Dysmenorrhea Market
Key Highlights
- In 2023, there were nearly 135 million prevalent cases of dysmenorrhea in 7MM.
- The current treatment options generally include pharmacological (NSAIDs, hormonal contraception, GnRH analogs) and non-pharmacological (e.g., TENS and supportive therapies) therapies.
- GnRH receptor agonists, like leuprorelin, effectively treat endometriosis-associated pain by suppressing estradiol. However, their efficacy is delayed due to an initial flare-up, and long-term use is limited by side effects like bone mineral density loss and hot flashes from hypoestrogenism.
- Treatment innovation for dysmenorrhea has been limited, leaving a critical need for new therapies. The introduction of GnRH antagonists offers a promising new option, particularly for women with dysmenorrhea who experience progestin resistance or side effects from progestin-based treatments.
- ORILISSA (elagolix), the first commercially available GnRH antagonist, approved for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis, either as a once-daily low dose or a twice-daily high dose. However, due to hypoestrogenic-induced bone mineral density loss and vasomotor symptoms, the maximum duration of treatment is 6 months for the high dose and 24 months for the low dose.
- Relugolix monotherapy was found to reduce pelvic pain in women with endometriosis. The addition of estradiol/norethisterone acetate mitigated relugolix-induced bone mineral density loss. The FDA and EMA both approved fixed-dose combinations of relugolix/estradiol/norethisterone (MYFEMBREE/RYEQO).
- With the convenience of a once daily oral dosing regimen, MYFEMBREE is a valuable addition to the options currently available for the management of endometriosis-associated pain.
- Preventing vasomotor symptoms, bone mineral density will be an important factor that constrains the long-term use of high-dose GnRH antagonists.
- The rising prevalence of dysmenorrhea which is attributed to changing lifestyles, addiction to smoking and alcohol, hormonal changes, and physical and mental stress will substantially contribute to the high growth of the market.
DelveInsight's “Dysmenorrhea – Market Insight, Epidemiology and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth analysis of dysmenorrhea, market, and clinical development in dysmenorrhea. In addition to this, the report provides historical and forecasted epidemiology and market data as well as a detailed analysis of the dysmenorrhea market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain ), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
Dysmenorrhea market report provides real-world prescription pattern analysis, emerging drugs assessment, market share, and uptake/adoption pattern of individual therapies, as well as historical and forecasted dysmenorrhea market size from 2020 to 2034 in 7MM. The report also covers current dysmenorrhea treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s underlying potential.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the UK, and Japan |
|
Dysmenorrhea Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
|
Dysmenorrhea Key companies |
|
|
Dysmenorrhea Key therapies |
|
|
Dysmenorrhea Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
Dysmenorrhea Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Dysmenorrhea Overview
Painful menstrual periods in medical terms are described as ‘dysmenorrhea’, which is often called menstrual cramps in simpler terms. Dysmenorrhea can be classified into two types: Primary Dysmenorrhea and Secondary Dysmenorrhea. Primary dysmenorrhea is common menstrual cramps related to the normal process of menstruation. These cramps are recurrent and are not due to other diseases. Pain can range from mild to severe, can typically last 12–72 hours, and can be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, fatigue, and even diarrhea. Whereas, in secondary dysmenorrhea, the pain is caused by any disorder in the woman's reproductive organs. Pain usually begins earlier in the menstrual cycle and lasts longer than common menstrual cramps. Contrary to the primary dysmenorrhea, in this type pain is not typically accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fatigue, or diarrhea. The most common cause of secondary dysmenorrhea is endometriosis.
Dysmenorrhea Diagnosis
The diagnosis for dysmenorrhea involves the doctor analyzing the menstrual history of the patient along with their family history too, followed by conducting tests such as MRI, ultrasound, laparoscopy, etc. if needed.
Further details related to country-based variations in diagnosis are provided in the report
Dysmenorrhea Treatment
The treatment pattern can be broadly divided into three parts: Pharmacological treatment, surgery, and non-pharmacological treatment. Pharmacological treatment comprises the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), hormonal contraception, and Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs. Whereas, currently used Non-pharmacological practice includes the use of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) and supportive therapies.
Dysmenorrhea Epidemiology
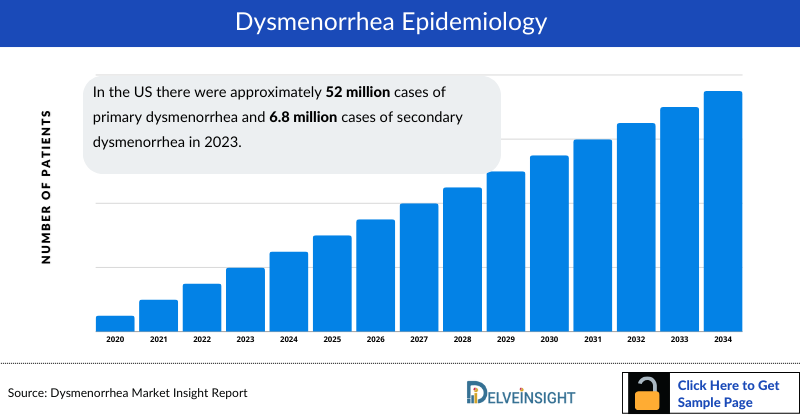
The dysmenorrhea epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented as Total Prevalent Cases of Dysmenorrhea and its Types (Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea), Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Dysmenorrhea and its Types (Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea), Severity-specific Prevalent Cases of Primary Dysmenorrhea, Severity-specific Prevalent Cases of Secondary Dysmenorrhea, and Treated cases of Primary and Secondary Dysmenorrhea in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
- In the US there were approximately 52 million cases of primary dysmenorrhea and 6.8 million cases of secondary dysmenorrhea in 2023.
