- The emerging pipeline of MAS holds a few significant key players, such as Electra Therapeutics, TJ Biopharma, AB2 Bio, Novartis, Deepcure, and others are evaluating their investigational therapies across various stages of clinical development.
- Several novel targeted therapies, targeting SIRP-a/ß1/? (ELA026), targeting Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) (Plonmarlimab), IL-18 inhibitor (Tadekinig alfa), dual IL-1ß and IL-18 inhibitor (MAS825), and others are currently under clinical evaluation, underscoring the growing landscape of innovative treatment options for patients with MAS/sHLH.
DelveInsight’s “Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) – Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of macrophage activation syndrome, historical and forecasted epidemiology, as well as macrophage activation syndrome market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The macrophage activation syndrome market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM macrophage activation syndrome market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current MAS treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
Study Period: 2020–2034
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
MAS Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
|
MAS Key Companies |
|
|
MAS Key Therapies |
|
|
MAS Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Disease Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Overview
MAS is a form of secondary Haemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (sHLH) occurring as a life-threatening complication of rheumatic diseases. It is most frequent in sJIA and AOSD. Similar to other forms of HLH, MAS is caused by excessive activation and expansion of T lymphocytes and macrophages, resulting in hyperinflammation. sHLH is mostly triggered by underlying secondary causes, including malignancies, infections, autoimmune diseases, or certain therapies and transplants. However, genetic defects may also contribute to the development of adult HLH cases or secondary HLH cases (MAS is characterised by fever, hepatosplenomegaly, cytopenias, liver dysfunction, coagulation abnormalities, and hyperferritinaemia, and may progress to multiple organ failure. MAS is treated with high-dose glucocorticoids with satisfactory response in two-thirds of the patients. In patients unresponsive to glucocorticoids, ciclosporin is usually added.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Diagnosis
The diagnosis of MAS is primarily clinical and relies on recognizing a constellation of symptoms, laboratory abnormalities, and exclusion of other causes of systemic inflammation. Patients typically present with persistent high fever, hepatosplenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, and signs of multiorgan involvement. Laboratory findings include cytopenias affecting at least two blood cell lineages, markedly elevated ferritin levels, hypertriglyceridemia, hypofibrinogenemia, and elevated liver enzymes. A decline in erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) despite ongoing inflammation can also be suggestive. In some cases, bone marrow aspiration may reveal hemophagocytosis, although its absence does not rule out MAS. Diagnosis is further supported by clinical criteria such as the 2016 EULAR/ACR/PRINTO classification criteria for MAS complicating sJIA, which incorporate laboratory thresholds for ferritin, platelet count, AST, triglycerides, and fibrinogen. Early recognition is critical, as MAS can rapidly progress to multiorgan failure if not promptly treated.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Treatment
The treatment of MAS focuses on rapidly suppressing the hyperinflammatory state and addressing any underlying trigger, such as infection, autoimmune disease flare, or malignancy. High-dose corticosteroids remain the mainstay of initial therapy and are often administered intravenously for quick control of inflammation. In refractory or severe cases, additional immunosuppressive agents such as cyclosporine, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), or biologic therapies targeting specific cytokines like anakinra (IL-1 receptor antagonist) or tocilizumab (IL-6 inhibitor) may be used. Etoposide is considered for patients with secondary HLH-like features or life-threatening disease. Supportive care, including management of cytopenias, organ dysfunction, and infections, is also essential. Recently, GAMIFANT, an interferon gamma (IFN?)–blocking antibody, has emerged as a targeted therapy for primary and secondary HLH, including MAS associated with Still’s disease. Early recognition and timely initiation of immunomodulatory therapy are crucial to improve outcomes and prevent fatal complications.
