Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Summary
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size in the 7MM + China was ~USD 107 million in 2024, which is expected to project to increase during the forecast period (2025–2034), estimates DelveInsight.
- The leading Underactive Bladder Syndrome Companies such as Otsuka (Taiho Pharmaceutical), ZERIA Pharmaceuticals, SFG Sciences (Juro Sciences), and others.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Insights and Forecast
- UAB presents with variable bladder contractility, voiding patterns, and comorbid conditions, highlighting the need for stratified or personalized therapeutic approaches. Patients experience difficulty with bladder emptying, incontinence, and frequent catheterization, creating a significant impact on independence and quality of life (QoL).
- Limited data exist on Underactive Bladder Syndrome Prevalence, with current literature offering few estimates; existing studies highlight significant gaps and limitations in understanding the disease’s epidemiology. Among the 7MM + China, China accounted for the highest Underactive Bladder Syndrome Diagnosed Prevalent Cases with more than 12 million in 2024, which is expected to rise by 2034.
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome remains clinically under-recognized, often misdiagnosed as an overactive bladder due to overlapping symptoms. Limited clinician awareness and inconsistent diagnostic criteria delay accurate detection, leading to inappropriate management and worsening patient burden.
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome management currently relies on a spectrum of interventions, beginning with conservative behavioral approaches and clean intermittent catheterization (CIC), and extending to pharmacotherapy, surgical procedures, and emerging regenerative modalities such as stem cell and gene therapies.
- Currently, CIC is the standard treatment in the management of patients who cannot have effective bladder emptying.
- Intermittent and indwelling catheterization, along with Sacral Neuro-modulation (SNM), serve as mainstay treatments but carry infection risks, economic burden, and patient dissatisfaction. These methods address symptoms rather than underlying pathophysiology.
- Pharmacotherapy in Underactive Bladder Syndrome remains exploratory, with current drug classes such as alpha-blockers, muscarinic agonists, cholinesterase inhibitors, and prostaglandin E2, illustrating ongoing efforts to counteract detrusor underactivity. However, their clinical utility remains modest, highlighting the continued struggle to achieve meaningful therapeutic outcomes.
- With the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market still dominated by CIC, developers are pivoting toward non-invasive, patient-friendly therapies to capture unmet demand. Oral candidates such as TAC-302 and ZG-802 reflect this shift, offering more convenient alternatives that could enhance adherence. However, evidence remains limited, and clinical validation is still early. As Underactive Bladder Syndrome awareness grows, targeted investment in differentiated non-invasive treatments could meaningfully expand the therapeutic landscape.
- The discontinuation of ASP8302 due to weak Phase II efficacy, alongside Ono’s strategic halt of ONO-8055, highlights the development risk in Underactive Bladder Syndrome R&D and reinforces the critical need for therapies with strong, clinically validated benefits to advance the field.
- The emerging Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline holds a few significant key Underactive Bladder Syndrome Companies, such as Otsuka Holdings (Taiho Pharmaceutical), Zeria Pharmaceutical, SFG Sciences (Juro Sciences), and others are evaluating their investigational therapies across various stages of clinical development.
- The emerging Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline remains narrow and regionally fragmented. Only a few investigational assets, such as TAC-302, ZG-802, and SFG-02, are currently in development, with active trials primarily limited to Japan. SFG-02 is expected to enter proof-of-concept studies in the US and Japan by 2026, but development has not yet expanded to Europe, reinforcing the challenge of geographic isolation, limited global data generation, and a lack of strong comparative evidence. This restricted pipeline activity significantly slows the ability to establish differentiated value, validate clinical outcomes across diverse populations, and support broader regulatory or commercial uptake.
Request for Unlocking the Sample Page of the "Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market"
Factors Contributing to the Growth of the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market
-
Rising Prevalence and Aging Population
Underactive bladder is more common among older adults, and with global populations aging rapidly, the number of UAB cases is increasing. This demographic shift is fueling demand for effective diagnostics and novel treatments.
