Complement Factor B (CFB) Inhibitor Market Forecast
- The CFB inhibitors market is emerging as a promising segment within the broader complement inhibition landscape. With the FDA's approval of FABHALTA (iptacopan) as the first oral monotherapy for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria and its subsequent approval for Primary IgAN, the clinical validation of CFB inhibition has gained significant momentum.
- CFB inhibitors are targeted therapies designed to block Complement Factor B (CFB), a key enzyme that drives the amplification loop of the alternative complement pathway, aiming to selectively control complement overactivation without completely shutting down innate immunity.
- FABHALTA (iptacopan) is the first and only FDA-approved Complement Factor B inhibitor, marking a significant breakthrough in complement-mediated disease treatment. Approved in December 2023 for Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH) as the first oral monotherapy, it demonstrated superior hemoglobin improvement without the need for transfusions. In August 2024, it also received accelerated approval to reduce proteinuria in adults with Primary Immunoglobulin A Nephropathy (IgAN) at risk of rapid progression.
- Multiple pharmaceutical companies are actively advancing investigational CFB inhibitors across various indications. For example, F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Ionis Pharmaceuticals are developing Sefaxersen (RG6299; IONIS-FB-LRx), an antisense oligonucleotide designed to inhibit complement factor B gene expression by binding to factor B mRNA. It is being evaluated in a Phase III clinical trial for the treatment of IgAN, with regulatory filing expected in 2027 or later.
- CFB inhibitors represent an exciting, next-generation approach to selectively modulate the complement system without fully crippling immune defenses.
- Despite the approval of FABHALTA, unmet needs remain with CFB inhibitors, including broader validation across diverse complement-mediated diseases, long-term safety data, and comparative effectiveness versus C5 inhibitors in conditions like PNH. Additionally, questions around optimal patient selection, management of breakthrough hemolysis, and potential off-target immune effects highlight the need for further clinical refinement and real-world evidence. Oral administration offers convenience, but maintaining consistent efficacy across variable disease severities remains a key challenge.
DelveInsight’s “CFB Inhibitor Market Size, Target Population, Competitive Landscape, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of the CFB inhibitors, historical and projected epidemiological data, competitive landscape as well as the CFB inhibitors market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The CFB inhibitors market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM CFB inhibitors market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers current CFB inhibitors treatment practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the CFB Inhibitor market’s potential.
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2025–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the UK, and Japan |
|
CFB Inhibitor Epidemiology |
Segmented by:
|
|
CFB Inhibitor Companies |
|
|
CFB Inhibitor Therapies |
|
|
CFB Inhibitor Clinical Relevance |
|
|
CFB Inhibitor Market |
Segmented by:
|
|
Analysis |
|
CFB Inhibitor Market: Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
CFB Inhibitors overview and clinical relevance
Complement Factor B (CFB) inhibitors are a new class of targeted therapies that modulate the alternative complement pathway at an early amplification step, offering selective control of complement-driven diseases while preserving overall immune defense. Their clinical relevance is underscored by FABHALTA’S approval, demonstrating that upstream inhibition at Factor B can achieve robust outcomes in disorders like PNH and IgAN, traditionally dominated by C5-targeted therapies. As first-generation CFB inhibitors enter clinical practice, they represent a paradigm shift toward oral complement inhibition, although long-term validation across broader indications and patient populations remains critical.
