Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)
May 07, 2025
Table of Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are reshaping the world of Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), bringing a new level of intelligence and efficiency to healthcare. SaMD refers to software designed for medical purposes that doesn’t rely on physical hardware. When integrated with AI/ML, these software applications can analyze vast amounts of data, detect complex patterns, and continuously improve over time. This fusion is unlocking powerful applications across various fields, like enhancing radiology with advanced image analysis, detecting arrhythmias in cardiology, and supporting tumor detection and treatment planning in oncology. With AI-enabled SaMDs, healthcare is becoming more personalized, accurate, and responsive, transforming how we approach patient care and medical decision-making.
A major advantage of AI/ML in SaMD is its potential to support clinical decision-making and reduce human error, particularly in time-sensitive or complex scenarios. However, it also brings challenges, such as ensuring data quality, algorithm transparency, regulatory compliance, and managing the lifecycle of continuously learning models. Regulatory bodies like the FDA and European Medicines Agency are evolving their frameworks to accommodate the unique characteristics of AI/ML-enabled SaMD, including the concept of a “predetermined change control plan” to address post-market algorithm updates. Overall, AI/ML integration in SaMD is a transformative step in digital health, offering scalable, intelligent solutions that enhance patient outcomes while reshaping traditional healthcare delivery models.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Icotec’s VADER Pedicle System; Terumo BCT’ Reveos Automated Whole Blood Processing System; ...
- Merck’s Remicade; Sanofi, Regeneron set Kevzara; Novartis to sever; Teva puts women’s...
- Edwards’ Sapien 3 with Alterra Prestent; Koios Medical’s breast, thyroid cancer-spotting AI; Line...
- Nitinotes Obtains CE Mark Approval for EndoZip™ System; FDA Grants 510(k) for Meduloc’s Innovativ...
- Bristol Meyers Squibb & AbbVie partner; BioLineRx’s collaboration with MD Anderson Cancer Ce...
Applications of AI/ML in Software as a Medical Device
With the rise of artificial intelligence and machine learning, SaMD has evolved to deliver smarter, more personalized, and efficient healthcare solutions. The integration of AI/ML into SaMD has revolutionized diagnostics, monitoring, treatment support, and decision-making in healthcare.
Disease Diagnosis and Detection
AI/ML-powered SaMD is increasingly used to aid in the early and accurate diagnosis of diseases. These tools analyze large volumes of medical data, including images, genetic data, and electronic health records, to detect patterns that are difficult to detect by humans. The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into Software as a Medical Device is revolutionizing healthcare, particularly in radiology and cardiology.
For Instance, in February 2025, Aidoc, a pioneering leader in clinical AI, received FDA clearance for its computer-aided detection tool (CADt AI) designed to assist in the triage of rib fractures. This AI-driven software functions as an image-processing prescription tool, supporting the prioritization and evaluation of radiological medical images. The clearance applies to an enhanced version of Aidoc’s Rib Fractures triage solution, developed using the company’s advanced CARE1 Foundation Model.
Predictive Analytics and Risk Stratification
AI/ML in SaMD is used to predict the likelihood of future medical events by analyzing patient history, vital signs, and real-time data.
For Instance, in April 2024, Prenosis Inc., an artificial intelligence company enabling precision medicine in acute care, developed an AI-powered SaMD diagnostic tool for sepsis ImmunoScoreTM, which received FDA marketing authorization. The software analyzes 22 diagnostic and predictive parameters using machine learning algorithms to assess a patient’s risk of sepsis within 24 hours. It integrates with electronic health records (EHRs) and is available through Roche’s Navify Algorithm Suite.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Optimization
AI/ML models help tailor treatment plans to individual patients by analyzing genetic, environmental, and lifestyle data. This leads to more effective and safer treatments.
For Instance, in August 2024, the Acumen Assisted Fluid Management (AFM) Software Feature by Edwards Lifesciences, LLC received FDA approval. The AFM software utilizes AI algorithms to optimize fluid management in patients, particularly during surgical procedures. By analyzing real-time hemodynamic data, it supports personalized fluid therapy decisions, enhancing patient outcomes.
