Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Summary
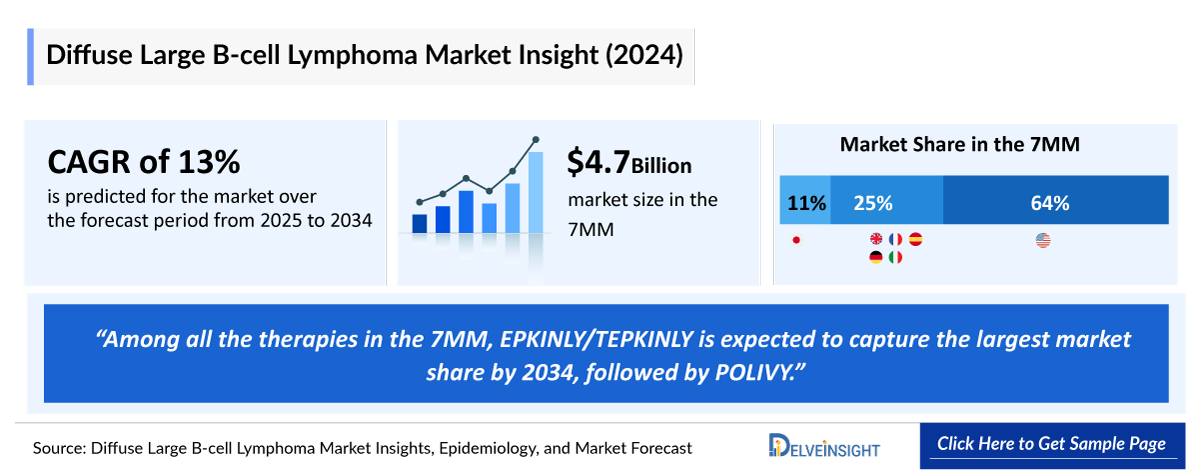
- The Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Size in the 7MM is expected to grow from USD 5,286 million in 2025 to USD 16,562 million in 2034.
- The Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.50% by 2034 in leading countries like the US, EU4, UK, and Japan.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market and Epidemiological Analysis
- The total market size in the 7MM for Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) is expected to grow with a significant CAGR during the forecast period (2025-2034). In 2024, the US accounted for the maximum share of the total market in the 7MM nearly USD 3,100 million in 2024.
- Despite being an aggressive lymphoma, DLBCL is considered potentially curable. Although it can occur in childhood, the occurrence of DLBCL generally increases with age, and most patients are over the age of 60 at diagnosis.
- RITUXAN, a CD20-targeting monoclonal antibody, continues to be the cornerstone of DLBCL treatment, demonstrating robust efficacy in combination regimens. This established efficacy solidifies its place in both first-line and relapsed settings.
- Chemotherapy-sensitive DLBCL patients may qualify for Autologous Stem Cell Transplant (ASCT), but many fail salvage chemotherapy, leading to poor prognosis. Advances in cellular therapies and bispecific antibodies are reshaping treatment options.
- Approximately 60% of DLBCL patients achieve remission with frontline R-CHOP therapy, while 40% either relapse or remain refractory. Traditionally, these patients undergo salvage chemotherapy with regimens like R-GemOx, R-ICE, or R-DHAP, though none have demonstrated clear superiority.
- YESCARTA, BREYANZI, and KYMRIAH are three FDA-approved CAR T-cell therapies for relapsed or refractory DLBCL, with no first-line approvals. Gilead/Kite is evaluating YESCARTA in the first-line setting, which could introduce significant competition to already approved first-line therapies.
- Off-the-shelf bispecific antibodies are gaining traction, targeting CD20 and CD3 on T cells to enhance immune response. Unlike monoclonal antibodies, they simultaneously bind two epitopes, improving therapeutic precision. While explored across hematologic and solid tumors, they have shown notable efficacy in B-NHL, positioning them as a potential breakthrough in treatment.