Further details related to indications are provided in the report…
CFB Inhibitor Epidemiology
The CFB inhibitors epidemiology chapter in the CFB Inhibitor markety report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented as total cases in selected indications for CFB inhibitors, total eligible patient pool in selected indications for CFB inhibitors, and total treated cases in selected indications for CFB inhibitors in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain), the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
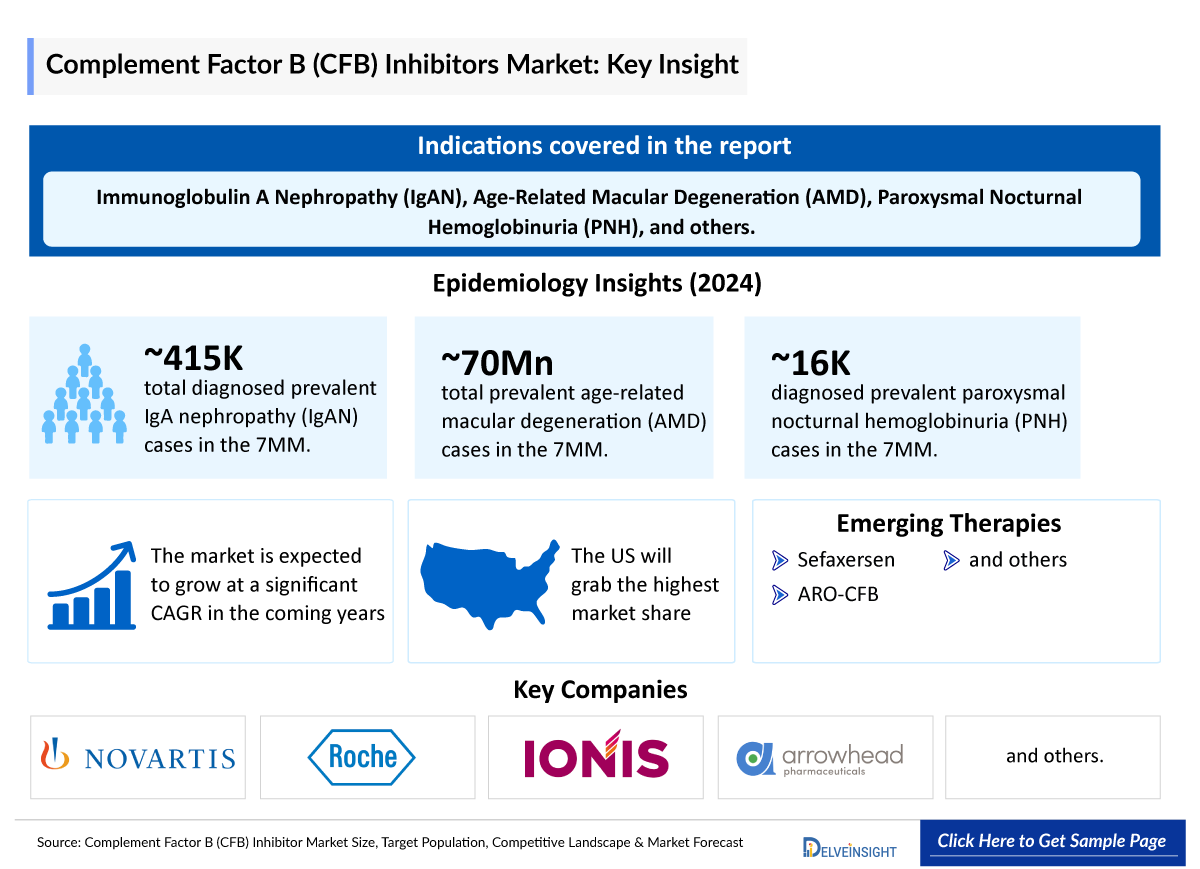
- According to DelveInsight’s estimates, there were approximately 415 thousand total diagnosed prevalent cases of IgAN in the 7MM in 2024.
- In 2024, the US accounted for around 133 thousand diagnosed prevalent cases of IgAN, expected to increase by 2034.
- Between EU4 and the UK, Germany had the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases of IgAN in 2024, with approximately 30 thousand cases, while Spain had the lowest, with around 5 thousand cases.
- In 2024, Japan recorded the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases of IgAN among the 7MM, nearly 175 thousand, which is expected to rise by 2034.
Age-Related Macular Degeneration
- The total prevalent cases of AMD in the 7MM was nearly 70 million in 2024.
- Among the 7MM, the US accounted for the highest prevalent cases of geographic atrophy in 2024 while Japan accounted for the least number of prevalent cases.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
- In 2024, the diagnosed prevalent cases of PNH were approximately 16 thousand cases in the 7MM, which will increase by 2034. In the 7MM, the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases of PNH were observed in the US.
- The total diagnosed cases of Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria in the US were around 8 thousand cases in 2024.
- The United Kingdom had the highest diagnosed prevalent cases of PNH among the EU4 and the UK, accounting for more than 50% of cases in 2024.
Note: Indications have been selected based on pipeline activity. Further details regarding these indications will be provided in the full report..
CFB Inhibitor Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the CFB inhibitor drugs market reports encloses a detailed analysis of CFB inhibitors’ marketed drugs and early, mid, and late-stage (Phase I, Phase II and Phase III) pipeline drugs. It also helps understand the CFB inhibitors' clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug and the latest news and press releases.
Marketed CFB Inhibitor Drugs
FABHALTA (iptacopan): Novartis
Iptacopan, also known as LNP023, is an oral, selective Factor B inhibitor targeting the alternative complement pathway, approved in the US under accelerated approval for adults with primary IgAN at risk of rapid disease progression. It is indicated to reduce proteinuria, a key marker of disease activity, based on interim data from the Phase III APPLAUSE-IgAN trial. Continued approval may require confirmation of clinical benefit in slowing kidney function decline. FABHALTA offers a novel mechanism that addresses complement dysregulation in IgAN. Due to its safety profile, FABHALTA is available only through a restricted distribution program under a REMS, known as the FABHALTA REMS, to ensure appropriate monitoring and use.