Remote Monitoring and Chronic Disease Management
AI/ML in SaMD enables real-time remote patient monitoring and automated alerts, especially for chronic disease management. AI software analyzes data from wearable sensors to detect early signs of diseases.
For Instance, in May 2024, the ASSURE Wearable ECG system from Kestra Medical Technologies, Inc. was approved by the FDA, which utilizes artificial intelligence in its algorithms. The ASSURE Detection Algorithm, specifically, incorporates Adaptive Patient Intelligence, which is a proprietary technology that learns and adapts to a patient’s heart rhythm to filter out noise and improve accuracy.
Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
AI-powered SaMD offers decision support tools to clinicians by analyzing patient data and recommending evidence-based actions. It provides Drug Interaction Alerts and diagnostic Assistance and can suggest treatments in line with the latest clinical guidelines based on patient-specific data.
For Instance, in June 2023, Huma Therapeutics announced that it received FDA Class II clearance for its disease-agnostic Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) platform. This disease-agnostic platform integrates with various external devices (e.g., heart rate monitors, glucose meters) to collect patient data. It hosts AI algorithms that support screening, diagnosis, dosing recommendations, clinical decision-making, and prognostication.
Additionally, AI/ML enables the extraction of high-dimensional features from medical images to create imaging biomarkers, which help in early disease characterization. NLP-based SaMD tools also analyze unstructured clinical notes, patient records, and other textual data for improved insights. Furthermore, AI/ML-powered SaMD applications analyze voice, facial expressions, and usage patterns to monitor and assess mental health conditions.
Moreover, AI/ML in SaMD supports preoperative planning, intraoperative navigation, and postoperative outcome prediction. AI/ML SaMD platforms support the design and management of clinical trials by identifying eligible patients, optimizing protocols, and analyzing outcomes.
Take a plunge into our latest blog, shedding light on how AI is revolutionizing mental health care. Click here to read!
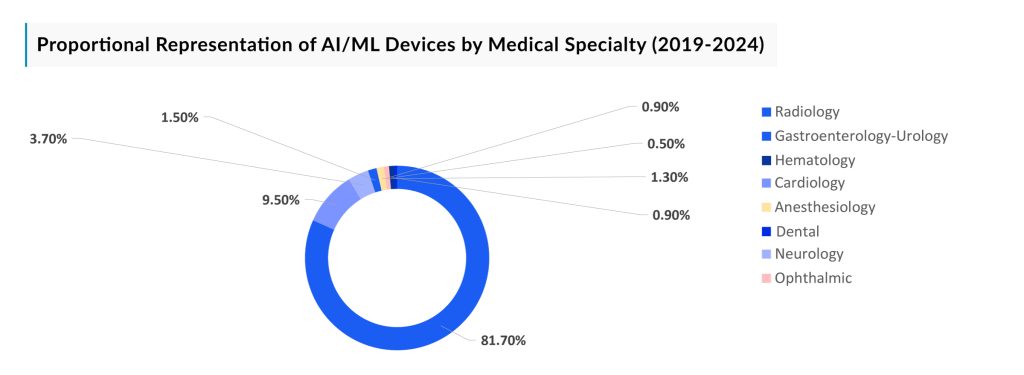
Widespread Adoption of AI/ML in SaMD in Disease Diagnostics
As of 2019 to 2024, there are approximately 699 FDA-approved AI/ML-enabled medical devices in radiology, 81 approved devices in cardiology, 32 for neurology, 13 approved for gastroenterology-urology, 11 approved for anesthesiology, 8 for ophthalmic, 8 for hematology, and 4 for dental.
Regulatory Landscape of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device
The regulatory landscape for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device is evolving rapidly. Regulatory bodies like the FDA, the European Union, and the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) are developing frameworks to ensure the safety and effectiveness of AI/ML-based medical software.