Further details related to treatment are provided in the report…
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Epidemiology
The disease epidemiology covered in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total diagnosed prevalent population of SLE, total diagnosed prevalent population of AOSD, total diagnosed prevalent population of sJIA, total incident population of kawasaki disease, total diagnosed prevalent population of MAS, gender-specific diagnosed prevalent population of MAS, and total treated cases of MAS in the 7MM market covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
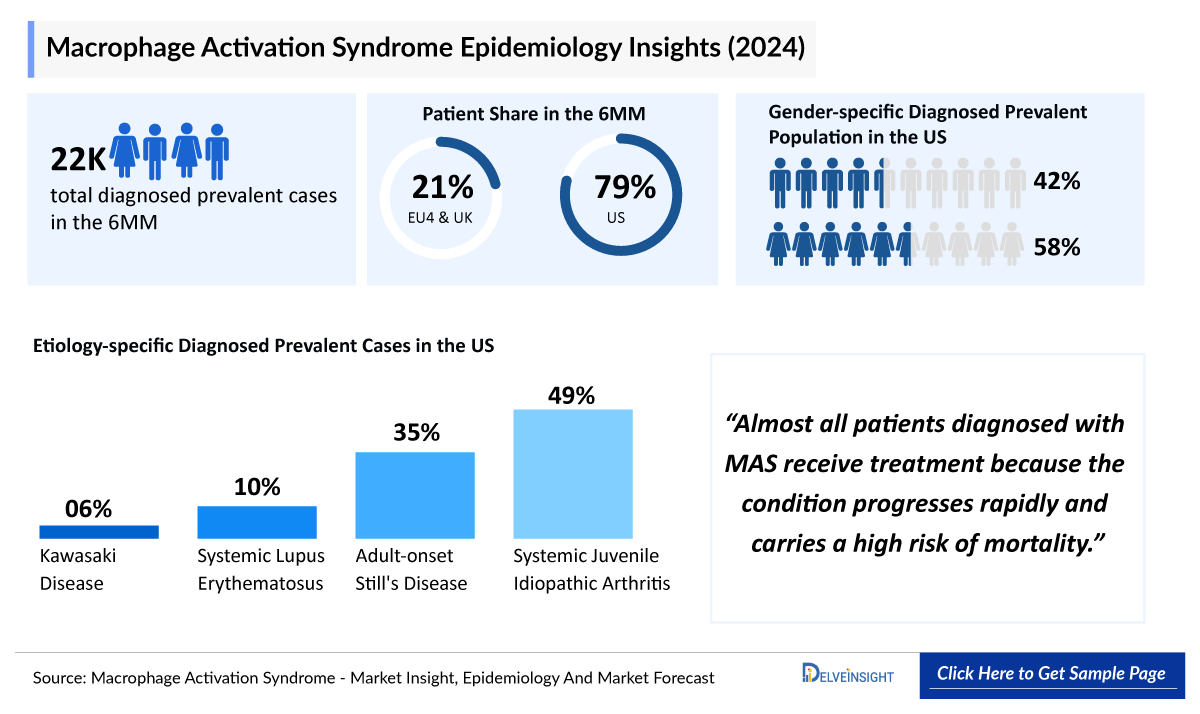
- The total diagnosed prevalent cases of MAS in the 6MM (US, EU4, and the UK) were about 22,000 in 2024; this number is expected to rise over the forecast period (2025–2034). This growth is driven by an increase in autoimmune, autoinflammatory, and infectious diseases with MAS as a complication.
- In 2024, MAS predominantly affected females in the United States, with ~10,000 cases (58%), while the Male population accounted for ~7,000 cases (the remaining 42%). These cases are expected to increase during the forecast period.
- MAS spans both pediatric and adult populations, occurring most frequently in children with sJIA and KD, while adult cases are more common in AOSD, SLE, and secondary triggers such as infections or malignancies.
- In EU4 and the UK, diagnosed prevalent cases of AOSD were more than 1,000 in 2024.
- Almost all patients diagnosed with MAS receive treatment because the condition progresses rapidly and carries a high risk of mortality.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Drug Chapters
The drug chapter of the MAS report encloses a detailed analysis of the marketed and the late-stage (Phase III and Phase II) pipeline drugs. Currently, Sobi’s GAMIFANT remains the only approved therapy, while the pipeline is led by emerging candidates such as Electra Therapeutics’ ELA026, TJ Biopharma’s plonmarlimab, AB2 Bio’s tadekinig alfa, and others. The drug chapter also helps understand the MAS clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, and the latest news and press releases.
Marketed Drugs
GAMIFANT (Emapalumab-lzsg): Sobi
Emapalumab-lzsg is the only approved anti-IFN? monoclonal antibody. GAMIFANT works by binding to and neutralizing IFN?. When IFN? is secreted in an uncontrolled manner, hyperinflammation occurs within the body.
