PD-1 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market
- The total PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size in the 7MM was estimated to be nearly USD 11,000 million in 2023, which is expected to show positive growth by 2034.
- In 2023, the US accounted for the maximum share of the total PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market in the 7MM, i.e., approximately 65%.
- PD-(L)1 therapies are mainly utilized in patients without genetic drivers. Merck’s KEYTRUDA is generally considered the ‘gold standard’ of care in 1L NSCLC when combined with platinum chemotherapy, regardless of PD-1 status.
- Interestingly, the position of leading brands in the current competitive landscape largely mirrors the order of their market entry. KEYTRUDA and OPDIVO continue to command the checkpoint inhibitor market due to their early entry and established track record.
- Acquired resistance to these anti-PD-(L)1 therapies is a key issue. Given the high unmet need in this area, many companies are exploring novel molecules and combinations in second-line NSCLC post-IO.
- When KEYTRUDA loses exclusivity, the introduction of biosimilars is expected to significantly impact the PD- (L)1 inhibitor market. This event could potentially reshape the competitive landscape and influence patients' treatment options.
- DATO-Dxd and TRODELVY target the non-actionable genomic aberration NSCLC market. DATO-DxD targets TROP2, not HER2-expressing malignancies, and uses half as many chemo agents and the same linker and payload as ENHERTU. Given Dato-DXd's advantage in treating NSCLC and its higher efficacy in early-stage studies, we anticipate that it could eventually surpass alternative therapy approaches presently being researched as the market's top TROP2 ADC for NSCLC.
- Emerging players such as Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Ono Pharmaceutical, Genentech/Hoffmann-La Roche, CStone, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, BeiGene, and others are evaluating their PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer therapies.
- The development of new targets beyond PD-(L)1 has faced challenges. TIGIT and TIM-3 were once promising new targets but have seen limited progress after experiencing high-profile failures. Despite this, both TIM-3 and TIGIT products are still in development.
- In May 2022, tiragolumab NSCLC trial, SKYSCRAPER-01, previously found the anti-TIGIT failed to improve PFS, but leaked overall survival data suggested it may be having a positive effect on overall survival. Recently, in July 2024, Roche halted another Phase II/III SKYSCRAPER-06 trial in first-line NSCLC because the combination of tiragolumab, + atezolizumab + pemetrexed, and carboplatin/cisplatin did not show a benefit over the established treatment comparator, pembrolizumab + pemetrexed and carboplatin/cisplatin. Roche hopes for tiragolumab mix in dust after multiple failure trials.
Request for Unlocking the Sample Page of the "PD-1 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market"
DelveInsight’s “PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” Report delivers an in-depth understanding of PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market Report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
|
|
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
|
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Companies |
|
|
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapies |
|
|
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market: Understanding and Algorithm
There are mainly two types of lung cancer: small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and NSCLC. NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. If untreated, SCLC can be fatal in a few weeks, in contrast to most cases of NSCLC. The results of the standard treatment of NSCLC are poor except for the most localized cancers. The newly diagnosed patients with NSCLC are potential candidates for studies evaluating new forms of treatment. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy PD-(L)1 is a type of immunotherapy that is used in the treatment of NSCLC. PD-L1 can be aberrantly expressed on tumor cells, allowing them to escape immune surveillance and consequent killing by the host adaptive immune system. In NSCLC, PD-(L)1 expression reported as the percentage of viable tumor cells showing membranous staining for PD-(L)1 at immunohistochemistry (tumor proportion score, TPS) is a predictive biomarker of response to ICI targeting.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Diagnosis
The diagnosis and staging of PD-(L)1 NSCLC are often done at the same time. The tests and procedures used in the diagnosis of NSCLC are Physical Exam and History, Laboratory Tests, Chest X-ray, CT scan (CAT scan), Sputum Cytology, Thoracentesis, Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the Lung, Bronchoscopy and other techniques.