-
Increased Disease Awareness and Diagnosis
Historically under-diagnosed, UAB is now receiving greater attention from urologists and primary care providers. Improved clinical awareness, better symptom recognition, and advances in diagnostic tools—like urodynamic testing—are contributing to higher detection rates and timely intervention.
-
Advancements in Research and Pathophysiological Understanding
Growing insights into the neurogenic and myogenic mechanisms underlying UAB are stimulating research into targeted drug candidates and therapeutic strategies. This enhanced scientific understanding is encouraging pharmaceutical and biotech innovation.
-
Expansion of the Clinical Pipeline
There is a rising number of clinical programs evaluating novel pharmacologic agents, neuromodulation techniques, and device-based therapies. A diversified pipeline increases market opportunity, accelerates competitive dynamics, and supports future treatment options beyond symptom management.
-
Technological Progress in Therapeutics and Devices
Emerging therapies such as bladder-targeted drug delivery systems, nerve stimulation devices, and regenerative medicine approaches are expanding treatment possibilities. Adoption of advanced diagnostics and monitoring technologies also contributes to optimized patient care.
-
Increasing Healthcare Access and Reimbursement Support
Improved healthcare infrastructure, broader insurance coverage, and supportive reimbursement policies are enhancing accessibility to diagnosis and treatment, especially in developed markets.
-
High Unmet Clinical Need
UAB significantly affects quality of life, leading to urinary retention, recurrent infections, and loss of independence. The lack of FDA-approved therapies and substantial unmet patient need is a major driver for research investment and market growth.
DelveInsight's “Underactive Bladder Market Insights, Epidemiology and Market Forecast– 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of the Underactive Bladder, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the Underactive Bladder Market Trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, Spain, Italy, and France) and the United Kingdom, Japan, and China.
The Underactive Bladder Treatment Market Report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM + China Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best of the opportunities and assesses the underlying potential of the market.
Scope of the Underactive Bladder Market | |
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the UK, Japan, and China |
|
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiology
|
Segmented By:
|
|
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapies |
|
|
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Companies |
|
|
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Understanding
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Overview
Underactive Bladder Syndrome is a condition marked by diminished bladder contractions, leading to incomplete emptying. Its causes range from nerve damage and diabetes to aging and specific medications. Risk factors include neurological disorders, pelvic surgeries, and chronic diseases. The burden of UAB is profound, encompassing recurrent urinary tract infections, potential kidney damage, and significantly diminished quality of life due to urinary retention and frequent catheterization. Early diagnosis and targeted management are crucial to alleviating these impacts and improving patient outcomes.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Diagnosis
Diagnosing UAB involves urodynamic testing, bladder scans, and patient history evaluations to assess bladder function, identify incomplete emptying, and determine underlying causes. Accuracy in diagnosis of UAB remains a significant challenge within the clinical setting, leading to widespread misdiagnosis or underdiagnoses. UAB is often erroneously interpreted as BOO or overactive bladder OAB due to overlapping symptoms. This diagnostic ambiguity significantly hampers the identification and appropriate management of UAB, resulting in inadequate treatment for many patients.The overlap in clinical presentation, such as urinary frequency, urgency, and hesitancy, between UAB, BOO, and OAB contributes to this confusion. Healthcare providers may mistakenly attribute symptoms to more commonly diagnosed conditions like BOO or OAB, overlooking the possibility of UAB. This misinterpretation is compounded by the lack of standardized diagnostic criteria and tools specifically tailored for UAB, further exacerbating the issue.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment
Treatment of UAB includes behavioral therapies, pelvic floor muscle exercises, medications to enhance bladder contractions, and, in severe cases, intermittent catheterization or sacral nerve stimulation to improve bladder emptying and alleviate symptoms. The therapeutic market for UAB faces significant challenges, characterized by a scarcity of effective treatment options and considerable challenges in managing this condition. UAB, which is particularly prevalent among the elderly, remains underdiagnosed and poorly addressed, underscoring a substantial medical necessity.
