IgG4-Related Disease: A Niche Autoimmune Disorder with Expanding Drug Development Interest
Jun 16, 2025
Table of Contents
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) was first identified as a systemic condition between 2001 and 2003 in a group of Japanese patients. Subsequently, in 2011, Japan’s Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare introduced the first diagnostic criteria for the disease.
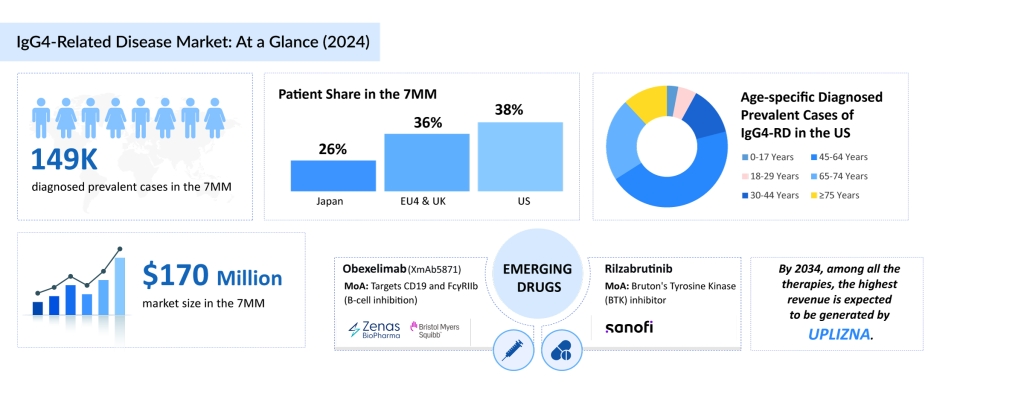
Although specific data on the period prevalence of IgG4-RD in the United States is limited, findings from long-term research at Massachusetts General Hospital led DelveInsight to estimate that approximately 57,000 individuals in the US were diagnosed with IgG4-RD in 2024. This number is projected to rise throughout the forecast period (2025–2034), driven by increased disease awareness from new therapies, a growing elderly population, and improvements in diagnostics, especially in understanding the disease’s pathophysiology and identifying biomarkers.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Notably, about 20–30% of diagnosed patients do not receive systemic treatment, choosing instead either surgical intervention or a watchful waiting approach.
UPLIZNA: First FDA-Approved Therapy for IgG4-RD Treatment
In April 2025, Amgen announced that the FDA had approved UPLIZNA as the first treatment for adults with IgG4-RD. UPLIZNA is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed to selectively and durably deplete CD19+ B cells, including plasmablasts and certain plasma cells, that play a key role in the disease’s progression. While its exact mechanism of action in IgG4-RD remains unclear, the treatment regimen consists of two initial doses followed by maintenance infusions every six months.
UPLIZNA received Breakthrough Therapy Designation from the FDA for IgG4-RD, highlighting both the serious nature of the condition and the urgent need for effective treatments. Its approval is based on findings from the MITIGATE trial, the first randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in this disease, which showed UPLIZNA’s ability to lower disease activity by reducing flares, while maintaining its known safety and efficacy.
This marks the second FDA-approved use for UPLIZNA, which was previously authorized in June 2020 for treating adults with AQP4-IgG+ Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD). The drug has also been granted Orphan Drug Designation for generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG), with regulatory submissions for this indication expected to conclude in the first half of 2025. In 2024, Amgen generated USD 379 million in revenue from UPLIZNA’s use in NMOSD alone. The recent approval for IgG4-RD significantly expands its market potential, as the new indication targets a patient population roughly twice the size of that for NMOSD.
IgG4-RD Treatment Pipeline Highlights: Obexelimab and Rilzabrutinib
The IgG4-RD treatment pipeline possesses some drugs in mid- and late-stage development to be approved in the near future. The emerging IgG4-RD treatment landscape holds a diverse range of therapeutic alternatives for treatment, including obexelimab (XmAb5871) (Zenas BioPharma and Bristol Myers Squibb) and rilzabrutinib (Sanofi). Among these emerging therapies, obexelimab has a promising potential to compete with UPLIZNA.