- With no approved first-line CAR T-cell therapy, Cemacabtagene ansegedleucel (Allogene Therapeutics) is an off-the-shelf, allogeneic CD19 CAR T-cell in Phase II ALPHA3 trial, assessing its role in first-line consolidation for LBCL patients with MRD post-standard treatment. Its market entry could offer a breakthrough option.
- Expected launch of potential therapies such as, Zilovertamab vedotin (Merck), Zamtocabtagene autoleucel (Miltenyi Biomedicine), Cemacabtagene ansegedleucel (Allogene Therapeutics), Rapcabtagene autoleucel (Novartis), Golcadomide (BMS), and others may increase the market size in the coming years, assisted by an increase in the population of DLBCL. It is expected that these therapies will help the market of DLBCL post-launch, in the 7MM, during the forecast period (2025-2034).
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Size and Forecasts
- 2025 Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Size: USD 5286 million in 2025
- 2034 Projected Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Size: USD 16,562 million in 2034
- Growth Rate (2025-2034): 13.5 % CAGR
- Largest Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market: United States
DelveInsight’s “Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of DLBCL, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as DLBCL market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM DLBCL market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current DLBCL treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
Scope of the DLBCL Market Report | |
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
DLBCL Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
|
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Companies |
|
|
Key Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Medications |
|
|
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
Key Factors Driving the Growth of the Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market
Increasing DLBCL Incidence and Aging Population
Global DLBCL incidence exceeds 150,000 cases annually, driven by aging populations (9% aged 65+). In the 7MM, incident cases are projected to reach ~87K by 2034.
Launch of Emerging Targeted DLBCL Therapies and Immunotherapies
The introduction of novel treatment options, such as CAR-T therapies (Allogene Therapeutics’s Cemacabtagene ansegedleucel, Miltenyi Biomedicine’s Zamtocabtagene autoleucel, Galapagos’s GLPG5101, Novartis’ Rapcabtagene Autoleucel, Lyell/ImmPACT Bio’s IMPT-314, and others), monoclonal antibodies (Genmab’s GEN3014), and bispecific antibodies (Roche/Biogen’s LUNSUMIO, AstraZeneca’s AZD0486, and others), is expected to propel the DLBCL treatment market.
Growing Investment in R&D and DLBCL Clinical Trials
More than 30 pharmaceutical diffuse large B-cell lymphoma companies, including Roche (Genentech), Biogen, AstraZeneca, Merck, Allogene Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, 2seventy bio, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, BeiGene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Otsuka Pharmaceutical, Gilead Sciences, Amgen, and others, are investing heavily in developing next-generation DLBCL therapies, resulting in a stronger pipeline and more approvals.
Improved DLBCL Diagnostic Capabilities and Early Detection
Improved diagnostic tools, such as PET-CT and next-generation sequencing, have boosted early detection rates in DLBCL by nearly 20%, enabling risk stratification and personalized treatment approaches. Early-stage diagnosis now accounts for approximately 35–40% of identified cases, resulting in significantly improved survival outcomes.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Disease and Understanding
NHL is a cancer of the lymphatic system, characterized by the abnormal accumulation of mature B-cell clones. Symptoms include painless swollen lymph nodes, weight loss, fever, night sweats, and fatigue. DLBCL, the most common and aggressive NHL subtype, arises in lymph nodes or extranodal sites like the gastrointestinal tract, skin, or brain. It often presents with rapid, painless swelling in the neck, armpits, or groin, along with systemic symptoms. Advances in treatment have made DLBCL curable through chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and gene therapies. R-CHOP is the standard regimen in the US, EU, and Japan. DLBCL is classified based on molecular subtypes (GCB, ABC), location (CNS, cutaneous, intravascular), and stage.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Diagnosis
DLBCL is diagnosed through an excisional lymph node biopsy, revealing large atypical cells positive for CD20 and CD79a. Immunohistochemistry determines the cell of origin, while FISH detects high-risk genetic features like double-hit or triple-hit disease. Commercial mutation tests are not standard for treatment decisions. A tissue biopsy is required for diagnosis, typically under local or general anesthesia. Most patients present with lymphadenopathy, and up to 40% have extranodal involvement. Common sites include the CNS, gastrointestinal tract, and bone, with 30% experiencing systemic B symptoms like fever and weight loss.