Currently, there is no approved therapy for UAB, the available supportive care treatments are limited, and very few have demonstrated validated outcomes. This is in stark contrast to the advancements seen in therapies for OAB, highlighting a critical gap in effective treatment options for UAB. UAB patients frequently experience feelings of helplessness due to difficulties in voiding or inadequate bladder emptying, emphasizing the urgent need for more effective therapies.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiology
As the market is derived using the patient-based model, the Underactive Bladder Syndrome epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total diagnosed prevalent cases of LUTS, total diagnosed prevalent cases of UAB, etiology-specific diagnosed prevalent cases of UAB, and total treated cases of UAB in the 7MM + China covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, Japan, and China from 2020 to 2034.
Key findings from the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiological Analysis
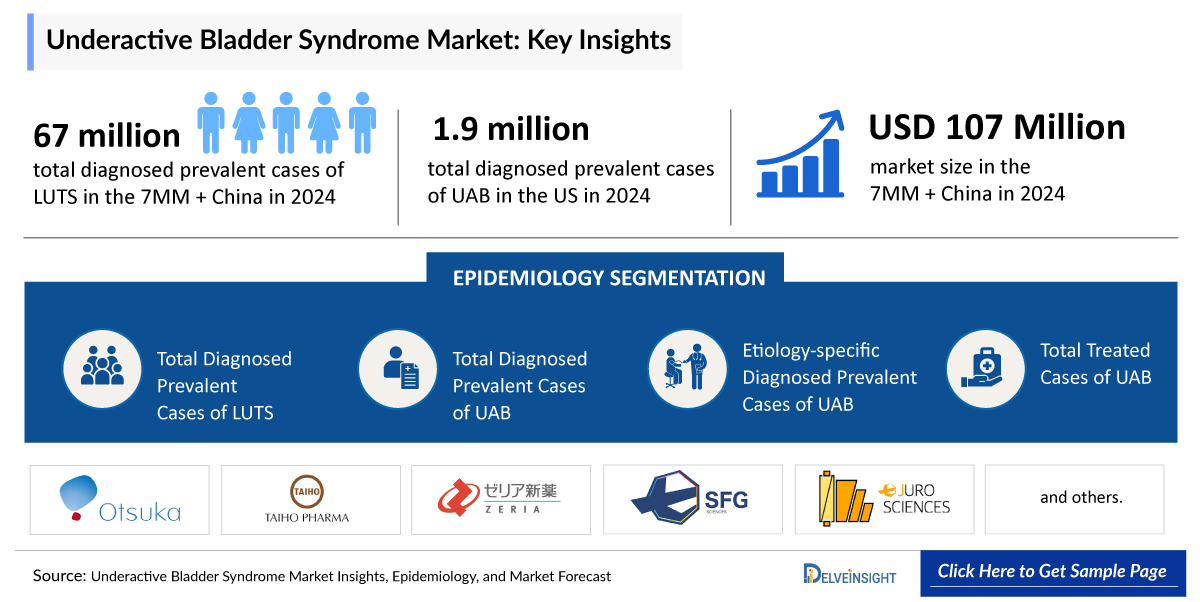
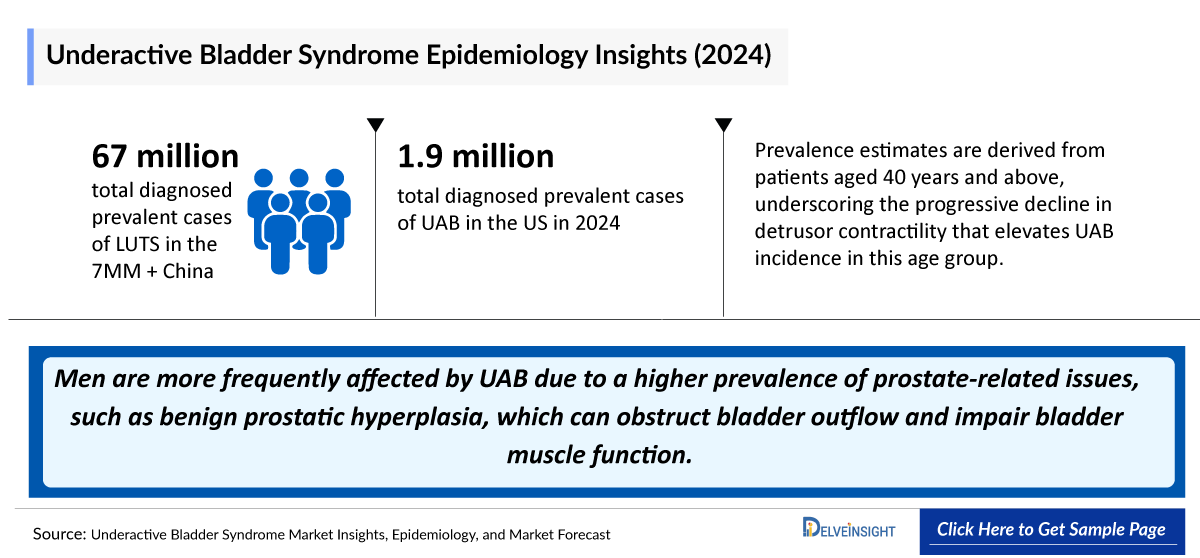
- As per DelveInsight’s estimations, the total diagnosed prevalent cases of LUTS in the 7MM + China were approximately 67 million cases in 2024 and are projected to increase during the forecast period. The anticipated rise in prevalent cases of moderate to severe LUTS in the US is attributed to an aging population, increased prevalence of obesity, and sedentary lifestyles.
- The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Diagnosed Prevalent Cases in the United States were approximately 1,900 thousand in 2024. Given the increasing prevalence of risk factors, increased awareness and diagnosis, higher occurrence of chronic conditions, improved healthcare access, and enhanced data collection for UAB in the United States population, the diagnosed prevalence is estimated to increase during the forecast period (2025–2034).
- Prevalence estimates are derived from patients aged 40 years and above, underscoring the progressive decline in detrusor contractility that elevates UAB incidence in this age group.
- Among the 7MM, EU4 and the UK accounted for nearly 13% diagnosed prevalent cases of Underactive Bladder Syndrome in 2024.
- Men are more frequently affected by UAB due to a higher prevalence of prostate-related issues, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia, which can obstruct bladder outflow and impair bladder muscle function.