- Among the EU4, Germany had the highest number of dysmenorrhea cases, i.e. nearly 13 million, and Spain had the lowest number of dysmenorrhea cases, i.e. nearly 8 million, in 2023.
- Dysmenorrhea occurs in 50–90% of adolescent girls and women of reproductive age and is a leading cause of absenteeism. Approximately 25–35% of women suffer from severe pain.
- Primary dysmenorrhea begins an average of 6–12 months following menarche, corresponding with the initiation of ovulatory cycles, and tends to recur with every menstrual cycle.
Dysmenorrhea Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the dysmenorrhea report encloses a detailed analysis of dysmenorrhea-marketed drugs and late-stage (Phase III and Phase II) pipeline drugs. It also deep dives into dysmenorrhea's pivotal clinical trial details, recent and expected market approvals, patent details, the latest news, and recent deals and collaborations.
Marketed Drugs
MYFEMBREE (relugolix/estradiol/norethisterone): Myovant Sciences and Pfizer
MYFEMBREE contains relugolix, which reduces the amount of estrogen produced by ovaries, estradiol which may reduce the risk of bone loss, and norethindrone acetate which is necessary when women with a uterus take estrogen. In August 2022, Myovant Sciences and Pfizer announced that the US FDA had approved MYFEMBREE as a one-pill, once-a-day therapy for the management of moderate to severe pain associated with endometriosis in pre-menopausal women, with a treatment duration of up to 24 months. The approval is supported by one-year efficacy and safety data, including 24-week data from Phase III SPIRIT 1 and SPIRIT 2 trials.
ORILISSA (Elagolix): AbbVie/Neurocrine Biosciences
ORILISSA is the first and the only orally-administered, non-peptide small molecule GnRH antagonist, which is specifically developed for women with moderate to severe endometriosis pain. It was approved by the US FDA under priority review in 2018. It represents the first FDA-approved oral treatment for the management of moderate-to-severe pain associated with endometriosis in over a decade. ORILISSA inhibits endogenous GnRH signaling by binding competitively to GnRH receptors in the pituitary gland.
|
Table 1: Comparison of Key Marketed Drugs | |||
|
Drug Name |
Company |
MoA |
US Approval |
|
MYFEMBREE (Relugolix) |
Myovant Sciences and Pfizer |
GnRH antagonist |
2022 |
|
DINAGEST (Dienogest) |
Mochida Pharmaceutical |
Progesterone receptor modulation |
2020 (Japan) |
|
ORILISSA (Elagolix) |
AbbVie/Neurocrine Biosciences |
GnRH antagonist |
2018 |
Note: Detailed current therapies assessment will be provided in the full report of dysmenorrhea.
Emerging Drugs
FSN-013: Fuji Pharma
FSN-013 is a 5th generation oral contraceptive, evaluated for dysmenorrhea in Japan. As per the company, this candidate has shown good pharmacodynamics outcomes for key evaluation items at the same level as an overseas trial and good tolerability. Fuji Pharma has obtained the development and commercialization rights of FSN-013 in Japan and Asian countries from Mithra Pharmaceuticals. In October 2023, Fuji Pharma and M3 submitted an application for marketing approval of FSN-013 (estetrol/drospirenone), co-developed in Japan, to the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) as scheduled indication of Dysmenorrhea. In the US, Europe, and other regions, the product is being sold by Mithra and its partners with the brand name of NEXTSTELLIS, indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy.
Note: Detailed emerging therapies assessment will be provided in the final report.
Drug Class Insights
GnRH antagonists’ therapies
Due to the fact that the available pharmacological therapies bring side effects, there is a need for the continued search for new options. All recognized methods of pharmacological treatment seem to have very similar therapeutic effects and that is why the use of GnRH antagonists in the therapy of dysmenorrhea has grown in importance lately. What is more, since the introduction of GnRH antagonists, new options for women with dysmenorrhea have been created, especially for those with progestin resistance or progestin-related side effects. GnRH antagonists may be beneficial in many ways when compared to other available older drugs.
MYFEMBREE and ORILISSA are approved GnRH antagonists for dysmenorrhea. The use of GnRH antagonists appears to reduce the doses of administered analgesics. Trials have revealed that women who took the higher doses of elagolix needed a significantly lower amount of pill counts of NSAIDs, opioids, or both combined when compared to placebo recipients.