The FDA regulates SaMD through established pathways like:
- 510(k) Premarket Notification
- De Novo Classification
- Premarket Approval (PMA)
Recent Guidance from FDA for AI/ML-Based Software as a Medical Device
As AI and ML technologies reshape healthcare, the FDA is developing guidelines to regulate Software as a Medical Device. These frameworks aim to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and continuous improvement of AI/ML-enabled devices. With a focus on transparency, adaptability, and standardization, the FDA’s initiatives help manufacturers navigate the evolving regulatory landscape. Below is an overview of key regulatory efforts from the FDA.
In January 2025, the FDA issued a draft guidance titled “Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Device Software Functions: Lifecycle Management and Marketing Submission Recommendations” for both industry and FDA staff. This guidance offers specific recommendations to support marketing submissions and lifecycle management of AI-enabled device software functions. Building on earlier FDA efforts, such as those related to Predetermined Change Control Plans (PCCPs) and Good Machine Learning Practices (GMLP), it addresses key considerations unique to AI technologies, including adaptivity and continuous learning. The framework aims to ensure safety, effectiveness, and transparency across the product lifecycle. It also highlights the need for robust premarket planning and postmarket monitoring to manage the evolving risks associated with AI-driven device modifications.
Robust Business Model for Software as a Medical Device
SaMD is regulated software used in digital therapeutics, disease management, and decision support tools. Unlike traditional medical devices, SaMDs have shorter product development cycles, different revenue shapes, and lower investment costs for additional features.
However, they have higher barriers to entry, such as regulatory compliance. SaMDs can target specific populations and access reimbursable markets. For SaMD companies to realize their potential, three critical factors are required: a strong business model, an effective operating model, and building stakeholder trust through clinical results. These factors will help position the companies for long-term success.
Challenges and Considerations in AI/ML-based Software as a Medical Device
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into Software as a Medical Device offers transformative potential for healthcare. However, it also introduces a complex array of challenges and considerations that span technical, regulatory, ethical, and clinical domains.
Data Quality, Bias, and Representativeness
AI/ML models rely heavily on high-quality data for training and validation. However, clinical datasets often contain inaccuracies, missing values, and inconsistencies. Such imperfections can compromise model performance and lead to erroneous clinical decisions. Ensuring data integrity is paramount to developing reliable AI/ML-based SaMDs. Additionally, training datasets that lack diversity can result in models that perform poorly across different populations. For instance, an AI model trained predominantly on data from one demographic may not generalize well to others, leading to disparities in healthcare outcomes. Addressing bias requires deliberate efforts to include diverse and representative data during model development.
For instance, AI-based dermatology apps like SkinVision have shown reduced accuracy for darker skin tones due to non-diverse training datasets that were primarily composed of light-skinned images. This can lead to misdiagnoses or missed detection of conditions such as melanoma in patients with darker skin.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
AI/ML-based SaMDs are susceptible to cybersecurity risks, including unauthorized access, data breaches, and malicious attacks. Such vulnerabilities can compromise patient safety and confidentiality. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential to protect against these threats. Compliance with data privacy regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), is critical. These regulations mandate stringent controls over the collection, storage, and sharing of personal health information. Ensuring adherence to these standards is a fundamental consideration in the development and deployment of AI/ML-based SaMDs.
For Instance, in May 2023, Rotech Healthcare reported that a cybersecurity breach at its partner, Philips Respironics, potentially impacted patient data. An unauthorized third party exploited software to access information stored on Respironics’ server, specifically involving the MOVEit Transfer application used for transferring patient files containing therapy data. The breach was detected in June 2023, and steps were taken to secure systems and investigate the issue.
Clinical Integration and Workflow
Incorporating AI/ML-based SaMDs into existing clinical workflows presents practical challenges. These tools must be compatible with electronic health record systems and align with clinicians’ practices to be effective. Disruptions to established workflows can hinder adoption and utilization. Clinicians require adequate training to effectively use AI/ML-based SaMDs. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of these tools is essential for informed decision-making. Promoting user acceptance involves demonstrating the reliability and benefits of the technology in enhancing patient care.