Obexelimab (XmAb5871) is a dual-function monoclonal antibody that targets both CD19 and FcγRIIb, markers commonly found on B cells. Its mechanism allows it to suppress B-cell activity, key drivers in numerous autoimmune disorders, without depleting these cells. The therapy’s novel action and self-administered subcutaneous (SC) dosing approach offer promising potential for effectively managing chronic autoimmune diseases driven by B-cell dysregulation.
In November 2024, Zenas BioPharma announced that it had completed targeted enrollment for its Phase III INDIGO trial, evaluating obexelimab in patients with IgG4-RD. The company expects to release topline results from the study by the end of 2025.
Rilzabrutinib is an oral, reversible, covalent inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK). It is being developed as a potential first- or best-in-class therapy for a range of immune-mediated conditions. BTK is a key signaling molecule in B cells, mast cells, and other innate immune cells, playing a vital role in driving inflammatory and autoimmune responses.
In its Q4 2024 update, Sanofi reported that the Phase II trial of rilzabrutinib demonstrated significant efficacy in reducing disease flares and minimizing the need for glucocorticoids. Previously, in September 2020, Sanofi completed the acquisition of Principia Biopharma for USD 100 per share in cash, strengthening its immunology pipeline with rilzabrutinib and other assets.
The expected launch of these IgG4-RD therapies shall further create a positive impact on the IgG4-RD treatment market.
Recent Developments in IgG4-RD Treatment Space
- In April 2025, Amgen announced that the FDA had approved UPLIZNA as the first and only treatment for adults living with IgG4-RD.
- In March 2025, Zenas BioPharma announced that the company anticipates reporting topline results for the INDIGO trial by the end of 2025.
- In November 2024, Amgen presented new data at the annual American College of Rheumatology (ACR) Convergence 2024, demonstrating a significant reduction in disease activity in patients with IgG4-RD following treatment with UPLIZNA.
- In August 2024, Amgen announced that the US FDA had granted Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) to UPLIZNA for the treatment of IgG4-RD based on data from the MITIGATE study.
Roadblocks in IgG4-RD Treatment
The approval of UPZILNA represents a breakthrough for the IgG4-RD market, becoming the first authorized treatment for this previously neglected disease. This milestone is expected to reshape the therapeutic landscape, boost diagnostic rates, and influence commercial strategies through pricing and physician uptake. Nevertheless, its long-term success will depend on factors like market awareness, real-world evidence, and emerging competition.
Patients may face higher out-of-pocket costs for IV-administered treatments like inebilizumab under Medicare Part B, which covers outpatient services, compared to oral or subcutaneous drugs under Medicare Part D. This could position obexelimab as a more cost-effective option.
Regulatory challenges remain, as there are no well-defined endpoints or precedents for IgG4-RD trials, adding uncertainty to future approvals. Furthermore, payers may hesitate to reimburse expensive biologics, particularly if off-label rituximab continues to offer a cheaper alternative, though this is not a concern in Japan, where rituximab is not approved for IgG4-RD due to insurance limitations.
Future of IgG4-RD Treatment Looks Promising
The future of IgG4-related disease treatment is increasingly optimistic, marked by the first FDA-approved therapy, UPLIZNA, setting a new precedent. This milestone not only validates IgG4-RD as a serious, distinct clinical entity but also opens the door for broader therapeutic innovation. The approval is expected to accelerate disease recognition, refine diagnostic pathways, and encourage earlier intervention, ultimately improving long-term outcomes. Moreover, as more real-world evidence emerges from inebilizumab use, it could guide more personalized and effective treatment regimens.
The total IgG4-RD market size in the 7MM was estimated to be nearly USD 170 million in 2024, and it is expected to grow positively by 2034. This change is mainly due to the increase in prevalence and the launch of upcoming therapies during the forecast period.
Looking ahead, the treatment landscape is poised for significant evolution. A wave of investigational agents, ranging from other B-cell depleting therapies to novel immune-modulating biologics, is under exploration, promising to expand options beyond corticosteroids and traditional immunosuppressants. Additionally, advances in biomarker discovery and precision medicine may enable better stratification of patients by disease activity, risk of relapse, or organ involvement, ensuring tailored approaches. As research deepens and awareness grows, the future of IgG4-RD care appears increasingly comprehensive and patient-centric.

Downloads
Article in PDF