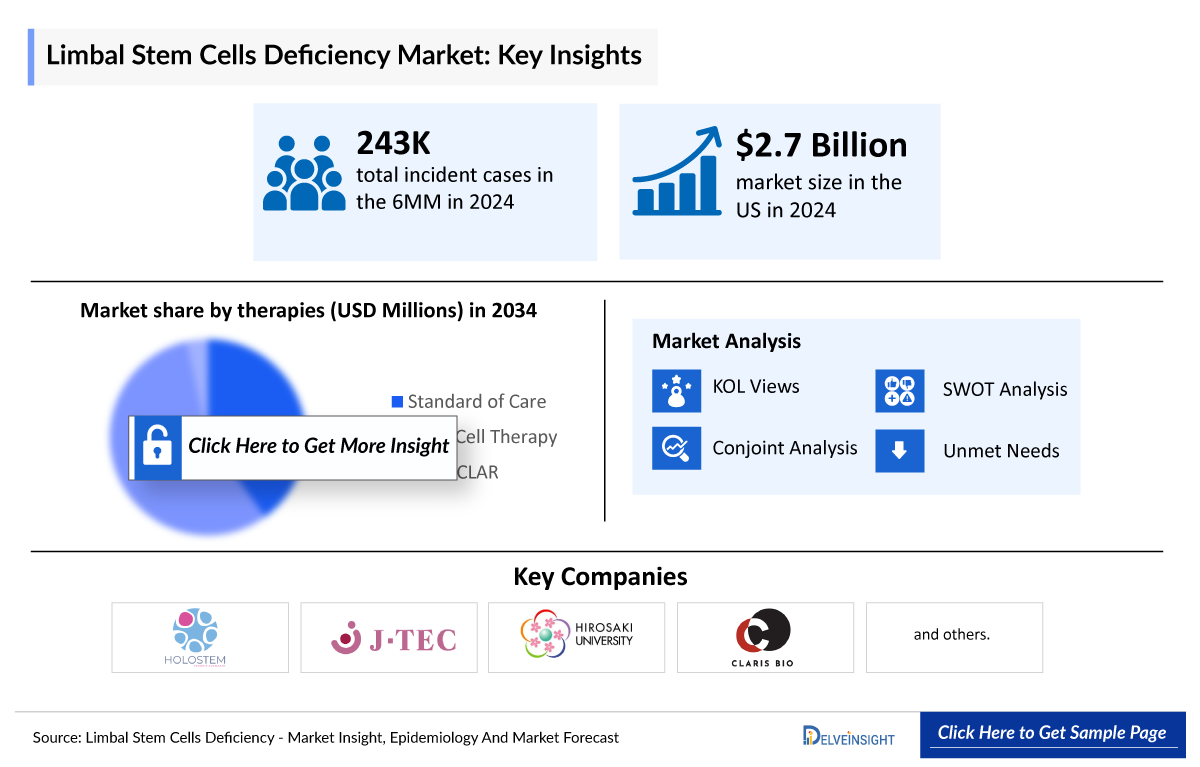
Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency (LSCD) Market Summary
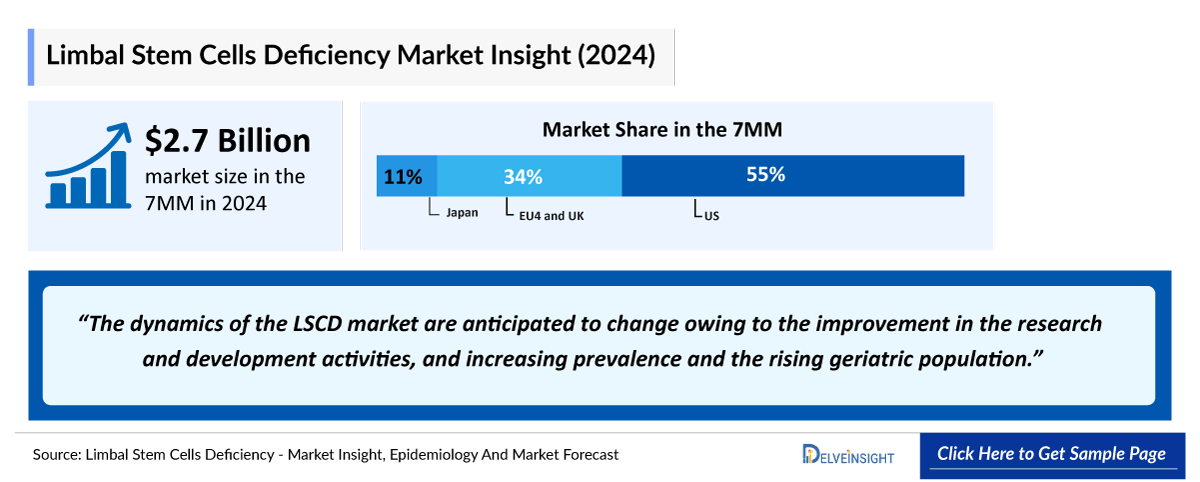
- In 2023, the Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market size was the highest in the US among the 7MM, accounting for approximately USD 1,500 million whereas it was the least for Spain, accounting approximately USD 127 million. This trend is further expected to be followed during the forecast period.