- In June 2025, Sobi announced that the US FDA approved GAMIFANT for the treatment of adult and pediatric (newborn and older) patients with HLH/MAS in known or suspected Still’s disease, including sJIA, with an inadequate response or intolerance to glucocorticoids, or with recurrent MAS. Earlier in February 2025, the US FDA had accepted Sobi’s supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for this indication.
- According to Sobi’s Q3 2025 presentation published in October 2025, the company anticipates submitting a regulatory application in the EU in 2026.
- In October 2025, Sobi showcased new findings from its immunology portfolio at the ACR Convergence 2025 in Chicago, presenting clinical results from completed studies of GAMIFANT.
|
Details of Marketed Drug | ||||||
|
Drug |
Developer |
MoA |
RoA |
Molecule Type |
Patient segment |
Approval |
|
Emapalumab-lzsg (GAMIFANT) |
Sobi |
IFNγ inhibitor |
IV infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
Adult and pediatric (newborn and older) patients with HLH/MAS in known or suspected Still’s disease, including sJIA, with an inadequate response or intolerance to glucocorticoids, or with recurrent MAS. |
US: 2025 |
Emerging Drugs
ELA026: Electra Therapeutics
ELA026 is a first-in-class monoclonal antibody that targets Signal Regulatory Proteins (SIRP) on the cell surface of myeloid cells and T lymphocytes, and selectively depletes pathological immune cells. This novel approach has potential therapeutic benefits across numerous diseases.
- In October 2025, ELA026 received BTD by the US FDA and European Medicines Agency Priority Medicines (PRIME) designation for sHLH.
- In October 2025, Electra Therapeutics announced an oversubscribed USD 183 million Series C financing. The round was co-led by Nextech and EQT Life Sciences, with participation from new investors Sanofi, HBM Healthcare Investments, and Mubadala Capital, as well as existing investors OrbiMed, Redmile Group, New Leaf Venture Partners, Westlake BioPartners, Cormorant Asset Management, Blue Owl Capital, and RA Capital Management.
- Proceeds from the financing will fund a global pivotal Phase II/III study of ELA026 in sHLH.
Tadekinig Alfa (r-hIL-18BP): AB2 Bio
Tadekinig alfa is a novel, recombinant human Interleukin-18 Binding Protein (IL-18 BP) that binds and inhibits IL-18, a major proinflammatory cytokine. In healthy people, a large excess of naturally occurring endogenous IL-18 BP keeps levels of systemic free IL-18 undetectable. The drug is currently undergoing a Phase III clinical trial.
- In January 2025, AB2 Bio announced that it had entered into an option and licensing agreement with Nippon Shinyaku in the US. Under the terms of the agreement, Nippon Shinyaku would have the exclusive right to commercialize Tadekinig alfa for its lead indication, primary monogenic IL-18 driven hyperinflammatory syndrome in patients with NLRC4 mutation and XIAP deficiency, in the US (including Guam, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands). AB2 Bio retains rights to Tadekinig alfa for all other indications in the US (including Guam, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands) and all indications in the rest of the world.
- AB2 Bio will continue to prepare for filing for a US Biologics License Application (BLA) approval for Tadekinig alfa in the indication
|
Comparison of Emerging Drugs Under Development for MAS | ||||
|
Drug Name |
Company |
Highest Phase |
Indication |
MoA |
|
ELA026 |
Electra Therapeutics |
II/III |
Pediatric and adult participants with treatment-naive and R/R sHLH |
Targets SIRP-α/β1/γ |
|
Plonmarlimab (TJM2/TJ003234)* |
TJ Biopharma |
III |
MAS/sHLH |
Targets human Granulocyte-macrophage Colony-stimulating Factor (GM-CSF) |
|
Tadekinig alfa (r-hIL-18BP) |
AB2 Bio |
III |
NLRC4-MAS mutation |
IL-18 inhibitor |
|
MAS825 |
Novartis |
II |
Pediatric and adult participants with Still's disease, including MAS |
IL-1β and IL-18 inhibitor |
|
*The drug is in Phase III for MAS/sHLH in China. Although the company claims global trials, no studies are registered or active in the 6MM regions. | ||||
Note: Detailed emerging therapies assessment will be provided in the final report.
