Is Parainfluenza Virus Contagious?
Jul 30, 2025
Table of Contents
Viral infections remain among the most disruptive public health challenges worldwide, impairing daily life, straining healthcare systems, and contributing to substantial morbidity and mortality. While many viral illnesses are self-limiting, others, such as influenza, viral pneumonia in children, and hepatitis, collectively account for over 1,000 deaths annually on a global scale.
Among these, respiratory viral infections are the most pervasive, affecting individuals across all age groups. Common culprits include influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), human parainfluenza virus (HPIV), adenovirus, and rhinovirus. These viruses are primarily responsible for flu-like symptoms and cold-related illnesses.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
Parainfluenza virus, in particular, is a significant respiratory pathogen. It affects both the upper and lower respiratory tracts, especially in infants, toddlers, and immunocompromised individuals. Understanding the parainfluenza incubation period and its contagious window is crucial, as it spreads easily via respiratory droplets and surfaces. Seasonal spikes in infection are commonly observed during the fall and spring.
According to the National Health Interview Survey by the National Center for Health Statistics, the common cold virus alone causes 35.6 acute illnesses per 100 individuals annually. Additionally, influenza and other respiratory infections account for nearly one-third of all physician visits in the United States. Importantly, parainfluenza virus infections represent about 6.8% of pediatric visits globally, reflecting a substantial clinical and economic burden.
As respiratory viruses continue to evolve and resurface, there is an increasing need for effective parainfluenza treatments, better diagnostic capabilities, and targeted research investments to address unmet needs in the growing parainfluenza virus infection market.
What is Parainfluenza?
Human parainfluenza viruses (HPIVs) are a group of organisms known to cause a variety of respiratory illnesses ranging from mild cold-like symptoms to severe lower respiratory infections. Common conditions caused by parainfluenza include croup, an inflammation of the larynx and trachea that leads to breathing difficulty, as well as pneumonia and bronchiolitis, particularly in children, where the symptoms tend to be more severe. These parainfluenza organisms are classified into four distinct subtypes based on their genetic and antigenic properties.
Typically, parainfluenza virus infections occur in early childhood and, although the fatality rate is relatively low, the virus can lead to repeated infections throughout life. To better understand the parainfluenza incubation period and reinfection dynamics, healthcare providers often rely on diagnostic testing. The incubation period of parainfluenza generally ranges from 2 to 6 days.
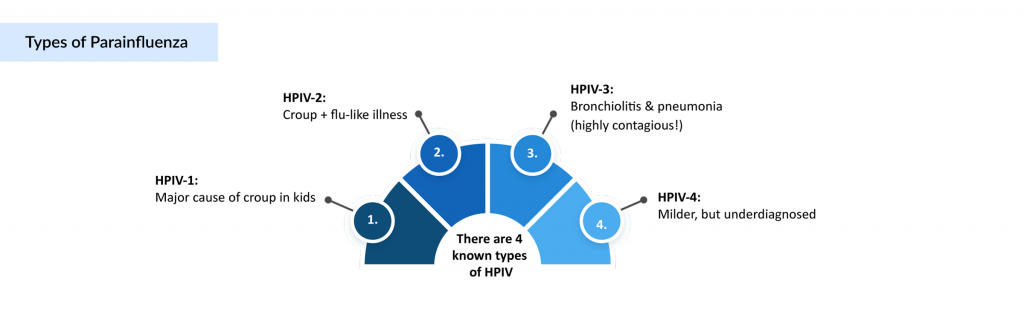
The parainfluenza virus contagious period depends on various factors, but parainfluenza is contagious even before symptoms become evident. Transmission usually happens through direct contact with an infected person, airborne respiratory droplets, or touching contaminated surfaces and then transferring the virus to the nose or mouth. This highlights why understanding how long parainfluenza is contagious and implementing early parainfluenza treatment are crucial steps in managing its spread. For instance, parainfluenza 3, one of the more common types, is notably transmissible, making it vital to track the parainfluenza 3 contagious period, especially during seasonal peaks.
Parainfluenza Viruses Infection Market
The parainfluenza virus infection market is evolving steadily, driven by advancements in diagnosis, rising awareness, and the anticipated launch of novel therapies. According to recent estimates, there were approximately 2.7 million incident cases of parainfluenza virus infection in 2023 across the 7MM (US, EU4, UK, and Japan). The United States alone accounted for over 1.45 million cases, followed by EU4 and the UK, which reported more than 990,000 combined cases. Within Europe, Spain recorded the highest burden, while the UK had the lowest reported incidence.
Parainfluenza, which is indeed contagious, spreads primarily via respiratory droplets and direct contact, particularly among children and immunocompromised individuals. The incubation period for parainfluenza typically ranges from 2 to 6 days, and understanding how long parainfluenza is contagious plays a key role in infection control. Recurrent infections are common due to the absence of long-term immunity and the circulation of multiple subtypes, including parainfluenza 1, 2, 3, and 4. Awareness around how contagious parainfluenza is, especially in adults, is increasingly essential as the virus continues to impact public health systems globally.
From a market standpoint, the Parainfluenza Virus Infection Drugs Market across the 7MM reached approximately USD 259 million in 2023, primarily comprising standard-of-care treatments. The US dominated the market, accounting for around 68% of the total share, followed by EU4 and the UK, which jointly held about 23%. Japan, the second-largest market after the US, is also projected to see substantial growth through 2034.
Pipeline development remains a focal point, with key players like Ansun Biopharma and AlloVir advancing investigational therapies aimed at improving parainfluenza treatment outcomes. Their ongoing R&D efforts are expected to boost the parainfluenza virus infection market size significantly in the coming years, especially as the demand grows for antiviral agents that address the recurring and often severe nature of human parainfluenza virus infections.
Parainfluenza Virus Infection – Unmet Needs
Despite the ongoing burden of illness caused by PIVs, there is currently no approved vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for these infections. The vast majority of cases rely on supportive care, and effective pharmaceutical interventions remain elusive. For croup associated with HPIV-1 or HPIV-2, corticosteroids have demonstrated benefit, but these are limited in scope and do not offer direct antiviral action.
Promising candidates such as DAS181 are under clinical development, showing potential in treating severe infections in high-risk groups. Ribavirin is occasionally administered off-label due to its in vitro activity, but its clinical utility remains controversial due to inconsistent results and a lack of randomized controlled trial data.
Additionally, live-attenuated intranasal vaccines are being explored using reverse genetics platforms for HPIV-1, -2, and -3, which may offer future prevention options in both children and adults. However, these candidates are still in the early stages of development.
Beyond therapeutics, enhanced genetic surveillance and virological monitoring are also pressing needs. These tools would not only improve outbreak detection but also support more precise targeting of vaccine and drug development.
The lack of standardized, approved therapies and the slow pace of clinical progress highlight the substantial unmet need for both prophylactic and curative solutions in this space.
Conclusion
Parainfluenza virus infections represent a clear and urgent opportunity for innovation in infectious disease care. The current reliance on symptomatic management underscores a major therapeutic gap, particularly for vulnerable populations. While investigational candidates like DAS181 and novel intranasal vaccines offer hope, the road to regulatory approval and widespread access remains long.
Investment in research, coupled with enhanced genomic surveillance and public health awareness, is essential to accelerate the development of effective antiviral drugs and vaccines. Bridging this unmet need would not only improve clinical outcomes but also unlock substantial commercial value in a market currently defined by limited treatment options and high clinical burden.

Downloads
Article in PDF