Excisional biopsy is preferred, but if inaccessible, core needle biopsy (CNB) and fine-needle aspiration (FNA) with additional testing may suffice. Immunophenotyping via immunohistochemistry or flow cytometry, along with cytogenetic analysis, confirms diagnosis and detects key chromosomal translocations. Staging involves CT or PET/CT scans, with bone marrow biopsy or lumbar puncture if needed. Limited-stage disease affects one area, while advanced-stage disease spreads to multiple organs.
Further details related to diagnosis are provided in the report…
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Treatment
DLBCL progresses rapidly, often requiring immediate treatment. The standard first-line regimen is R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone), typically given in 21-day cycles for up to six cycles, with shorter cycles or fewer cycles plus radiation used in limited-stage disease. Variants include R-CHOEP (adding etoposide) and R-EPOCH, a continuous infusion regimen preferred in cases such as HIV-associated DLBCL. While toxicity profiles vary, no regimen has proven superior in efficacy. Another option is pola-R-CHP (polatuzumab vedotin plus R-CHP), with or without radiation.
Advancements in precision medicine are shaping DLBCL treatment by tailoring therapies to genetic subtypes. Ibrutinib, used in other lymphomas, has shown greater effectiveness in the ABC subtype, which is less responsive to R-CHOP. A Phase III trial is evaluating its addition to standard chemotherapy for non-GCB subtypes. Similarly, lenalidomide combined with R-CHOP has shown promise in ABC-DLBCL. Ongoing research aims to refine targeted treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Further details related to treatment are provided in the report…
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Epidemiology
The DLBCL epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total incident cases of DLBCL, gender-specific cases of DLBCL, age-specific cases of DLBCL, type-specific cases of DLBCL, stage-specific incident cases of DLBCL, and treated cases of DLBCL in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
Key Findings from Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Epidemiological Analyses and Forecast
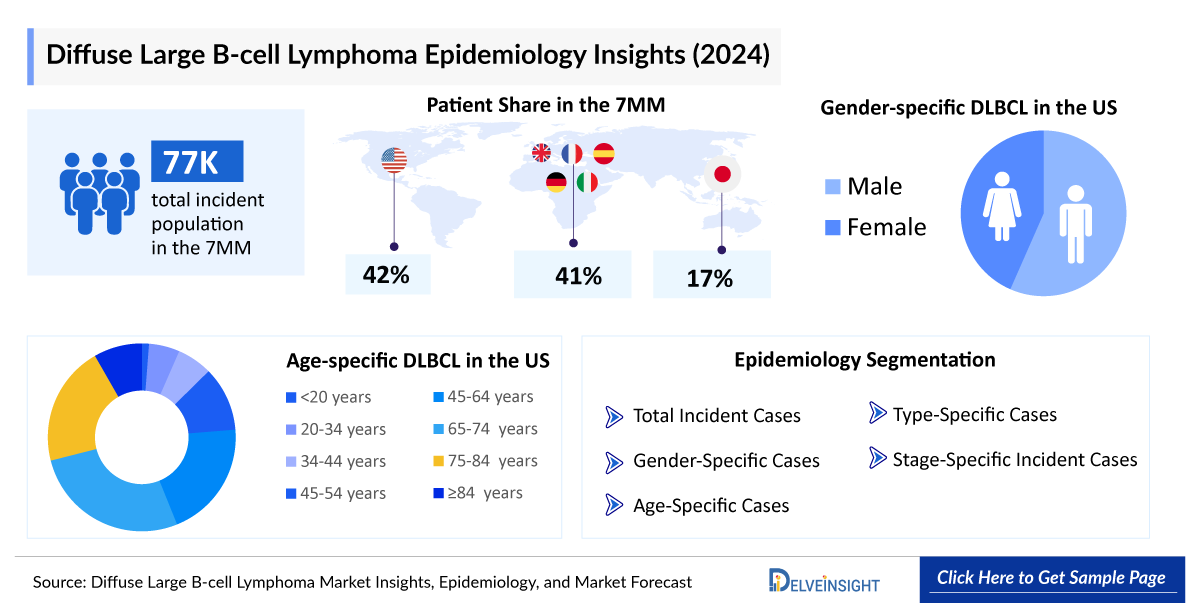
- In 2024, the total incident cases of DLBCL were about 77,000 in the 7MM. These cases are projected increase by 2034.