Further details related to diagnosis are provided in the report…
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
The results of the standard treatment of NSCLC are poor except for the most localized cancers. Newly diagnosed patients with NSCLC are potential candidates for studies evaluating new forms of treatment. Different types of treatment are available for NSCLC; however, mainly 10 types of standard treatment are used, which include Surgery, Radiation therapy, Chemotherapy, Targeted therapy, Immunotherapy, Laser therapy, Photodynamic therapy (PDT), Cryosurgery, Electrocautery, and Watchful waiting.
Several PD-(L)1 are expected to enter the NSCLC market; however, given the physicians’ familiarity with the existing products on the market, we do not expect new entrants to disrupt the market significantly.
In the US, KEYTRUDA, OPDIVO, TECENTRIQ, IMFINZI, and LIBTAYO are the five main PD-(L)1 players. Both KEYTRUDA and OPDIVO were introduced in 2014 and had a sizable time advantage over rival drugs. KEYTRUDA and OPDIVO dominate the PD-1 market and, to some extent, compete with PD-(L)1.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Epidemiology
The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Total Incident Cases of NSCLC, Gender-specific Cases of NSCLC, Age-specific Cases of NSCLC, Total Incident Cases of NSCLC by Histology, Total Incident Cases of NSCLC by Stage, and Total Cases of NSCLC by Genetic Mutations/Biomarkers in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
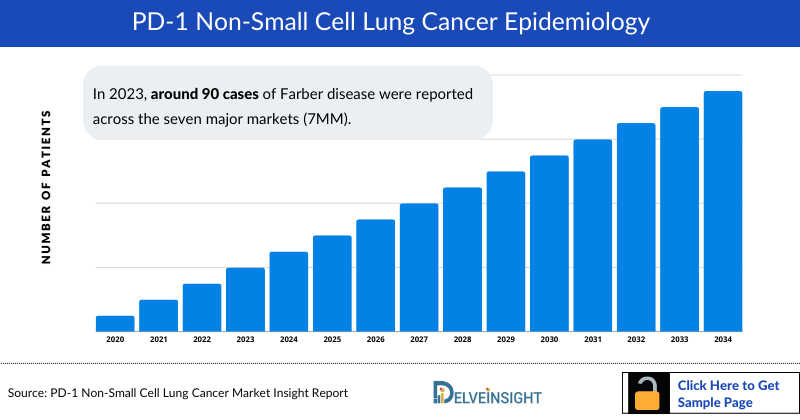
- The total number of incident cases of NSCLC in the 7MM was nearly 524,000 cases in 2023 and is projected to increase during the forecasted period.
- In 2023, the incidence of NSCLC cases in the United States was~56% in males and~ 44% in females.
- In 2023, the total number of cases of NSCLC in EU4 and the UK was estimated to be nearly 203,220. Among EU4 and the UK, the highest number of cases of NSCLC was found in Germany.
- The biomarker testing rate for PD-(L)1 in the US is around 85%. In Japan, the PD-(L)1 testing rate is more compared to EU4 and the UK.
- The total number of PD-(L)1 NSCLC cases in the US was nearly 101,300 in 2023.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer report encloses a detailed analysis of the marketed and the late-stage (Phase III) PD-1 Non-small cell lung cancer pipeline drug. The marketed drugs segment encloses drugs such as KEYTRUDA (Merck), OPDIVO (Bristol-Myers Squibb/Ono Pharmaceutical), TECENTRIQ (Genentech/Hoffmann-La Roche), LIBTAYO (Regeneron/Sanofi), and TIZVENI (BeiGene). The drug chapter also helps understand the PD-(L)1 NSCLC clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, and the latest news and press releases.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Marketed Drugs
- KEYTRUDA (pembrolizumab): Merck
KEYTRUDA is a PD-1-blocking antibody. It is mainly used for advanced cancers that have spread to other body parts or are not responding to other treatments. In some cancers, it is only given to patients whose tumors produce high protein levels known as PD-(L)1. In NSCLC, it is in combination with pemetrexed and platinum chemotherapy as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non squamous NSCLC, with no EGFR or ALK genomic tumor aberrations. Combining with carboplatin and either paclitaxel or paclitaxel protein-bound as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic squamous NSCLC.