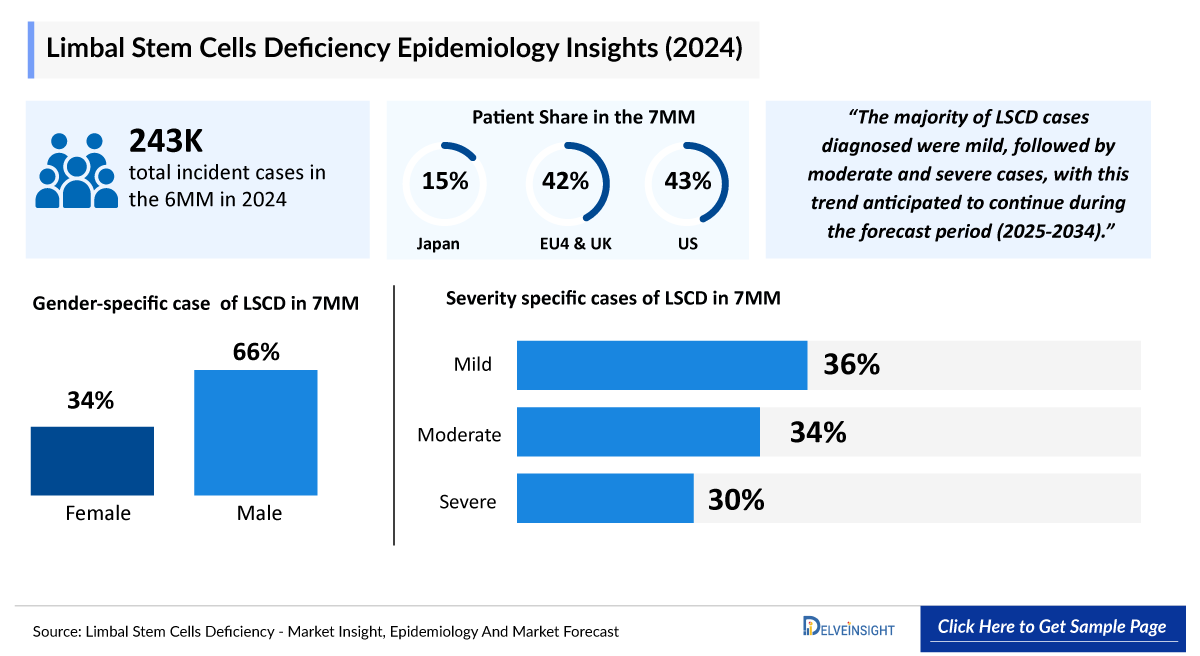
- There were 103 thousand diagnosed prevalent cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) in the US in 2023, whereas Japan accounted for 37 thousand of patients. The total diagnosed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency prevalence of both the US and Japan are anticipated to increase at a significant CAGR.
- In 2023, Germany reported the highest cases of type-specific diagnosed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) prevalence in EU4 and the UK, where nearly 15 thousand cases were of unilateral type and ~9 thousand cases of bilateral type.
- The diagnosed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency prevalent cases were classified by gender, with 66 thousand cases in males and 37 thousand cases in females in 2023 in the US.