- Among EU4 and the UK, the highest number of incident cases of DLBCL were found in Germany (~7,700), followed by France. At the same time, Spain accounted for the lowest number of incident cases in 2024.
- In Japan, males were more affected by DLBCL than females.
- Among EU4 countries and UK, the age group of 75-84 years accounted for the highest cases of DLBCL in 2024, followed by 65-74 years and more than 84 years. In contrast, the least cases were found in the age group of less than 20 years.
- Up to 50% of patients with R/R DLBCL are ineligible for transplantation because of pre-existing comorbidities or advanced age.
- About 30–40% of people with DLBCL use to have localized Stage I or II diseases when they are diagnosed. The rest may have widespread disease at the time of diagnosis.
- DLBCL has many subtypes and according to analysis, DLBCL, NOS accounts of majority of B-cell patient population, in the US there were about 27,000 cases observed for DLBCL, NOS in 2024, which are expected to reach 33,000 by 2034.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Epidemiology Segmentation
- total incident cases
- gender-specific cases
- age-specific cases
- type-specific cases
- stage-specific incident cases
- treated cases
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Drug Analysis
The drug chapter segment of the DLBCL report encloses a detailed analysis of the marketed and the late, mid, and early stage (Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I/II) pipeline drugs. The marketed drugs segment encloses drugs such as YESCARTA (Gilead/Kite), KYMRIAH (Novartis), KEYTRUDA (MSD), POLIVY + BR/R-CHP (Roche-Genentech/Chugai Pharmaceuticals), XPOVIO (Karyopharm therapeutics), TREAKISYM (SymBio Pharmaceuticals), COLUMVI (Genentech), MONJUVI/MINJUVI (MorphoSys/Incyte), and others. The drug chapter also helps understand the DLBCL clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, and the latest news and press releases.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Marketed Drugs
-
ZYNLONTA (loncastuximab tesirine-lpyl): ADC Therapeutics/SOBI
ZYNLONTA is a CD19-directed ADC. Once bound to a CD19-expressing cell, ZYNLONTA is internalized by the cell, where enzymes release a Pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) payload. The potent payload binds to a minor DNA groove with little distortion, remaining less visible to DNA repair mechanisms. This ultimately results in cell cycle arrest and tumor cell death.
In July 2025, ADC Therapeutics provided anticipated milestones for ZYNLONTA. LOTIS-7 trial to share more mature data by H2 2025, full enrolment of patients (100) in recommended dose by H1 2026.The company also plans to submit LOTIS-7 data at EHA and ICML in H1 2025, and from H2 2025 engage with regulatory agencies and evaluate compendia strategies. For LOTIS-5 trial, the company plans to reach prespecified number of PFS events by end of 2025, potential BLA submission to regulatory authorities by H1 2026, and potential confirmatory approval in 2L+ DLBCL by H1 2027.
-
EPKINLY/TEPKINLY (epcoritamab-bysp): Genmab and AbbVie
EPKINLY/TEPKINLY (epcoritamab-bysp) is the first and the only bispecific antibody approved for 3L+ DLBCL. It is co-developed and commercialized by Genmab and AbbVie. Epcoritamab, marketed as EPKINLY (in the US and Japan), is being developed and commercialized in collaboration with AbbVie. Epcoritamab received accelerated FDA approval in May 2023 for the treatment of adults with R/R DLBCL and, in September 2023, was granted both conditional marketing authorization by the EC (TEPKINLY) and approval by the Japan MHLW.