The dominance of KEYTRUDA in the oncology drugs market highlights the success of Merck's commercial tactics and the direction of its R&D department. The department is also tasked with evaluating the efficacy of this blockbuster in combination with drugs such as vibostolimab, quavonlimab, and faveselimab.
- OPDIVO (nivolumab): Bristol-Myers Squibb/Ono Pharmaceutical
OPDIVO by Bristol-Myers Squibb is a human immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 monoclonal antibody directed against the negative immunoregulatory human cell surface receptor PD-1, with immune checkpoint inhibitory and antineoplastic activities. It is a prescription medicine used to treat people with unresectable or metastatic melanoma, metastatic NSCLC, SCLC, advanced renal cell carcinoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN), urothelial carcinoma, microsatellite instability-high (MSI-H) or mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma.
To tackle the biosimilar impact, Bristol Myers Squibb has already developed the subcutaneous formulation of OPDIVO. In May 2024, the FDA accepted a biologics license application (BLA) seeking the approval of OPDIVO co-formulated with Halozyme’s proprietary recombinant human hyaluronidase (rHuPH20; subcutaneous nivolumab)
|
Product |
Company |
RoA |
MoA |
First Approval |
|
KEYTRUDA (Pembrolizumab) |
Merck |
IV infusion |
PD-1 Inhibitor |
US: 2015, EU: 2016; JP: 2016 |
|
OPDIVO (nivolumab) |
Bristol-Myers Squibb/Ono Pharmaceutical |
IV infusion |
PD-1 Inhibitor |
US: 2015, EU: 2015, JP: 2015 |
|
TECENTRIQ (atezolizumab) |
Genentech/ Hoffmann-La Roche |
IV infusion |
PD-L1 Inhibitor |
US:2016, EU: 2017 JP: 2018 |
|
LIBTAYO (cemiplimab-rwlc) |
Regeneron/Sanofi |
IV infusion |
PD-1 inhibitor |
US: 2022, EU: 2021, JP: 2022 |
|
TIZVENI (tislelizumab) |
BeiGene |
IV infusion |
PD-1 inhibitor |
EU: 2024 |
Note: Detailed list will be provided in the final report.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Emerging Drugs
- Sugemalimab (CS1001): CStone
Sugemalimab is an investigational anti-PD-(L)1 monoclonal antibody discovered by CStone. In December 2022, EQRx announced the acceptance of the Marketing Authorization Application by the UK’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency for sugemalimab in metastatic NSCLC. The application was based on data from the pivotal Phase III GEMSTONE-302 trial, which assessed sugemalimab in combination with chemotherapy as the first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC.In May 2023, CStone announced that they would regain rights for developing and commercializing sugemalimab outside Greater China upon terminating the license agreement for sugemalimab between CStone and EQRx. Upon transition completion, CStone will lead the regulatory process for sugemalimab MAA reviews by the EMA and the UK MHRA.
- Datopotamab Deruxtecan: Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca
Datopotamab Deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) is an investigational TROP2-directed ADC. Designed using Daiichi Sankyo’s proprietary DXd ADC technology, Datopotamab Deruxtecan is one of five lead ADCs in the oncology pipeline of Daiichi Sankyo and one of the most advanced programs in AstraZeneca’s ADC scientific platform.
