Obesity Epidemiology
Key Highlights
- Obesity is a chronic complex disease defined by excessive fat deposits that can impair health. Obesity can lead to increased risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease. It can affect bone health and reproduction, and it increases the risk of certain cancers.
- The diagnosis of overweight and obesity is made by measuring people's weight and height and by calculating the Body Mass Index (BMI): weight (kg)/height² (m²). The body mass index is a surrogate marker of fatness and additional measurements, such as the waist circumference, can help the diagnosis of obesity. The BMI categories for defining obesity vary by age and gender in infants, children, and adolescents.
- Obesity management for individuals with a BMI of 25 kg/m² or higher includes diet, exercise, and behavioral modification as foundational approaches. For those with a BMI of 27 kg/m² or higher with comorbidities or a BMI over 30 kg/m², pharmacotherapy can be added to enhance adherence to lifestyle changes.
- In 2023, the United States accounted for the highest prevalent cases of Obesity.
- In the EU4 and the UK, Germany recorded the highest number of obesity cases, followed by the United Kingdom, while Spain had the fewest cases in 2020.
- In the United States, individuals of the ≥19 age group accounted for the highest number of prevalent cases of obesity in 2023.
Report Summary
- The report offers extensive knowledge regarding the epidemiology segments and predictions, presenting a deep understanding of the potential future growth in diagnosis rates, disease progression, and diagnostic guidelines. It provides comprehensive insights into these aspects, enabling a thorough assessment of the subject matter.
- The report includes qualitative insights that provide an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, including experts from various hospitals and prominent universities, patient journey, and preferences.
The table given below further depicts the key segments provided in the report
|
Study Period |
2021-2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
Obesity Disease Understanding and Diagnosis
Obesity Overview
Obesity is a chronic condition marked by an excessive accumulation of body fat, posing significant health risks. It is defined by a BMI of 30 or higher and is increasingly recognized as a serious health concern that affects individuals' overall well-being. Obesity is categorized into three classes based on BMI: Class 1 (30-34.9), Class 2 (35-39.9), and Class 3 (40 and above), with each class corresponding to escalating health risks and complications. The development of obesity is influenced by a combination of genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and environmental conditions. Key contributors include sedentary behavior, poor dietary habits, and socioeconomic factors. Common signs of obesity include weight gain, difficulty with physical activity, and psychological effects such as low self-esteem and depression, all of which increase the risk of serious health issues like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory problems. The pathophysiology of obesity involves complex interactions between genetic and hormonal factors, particularly the leptin-melanocortin signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in regulating appetite and energy expenditure.
Further details are provided in the report…
Obesity Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Obesity involves proper evaluation of the weight status, which considers many factors and uses various tools and diagnostic tests, including BMI, waist circumference measurement, physical exams, and lab tests to check for comorbidities.
Childhood obesity is diagnosed by comparing a child’s weight and height to CDC growth charts. A child in the 85th to 94th percentile is classified as overweight, while those in the 95th percentile or higher are considered obese. Pediatricians assess factors such as family history, eating habits, activity levels, and psychosocial factors. Lab tests may include cholesterol, blood sugar, and hormone screenings.
In adolescents, obesity is diagnosed using BMI, with a value of 30 or higher placing them in the 95th percentile or above. A full medical evaluation is conducted, including physical exams, medical history, lab tests, and X-rays. Teens with BMI between the 85th and 95th percentiles undergo further screening for family history, blood pressure, cholesterol, BMI trends, and psychological concerns.
Further details are provided in the report…
Obesity Epidemiology
The Obesity epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total prevalent cases, and total treated cases of obesity in the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2021 to 2034.
- Among the 7MM, the United States accounted for the highest number of cases of obesity in 2023, with nearly 119,000,000 cases. These cases are anticipated to increase by 2034.
- In the United States, individuals of ≥19 year age group account for the highest number of cases of obesity in 2023.
- Among EU4 and the UK, Germany accounted for the highest number of prevalent cases in 2023, while Spain accounted for the least.
Total Prevalent Cases of Obesity in the United States (2023)
Further details related to epidemiology will be provided in the report…
KOL Views
To stay abreast of the latest trends, we conduct primary research by seeking the opinions of Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs) and Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) who work in the relevant field. This helps us fill any gaps in data and validate our secondary research.
We have reached out to industry experts to gather insights on various aspects of Obesity, including the evolving population landscape, patients’ reliance on conventional therapies, their acceptance of therapy switching, drug uptake, and challenges related to accessibility. The experts we contacted included medical/scientific writers, professors, and researchers from prestigious universities in the US, Europe, the UK, and Japan.
Our team of analysts at Delveinsight connected with more than 15 KOLs across the 7MM. We contacted institutions such as the Yale University School of Medicine, Tokyo Institute of Psychiatry, University of Chieti-Pescara, etc., among others. By obtaining the opinions of these experts, we gained a better understanding of analyzing the overall epidemiology scenario.
The opinions of experts from various regions have been provided below:
“The current medications for obesity management are just the beginning, with next-generation therapies like the combined GLP1/GIP agonist tirzepatide leading the way. Emerging treatments, including triple agonists (GLP1/GIP/glucagon) and amylin/GLP1 combinations, show great promise. Additionally, oral GLP1 agonists like high-dose semaglutide and orforglipron will expand accessibility. These advancements not only enhance weight management but are likely to significantly reduce obesity-related complications, marking a new era in obesity treatment.”
MD, Nephrologist, US
“The evolving approach to obesity treatment, viewing it as an endocrine disease and addressing it hormonally, is transforming care. By targeting the underlying hormonal imbalances, this new direction offers patients and providers a broader range of therapeutic options. Tailoring treatment to individual needs, based on the most effective drug for each patient, marks a significant shift in how obesity is managed, opening the door to more personalized and effective long-term outcomes.”
-MD, Japan
Obesity Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Obesity Population Size and Trends
Obesity Report Key Strengths
- Eleven-year Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Obesity Epidemiology Segmentation
Explore obesity market size, patient segmentation, emerging therapies, growth drivers, and forecast outlook to 2034 with this comprehensive market insight report.
Key Questions
- Would there be any changes observed in the current epidemiology trend?
- Will there be any improvements in Obesity diagnosis?
- Would the diagnostic testing space experience a significant impact and lead to a positive shift in the treatment landscape of Obesity?

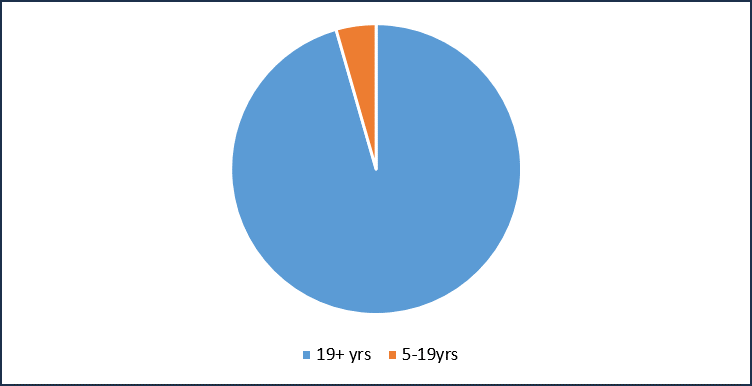
-pipeline.png&w=256&q=75)