In June 2025, Genmab announced new results from the Phase Ib/II EPCORE NHL-2 trial Arm 10 (NCT04663347), evaluating epcoritamab, in combination with rituximab, ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide (R-ICE) in adult patients with R/R DLBCL who are eligible for autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT). As per the presentation of Genmab at J.P. Morgan Healthcare Conference 2025, the company is expecting to launch EPKINLY for 3L+ R/R DLBCL in 2025, for 2L R/R DLBCL from 2027e-2030e and the launch for 1L DLBCL from 2027e-2031e.
In December 2024, Abbvie presented the results of the EPCORE NHL-1 and EPCORE NHL-2 trials of EPKINLY at ASH 2024.
Comparison of Marketed Drugs | |||||
|
Product |
Company |
RoA |
MoA |
Molecule Type |
US Approval |
|
RITUXAN/MABTHERA |
Biogen IDEC/Genentech/Chugai Pharmaceuticals |
CD20-directed antibody |
IV Infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
February 2006 |
|
YESCARTA |
Gilead/Kite |
CD19-directed genetically modified autologous T-cell immunotherapy |
IV |
CAR-T-cell therapy |
October 2017, April 2022 |
|
KYMRIAH |
Novartis |
CD19-targeted CART- cell immunotherapy |
IV |
CAR-T-cell therapy |
May 2018 |
|
KEYTRUDA |
Merck |
PD-1 targeted therapy |
IV Infusion |
Monoclonal antibody |
June 2018 |
|
POLIVY + BR/R-CHP |
Roche-Genentech/Chugai Pharmaceuticals |
CD79b targeted anti-mitotis |
IV |
Antibody-drug conjugate |
June 2019, April 2023 |
|
XPOVIO |
Karyopharm therapeutics |
Nuclear Export (SINE) inhibitor |
Oral |
Small molecule |
June 2020 |
|
MONJUVI/MINJUVI + REVLIMID |
MorphoSys/Incyte |
CD19- Inhibitors |
IV |
Monoclonal antibody |
July 2020 |
|
EPKINLY/TEPKINLY |
Genmab and AbbVie |
CD20 x CD3 |
SC |
Bispecific antibody |
May 2023 |
|
COLUMVI |
Genentech/Roche |
CD20 x CD3 |
IV infusion |
Bispecific antibody |
June 2023 |
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Emerging Drugs
Zilovertamab Vedotin (MK-2140): Merck
Zilovertamab vedotin is an investigational ADC that targets ROR1. ROR1 is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in multiple hematologic malignancies. Merck is committed to research with zilovertamab vedotin across B-cell malignancies and is establishing a robust program of clinical trials under the name waveLINE.
In May 2025, Merck announced results from the dose confirmation portion of the Phase II/III waveLINE-003 study evaluating zilovertamab vedotin in combination with SoC rituximab and gemcitabine-oxaliplatin (R-GemOx) for the treatment of R/R DLBCL. This data was further presented at ASCO 2025.
According to the JP Morgan Healthcare Conference data readout, the Phase II NCT05144841 (waveLINE-004) trial of zilovertamab vedotin for R/R DLBCL is expected by 2025. The Phase II/III NCT05139017 (waveLINE-003) trial for R/R DLBCL is anticipated between 2026 and 2027, while the Phase III NCT06717347 (waveLINE-010) trial for DLBCL is projected beyond 2028.
In December 2024, Merck presented the first data from the Phase II waveLINE-007 trial evaluating zilovertamab vedotin + R-CHP at the 66th ASH annual meeting and exposition.
CALQUENCE (acalabrutinib): AstraZeneca
CALQUENCE is a next-generation, selective inhibitor of BTK. CALQUENCE binds covalently to BTK, thereby inhibiting its activity. In B cells, BTK signaling activates pathways necessary for B-cell proliferation, trafficking, chemotaxis, and adhesion. As part of an extensive clinical development program, AstraZeneca is currently evaluating CALQUENCE alone and in combination for the treatment of multiple B-cell blood cancers, including CLL, MCL, and DLBCL.