In February 2024, the BLA for datopotamab deruxtecan was accepted in the US for the treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC who have received prior systemic therapy. The BLA was based on results from the pivotal TROPION-Lung01 Phase III trial in which datopotamab deruxtecan demonstrated a statistically significant improvement for the dual primary endpoint of progression-free survival (PFS) compared to docetaxel, the current standard of care, in patients with locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC treated with at least one prior line of therapy. The regulatory agency has set a Prescription Drug User Fee Act date in Q4 2024 for making its decision on approving dato-DXd in the population as mentioned earlier
|
Comparison of Emerging Drugs Under Development for PD-(L)1 NSCLC | ||||||
|
Product |
Company |
Mechanism of Action |
Phase |
Indication |
ROA |
Molecular Type |
|
Sugemalimab (CS1001) |
EQRx/CStone |
PD-1 Inhibitor |
Registration in Europe |
Advanced NSCLC |
Intravenous infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
|
Datopotamab deruxtecan |
Daiichi Sankyo/ AstraZeneca |
TROP2-directed DXd |
III |
Advance NSCLC with and without actionable oncogenic alterations (AGA) |
Intravenous infusion |
Antibody-drug conjugate |
|
Ociperlimab + Tislelizumab |
BieGene |
Anti-TIGIT |
III |
1L PD-L1 high NSCLC |
Intravenous infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
|
TRODELVY (sacituzumab govitecan) + pembrolizumab |
Gilead Sciences |
TROP-2-expressing cancer cells |
III |
2-3L metastatic non-small cell lung cancer |
Intravenous infusion |
Antibody-drug conjugate |
|
JEMPERLI (dostarlimab) |
GlaxoSmithKline |
PD-1 Inhibitor |
II |
NSCLC |
Intravenous infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
Note: Detailed list will be provided in the final report.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market Insights
Checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-(L)1 have emerged as dominant forces in the immunotherapy landscape for cancer treatment, with ten PD-(L)1 inhibitors approved, comprising seven PD-1 and three PD-L1 inhibitors in the United States. Their efficacy has been notable across various solid tumors, with KEYTRUDA being a standout among these agents, approved for a remarkable twenty indications and holding a significant market presence for several years. However, recent concerns over adverse events have prompted a shift towards combination approaches aimed at enhancing both efficacy and safety. This strategy involves combining PD-(L)1 inhibitors with other checkpoint inhibitors such as CTLA-4, TIGIT, and LAG-3, as well as exploring novel targets like TROP-2. Due to its numerous indication approvals, which led to a comprehensive FDA label and widespread use across a number of indications, PD-1 exceeds the sales of PD-L1 in the 7MM market. Despite their potential, immune checkpoint inhibitors face challenges, including immune-related side effects and high costs, highlighting the critical need for reliable biomarkers to identify patients who would benefit most from these treatments.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Outlook
Till the last decade, chemotherapy was used as the standard of care in the advanced and metastatic stages until the first ICI ‘KEYTRUDA’ got approved in 2015 as a second-line treatment option for such advanced patients; a similar path was followed by TECENTRIQ who entered the market in 2016. These therapies entered the first-line domain after 2016 and expanded their labels by expanding the targetable pool. In 2020, OPDIVO + ipilimumab was approved as a 1L treatment for patients with metastatic NSCLC. In the United States, OPDIVO sales are largely fueled by continued demand growth across indications such as NSCLC, melanoma, renal cancer, and upper gastrointestinal cancers. Chinese companies are trying to enter the US and EU markets, especially the EU markets where TIZVENI-approved in 2024 and sugemalimab is currently under review.
The new area of development in NSCLC includes TROP-2-directed ADC’s, TIGIT, and LAG-3 inhibitors majorly being targeted by the researchers and the big companies such as AstraZeneca, Daiichi Sankyo, Hoffmann-La Roche, Gilead Sciences, and others have their potential candidates in late stages of development. Although there is only one ADC approved for NSCLC, and it is only for a limited subgroup (HER2m NSCLC), companies are attempting to target a larger NSCLC population, particularly in areas where KEYTRUDA is the market leader. Targeting the non-actionable genomic aberration, NSCLC markets are DATO-Dxd and TRODELVY.
Key Findings
- TThe total PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size in the US was estimated to be USD 6,200 million in 2023, and it is expected to increase due to the launch of emerging therapies and label expansion of current therapies.
- The development of the TIGIT class in NSCLC has been hampered by the fact that several high-profile TIGIT clinical studies have revealed underwhelming results. Effective combinations to augment current ICIs have historically been challenging as seen with Merck's and Roche's recent anti-TIGIT/PD-1 disappointment.
- Several PD-L1 are expected to enter the NSCLC market; however, given the physicians’ familiarity with the existing products on the market, we do not expect new entrants to disrupt the market significantly.