Drug Class Insights
The approved candidates for MAS therapy fall under the IFN? inhibitor class; while the emerging drugs fall under different drug classes like ELA026 (Targets SIRP-a/ß1/?), plonmarlimab (targets GM-CSF), tadekinig alfa (IL-18 inhibitor), MAS825 (IL-1ß and IL-18 inhibitor), and others.
IFN? inhibitor: IFN? plays a central role in the pathogenesis of MAS by driving excessive immune activation and cytokine release. In MAS, persistent activation of T cells and macrophages leads to uncontrolled production of IFN?, which further amplifies macrophage activation, promotes hemophagocytosis, and sustains a cycle of hyperinflammation. IFN? enhances the expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-a, and IL-18, and contributes to tissue damage and multiorgan dysfunction. IFN? inhibitors, such as GAMIFANT, are monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to and neutralize circulating IFN?, thereby interrupting this pathogenic feedback loop. By blocking IFN? signaling, these agents reduce macrophage activation, suppress downstream inflammatory cascades, and help restore immune homeostasis. In MAS and secondary HLH, IFN? inhibition has been shown to normalize inflammatory markers, improve cytopenias, and reverse organ dysfunction. Thus, targeted IFN? blockade offers a mechanism-based therapeutic approach aimed at controlling the core driver of hyperinflammation in MAS.
Note: Detailed insights will be provided in the final report.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Market Outlook
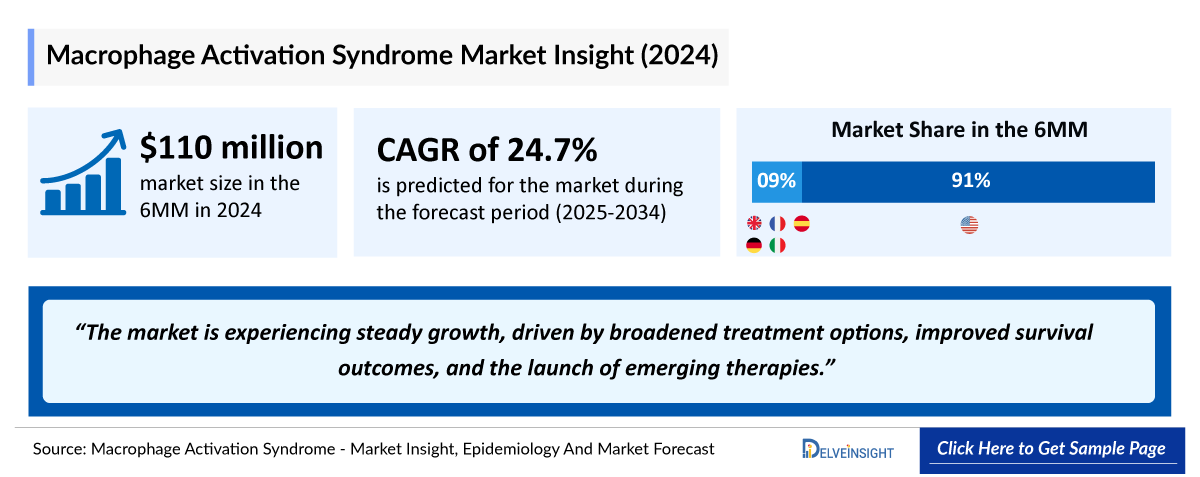
MAS is potentially fatal; so, early diagnosis and timely treatment are essential. Early immunomodulation treatment is associated with a reduction in mortality, both in adults and children. Although glucocorticoids are the cornerstone for the treatment of MAS, additional immunosuppressive and biologic treatments are more and more often used. The basic principles of treatment are control of triggering factors, supportive care, and relief of hyperinflammation. Systemic steroids and Cyclosporine A are frequently used as a first-line treatment. For the treatment of refractory MAS, cytokine-specific biologic agents such as anakinra have recently become preferred over traditional immunosuppressive agents such as etoposide. MAS might be underrecognized in pediatric patients with infectious and inflammatory diseases due to its diverse clinical presentations.
Currently, GAMIFANT stands out as the first and only FDA sole treatment option for the treatment of adult and pediatric (newborn and older) patients with HLH/MAS in known or suspected Still’s disease, including sJIA, with an inadequate response or intolerance to glucocorticoids, or with recurrent MAS. The recent approval of GAMIFANT represents a pivotal advancement in the management of MAS, marking the first targeted therapy to address this complex hyperinflammatory condition.