According to AstraZeneca, the Phase III ESCALADE (NCT04529772) trial data readout for CALQUENCE in DLBCL is expected beyond 2025.
LUNSUMIO (mosunetuzumab): Roche (Genentech) and Biogen
LUNSUMIO (mosunetuzumab, anti-CD20/CD3 TDB, RG7828) is a humanized full-length T-cell-dependent bispecific antibody designed to target both CD20 on B cells and CD3 on T cells. This dual-targeting antibody is designed to redirect T cells to attack cancer cells. A robust clinical development program for LUNSUMIO is ongoing, investigating the molecule as a monotherapy and in combination with other medicines for the treatment of people with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, including follicular lymphoma, DBCL, and other blood cancers.
In June 2025, Roche announced that the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) recently added LUNSUMIO and POLIVY to the NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines) as a category 2A recommendation for the treatment of people with second-line (2L) DLBCL who are not intended to proceed to transplant.
According to Roche’s pipeline, the company plans in the US and Japan to file for LUNSUMIO plus POLIVY in 2L+ SCT-ineligible DLBCL by 2025.
The pivotal Phase III readout for LUNSUMIO in 2L+ DLBCL is expected in 2025.
Comparison of Emerging Drugs | ||||||
|
Product |
Company |
Phase |
Indication |
RoA |
MoA |
Molecule Type |
|
LUNSUMIO (mosunetuzumab) |
Roche (Genentech) and Biogen |
III |
2L+ SCT-ineligible DLBCL; previously untreated DLBCL |
SC |
Anti-CD20/CD3 |
Bispecific antibody |
|
CALQUENCE (acalabrutinib) |
AstraZeneca |
III |
Previously untreated DLBCL and R/R DLBCL |
Oral |
BTK inhibitor |
Small molecule |
|
NKTR-255 + CD19 CAR-T cell therapy |
Nektar Therapeutics |
II/III |
R/R LBCL |
IV |
IL-15 receptor agonist |
Recombinant protein |
|
Zilovertamab vedotin |
Merck |
III |
Previously untreated, R/R DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Selectively targets receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1) |
ADC |
|
Cemacabtagene ansegedleucel |
Allogene Therapeutics |
II |
1L Consolidation and Adult Subjects with R/R LBCL and 3L |
IV infusion |
Targeting CD19 |
Allogeneic CAR T cell therapy |
|
Zamtocabtagene autoleucel (MB-CART2019.1) |
Miltenyi Biomedicine |
II |
R/R DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Targets the combination of CD19 and CD20 |
Autologous Chimeric Antigen Receptor cell therapy |
|
AZD0486 |
AstraZeneca |
II |
1L DLBCL ; LBCL; 2L+DLBCL |
SC injection or IV infusion |
CD19 x CD3 T-cell engager |
Bispecific antibody |
|
GLPG5101 |
Galapagos |
I/II |
Patients with R/R NHL, including DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Anti-CD19 |
Autologous CAR T-cell therapy |
|
Rapcabtagene Autoleucel (YTB323) |
Novartis |
I/II |
3L+ DLBCL and 1L high-risk LBCL |
IV infusion |
Targets CD19 |
Autologous CAR-T-cell therapy |
|
IMPT-314 |
Lyell/ImmPACT Bio |
I/II |
R/R Aggressive B-cell NHL, including DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Dual-targeting CD19/CD20 |
Autologous CAR T-cell therapy |
|
Tulmimetostat (CPI-0209) |
Constellation Pharmaceuticals |
I/II |
R/R DLBCL |
Oral |
EZH1/EZH2 inhibitor |
Small molecule |
|
GEN3014 |
Genmab |
I/II |
R/R DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Targets CD38 |
Monoclonal antibody |
|
AVM0703 |
AVM Biotechnology |
I/II |
R/R DLBCL |
IV infusion |
NKT-like cells |
Small molecule |
|
Obecabtagene Autoleucel (Obe-cel) |
Autolus Therapeutics |
I |
R/R DLBCL |
IV infusion |
Targets CD19 |
Autologous CAR-T-cell therapy |
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Drug Class Analysis
The drug classes include BTK inhibitor, IL-15 receptor agonist, selective targets of receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 1 (ROR1), targeting CD19, dual-targeting CD19/CD20, CD19 x CD3 T-cell engager, CD47-SIRPa fusion protein, LAG-3 and PD-1 targets, and others.
