Overcoming Adherence Challenges in Growth Hormone Deficiency Treatment: The Promise of Long-Acting and Oral Therapies
Aug 01, 2025
Table of Contents
Growth hormone deficiency (GHD) is a rare condition that arises from inadequate secretion of growth hormone by the anterior pituitary gland. It can originate from birth (congenital), develop later in life (acquired), or occur without a known cause (idiopathic), underscoring the complex mix of genetic, environmental, and diagnostic influences. Idiopathic GHD remains particularly difficult to address due to the absence of clear underlying causes, pointing to gaps in the current understanding of its biological mechanisms.
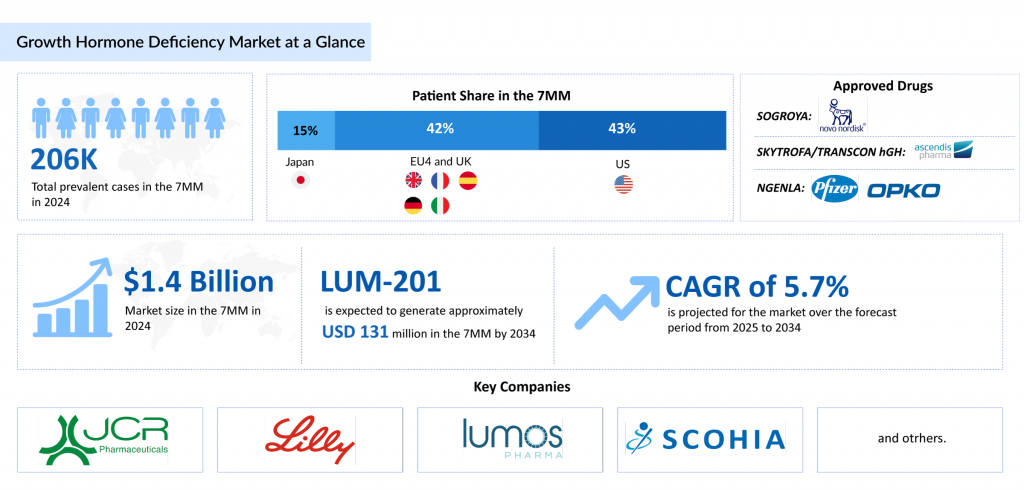
DelveInsight estimated that in 2023, there were approximately 206K prevalent cases of GHD across the 7MM, with around 165K of these being diagnosed. This number is projected to increase by 2034. In 2023, the United States reported the highest number of diagnosed GHD cases among the 7MM, according to DelveInsight. Treatment is personalized, with a focus on the specific needs of each patient. In children, the primary concern is impaired growth, while adults typically face issues such as altered body composition, decreased bone density, and a diminished quality of life.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
SKYTROFA: A Long-Acting Leap in Growth Hormone Therapy
SKYTROFA (lonapegsomatropin-tcgd), also known as TransCon hGH, is a pegylated long-acting human growth hormone developed for once-weekly subcutaneous administration. It is approved in both the U.S. and the European Union for use in pediatric patients aged one year and older, weighing at least 11.5 kg, who have growth failure due to inadequate endogenous growth hormone production. The drug functions by binding to growth hormone receptors on cell surfaces, initiating intracellular signaling pathways that produce direct tissue and metabolic effects, as well as indirect effects via insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1). These effects include stimulating chondrocyte differentiation, increasing liver glucose production, promoting protein synthesis, and driving lipolysis. Regulatory highlights include FDA approval in August 2021 for pediatric growth hormone deficiency and EU authorization in January 2022 for children and adolescents aged 3 to 18 years.
In July 2025, Ascendis Pharma A/S announced that the FDA approved SKYTROFA for treating adults with growth hormone deficiency, expanding its indication to include adult patients. This approval was supported by data from the Phase III foresiGHt trial, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, and open-label study that evaluated the safety and efficacy of once-weekly TransCon hGH versus daily somatropin and placebo in adults with GHD.
From SOGROYA to NGENLA: A Comparative Look at Modern Growth Hormone Deficiency Treatments
The management of growth hormone deficiency is supported by a variety of treatment options designed to accommodate different patient needs. For example, SOGROYA provides a long-acting formulation that reduces the frequency of injections, thereby improving patient convenience. In adults, it functions as a replacement therapy for GHD by binding to dimeric GH receptors on cell membranes, initiating signal transduction pathways and pharmacodynamic effects, many of which are mediated by liver-derived IGF-1. Key regulatory milestones include US FDA approval in August 2020 for adult GHD and April 2023 for pediatric growth failure, EMA approval in March 2021, and PMDA approvals in January 2021 for adults and June 2023 for children with short stature before epiphyseal closure.
Another noteworthy advancement is NGENLA, approved for children aged 3 and older with growth failure. Unlike GENOTROPIN, which requires daily administration, NGENLA allows for once-weekly subcutaneous injections via a customizable delivery device. It acts by binding to GH receptors and activating the STAT5b signaling pathway, ultimately increasing IGF-1 levels to promote linear growth and metabolic effects. It has received approvals in the US, Europe, and Japan for pediatric GHD and is currently undergoing global Phase III evaluation for adult GHD.
Regulatory highlights include US FDA approval in June 2023, EC approval in February 2022, and PMDA clearance in January 2022. In July 2024, OPKO Health entered into a $250 million non-dilutive note purchase agreement with HealthCare Royalty, backed by profit-sharing proceeds from Pfizer as part of their 2014 global partnership.