- In 2024, neurogenic causes accounted for the majority of UAB cases in Japan at approximately 85%, followed by idiopathic etiologies, while myogenic impairment due to detrusor muscle dysfunction represented a smaller proportion. The remaining cases were linked to other factors, including post-surgical and medication-related causes.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiological Segmentation in the 7MM
- Total Diagnosed Prevalent Cases of LUTS
- Total Underactive Bladder Syndrome Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Etiology-Specific Diagnosed Prevalent Cases
- Total Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treated Cases
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drug Analysis
The drug chapter segment of the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market Report encloses a detailed analysis of Underactive Bladder Syndrome mid -stage (Phase-II) Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline Drugs. It also helps to understand the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Clinical Trials details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug, and the latest news and press releases.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Emerging Drugs
-
TAC-302: Otsuka Holdings (Taiho Pharmaceutical)
The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market Report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM + China UAB market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current UAB treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best of the opportunities and assesses the underlying potential of the market. Results from the Phase II trial, published in 2022, showcased the efficacy of TAC-302 in patients with detrusor underactivity. However, there is currently no information available regarding any additional clinical trials.
-
ZG-802 (acotiamide): ZERIA Pharmaceutical
ZG-802, also known as acotiamide, is a promising therapeutic candidate developed by ZERIA Pharmaceutical, targeting UAB. ZG-802 is a small molecule, it offers a convenient oral administration route, potentially simplifying treatment regimens for patients. ZG-802 functions as a lower urinary tract function modulator, aiming to address the impaired bladder function characteristic of UAB. ZG-802 has demonstrated promising efficacy and safety profiles in early clinical trials, paving the way for further development.