- In 2023, KEYTRUDA captured the largest PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market Size, approximately USD 3,500 million, in the US for the PD-(L)1 NSCLC market.
- Front-line NSCLC represents a large market, currently only being dominated by anti-PD 1 drugs and anti-PD-1 + CTx combination, leaving a significant opportunity for therapy beyond anti-PD1 to deliver higher clinical benefit.
- According to GlaxoSmithKline H1 2024 presentation, the company anticipates Phase III data readout of JEMPERLI + cobolimab COSTAR, 2L NSCLC in 2025.
- In April 2024, BeiGene announced that the European Commission (EC) had approved TIZVENI (tislelizumab) as a treatment for NSCLC across three indications, including first- and second-line use.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2020–2034. The landscape of PD-(L)1 NSCLC treatment has experienced a profound transformation with the uptake of novel drugs. These innovative therapies are redefining standards of care. Furthermore, the increased uptake of these transformative drugs is a testament to the unwavering dedication of physicians, oncology professionals, and the entire healthcare community in their tireless pursuit of advancing cancer care.
This momentous shift in treatment paradigms is a testament to the power of research, collaboration, and human resilience. In the emerging therapies, Dato-DXd has the upper hand; findings from the Phase III TROPION-Lung01 trial support the BLA for Dato-DXd as a treatment for those with advanced nonsquamous NSCLC. Dato-DXd's advantage in treating NSCLC and its higher efficacy in early-stage studies, this drug is expected to surpass alternative therapy eventually approaches presently being researched as the market's top TROP2 ADC for NSCLC.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer ASCO Uptake
|
ASCO 2024 Update | |||||
|
Product |
Company |
Indication |
Abstract ID |
Trial ID |
Outcome |
|
Acasunlimab |
Genmab |
NSCLC |
Abstract- 2533 |
NCT05117242 |
In PD-L1+ patients with mNSCLC following progression on prior checkpoint inhibitor treatment, acasunlimab + pembrolizumab combo showed a manageable safety profile and promising efficacy, with deeper responses and durable disease control in patients treated Q6W. |
|
Dato-DXd + pembrolizumab |
Daiichi Sankyo/ AstraZeneca |
Advanced NSCLC |
Abstract-8617 |
NCT04526691 |
As 1L therapy for aNSCLC, Dato-DXd + pembrolizumab with or without Pt-CT continues to demonstrate durable antitumor activity. Efficacy was observed regardless of PD-L1 expression. Tolerability of the combinations was as expected based on known profiles of the individual agents, with no new safety signals observed. To date, this is the largest dataset reported for any ADC combined with an anti-PD-1/L1 agent in the 1L setting for advanced NSCLC |
|
TRODELVY vs. Docetaxel |
Gilead Sciences |
mNSCLC |
LBA8500 |
NCT05089734 |
Although statistical significance was not met, OS numerically improved with TRODELVY vs. docetaxel, which was consistent across histologies. Clinically meaningful improvement in OS was noted in mNSCLC non responsive to the last anti–PD-(L)1 containing regimen. TRODELVY was better tolerated than docetaxel and consistent with its known safety profile, with no new safety signals. |
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Pipeline Development Activities
The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report provides insights into therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I. It also analyzes key PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Companies involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for PD-(L)1 NSCLC emerging therapy.