Key Factors Driving Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency (LSCD) Market
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Patient Pool and Rising Prevalence
In 2023, the diagnosed prevalence of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) in the 7MM was approximately 241 thousand cases, with the US accounting for 103 thousand and Japan for 37 thousand. In the EU4 and the UK, Germany reported the highest type-specific prevalence, with ~15 thousand unilateral and ~9 thousand bilateral cases. Male patients represented a larger share of the US population at 66 thousand cases versus 37 thousand females. These numbers are expected to grow at a significant CAGR during the forecast period.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Disease Insights and Market Drivers
LSCD severity is categorized into mild, moderate, and severe cases, with mild cases being the most prevalent in Japan in 2023. The increasing awareness of ocular surface disorders, advances in stem cell-based regenerative medicine, and unmet need for effective treatments are key drivers expanding the LSCD market. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial to prevent vision impairment and improve quality of life.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Treatment Landscape
Currently, only HOLOCLAR (autologous human corneal epithelial cells containing stem cells) and OCURAL (autologous oral mucosa-derived epithelial cell sheet) are approved for the treatment of LSCD. These therapies represent pioneering regenerative approaches, offering targeted repair of damaged ocular surfaces and partial restoration of vision.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Emerging Therapies
Several investigational therapies are in development to address LSCD. LSC 2 by Rheacell, an allogeneic ABCB5-positive limbal stem cell therapy, is in Phase I/II trials. KPI-012 by Kala Pharmaceuticals, a topically dosed MSC-S platform therapy containing growth factors and proteins for ocular surface repair, is in preclinical development for partial LSCD. Surrozen’s regenerative therapeutics program is in the discovery stage, exploring novel approaches for restoring ocular surface integrity.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Clinical Trials and Competitive Landscape
The LSCD pipeline is dominated by regenerative and stem cell-based therapies, highlighting significant clinical potential. Companies like Rheacell, Kala Pharmaceuticals, and Surrozen are advancing innovative therapies, aiming to expand treatment options and address the unmet needs of patients with LSCD across the 7MM.
DelveInsight’s “Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) – Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of the LSCD, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the LSCD market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, and France) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market size, market share of the individual Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current LSCD treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best of the opportunities and assess the underlying potential of the Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency market.
Geography Covered
- The United States
- EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom
- Japan
Study Period: 2020–2034
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency is an ocular surface disease caused by a decrease in the population and/or function of corneal epithelial stem/progenitor cells; this decrease leads to the inability to sustain the normal homeostasis of the corneal epithelium. The disease is characterized by conjunctivalization (i.e., replacement of the normal corneal epithelium by conjunctival epithelium) and/or other signs of epithelial dysfunction such as persistent or recurrent epithelial defects with or without neovascularization, ocular surface inflammation, and scarring.
Patients suffering from LSCD may present symptoms related to poor epithelial wound healing and recurrent erosions. Patients often experience chronic conjunctival redness, decreased vision, photophobia, foreign body sensation, tearing, blepharospasm, and recurrent episodes of pain from recurrent epithelial breakdown. The pain, photophobia, and discomfort are often debilitating. However, most of these symptoms are nonspecific and inadequate to diagnose correctly.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Diagnosis
Slit-lamp biomicroscopy has been the most commonly used method to diagnose LSCD. Impression cytology is a well-established method to diagnose ocular surface diseases. The presence of goblet cells on the cornea indicates the invasion of conjunctival cells, a hallmark of LSCD. Impression cytology’s identification of goblet cells on the specimens taken from corneal surfaces has been considered the “gold standard” in the currently used diagnosis system for LSCD. Recent advancements in diagnosing LSCD include in vivo imaging, anterior segment OCT, and molecular methods.
Further details related to country-based variations are provided in the report…
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Treatment
Various treatment strategies have been described in the management of partial LSCD. Conservative management involves the cessation of toxic stimuli and the use of preservative-free lubricating eye drops. After that, topical corticosteroids, topical ciclosporin, topical Vitamin A, 1% silver nitrate solution, liquid nitrogen cryotherapy, mechanical debridement of the ingrowing conjunctival epithelium, and amniotic membrane transplantation (AMT) can be used. In more extensive or severe cases of LSCD, initial therapy with a scleral contact lens may be helpful. If this is ineffective, the replacement of stem cells by limbal transplantation is an alternative.
Currently, HOLOCLAR and OCURAL are the two approved treatments in the treatment domain of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency. They are approved in Europe and Japan, respectively.