For Instance, A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) found that only 14% of physicians reported using AI in their clinical practice, citing concerns about accuracy and reliability. Another study published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that 71% of oncologists reported being skeptical about the use of AI in cancer diagnosis and treatment.
Post-Market Surveillance and Lifecycle Management
AI/ML models may experience performance drift over time due to changes in clinical practices or population health trends. Ongoing monitoring and validation are necessary to maintain the accuracy and reliability of these tools in real-world settings. Regular updates to AI/ML-based SaMDs are required to incorporate new data and improve performance. However, each update must be carefully managed to ensure continued compliance with regulatory standards and to prevent unintended consequences.
For Instance, A study at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center evaluated a deep learning model for auto-segmentation in prostate cancer radiotherapy. Trained on data from 2006 to 2011, the model’s performance declined when applied to data from 2012 to 2022, particularly after 2015. Factors contributing to this drift included changes in physician contouring styles, imaging protocols, and the introduction of new clinical practices. This case underscores the need for continuous monitoring and updating of AI models to maintain clinical accuracy.
Future Opportunities of AI/ML-Based Software as a Medical Device
The future of Artificial Intelligence (AI)/Machine Learning (ML)-based Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is filled with vast and transformative opportunities that span across multiple facets of healthcare delivery, diagnostics, treatment, and patient engagement.
We have curated a blog focusing solely on AI in Diagnostics. Click here to learn about the vast field now!
Recent Real-World Examples and Case Studies of AI/ML-Based SaMD Implemented Across Healthcare Domains
- In June 2023, Eko Health, a leader in digital health technology for heart and lung disease detection, launched its next-generation digital stethoscope, CORE 500™, marking over a decade of innovation in digital auscultation. The CORE 500™ featured AI software, high-fidelity audio, a full-color display, and a 3-lead ECG to enhance diagnostic accuracy and early disease detection. Eko’s Sensora platform used AI algorithms to identify conditions like low ejection fraction and heart murmurs during routine exams. In April 2024, Eko received FDA clearance for its low ejection fraction AI algorithm, developed with the Mayo Clinic. In June 2024, the company raised $41 million in Series D funding to expand its AI-based cardiac screening tools globally.
- In December 2024, according to the case study published by PeriGen, at the Area 25 Health Centre in Lilongwe, Malawi, AI-enabled fetal monitoring software developed by PeriGen has been instrumental in reducing stillbirths and neonatal deaths by 82% over three years. The system provides continuous real-time monitoring of fetal vital signs during labor, enabling early detection of distress and timely interventions.
- In June 2024, Sword Health, a Portuguese digital health company, offered AI-driven virtual physical therapy solutions. Their platform included features like ‘Phoenix,’ which uses natural language processing and computer vision to provide real-time feedback during therapy sessions. Clinical studies have shown that their digital therapy achieves outcomes comparable to traditional in-person therapy, with higher engagement rates.
- In April 2021, Empatica’s EmbracePlus, a wearable device, received FDA clearance and CE marking for its health monitoring capabilities. It continuously monitors physiological signals such as pulse rate, skin temperature, and electrodermal activity. It has been used in various applications, including early detection of COVID-19 infections and monitoring astronauts’ health during space missions.
- In March 2023, Nuance Communications, a Microsoft company, announced Dragon Ambient eXperience (DAX™) Express, a fully automated clinical documentation tool that integrates conversational and ambient AI with OpenAI’s GPT-4. Building on the DAX solution launched in 2020, DAX Express marked a major step in reducing clinicians’ administrative burden. It extended the Dragon Medical portfolio and brought advanced AI to over 550,000 users, powered by GPT-4 and Microsoft Azure.
