Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa Market
Key Highlights
- Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of rare inherited disorders caused by mutations in various structural proteins of the skin. Around 15 genes encoding proteins of the skins are involved in the pathogenesis of EB. It is classified into various subtypes, depending on the location of the target proteins and the level of the blisters.
- DEB is divided mainly into six types: dominant DEB (DDEB), recessive DEB (RDEB), RDEB-generalized severe (GS), RDEB-generalized intermediate (GI), RDEB-unknown subtypes, and RDEB-other.
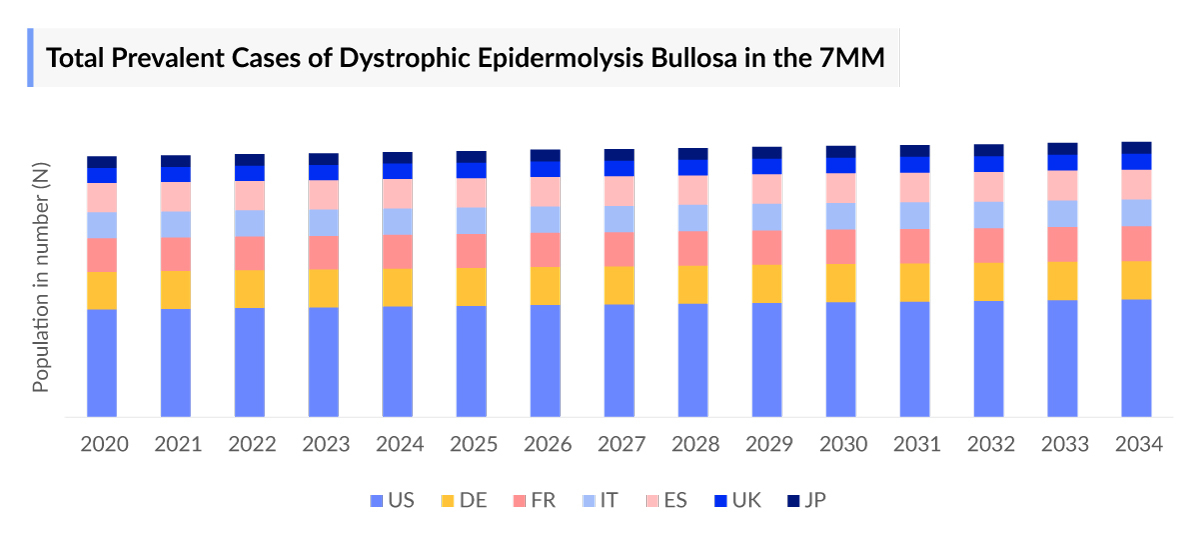
- In 7MM, the total diagnosed prevalent cases of DEB in 2023 were ~6,500 cases out of which the highest cases were seen in the US ~ 3,500 cases i.e. approximately 50% cases.
- The market is anticipated to witness a substantial positive shift owing to the expected market launch of one-time gene therapies, and raised awareness.
- The total market size in the 7MM of DEB was found to be ~USD 550 Million in 2023, which is further expected to increase in the forecasted period.
- The United States accounts for the largest market size of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB), in comparison to EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, France), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Currently VYJUVEK and FILSUVEZ is approved for the treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB). Current management strategies aim to provide symptomatic relief, for example, management of pain and itch, treatment of problems such as chronic wounds and infection, and prevention of complications, where possible.
- DEB pipeline possesses potential drugs like D-Fi (FCX-007), ALLO-ASC-SHEET, and others.
- Severity-specific prevalence data suggests that the cases of the moderate type are much higher than the severe type of DEB.
DelveInsight's “Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) – Market Insights, Epidemiology and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB), historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, and France) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) market report provides real-world prescription pattern analysis, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and historical and forecasted 7MM Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s underlying potential.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the UK, and Japan |
|
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Epidemiology |
Segmented by: Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of DEB Age-Specific Cases of DEB Type-specific Cases of DEB Severity-specific Cases of DEB |
|
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Market |
Segmented by: · Region · Therapies |
|
Analysis |
· KOL Views · SWOT Analysis · Reimbursement · Conjoint Analysis · Unmet needs |
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Overview, Country-Specific Treatment Guidelines and Diagnosis
Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) is the major subtypes of epidermolysis bullosa (EB). EB is a group of skin diseases that cause various degrees of skin and mucous membrane fragility. The skin becomes fragile when proteins essential for skin integrity are absent, reduced, or abnormal. EB is classified into four main types and several clinical subtypes. The main classification relates to the layer of skin in which the formation of blisters occurs: EB simplex (EBS; intraepidermal layer), junctional EB (JEB; within the lamina lucida of the basement membrane), dystrophic EB (DEB; below the basement membrane), and Kindler’s EB (KEB; mixed skin cleavage pattern).