Take Your Research to the Next Level! Click Here to Get Access to the Full Pipeline Report @ PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Drugs
KOL Views
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on PD-(L)1 NSCLC evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including oncologists, radiation oncologists, surgical oncologists, and others.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 30+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as MD, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, MD, Duke Cancer Institute at Duke University, PhD, MD, MPH, Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center, Michigan State University, Director, Massachusetts General Hospital etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or PD-(L)1 NSCLC market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
|
Region |
KOL Views |
|
United States |
“Patients with NSCLC that doesn’t respond to checkpoint inhibitors known as PD(L)-1 inhibitors have few treatment options. In this trial, we tested a PDL-1 inhibitor in combination with a drug that targets a different immune checkpoint protein, CTLA-4 — an approach that has shown promise in laboratory research but hasn’t been extensively tested in patients whose NSCLC is resistant to PD(L)-1 inhibitors.” |
|
United States |
“I would say that based upon the success of checkpoint inhibitors in the metastatic and locally advanced setting, we’re now seeing checkpoint inhibitors move to both the adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings in non-small cell lung cancer. I think you’re hearing from all of us that we’d be more ready to adopt adjuvant PD-1 pathway blockade despite seeing some promising new adjuvant data using the combination of chemo plus PD-1 pathway blockade. Most of us now want to see event-free survival data rather than just pathCR data, but it is a very exciting area. And we eagerly await long-term follow-up for all of these studies.” |
|
France |
“Currently, immune checkpoint inhibitors treatment, particularly anti-PD-1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies, is a cornerstone in non-small cell lung cancer therapy. There is significant interest in exploring combination therapies involving approved and investigational agents alongside PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors, which will certainly provide data about the pharmacodynamic and clinical properties of these associations, enhancing our understanding of ICIs and cancer immunotherapy. Additionally, there is a pressing need for new predictive biomarkers, given the evolving role of PD-L1 in treatment strategies combining chemotherapy and immunotherapy and the absence of other validated predictors.” |
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy. In efficacy, the trial’s primary and secondary outcome measures are evaluated; for instance, in event-free survival, one of the most crucial primary outcome measures is event-free survival and overall survival.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated, wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and this clearly explains the drug's side effects in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Access and Reimbursement
The current scenario of therapeutics for NSCLC is mainly based on the use of targeted therapies and immunotherapy. The current paradigm is mainly associated with treatment specific to mutations that occur in NSCLC.
|
IQWiG Assessment for NSCLC Therapies | |||
|
Drug Name |
Indication |
Result of Dossier Assessment |
Date of Decision |
|
KEYTRUDA |
First-line treatment of metastatic non-squamous NSCLC in adults whose tumors have no EGFR or ALK-positive mutations |
PD-(L)1 expression <50%: proof of major added benefit for women, indicating minor added benefit for men. PD-(L)1 expression ≥50%: a hint of a major added benefit for women and a hint of lesser benefit for men |
August 2019 |
|
First-line treatment of metastatic squamous NSCLC in adults |
PD-(L)1 expression <50%: indication of major added benefit. PD-(L)1 expression ≥50%: added benefit not proven |
August 2019 | |
|
OPDIVO |
First-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC in adults whose tumors have no sensitizing EGFR mutation or ALK translocation |
|
April 2021 |
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report
- The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer therapeutics market report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview, explaining its causes, signs, symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently used therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer epidemiology segments and forecasts, disease progression, and treatment guidelines has been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market, historical and forecasted PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market Size, PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market Share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market.
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report Insights
- Patient-based PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Forecasting
- Therapeutic Approaches
- PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Pipeline Drugs Analysis
- PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size and Trends
- Existing and Future PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market Opportunity
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report Key Strengths
- 11 Years PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- PD-(L)1 NSCLC Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Drugs Uptake and Key PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Forecast Assumptions
PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report Assessment
- Current PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market Practices
- PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Unmet Needs
- PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Pipeline Drugs Analysis Profiles
- PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT Analysis and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs
- What was the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Market Size, the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market Sxize by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2023, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved therapies?
- What can be the future treatment paradigm of PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer?
- What will be the impact on the sales of KEYTRUDA after its patent expiry?
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of PD-(L)1 NSCLC? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population with PD-(L)1 NSCLC?
- Who is the major competitor of OPDIVO in the market?
- What are the current options for the treatment of PD-(L)1 NSCLC? What are the current guidelines for treating PD-(L)1 NSCLC in the US, Europe, and Japan?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies being developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- What recent novel therapies, targets, PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Mechanisms of Action are explored in combination with PD-(L)1?
Reasons to Buy
- The PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics Market Report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market opportunity in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the PD-1 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Drugs Market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the Analyst view section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of current therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet need of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Stay Updated with us for Recent Articles @ Latest DelveInsight Blogs

.png)
-pipeline-report.png&w=256&q=75)