- The market size of MAS in the 6MM (US, EU4 and the UK) was approximately USD 110 million in 2024.
- The emerging pipeline of MAS holds a few products in development by prominent key players such as ELA026 (Electra Therapeutics), plonmarlimab (TJ Biopharma), tadekinig alfa (AB2 Bio), MAS825 (Novartis), and others.
- As per the analysis, tadekinig alfa (r-hIL-18BP) is projected to enter the US market by 2026.
- GAMIFANT is a recognized, first-in-class targeted treatment in the US for HLH and MAS. Sobi is strategically pursuing European market entry by targeting MAS in 2026, intending to address the EMA's previous pHLH rejection by highlighting the significant clinical need and the favorable outcomes observed in MAS patients.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2025–2034, which depends on the competitive landscape, safety, efficacy data, and order of entry. It is important to understand that the key players evaluating their novel therapies in the pivotal and confirmatory trials should remain vigilant when selecting appropriate comparators to stand the greatest chance of a positive opinion from regulatory bodies, leading to approval, smooth launch, and rapid uptake. Tadekinig alfa (r-hIL-18BP) is projected to enter the US market by 2026, and is anticipated to achieve a medium uptake.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies, drug uptake in the report…
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Activities
The report provides insights into therapeutic candidates in Phase III and II. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for MAS emerging therapies. In January 2025, AB2 Bio entered into an option and licensing agreement with Nippon Shinyaku in the US. Under the terms of the agreement, Nippon Shinyaku would have the exclusive right to commercialize Tadekinig alfa for its lead indication, primary monogenic IL-18 driven hyperinflammatory syndrome in patients with NLRC4 mutation and XIAP deficiency, in the US (including Guam, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands).
KOL Views
To keep up with the real-world scenario in current and emerging market trends, we take opinions from Key Industry leaders working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on the evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including Medical/scientific writers, rheumatologists, researchers of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, and an Associate Professor at Bristol Royal Hospital for Children, and Others.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 20+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 10+ KOLs in the 7MM. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or MAS market trends.
|
Region |
KOL Views |
|
United States |
“MAS is a potentially fatal inflammatory condition that can lead to multiorgan failure if inadequately treated. In the absence of validated diagnostic criteria, recognition is often delayed. A firm understanding of the pathogenesis of MAS can guide diagnosis and direct therapy toward target-specific treatment.” - MD, University of Alabama, US |
|
France |
“MAS remains a severe and potentially life-threatening complication of Still’s disease, and the effectiveness of novel therapies targeting IL-1 or IFN-γ supports their use in patients who do not respond to high-dose glucocorticoids, as well as consideration at disease onset in those presenting with severe or life-threatening MAS.” - MD, Sorbonne Université, France |
Qualitative Analysis
We perform qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT and Conjoint analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis evaluates approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, designation, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyse the effectiveness of therapy.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated, wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Market Access and Reimbursement
The report provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc. Reimbursement is a crucial factor that affects the drug’s access to the market. Often, the decision to reimburse comes down to the price of the drug relative to the benefit it produces in treated patients. To reduce the healthcare burden of these high-cost therapies, many payment models are being considered by payers and other industry insiders.
GAMIFANT Cares
GAMIFANT Cares offers access and reimbursement support to help patients access GAMIFANT in both inpatient and outpatient settings. GAMIFANT Cares provides information regarding patient insurance coverage and financial assistance information that may be available to help patients with financial needs.
- Evaluate a patient’s insurance coverage, including benefits investigation, prior authorization, and appeal support.
- Identify potential financial assistance options that may be available to help patients with financial needs.
- Provide a Benefit Investigation Summary and, if applicable, any prior authorization requirements.
- Answer logistical questions and provide information and confirmation around the specialty pharmacy fulfillment process.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of MAS, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines has been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies and the elaborate profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the MAS market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM MAS market.
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- MAS Pipeline Analysis
- MAS Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Report Key Strengths
- 10 Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- MAS Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Macrophage Activation Syndrome (MAS) Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Analyst Views
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs
- What is the historical and forecasted MAS patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- What was the MAS total market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%), distribution in 2024, and what would it look like in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- Which drug is expected to generate the highest revenue by 2034?
Reasons to Buy
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the MAS market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights into the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.