The diagnosis of DEB is established in a proband with characteristic clinical findings and either biallelic pathogenic variants (RDEB) or a heterozygous pathogenic variant (DDEB) in COL7A1 identified on molecular genetic testing. If molecular genetic testing is not diagnostic, examination of a skin biopsy with direct IF for specific cutaneous markers and/or EM may be necessary. Routine histology is not useful.
Further details related to country-based variations in diagnosis are provided in the report
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Treatment
Current DEB therapy focuses on modern wound care and minimizing factors that trigger blistering and hinder wound healing. This includes maintaining high personal hygiene standards and intensive moisturizing. Blisters typically heal well with everyday skin care and disinfection, utilizing effective aqueous disinfectants. Avoiding adhesives and compressive dressings is crucial to prevent new blisters. Silicon-based wound care products are beneficial, especially for challenging skin areas. Systemic therapy is generally unnecessary, but short-term use of antibiotics or corticosteroids may be indicated. For severely affected patients with extra-cutaneous involvement, multidisciplinary management involving various specialists like pediatricians, dermatologists, and others is essential.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Epidemiology
The Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2024 to 2034. The Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) epidemiology is segmented with detailed insights into diagnosed prevalent cases, age-specific cases, type-specific cases, severity-specific cases of DEB.
- The US accounted for the highest total prevalent cases of DEB in the 7MM, with a total of 3,500 cases.
- In 2023, the age bracket most affected by DEB comprised individuals between 1 and 9 years old ~1,300 cases.
- Among the EU4 and the UK countries, the highest number of cases of DEB were in UK ~33%.
- Roughly 48% of DEB cases in 2023 were classified as moderate in severity.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Recent Developments
- In September 2025, Krystal Biotech, Inc. announced that the U.S. FDA approved a label update for VYJUVEK® (beremagene geperpavec-svdt), expanding its use to include dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB) patients from birth. The update also provides patients with full flexibility in applying VYJUVEK and managing wound dressings.
- In April 2025, the FDA approved Abeona Therapeutics' ZEVASKYN, a groundbreaking treatment for Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (RDEB). This approval marks the third treatment for the rare condition, highlighting progress in RDEB care. ZEVASKYN, the first autologous, cell-based gene therapy for RDEB, aims to enhance collagen VII expression at wound sites by integrating the COL7A1 gene, offering new hope and treatment options for patients and their families.
- In April 2025, Abeona Therapeutics Inc. announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved ZEVASKYN™ (prademagene zamikeracel), the first and only autologous cell-based gene therapy for treating wounds in adult and pediatric patients with recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). ZEVASKYN is the only FDA-approved treatment for RDEB wounds with a single application.
- In November 2024, Abeona Therapeutics Inc. (Nasdaq: ABEO) announced that the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has accepted its resubmitted Biologics License Application (BLA) for prademagene zamikeracel (pz-cel), an investigational autologous cell-based gene therapy for recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB). The FDA has set a target action date of April 29, 2025, under the Prescription Drug User Fee Act (PDUFA).
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Drug Chapter
The drug chapter segment of the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) report encloses a detailed analysis of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) marketed drugs and late-stage (Phase III and Phase II) pipeline drugs. It also deep dives into the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) pivotal clinical trial details, recent and expected market approvals, patent details, the latest news, and recent deals and collaborations.
Marketed Drugs
VYJUVEK (beremagene geperpavec): Krystal Biotech
VYJUVEK is a herpes-simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) vector-based gene therapy approved for the treatment of wounds in patients 6 months of age and older with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa with mutations in the collagen type VII alpha 1 chain (COL7A1) gene. It is a topical gel that addresses the genetic cause of DEB by restoring functional copies of the COL7A1 gene to patients.
Upon topical application to the wounds, VYJUVEK can transduce both keratinocytes and fibroblasts. Following entry of VYJUVEK into the cells, the vector genome is deposited in the nucleus. Once in the nucleus, 14 transcription of the encoded human COL7A1 is initiated. The resulting transcripts allow for production and secretion of COL7 by the cell in its mature form. These COL7 molecules arrange themselves into long, thin bundles that form anchoring fibrils. The anchoring fibrils hold the epidermis and dermis together and are essential for maintaining the integrity of the skin. Patients with autosomal dominant DEB (DDEB) have lower than normal functional anchoring fibrils, and patients with RDEB have no functional anchoring fibrils.
Vyjuvek is the First FDA-approved gene therapy treatment for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa.