Comparison of Emerging Drugs Under Development | |||||
|
Drug Name |
Company |
Highest Phase |
Indication |
MoA |
Age Group |
|
TAC-3021 |
Otsuka Holdings (Taiho Pharmaceutical) |
II |
Detrusor underactivity with OAB |
Nerve growth factor stimulants |
20 Years and older |
|
ZG-802 (acotiamide)2 |
ZERIA Pharmaceutical |
II |
UAB |
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor |
18 years and older |
|
SFG-023 |
SFG Sciences (Juro Sciences) |
I |
UAB |
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor |
18 to 45 Years |
NOTE: Astellas Pharma has discontinued the development of ASP8302 for underactive bladder after the Phase II study did not meet its primary endpoint. Ono Pharmaceutical halted the development of ONO-8055 for underactive bladder due to strategic reasons. | |||||
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drug Class Insights
The existing Underactive Bladder Syndrome treatment mainly include different off-label drugs targeting the symptoms of UAB. Pharmacological options for Underactive Bladder Syndrome remain limited and diverse in mechanism, with no consistently effective standard of care. Parasympathomimetics and a1-adrenoceptor antagonists are used in clinical practice, but their therapeutic benefit is variable and often offset by significant side effects. Cholinesterase inhibitors represent another option, yet their performance in achieving reliable clinical improvement remains inconsistent. The development landscape is gradually expanding, with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors such as ZG-802 and SFG-02 advancing through clinical programs. Likewise, TAC-302, an orally administered small molecule aimed at treating detrusor underactivity in patients who also present with overactive bladder symptoms, is progressing in clinical trials and contributing to a more active Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Outlook
The current market outlook for Underactive Bladder Syndrome treatments reveals a complex landscape with a significant need for advanced therapeutic options. UAB, characterized by weak or insufficient bladder contractions, leads to slow or incomplete emptying. Effective management necessitates thorough neurologic and urodynamic evaluations, with primary goals including the prevention of upper urinary tract injury, avoidance of bladder overdistension, and reduction of residual urine.
Lifestyle modifications and conservative management form the cornerstone of initial Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment. Techniques such as scheduled voiding and double voiding aim to improve bladder emptying efficiency. Intermittent self-catheterization (ISC) remains the gold standard for ensuring complete bladder emptying, although it requires extensive patient training and support due to its complexity and potential discomfort. Alpha-blockers like tamsulosin and doxazosin are commonly prescribed to reduce urethral resistance, facilitating easier bladder emptying.
Pharmacological treatments for UAB are currently limited, with no drugs universally validated for the condition. Parasympathomimetics, such as bethanechol, are intended to stimulate bladder contractions, but they often show inconsistent efficacy and can cause serious side effects like bradycardia and bronchospasm. Alpha-1 adrenoceptor antagonists, including urapidil, indoramin, and doxazosin, are sometimes used off-label to reduce urethral resistance. Cholinesterase inhibitors, such as distigmine, work by increasing acetylcholine levels, which may enhance bladder contractions and are the choice of many physicians. Muscarinic receptor agonists like bethanechol have produced mixed results in clinical trials.
Advanced and emerging therapies offer promising avenues for Underactive Bladder Syndrome Management. Neuromodulation techniques, such as sacral neuromodulation, are being explored to improve bladder function by modulating neural pathways. Botulinum toxin injections, used to relax the external sphincter in cases of functional bladder outlet obstruction, can reduce resistance to urine flow. Few new drugs are being developed and tested as potential treatments for UAB; the emerging drugs include TAC-302, ZG-802, SFG-02, and others.