- In August 2024, the US FDA granted accelerated approval to Novartis for FABHALTA, making it the first and only oral complement inhibitor approved to reduce proteinuria in adults with primary IgAN who are at risk of rapid disease progression, typically defined by a UPCR of 1.5 g/g or higher.
- In December 2023, the US FDA approved FABHALTA as the first oral monotherapy for adults with PNH. The approval was primarily supported by the Phase III APPLY-PNH trial, which evaluated patients with residual anemia (hemoglobin <10 g/dL) despite prior anti-C5 therapy. Patients who switched to FABHALTA showed superior improvements in hemoglobin levels without the need for RBC transfusions and achieved higher transfusion avoidance rates compared to those who remained on anti-C5 treatments. Additional support came from the Phase III APPOINT-PNH study, which assessed FABHALTA in complement inhibitor–naïve patients.
|
Product |
Company |
Indication |
|
FABHALTA (iptacopan) |
Novartis |
|
Note: Detailed current therapies assessment will be provided in the full report of CFB Inhibitor.
Emerging CFB Inhibitor Drugs
Sefaxersen (RG6299; IONIS-FB-LRx): F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Ionis Pharmaceuticals
Sefaxersen (RG6299; IONIS-FB-LRx), developed in collaboration between Roche and Ionis Pharmaceuticals, is an antisense oligonucleotide designed to inhibit complement factor B gene expression by binding to factor B mRNA. It is being evaluated in a Phase III clinical trial for the treatment of IgAN, with regulatory filing expected in 2027 or later.
- In October 2018, Ionis Pharmaceuticals announced a collaboration with Roche to develop IONIS-FB-LRx for the treatment of complement-mediated diseases. Under the agreement, Ionis received a USD 75 million upfront payment and is eligible for up to USD 684 million in development, regulatory, and sales milestone payments, along with license fees.
- In July 2022, Roche exercised its option to license IONIS-FB-LRx following positive Phase II results. Roche is now responsible for global development, regulatory, and commercialization activities and associated costs, excluding the open-label Phase II study in patients with IgA nephropathy, which remains under Ionis’ conduct and funding.
- In July 2024, Roche discontinued development of sefaxersen for the treatment of geographic atrophy, following the completion of the Phase II study, which showed a favorable safety profile and target engagement, but insufficient efficacy to advance into Phase 3 development.
Note: Detailed emerging therapies assessment will be provided in the final report.
|
List of Emerging Drugs | |||||
|
Drug Name |
Company |
Indication |
ROA |
Phase |
NCT ID |
|
Sefaxersen (RG6299; IONIS-FB-LRx) |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche/Ionis Pharmaceuticals |
IgAN |
SC |
III |
NCT05797610 among others |
|
ARO-CFB |
Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals |
Complement mediated disease |
- |
I |
NCT06209177 |
|
XX |
XX |
XX |
XX |
XX |
XX |
Note: The emerging drug list is indicative, the full list will be given in the final report.
CFB Inhibitor Market Outlook
The CFB inhibitors market is emerging as a promising segment within the broader complement inhibition landscape. With the FDA's approval of FABHALTA (iptacopan) as the first oral monotherapy for PNH and its subsequent approval for Primary IgAN, the clinical validation of CFB inhibition has gained significant momentum. This positions CFB inhibitors as a strategic alternative to traditional C5-targeted therapies, offering potential advantages in terms of efficacy and safety profiles.
IONIS-FB-LRx, an antisense oligonucleotide targeting CFB, has been investigated in various indications. In geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the Phase II GOLDEN study demonstrated favorable safety profiles and target engagement. However, the study did not meet its primary endpoint, leading to the discontinuation of this indication.
Conversely, in primary IgAN, IONIS-FB-LRx exhibited a 44% mean reduction in proteinuria at 6 months in a Phase II open-label study, supporting its progression into Phase III trials. The ongoing IMAGINATION trial (NCT05797610) is a global, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the efficacy and safety of IONIS-FB-LRx in adults with biopsy-confirmed primary IgAN. This trial aims to assess a broad range of outcomes over 105 weeks, including proteinuria reduction and renal function preservation. The promising Phase II results and the initiation of the Phase III trial underscore the potential of CFB inhibition in complement-mediated renal diseases.
