Pemphigus Vulgaris Epidemiology
Key Highlights
- According to the National Organization for Rare Disorders (2023), pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is a severe, rare autoimmune disorder marked by painful blisters and erosions on the skin and mucous membranes, including the mouth, throat, and sometimes genital areas. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks desmogleins, proteins essential for cell adhesion in the epidermis, leading to cell separation and blister formation.
- Blisters associated with pemphigus are typically flaccid and fragile, forming mainly on areas like the scalp, face, chest, and back, and particularly within mucous membranes such as the mouth. They rupture easily, often resulting in painful, open sores that are slow to heal. Unlike pemphigoid, which affects deeper skin layers and produces firmer, more resilient blisters, pemphigus involves more superficial skin layers, resulting in delicate, easily ruptured blisters.
- In Pemphigus Vulgaris, autoantibodies specifically target desmogleins (proteins crucial for cell-to-cell adhesion) in the epidermis. This leads to the breakdown of cellular connections, resulting in the separation of skin cells (acantholysis) and subsequent blister formation.
- Diagnosing Pemphigus Vulgaris involves differentiating it from other blistering diseases, such as bullous pemphigoid or other types of pemphigus, through biopsy and antibody testing, particularly identifying anti-desmoglein antibodies.
- In 2023, the United States accounted for the highest diagnosed prevalent cases of Pemphigus Vulgaris followed by Germany.
- In the 7MM, Females reported more cases than males for Pemphigus Vulgaris.
- In the United States, individuals of the 60-69 year age group reported the highest number of pemphigus Vulgaris cases.
Report Summary
- The report offers extensive knowledge regarding the epidemiology segments and predictions, presenting a deep understanding of the potential future growth in diagnosis rates, disease progression, and diagnostic guidelines. It provides comprehensive insights into these aspects, enabling a thorough assessment of the subject matter.
- The report also encompasses a comprehensive analysis of Pemphigus Vulgaris, providing an in-depth examination of its historical and projected data from 2021 to 2034. It includes detailed assumptions and the underlying rationale for the methodology.
- The report also encompasses a comprehensive analysis of Pemphigus Vulgaris, providing an in-depth examination of its historical and projected data from 2021 to 2034. It includes detailed assumptions and the underlying rationale for the methodology.
- The report includes qualitative insights that provide an edge in understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, including experts from various hospitals and prominent universities, patient journey that help shape and drive the Pemphigus Vulgaris landscape.
The table given below further depicts the key segments provided in the report:
|
Study Period |
2021-2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
Pemphigus Vulgaris Disease Understanding
Pemphigus Vulgaris Overview, and Diagnosis
Pemphigus is a rare autoimmune blistering disorder that affects the outermost layer of the skin (epidermis) and mucous membranes. It is characterized by the formation of fragile blisters and lesions that rupture easily, leaving painful sores. This condition arises when the immune system mistakenly produces autoantibodies—particularly against proteins called desmoglein 1 and desmoglein 3, which are essential for maintaining the adhesion between skin cells. The disruption of these cellular junctions leads to a loss of skin integrity, causing the skin cells to separate, a process known as acantholysis. As a result, fluid accumulates between the skin layers, leading to the formation of blisters.
The current diagnosis of PV involves a combination of clinical assessment, histopathological examination, and advanced immunological techniques such as direct and indirect immunofluorescence and ELISA. The diagnosis of PV should be suspected in any patient with mucocutaneous erosions or blisters. The oral mucosa is the first site of involvement in the majority of cases, and PV may remain confined to the mucosal surfaces or extend to involve the skin (average lag period of 4 months).