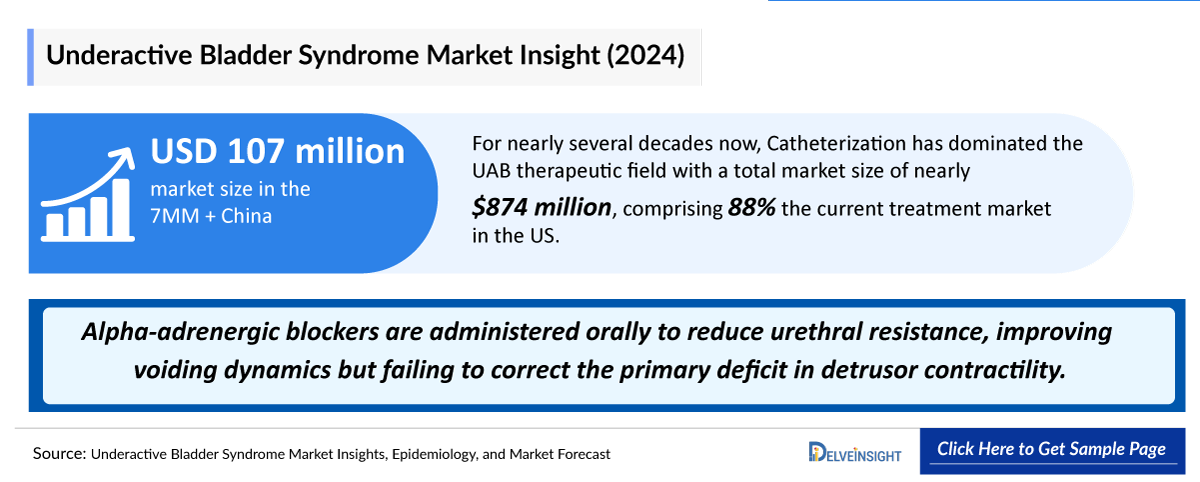
- According to the estimates, the 7MM + China had a Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size of ~USD 107 million in 2024, which is expected to project to increase during the forecast period (2025–2034).
- Current first-line pharmacologic management of Underactive Bladder Syndrome relies on oral parasympathomimetic agents such as bethanechol, intended to enhance detrusor muscle contraction, although their clinical utility is limited due to modest efficacy and cholinergic side effects.
- Alpha-adrenergic blockers (e.g., tamsulosin, silodosin) are administered orally to reduce urethral resistance, improving voiding dynamics but failing to correct the primary deficit in detrusor contractility.
- By 2034, TAC-302 therapy is anticipated to capture the highest market in the 7MM + China.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the rate of uptake of the potential Underactive Bladder Syndrome drugs expected to get launched in the market during the forecast period 2025–2034. For example, for TAC-302, we expect the drug uptake to be medium due to the slow developmental progress and no further updates from the company despite the high unmet need, and years to the peak is expected to be 7 years from the year of launch.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Clinical Trials Activities
The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapeutics Market Report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in Phase II and Phase I stage. It also analyzes key Underactive Bladder Syndrome Companies involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline Development Activities
The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapeutics Market Report covers detailed information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for Underactive Bladder Syndrome emerging therapies.
Latest KOL- Views on Underactive Bladder Syndrome
To keep up with current market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs' opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on UAB evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient’s therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake along with challenges related to accessibility, include Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; Department of Urologic Surgery, Nashville, Tennessee, US; Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg, Germany; Southmead Hospital, United Kingdom; Department of Urology, University Hospital of Rennes, Rennes, France; Department of Urology, Sakurajyuji Hospital, Japan, and others.
Delveinsight’s analysts connected with 10+ KOLs to gather insights, however, interviews were conducted with 5+ KOLs in the 7MM + China. Centers such as the California Northstate University and Newcastle University, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental Health, etc. were contacted. Their opinion helps to understand and validate current and emerging therapies and treatment patterns or Underactive Bladder Syndrome market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Region |
KOL Views |
|
United States |
“Rapid progress in biomedical engineering is enabling novel “artificial bladder” concepts designed to restore voiding function in UAB. Emerging platforms range from fully implantable, wireless systems that monitor bladder activity and deliver closed-loop electrical stimulation, to magnetic soft-robotic devices that apply direct mechanical compression—both demonstrating promising results in preclinical UAB models.” - MD, California Northstate University, US |
|
Italy |
“The exact cause and optimal treatment approach for this condition remain uncertain. By carefully examining patient histories and conducting specific diagnostic evaluations, risk factors can be identified to make informed treatment decisions. Nevertheless, continued research is crucial to improve the understanding and advance treatment options for underactive bladder.” - MD, University of Padova, Italy |
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Qualitative Analysis Report
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis, and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market Landscape.