CFB Inhibitor Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential approved and emerging CFB inhibitors expected to be launched in the CFB Inhibitor market during 2020–2034.
CFB Inhibitor Pipeline Development Activities
The CFB Inhibitor market report provides insights into different therapeutic candidates in phase III phase II, and phase I. It also analyzes key CFB Inhibitor companies involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
The presence of numerous drugs under different stages is expected to generate immense opportunity for CFB inhibitors’ market growth over the forecasted period.
KOL Views on CFB Inhibitor
To keep up with current and future CFB Inhibitor market trends, we take Industry Experts’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry experts were contacted for insights on CFB inhibitors’ evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, drug uptake, along challenges related to accessibility.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 25+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 10+ KOLs in the 7MM.
Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or CFB inhibitors’ market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the CFB Inhibitor market and the unmet needs.
"CFB inhibitors are emerging as a promising class of therapeutics targeting the alternative complement pathway. Their potential to modulate complement activation at an early amplification step offers a novel approach to treating complement-mediated diseases. Ongoing clinical trials are evaluating the efficacy and safety of these inhibitors in conditions such as IgA nephropathy, with early results indicating potential benefits. However, further studies are needed to fully understand their long-term impact and optimal use in clinical practice."
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving treatment landscape.
CFB Inhibitor Market Access and Reimbursement
The CFB Inhibitor market report further provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenario of approved therapies, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Novartis Patient Support
If the patient has private insurance, they may be eligible for a USD 0 Co-pay Plus offer for FABHALTA through Novartis Patient Support.
Co-pay Plus: Limitations apply. Patients with commercial insurance coverage for FABHALTA may receive up to USD 20,000 in annual co-pay benefits for the cost of FABHALTA and up to USD 1,000 for qualifying vaccination costs (excluding administrative fees). The patient is responsible for any costs once the limit is reached in a calendar year.
Scope of the CFB Inhibitor Market Report
- The CFB Inhibitor market report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview of CFB inhibitor, explaining their mechanism, and therapies (current and emerging).
- Comprehensive insight into the competitive landscape, forecasts, and the future growth potential of treatment rate, drug uptake, and drug information have been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies that will impact the current landscape.
- A detailed review of the CFB inhibitor market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the CFB Inhibitor market report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The CFB Inhibitor market report provides an edge while developing business strategies, by understanding trends, through SWOT analysis, expert insights/KOL views, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM CFB inhibitor market.
CFB Inhibitor Market Report Insights
- CFB Inhibitor Patient Pool
- CFB Inhibitor Therapeutic Approaches
- CFB Inhibitor Pipeline Analysis
- CFB Inhibitor Market Size
- CFB Inhibitor Market Trends
- Existing and future CFB Inhibitor Market Opportunity
CFB Inhibitor Market Report Key Strengths
- 10 Years Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Key Cross Competition
- CFB Inhibitor Drugs Uptake
- Key CFB Inhibitor Market Forecast Assumptions
CFB Inhibitor Market Report Assessment
- Current Treatment Practices
- CFB Inhibitor Unmet Needs
- CFB Inhibitor Pipeline Product Profiles
- CFB Inhibitor Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT)
Key Questions
- What was the CFB inhibitor market size, the market size by therapies, market share (%) distribution, and what would it look like in 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- Which CFB Inhibitor is going to be the largest contributor in 2034?
- Which is the most lucrative market for CFB inhibitor?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved CFB Inhibitor therapies?
- How has the reimbursement landscape for CFB inhibitor evolved since the first one was approved? Do patients have any access issues that are driven by reimbursement decisions?
- What are the risks, burdens, and unmet needs of treatment with CFB inhibitor? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM for the patient population of CFB inhibitor?
- What are the key factors hampering the growth of the CFB inhibitor market?
- What are the indications for which recent novel therapies and technologies have been developed to overcome the limitations of existing treatments?
- What key designations have been granted to the therapies for CFB inhibitor?
- What is the cost burden of approved CFB Inhibitor therapies on the patient?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred therapy options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the country-specific accessibility issues of expensive, recently approved CFB Inhibitor therapies?
Reasons to buy
- The CFB Inhibitor market report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing dynamics driving the CFB inhibitor Market.
- Understand the existing CFB Inhibitor market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- Distribution of historical and current patient share based on real-world prescription data along with reported sales of approved products in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying strong upcoming CFB Inhibitor companies in the CFB Inhibitor market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of indication-wise current and emerging CFB Inhibitor therapies under the attribute analysis section to provide visibility around leading indications.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing CFB Inhibitor market so that the upcoming CFB Inhibitor companies can strengthen their development and launch strategy.