Hyperparathyroidism Epidemiology
Key Highlights
- Hyperparathyroidism is a condition characterized by the excessive production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands, leading to elevated calcium levels in the blood, known as hypercalcemia.
- The excess PTH increases calcium release from bones, enhances calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, and increases calcium absorption in the intestines, disrupting normal calcium-phosphate balance.
- There are three main types of hyperparathyroidism: Primary Hyperparathyroidism, Secondary Hyperparathyroidism, and Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism.
- Chronic hyperparathyroidism can lead to serious health issues such as osteoporosis, increased risk of fractures, kidney stones, and cardiovascular problems due to prolonged high calcium levels affecting heart function, with symptoms that can be asymptomatic or include fatigue, depression, bone pain, abdominal discomfort, and cardiac arrhythmia.
- Diagnosis is usually made through routine blood tests that reveal elevated serum calcium and PTH levels. Imaging studies may also be used to identify any abnormalities in the parathyroid glands.
- In 2024, the United States accounted for the highest diagnosed prevalent cases of Hyperparathyroidism among the 7MM, with ~2,600,000 cases. The majority of these cases, about 60% were of primary hyperparathyroidism.
- In the EU4 and the UK, Germany recorded the highest diagnosed prevalent cases of Hyperparathyroidism, followed by the United Kingdom, while Spain had the fewest cases in 2024.
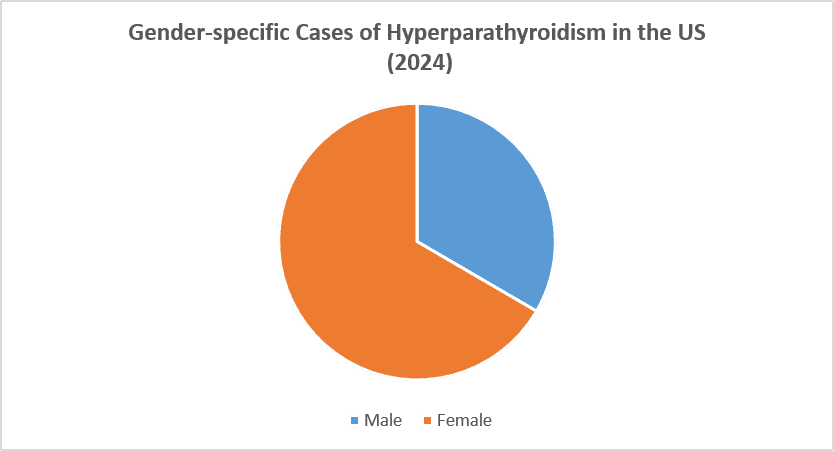
- Females are fairly more affected by Hyperparathyroidism than males in 2024.
- In 2024, individuals aged ≥60 years accounted for the highest number of cases, with around 1,525,000 cases.
DelveInsight’s “Hyperparathyroidism– Epidemiology Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of Hyperparathyroidism, historical and forecasted epidemiology in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The table given below further depicts the key segments provided in the report:
|
Study Period |
2021-2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the UK, and Japan |
|
Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
Hyperparathyroidism: Disease Understanding
Hyperparathyroidism Overview, and Diagnosis
Hyperparathyroidism is a condition characterized by excessive production of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands, which are located near the thyroid gland in the neck. This overproduction leads to elevated calcium levels in the blood, a condition known as hypercalcemia, which can cause various health issues. There are three forms of hyperparathyroidism, each with a different cause.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism: One or more of the parathyroid glands grows too large and releases too much PTH, which leads to elevated levels of calcium (because of excessive production of calcitriol and release of calcium from the bones).
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism: Blood-calcium or vitamin D levels are so low—often due to dietary deficiency—they cause the parathyroid glands to release excessive levels of PTH to counteract the deficiency by inducing excessive release of calcium from bone.
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism: Chronically reduced calcium and vitamin D deficiency—or reduced calcitriol synthesis due to kidney disease—cause all four parathyroid glands to grow and produce PTH regardless of whether the body needs the hormone, leading to elevated levels of calcium levels (because of excessive release of calcium from the bones) (Yale Medicine)
Hyperparathyroidism is typically diagnosed through blood tests that reveal elevated levels of calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH). Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be used to identify any abnormalities in the parathyroid glands, such as tumors or enlargement.
Hyperparathyroidism Epidemiology
The Hyperparathyroidism epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by the total prevalent cases total diagnosed prevalent cases,type-specific cases, age-specific cases, gender-specific cases, and total treated cases of Hyperparathyroidism in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2021 to 2034.
- In the United States, primary hyperparathyroidism accounted for the highest number of cases in 2024 with around 1,400,000 cases.
- In 2024, around 65% of hyperparathyroidism cases accounted for by females in 7MM.
- In EU4 and the UK, individuals aged ≥60 years accounted for the highest number of cases, with around 1,421,000 cases in 2024.
- In Japan, the diagnosed prevalence of hyperparathyroidism was around 480,000, in 2024.
- In 2024, hyperparathyroidism was more prevalent in females, with around 3,600,100 cases reported across the 7MM, compared to around 1,800,000 cases in males, highlighting a significant gender disparity in its occurrence.
Scope of the Report
- The report covers a segment of an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of Hyperparathyroidism, explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, and pathogenesis.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, and disease progression have been provided.
- A detailed review of current challenges in establishing diagnosis and diagnosis rate is provided.
Hyperparathyroidism Report Insights
- Patient Population
- Country-wise Epidemiology Distribution
Hyperparathyroidism Report Key Strengths
- Ten-year Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Hyperparathyroidism Epidemiology Segmentation
Hyperparathyroidism Report Assessment
- Epidemiology Segmentation
- Current Diagnostic Practices
FAQs
Epidemiology Insights
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and unmet needs of Hyperparathyroidism? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM with respect to the patient population pertaining to Hyperparathyroidism?
- What is the historical and forecasted Hyperparathyroidism patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- What is the diagnostic pattern of Hyperparathyroidism?
- Which clinical factors will affect Hyperparathyroidism?
- Which factors will affect the increase in the diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism?
Reasons to buy
- Insights on disease burden, details regarding diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- To understand the change in Hyperparathyroidism cases in varying geographies over the coming years.
- A detailed overview of total prevalent cases of Hyperparathyroidism, total diagnosed prevalent cases of Hyperparathyroidism, type-specific cases of Hyperparathyroidism, gender-specific cases of Hyperparathyroidism, age-specific cases of Hyperparathyroidism and total treated cases is included.
- Detailed insights on various factors hampering disease diagnosis and other existing diagnostic challenges.