FILSUVEZ (birch triterpenes): Chiesi
Oleogel-S10 is herbal medicinal product that contains birch triterpenes from birch bark. The drug is a keratinocyte modulator; transient receptor potential channel stimulants are being used to speed up the healing of wounds in adults and children with DEB. The US FDA has granted Rare Pediatric Disease Designation, Fast Track, and Priority Review for the treatment of DEB. Further, it has been granted Orphan Drug Designation by the US FDA and EMA.
Oleogel-S10 (Filsuvez) has been approved by the EMA for the treatment of the cutaneous manifestations of DEB.
|
Therapy Name |
Company Name |
ROA |
MOA |
Phases |
Any Special Status |
|
D-Fi (FCX-007) |
Castle Creek Biosciences |
Intradermal Injection |
gene therapy |
III |
Orphan; Rare Pediatric Disease; Fast Track; regenerative medicine advanced therapy (RMAT) |
Emerging Drugs
D-Fi (FCX-007): Castle Creek Biosciences
D-Fi (FCX-007) is an investigational gene therapy to address the deficiency of functional type VII collagen protein (COL7) in patients with Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (DEB). It is a genetically-modified autologous fibroblast that encodes the gene for COL7 and treats wounds locally via injection. Furthermore, the company is conducting a Phase III clinical trial (NCT04213261) to determine whether the administration of FCX-007, in addition to the standard of care, improves wound healing in children, adolescents, and adults with RDEB.
The US FDA and EMA have granted orphan drug designation to FCX-007 for the treatment of DEB. In addition, FCX-007 has been granted are pediatric disease, fast track, and regenerative medicine advanced therapy designations by the FDA.
Note: Detailed emerging therapies assessment will be provided in the final report.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Market Outlook
Key players, such as Castle Creek Biosciences, Chiesi, Krystal Biotech, Abeona Therapeutics and others are evaluating their lead candidates in different stages of clinical development, respectively. They aim to investigate their products for the treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB).
- • In 2023, the United States represented the largest market size of ~USD 400 million approximately among the 7MM.
- • Among EU4 and the UK, UK accounted for the highest market size ~ USD 50 million of DEB.
- • The least market size of DEB was accounted by Spain in 7MM which is ~USD 20 million.
- • DelveInsight’s analysis predicts an increase in the market due to launch of emerging therapies.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2024–2034, which depends on the competitive landscape, safety, and efficacy data along with order of entry. It is important to understand that the key players evaluating their novel therapies in the pivotal and confirmatory trials should remain vigilant when selecting appropriate comparators to stand the greatest chance of a positive opinion from regulatory bodies, leading to approval, smooth launch, and rapid uptake.
Further detailed analysis of emerging therapies drug uptake in the report…
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III and Phase II stages. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) emerging therapies.
KOL Views
To keep up with the real-world scenario in current and emerging market trends, we take opinions from Key Industry leaders working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts were contacted for insights on the evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 10+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 5+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such Children’s Hospital Stanford, UCSF Health dermatologist, University of Colorado School of Medicine, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging treatment patterns of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB). This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
|
Region |
KOL Views |
|
United States |
“The different mutational process appears to promote cancers caused by chronic tissue damage, as observed in RDEB. This is potentially an invisible force that also contributes to a much broader range of cancers.” |
|
United states |
“The access to stem cell biology, gene-editing tools and bioengineering and transplant biology will all crystalize in better ways to treat these epidermolysis bullosa.” |
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of gaps in disease diagnosis, patient awareness, physician acceptability, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Market Access and Reimbursement
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of currently used therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB), explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, and disease progression along with country specific treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of both the current and emerging therapies, along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies, will have an impact on the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help in shaping and driving the 7MM Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) market.
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Therapeutic Approaches
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Pipeline Analysis
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Report Key Strengths
- Eleven Years Forecast
- 7MM Coverage
- Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Epidemiology Segmentation
- Inclusion of Country specific treatment guidelines
- KOL’s feedback on approved and emerging therapies
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- Drugs Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
FAQs
- What is the growth rate of the 7MM Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) treatment market?
- What was the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) total market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like in 2034? What are the contributing factors/key catalysts for this growth?
- Is there any unexplored patient setting that can open the window for growth in the future?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends? Although multiple expert guidelines recommend testing for targetable mutations before therapy initiation, why do barriers to testing remain high?
- What are the current and emerging options for the treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB)?
- How many companies are developing therapies for the treatment of Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB)?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- Patient/physician acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies?
Reasons to buy
- The report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa (DEB) Market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years
- Understand the existing market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of access and reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of expensive off-label therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.

.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)