- Dual-targeting CD19/CD20
Dual-targeting CD19/CD20 CAR T-cell therapies in DLBCL enhance antigen coverage and reduce relapse risk. Zamtocabtagene autoleucel targets both antigens to prevent tumor escape, while IMPT-314 uses an "OR"-gated platform to activate against either CD19 or CD20, improving persistence with naive/memory T-cells.
CD19-specific therapies include cemacabtagene ansegedleucel, an allogeneic CAR-T with MRD-based risk stratification. AZD0486, a bispecific T-cell engager (BiTE), links CD19 to CD3 for improved immune response. Rapcabtagene autoleucel (YTB323) optimizes CD19 CAR-T therapy for controlled activation, balancing efficacy and toxicity.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Outlook
Before the advent of rituximab, DLBCL was primarily treated with chemotherapy alone. The approval of rituximab in 2006, based on clinical trials demonstrating superior efficacy when combined with CHOP or other anthracycline-based regimens, marked a pivotal advancement in frontline therapy. This milestone redefined the treatment paradigm and established chemo-immunotherapy as the new standard of care. In recent years, deeper insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying lymphomagenesis, including altered signaling pathways, gene regulation, protein stability, and the tumor microenvironment, have driven the development of targeted therapies. These include monoclonal antibodies, small molecule inhibitors, and cell-based therapies, designed to enhance tumor control while reducing systemic toxicity.
Gene expression profiling has identified biologically distinct DLBCL subtypes with differing clinical behaviors, paving the way for biomarker-driven treatment strategies. While not yet fully integrated into routine care, these molecular insights are expected to inform future personalized approaches. Immunotherapies have emerged as a transformative strategy in DLBCL, offering the potential for long-lasting remissions. Checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1/PD-L1 and CTLA-4, along with CAR T-cell therapies, have shown encouraging efficacy, particularly in relapsed or refractory cases. However, immune-related toxicities—including dermatologic reactions, colitis, hepatotoxicity, and endocrinopathies—remain challenges, especially with checkpoint blockade.
CAR T-cell therapies targeting CD19 have redefined treatment for patients with refractory DLBCL, becoming a new standard for those who have failed at least two prior regimens. Despite challenges related to cost and reimbursement, market access has expanded due to strong clinical demand and demonstrated benefit. Ongoing innovation in CAR T-cell design aims to enhance safety and efficacy, positioning next-generation products as key drivers in the evolving therapeutic landscape.
- Among EU4 and the UK, Germany expected to capture the maximum market share, followed by France and Italy by 2034.
- The current standard of care for the first-line treatment of DLBCL is rituximab + other chemotherapy combinations.
- Among all the therapies in the 7MM, EPKINLY/TEPKINLY is expected to capture the largest market share with an expected revenue of ~USD 3 billion by 2034.
- The DLBCL market is becoming more competitive owing to the introduction of POLIVY + R-CHP in the first-line setting, and the expansion of CAR T-cell therapies in earlier lines (second-line). The space beyond the third-line plus setting has recently gained popularity as a result of the expansion of the labels of approved drugs into earlier lines.