Due to the poor understanding of etiology, patients currently have significant unmet needs. Also, the complex diagnosis, challenging treatment, and management of LSCD and the challenges of stem cell-based therapy for corneal blindness due to LSCD are additional healthcare burdens.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Epidemiology
As the Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency market is derived using a patient-based model, the limbal stem cells deficiency epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD), Gender-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD), Type-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD), Severity-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD), Cause-specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) in the 7MM covering, the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
- There were 241 thousand diagnosed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency prevalent cases estimated to have occurred in the 7MM in 2023, of which 103 thousand of the accounted cases were estimated to be from the US alone, and these cases are anticipated to increase during the forecast period.
- The type-specific cases of LSCD were distributed into unilateral and bilateral categories. In 2023, Japan reported 24 thousand cases of Unilateral and 13 thousand cases of Bilateral LSCD.
- The diagnosed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency prevalence was further divided into Gender-specific categories. The gender-specific diagnosed prevalent cases of LSCD are categorized into Males and Females, with 66 thousand and 37 thousand cases, respectively, in the US in 2023. These numbers are expected to increase by 2034.
- The cause-specific diagnosed prevalent cases of LSCD were categorized into ocular surgeries, chronic ocular surface inflammatory diseases, and chemical burn or thermal injury. Among EU4 and the UK, Germany reported the highest number of cases related to ocular surgeries, chronic ocular surface inflammatory diseases, and chemical burn or thermal injury, with 13 thousand, 7 thousand and 5 thousand cases, respectively, in 2023, which are anticipated to increase by 2034.
- The severity-specific cases of LSCD were categorized into Mild, Moderate, and Severe, with mild cases being the highest and severe cases the lowest in Japan in 2023. These numbers are anticipated to increase by 2034.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the LSCD report encloses a detailed analysis of LSCD late-stage, mid-stage, and mid-early stage (Phase-III, Phase-II/III, Phase-II) limbal stem cells deficiency pipeline drugs. It also helps understand the LSCD clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug and the latest news and press releases.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Marketed Drugs (Included Information)
HOLOCLAR: Holostem Terapie Avanzate/Chiesi Pharmaceuticals
HOLOCLAR is a stem-cell treatment used in the eye to replace damaged cells on the surface (epithelium) of the cornea, the transparent layer in front of the eye covering the iris (the colored part). It is used in adult patients with moderate-to-severe LSCD caused by burns, including chemical burns, to the eyes. Patients with this condition do not have enough limbal stem cells, which act as a regeneration system, replenishing the outer corneal cells when damaged.
HOLOCLAR consists of a transparent circular sheet of 300,000–1,200,000 viable autologous human corneal epithelial cells (79,000–316,000 cells/cm2), including on average 3.5% (0.4–16%) limbal stem cells, and stem cell-derived transient amplifying and terminally differentiated cells, attached on a supportive 2.2 cm diameter fibrin layer and maintained in the transport medium.
The HOLOCLAR mechanism of action (MOA) is the replacement of corneal epithelium and lost limbal stem cells in patients where ocular burns have destroyed the limbus.
In February 2015, the European Commission granted a conditional marketing authorization under Regulation (EC) number 726/2004 to HOLOCLAR.
Chiesi, together with Holostem, received marketing authorization in Europe in 2018. In August 2017, the UK’s National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) recommended HOLOCLAR for treating LSCD in adults with eye burns.
Detailed marketed Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies list will be provided in the final report…
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Emerging Drugs
The emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency treatment pipeline remain scanty as the Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency treatment market does not comprise many active pharma players. Keeping in view of the same, only a handful of companies are actively treating LSCD and are majorly in the early stage of development. It will be difficult to calibrate the success rate of the emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies, but if approved, they are likely to change the LSCD market dynamics during the forecast period.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Market Outlook
Many strategies have been used in treating LSCD, the common goal of which is to regenerate a self-renewing, transparent, and uniform epithelium on the corneal surface. The development of these techniques has frequently resulted from collaboration between stem cell translational scientists and ophthalmologists. Direct transplantation of autologous or allogeneic limbal tissue from a healthy donor eye is regarded by many as the technique of choice. Expansion of harvested LSCs in vitro allows smaller biopsies to be taken from the donor’s eye and is considered safer and more acceptable to the patients. This technique may be utilized in unilateral (autologous) or bilateral (living-related donor) cases. Recently developed, simple limbal epithelial transplant (SLET) can be performed with equally small biopsies but does not require in vitro cell culture facilities. In the case of bilateral LSCD, where autologous limbal tissue is unavailable, autologous oral mucosa epithelium can be expanded in vitro and transplanted to the diseased eye.