NGENLA is expected to launch in the US for adult GHD in 2026. It is projected to achieve a peak market share of 7%, reaching its peak in the 9th year post-launch, with a slow-to-medium uptake.
OMNITROPE, a biosimilar, offers a more affordable option while maintaining efficacy. Meanwhile, GROWJECT is favored for its easy-to-use delivery mechanism that simplifies treatment. Established therapies like HUMATROPE and GENOTROPIN remain widely used due to their proven track records in clinical practice. Together, these treatments form a robust portfolio that supports personalized approaches for both children and adults with GHD.
Emerging Therapies for GHD Treatment: A Limited but Promising Pipeline
Despite the proven benefits of approved growth hormone deficiency in stimulating growth and enhancing metabolic outcomes, several limitations remain. Daily injections can hinder adherence, especially among pediatric patients, leading to inconsistent results. Additionally, current formulations often fail to mimic the body’s natural pulsatile GH secretion, potentially affecting downstream biological responses. Other concerns include injection-site discomfort, fluctuations in IGF-1 levels between doses, and the financial burden of lifelong therapy. These challenges underscore an unmet need for more convenient, physiologically aligned, and cost-effective solutions in the treatment of GHD.
The emerging growth hormone deficiency pipeline remains less competitive, with few assets in development, including LUM-201 (Lumos Pharma) and SCO-240 (SCOHIA PHARMA), among others, highlighting an opportunity for innovative therapies to improve patient compliance.
LUM-201 (ibutamoren), being developed by Lumos Pharma, is an oral small molecule drug candidate intended to stimulate the release of growth hormone by activating the growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Unlike conventional therapies that rely on daily injections, LUM-201 provides a more convenient oral alternative for treating pediatric growth hormone deficiency, which may lead to better adherence and enhanced patient experience.
Results from Phase II studies, OraGrowtH210 and OraGrowtH212, have shown encouraging outcomes. A daily dose of 1.6 mg/kg led to an annualized height velocity (AHV) of 8.2 cm at six months and 8.0 cm at 12 months, outcomes comparable to those seen with daily recombinant human growth hormone therapy.
The safety profile observed was favorable, with no serious adverse events linked to treatment and no trial discontinuations due to side effects. The most frequently reported treatment-related side effects were increased appetite, limb pain, and joint pain, which were generally mild and manageable. No significant issues were observed in lab results or ECG readings. These data support moving LUM-201 into Phase III trials to further validate its long-term safety and efficacy.
LUM-201 is expected to launch in the United States in 2028 and is projected to achieve a peak market share of about 13.5% by the seventh year after launch, following a moderate uptake trajectory.
SCO-240, an orally administered small molecule developed by SCOHIA PHARMA, selectively inhibits Somatostatin Receptor 5 (SSTR5), a receptor involved in hormone secretion regulation. While the full function of SSTR5 in humans remains unclear, SCO-240 has demonstrated potential in stimulating growth hormone release.
In a Phase I clinical study, SCO-240 significantly increased GH levels without impacting other pituitary hormones, supporting the therapeutic promise of targeting SSTR5 in GH-related conditions. The drug was well-tolerated, showed a favorable safety profile, and was suitable for once-daily oral administration.
Data from this study were presented in June 2023 at the 96th Annual Congress of the Japan Endocrine Society, emphasizing the compound’s potential in treating GH deficiency and possibly other conditions such as female infertility and alopecia.
In February 2024, SCO-240 was selected for Japan’s Orphan Drug Prior to Designation support program by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), securing funding for further development in pediatric growth hormone deficiency.
The anticipated launch of these emerging therapies are poised to transform the growth hormone deficiency treatment landscape in the coming years. As these cutting-edge therapies continue to mature and gain regulatory approval, they are expected to reshape the growth hormone deficiency treatment landscape, offering new standards of care and unlocking opportunities for medical innovation and economic growth.
What Lies Ahead in the GHD Treatment?
The future of growth hormone deficiency treatment is poised for transformation with the advent of long-acting growth hormone (LAGH) therapies. Traditional daily recombinant human growth hormone (rhGH) injections, while effective, often suffer from poor adherence due to the burden of daily administration, especially in pediatric populations. LAGH formulations, such as somapacitan and lonapegsomatropin, are engineered to maintain therapeutic levels of growth hormone with weekly or even less frequent dosing. These advances not only promise better compliance but may also improve long-term outcomes and quality of life for patients. Moreover, real-world data and post-marketing surveillance will be critical in evaluating their sustained efficacy and safety across diverse patient populations.
DelveInsight estimates that the market size for growth hormone deficiency is expected to grow from USD 1.4 billion in the 7MM in 2024 at a significant 5.7% CAGR by 2034. This growth across the 7MM is expected to be fueled by the launch of novel therapies such as LUM-201 and SCO-240, among others. Additionally, the increasing prevalence, attributed to advancements in diagnostic capabilities, improved survival rates of premature infants, a rise in pituitary disorders, and environmental influences like endocrine-disrupting chemicals, is projected to boost the demand for growth hormone replacement therapies.
Beyond delivery innovations, the future of GHD treatment may also involve more personalized approaches. Advances in genetic screening and biomarker discovery could enable earlier and more precise diagnosis, allowing clinicians to tailor therapy based on individual risk profiles and growth potential. Digital health tools, such as smart injection devices and AI-powered adherence tracking, are likely to be increasingly integrated into care plans, helping clinicians optimize treatment and monitor progress in real-time. Additionally, research into alternative anabolic agents or gene therapy holds potential for curative options, marking a paradigm shift in how GHD is managed over the long term.

Downloads
Article in PDF