- The potential therapies expected to be launched in the forecast period for first R/R transplant ineligible include LUNSUMIO (mosunetuzumab) + POLIVY, Zilovertamab vedotin + R-GemOx, XPOVIO ± R-GDP, COLUMVI + GemOx, and various others.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2024–2034. The landscape of DLBCL treatment has experienced a profound transformation with the uptake of novel drugs. These innovative therapies are redefining standards of care. Furthermore, the increased uptake of these transformative drugs is a testament to the unwavering dedication of physicians, oncology professionals, and the entire healthcare community in their tireless pursuit of advancing cancer care. This momentous shift in treatment paradigms is a testament to the power of research, collaboration, and human resilience.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights into therapeutic candidates in Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I/II. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Latest KOL Views on Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on DLBCL evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including oncologists, radiation oncologists, surgical oncologists, and others.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 15+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 7+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as - UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, MD Anderson Cancer Center, Columbia University, Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital, University of California San Diego, Hackensack University Medical Center, Kindai University, University of Cambridge, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Saint Louis University School of Medicine, University of Lübeck, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or DLBCL market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
DLBCL Clinical Trials and Registrational Updates
- In March 2025, Imugene Ltd received FDA Fast Track designation for its allogeneic CAR T-cell therapy, azer-cel (azercabtagene zapreleucel), for treating relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
- In February 2025, Pfizer Inc. announced the FDA's approval of ADCETRIS® (brentuximab vedotin) in combination with lenalidomide and a rituximab product for treating adult patients with certain types of relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL).
- In January 2025, Roche announced that it received 510(k) clearance from the U.S. FDA for its VENTANA® Kappa and Lambda Dual ISH mRNA Probe Cocktail, a highly-sensitive in-situ hybridization (ISH) test. The test aids pathologists in distinguishing B-cell malignancies from normal reactive responses to infections, enabling quicker treatment decisions. This follows the assay’s CE Mark approval in June 2024.
- In September 2023, AbbVie announced that the European Commission (EC) has granted conditional marketing authorization for TEPKINLY (epcoritamab) as a monotherapy for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory R/R DLBCL after two or more lines of systemic therapy. TEPKINLY is the first and only subcutaneous T-cell engaging bispecific antibody approved for the treatment of this patient population in the European Union (EU).
- In June 2023, Genentech announced that the US FDA approved COLUMVI (glofitamab) for the treatment of adult patients with R/R DLBCL not otherwise specified or large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) arising from follicular lymphoma, after two or more lines of systemic therapy. This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate and durability of response in the Phase I/II NP30179 study.
- In May 2023, the US FDA granted accelerated approval to EPKINLY (epcoritamab) for the treatment of patients with R/R DLBCL not otherwise specified , including DLBCL arising from indolent lymphoma, and high-grade B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Report Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy. In efficacy, the trial’s primary and secondary outcome measures are evaluated; for instance, in event- free survival, one of the most crucial primary outcome measures is event-free survival and overall survival.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated, wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and this clearly explains the drugs side effects in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Access and Reimbursement
EPKINLY/TEPKINLY (epcoritamab-bysp): Genmab and AbbVie
MyNavCare
This support system can help patients receive personalized support throughout the treatment journey. The following are its provisions
- With MyNavCare, the patient gains access to additional resources and medication information. It provides information about treatment access and financial support provides insights about independent organizations that may provide additional assistance and additional tools and resources that may help along the way.
- MyNavCare may be able to help uninsured or underinsured patients receive financial assistance and information. This includes
- Co-pay Assistance Program for commercially insured patients
- Independent Patient Assistant Foundation information
- Genmab Patient Assistance Program
Patient Engagement Liaison provides ongoing support throughout treatment. It helps in providing information about the indication, connecting with third parties, and offering resources and care partners.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Scope of the Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of DLBCL, explaining its causes, signs, symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently used therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, disease progression, and treatment guidelines has been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the DLBCL market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM DLBCL market.
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- DLBCL Pipeline Analysis
- DLBCL Market Size and Trends
- Existing and Future Market Opportunity
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report Key Strengths
- 10 Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- DLBCL Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT Analysis and Conjoint Analysis)
Key Questions Answered in the Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report
- What was the DLBCL market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2024, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved therapies?
- What can be the future treatment paradigm of DLBCL?
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of DLBCL? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population with DLBCL?
- What are the current options for the treatment of DLBCL? What are the current guidelines for treating DLBCL in the US, Europe, and Japan?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies being developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
Reasons to Buy the Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma Market Report
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the DLBCL market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the Analyst view section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of current therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.