Conjoint Analysis is done to analyze multiple approved and emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy. Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the acceptability, tolerability, and adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement is a crucial point for any drug after its approval. Many drugs or therapies are not properly recognized by the reimbursement body and may fail to get reimbursed or their reimbursement process gets delayed. CPAP being the first-line therapy for UAB is currently included in the list of products and services qualifying for reimbursements and funded under the indications established because of the clinical symptoms reported (with the exclusion of any other sleep disorder) and an AHI score that must be =15. The report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Scope of the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report
- The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, descriptive overview, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight has been provided into the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression along with treatment guidelines.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of both the current and emerging therapies along with the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will have an impact on the current Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market Landscape.
- A detailed review of the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Market; historical and forecasted Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size, Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM + China drug outreach.
- The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapeutics Market Report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preference that help in shaping and driving the 7MM + China Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market.
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report Insights
- Patient-based Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Forecasting
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapeutic Approaches
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline Analysis
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size and Trends
- Existing and future Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market Opportunity
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report Key Strengths
- 10-Year Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Forecast
- 7MM + China Coverage
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Conjoint analysis
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Uptake
- Key Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Forecast Assumptions
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report Assessment
- Current Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Practices
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Unmet Needs
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Pipeline Drugs Profiles
- Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market Attractiveness
- Underactive Bladder SyndromeQualitative Analysis (SWOT and Conjoint Analysis)
Key Questions Answered in the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Insights:
- What was the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Size, the Underactive Bladder Syndrome market size by therapies, and market share (%) distribution in 2020, and how it would all look in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- What are the unmet needs are associated with the current treatment market of UAB?
- How is TAC-302 going to compete with the first line of therapy for UAB after approval?
- Which drug is going to be the largest contributor in 2034?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and off-label therapies?
- How would the market drivers, barriers, and future opportunities affect the market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
Underactive Bladder Syndrome Epidemiology Insights:
- What are the disease risk, burden, and unmet needs of Underactive Bladder Syndrome? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM + China concerning the patient population of Underactive Bladder Syndrome?
- What is the historical and forecasted Underactive Bladder Syndrome patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, Japan, and China?
- Why do only limited patients appear for diagnosis? Why is the current year diagnosis rate not high?
- Which severity stage is more prevalent and why?
- What factors are affecting the diagnosis of the indication?
Current Underactive Bladder Syndrome Treatment Scenario, Marketed Drugs, and Emerging Therapies:
- What are the current options for the treatment of Underactive Bladder Syndrome? What are the current treatment guidelines for the treatment of Underactive Bladder Syndrome in the US and Europe?
- How many companies are developing therapies for the treatment of Underactive Bladder Syndrome?
- How many emerging therapies are in the mid-stage and late stage of development for the treatment of Underactive Bladder Syndrome?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitation of existing therapies?
- What are the key designations that have been granted for the emerging therapies for Underactive Bladder Syndrome?
- What is the cost burden of current therapies on the patient?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved therapies? Focus on reimbursement policies.
- What are the 7MM + China historical and forecasted market of Underactive Bladder Syndrome?
Reasons to Buy the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Market Report
- The Underactive Bladder Syndrome Therapeutics Market Report will help in developing business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market.
- Insights on patient burden/disease Underactive Bladder Syndrome Prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- To understand the existing Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market opportunity in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identification of strong upcoming players in the Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market will help in devising strategies that will help in getting ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of Access and Reimbursement policies of approved therapies, barriers to accessibility of off-label expensive therapies, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand the perspective of Key Opinion Leaders’ around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet need of the existing Underactive Bladder Syndrome Drugs Market so that the upcoming players can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Stay updated with us for Recent Articles @ New DelveInsight Blogs