- Currently, the only medications approved to treat LSCD patients are HOLOCLAR (autologous human corneal epithelial cells containing stem cells) and OCURAL (human [autologous] oral mucosa-derived epithelial cell sheet).
- The total Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency market size of LSCD in the 7MM is approximately USD 2,690 million in 2023 and is projected to increase during the forecast period (2024–2034).
- The Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency market size in the 7MM is anticipated to increase at a significant CAGR due to the advancing Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency treatment market.
- Among the EU4 countries, Germany, France, and Italy accounted for the largest Limbal Stem Cells Deficiency market sizes of USD 220 million, USD 180 million, and USD 160 million in 2023, while Spain was at the bottom with USD 120 million.
- Japan accounted for a market size of USD 290 million in 2023, but these dynamics are expected to change in the forecast period.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Drug Uptake
This section focuses on the sales uptake of potential drugs that have recently been launched or are anticipated to be launched in the Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market between 2020 and 2034. It estimates the market penetration of LSCD drugs for a given country, examining their impact within and across classes and segments. It also touches upon the financial and regulatory decisions contributing to the probability of success (PoS) of the drugs in the LSCD market.
Further detailed analysis of emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies drug uptake is in the report…
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Pipeline Development Activities
The report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase III, II, and I. It also analyzes key players involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline Development Activities
The report covers detailed information on designations, collaborations, mergers and acquisitions, licensing, and patent details for LSCD emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies.
KOL Views
To keep up with the current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on LSCD evolving Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency treatment market, patient reliance on conventional Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, include Cincinnati Eye Institute, David Geffen School of Medicine, Biosciences Institute, Newcastle University, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK, and Department of Ophthalmology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 50+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers such as the Cincinnati Eye Institute David Geffen School of Medicine, Biosciences Institute, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, and Osaka, Japan, etc., were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies and Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency treatment patterns or LSCD market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel LSCD treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
Market Access and Reimbursement
The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of LSCD, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies will impact the current treatment landscape.
- A detailed review of the Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market.
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency Therapeutic Approaches
- Pipeline Analysis
- LSCD Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Market Opportunity
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Report Key Strengths
- 11 Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Drug Uptake and Key Market Forecast Assumptions
Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- Unmet Needs
- Pipeline Product Profiles
- Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT Analysis)
Key Questions
Market Insights
- What was the total Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) market size, the Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency market size by therapies, and market share (%) distribution in 2020, and how would it all look in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- How much of the market will new therapies capture after their launch?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for HOLOCLAR and OCURAL?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
Epidemiology Insights
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM with respect to the patient population pertaining to Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
- What is the historical and forecasted Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- How many male and female patients have Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
- How many Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) patients are in the severity groups of Mild, Moderate, and Severe?
- What factors affect the diagnosis of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
Current Treatment Scenario, Marketed Drug, and Emerging Therapies
- What are the current options for the standard of care for Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)? What are the current guidelines for treating Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) in the US and Europe?
- How many Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency companies are developing therapies for treating Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
- How many emerging therapies are in the mid-stage and late development stage for treating Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- What are the patents of emerging therapies for Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
- What will impact the market after the expected patent expiry of the emerging drug?
- What is the cost burden of marketed therapies on patients?
- What will the patient acceptability regarding preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of recommended therapies?
- What are the 7MM historical and forecasted market of Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD)?
Reasons to buy
- The report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency (LSCD) Market.
- Insights on patient burden/Limbal Stem Cell Deficiency prevalence, accuracy/evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- To understand the existing market opportunity in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data and reported sales of current products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming players in the market will help devise strategies that will help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and potential of current and emerging therapies to provide visibility around leading emerging drugs.
- Highlights of Market Access and Reimbursement policies for HOLOCLAR and OCURAL.
- To understand the perspective of Key Opinion Leaders around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Get a sneak-peak into our blog:


-pipeline.png&w=256&q=75)