- In October 2024, a case study published by Microsoft elaborated that it developed two AI models, MedImageInsight and MedImageParse, to enhance medical imaging analysis. MedImageInsight assists with image classification, aiding radiologists in quickly identifying abnormalities, while MedImageParse offers detailed image segmentation, helping pinpoint exact locations and characteristics of potential issues within medical images.
Additionally, IDx-DR is an AI-based diagnostic system that uses deep learning to analyze retinal images for signs of diabetic retinopathy. It can detect the condition with high accuracy in just 20 seconds, significantly improving early detection and treatment. IDx-DR is already being used in clinics across the US.
Moreover, Paige is an AI-based diagnostic software that assists pathologists in identifying cancerous tissues with high precision. It uses deep learning algorithms to analyze digital images of tissue samples, improving the accuracy of cancer detection by up to 70% compared to traditional methods.
Key Players that are focused on AI/ML-Enabled Software as a Medical Device
As AI and machine learning continue to reshape the healthcare landscape, numerous companies are leading the way in developing innovative Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) solutions. These technologies are empowering healthcare providers with more accurate diagnostics, streamlined workflows, and improved patient outcomes. Below are some of the key players driving the adoption of AI/ML-enabled SaMD across various medical fields, offering advanced solutions in radiology, cardiology, pathology, and more. Their products are revolutionizing traditional practices and providing new opportunities for more precise and efficient care.
Conclusion: The Evolving Role of AI/ML in SaMD
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning into Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) is revolutionizing the healthcare landscape. These AI/ML-powered solutions are not only enhancing diagnostic accuracy and operational efficiency but are also unlocking new possibilities for personalized medicine. By enabling real-time, adaptive, and data-driven clinical decisions, AI-driven SaMDs are empowering clinicians to deliver more precise, targeted care.
From radiology and cardiology to pathology and remote patient monitoring, these intelligent software solutions are transforming traditional practices, offering scalable tools that enhance patient outcomes. As regulatory frameworks evolve to address the unique challenges of continuously learning algorithms, the future of AI/ML in SaMD hinges on a balance of innovation and accountability. This technological shift is driving the medical industry toward a more predictive, preventive, and participatory model of care, transforming software from a passive tool into an active participant in clinical decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
AI/ML-enabled SaMD refers to standalone medical software that incorporates artificial intelligence or machine learning algorithms to support diagnosis, monitoring, therapy, or decision making—without relying on physical hardware. These systems can analyze complex data (e.g. imaging, EHRs, sensor inputs) to detect patterns, make predictions, or assist clinicians.
Key applications include disease diagnosis and detection, predictive analytics and risk stratification, personalized treatment optimization, remote monitoring of chronic diseases, and clinical decision support systems (CDSS). For example, AI tools help interpret radiology images, forecast disease progression, tailor therapy plans, or alert clinicians to deteriorating patient status.
Regulators like the FDA, EMA, and IMDRF are updating frameworks to manage AI/ML’s unique features, such as continuous learning. The FDA has introduced concepts like a Predetermined Change Control Plan (PCCP) and is embracing a Total Product Lifecycle (TPLC) regulation model for adaptive AI/ML devices.
Challenges include data quality and representativeness (bias), cybersecurity and privacy concerns, integration with clinical workflows, and monitoring algorithm performance over time (model drift). Ensuring transparent, explainable AI and maintaining compliance during updates is also critical.
Future prospects include broader deployment in precision medicine (integrating multi-omics), real-time remote monitoring, digital twins, enhanced clinical decision support, and optimizing drug development and trials. AI/ML-enabled SaMD can become a core component in delivering predictive, preventive, and personalized healthcare.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Medtronic Launches Infusion Set for Insulin Pumps; Penumbra’s Virtual Reality-Based Rehabil...
- Ethicon’s ETHIZIA Hemostatic Sealing Patch; FDA Approves Medtronic’s Minimally Invasive Device to...
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Applications Driving Healthcare Innovation
- What is Cholangiocarcinoma (CCA)?
- FDA Approves Zimmer Biomet’s Oxford® Cementless Partial Knee; ReCerf® Sets Milestone as First All...