Further details related to country-based variations are provided in the report…
Pemphigus Vulgaris Epidemiology
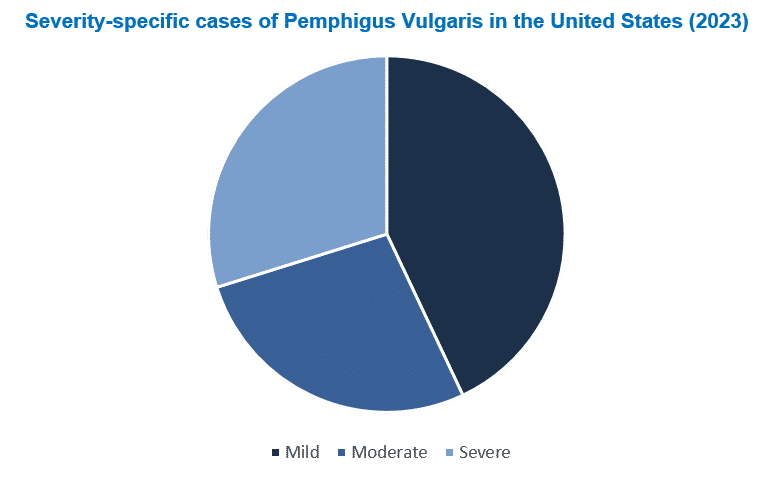
The Pemphigus Vulgaris epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total diagnosed prevalent cases, Gender-specific cases, Age-specific cases, Severity-specific cases, and total treated cases of Pemphigus Vulgaris in the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2021 to 2034.
- Among the 7MM, the United States accounted for the highest number of cases of PV in 2023, with nearly 40,000 cases. These cases are anticipated to increase by 2034.
- In the United States, individuals of the 60-69 year age group account for the highest number of cases of PV in 2023.
- In the 7MM, the prevalence of females is more than males in Pemphigus Vulgaris.
- Among EU4 and the UK, Germany accounted for the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases in 2023, while Spain accounted for the least.
KOL Views
To stay abreast of the latest trends in the market, we conduct primary research by seeking the opinions of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) and Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) who work in the relevant field. This helps us fill any gaps in data and validate our secondary research.
We have reached out to industry experts to gather insights on various aspects of Pemphigus Vulgaris, including the evolving treatment landscape, patients’ reliance on conventional therapies, their acceptance of therapy switching, drug uptake, and challenges related to accessibility. The experts we contacted included medical/scientific writers, professors, and researchers from prestigious universities in the US, Europe, the UK, and Japan.
Our team of analysts at Delveinsight connected with more than 15 KOLs across the 7MM. We contacted institutions such as the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, University of California, etc., among others. By obtaining the opinions of these experts, we gained a better understanding of the current and emerging treatment patterns in the Pemphigus Vulgaris market, which will assist our clients in analyzing the overall epidemiology and market scenario.
The opinions of experts from various regions have been provided below:
“In the US, pemphigus vulgaris shows a slightly higher prevalence among women, with rituximab becoming the preferred treatment due to its efficacy in achieving sustained remission. Nonetheless, refractory cases and corticosteroid side effects remain significant clinical challenges, particularly in older patients, demanding further research into alternative therapies.”
“Emerging Chimeric Autoantibody Receptor T-cell (CAART) therapies offer a promising new approach in the treatment of Pemphigus Vulgaris (PV), particularly in cases resistant to conventional therapies. While current treatments such as corticosteroids and rituximab remain the cornerstone of management, CAART technology holds the potential for targeting the specific autoantibodies driving the disease. Early-phase trials in the US show encouraging results, with reduced relapse rates and fewer side effects, offering hope for more durable and patient-specific treatment options.”
Pemphigus Vulgaris Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Pemphigus Vulgaris Epidemiology Segmentation
- Existing Epidemiological Trends and Predictions
Pemphigus Vulgaris Report Key Strengths
- Eleven-year Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Pemphigus Vulgaris Epidemiology Segmentation
Pemphigus Vulgaris Report Assessment
- Epidemiological Trends and Disease Progression
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT, Expert Insights, Unmet Needs)
Key Questions
- Would there be any changes observed in the epidemiological trends of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
- Will there be improvements in the understanding of Pemphigus Vulgaris progression?
- Would research advances lead to better epidemiological data for Pemphigus Vulgaris?
- How will the diagnostic testing space impact the epidemiology of Pemphigus Vulgaris?
- How will the prevalence and incidence of Pemphigus Vulgaris evolve in the coming years?
Reasons to buy
- Insights on disease burden, details regarding diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- To understand the change in Pemphigus Vulgaris cases in varying geographies over the coming years.
- A detailed overview of total incident population, type-specific cases, gender-specific cases, stage-specific cases, treatment-eligible incident population in early and advanced stages of Pemphigus Vulgaris is included.
- To understand the perspective of key opinion leaders around the current challenges with establishing the diagnosis and insights on the treatment-eligible patient pool.
- Detailed insights on various factors hampering disease diagnosis and other existing diagnostic challenges.