Dysmenorrhea Market Outlook
ORILISSA and MYFEMBREE face competition from several FDA-approved treatments for conditions like endometriosis, uterine fibroids, infertility, and central precocious puberty. Other medications, including oral contraceptives, NSAIDs, and pain relievers like opioids, which manage symptoms rather than treat the underlying condition, further contribute to the competitive landscape.
Key Findings
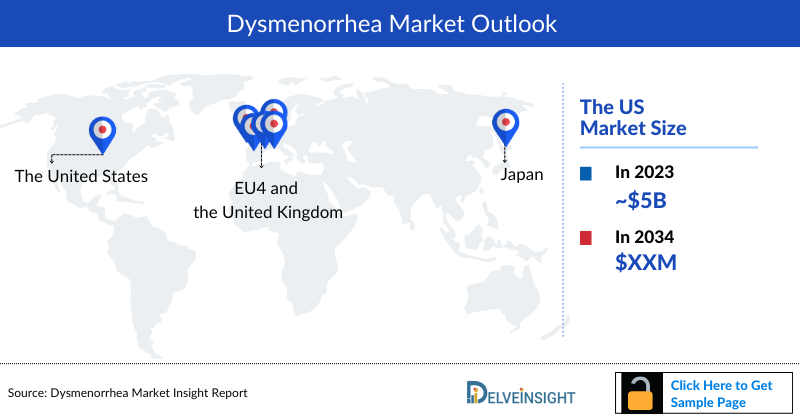
- In 2023, the US accounted for the largest market size for dysmenorrhea, i.e. more than USD 5 billion, followed by Japan, EU4, and then the UK.
- Among the EU4 and the UK, Germany had the highest market size for dysmenorrhea in 2023.
Managing pain in endometriosis remains a significant challenge, and an optimal treatment is still lacking for many patients. GnRH antagonists show promise as a new class of drugs but come with various side effects, primarily related to hypoestrogenism, including reduced bone mineral density, hot flashes, and mood or sleep disturbances. However, their pharmacokinetic profile tends to be less harmful compared to GnRH agonists.
Dysmenorrhea drug uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2024–2034, which depends on the competitive landscape, safety, and efficacy data along with order of entry. It is important to understand that the key players evaluating their novel therapies in the pivotal and confirmatory trials should remain vigilant when selecting appropriate comparators to stand the greatest chance of a positive opinion from regulatory bodies, leading to approval, smooth launch, and rapid uptake.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Dysmenorrhea Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III and Phase II stages. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for dysmenorrhea therapies.
KOL Views
To keep up with the real-world scenario in current and emerging market trends, we take opinions from Key Industry leaders working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on the evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, including Medical/scientific writers, Professors, and Others.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 20+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 10+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as the University of Nebraska Medical Center, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or dysmenorrhea market trends.
|
KOL Views |
|
“Primary dysmenorrhea classically begins within about 2 years of menarche or once ovulatory cycles have been established. It is more often a diagnosis made in adolescents and young adults. The cyclic pain starts within a few hours of the onset of menses and usually resolves within 72 hours. The pain is located midline in the pelvis and may radiate to the lumbar area of the back or upper legs.” Professor, University of Siena, Italy |
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
In efficacy, the trial’s primary and secondary outcome measures are evaluated; for instance, in event-free survival, one of the most important primary outcome measures is event-free survival and overall survival.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement may be referred to as the negotiation of a price between a manufacturer and payer that allows the manufacturer access to the market. It is provided to reduce the high costs and make the essential drugs affordable. Health technology assessment (HTA) plays an important role in reimbursement decision-making and recommending the use of a drug. These recommendations vary widely throughout the seven major markets, even for the same drug. In the US healthcare system, both Public and Private health insurance coverage are included. Also, Medicare and Medicaid are the largest government-funded programs in the US. The major healthcare programs including Medicare, Medicaid, Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and the state and federal health insurance marketplaces are overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). Other than these, Pharmacy Benefit Managers (PBMs), and third-party organizations that provide services, and educational programs to aid patients are also present.
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of currently used therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview of dysmenorrhea, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, and disease progression along treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of both the current and emerging therapies, along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies, will have an impact on the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the dysmenorrhea market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help in shaping and driving the 7MM dysmenorrhea market.
Dysmenorrhea Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Dysmenorrhea Pipeline Analysis
- Dysmenorrhea Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Dysmenorrhea Report Key Strengths
- Eleven Years Forecast
- 7MM Coverage
- Dysmenorrhea Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Dysmenorrhea Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs
- What is the historical and forecasted dysmenorrhea patient pool/patient burden in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- Which combination treatment approaches will have a significant impact on the dysmenorrhea drug treatment market size?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
- What are the current and emerging options for the treatment of dysmenorrhea?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies?
- How is the sales trend of GnRH antagonists approved for dysmenorrhea?
- Which drug is expected to be the major contributor for dysmenorrhea market by 2034?
Reasons to buy
- The report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the dysmenorrhea market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease Incidence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.