Emerging Therapies for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Treatment: The Road to Progress
Nov 03, 2023
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a rare genetic disorder caused by mutations in cholesterol trafficking proteins. There are two main types, with Type C1 being the most prevalent, accounting for around 95% of cases. While specific epidemiological data on NPC is limited, estimates suggest a prevalence of approximately 1 in 150,000 live births in Western Europe, based on cases identified over a 15-year period in France, Germany, and the UK.
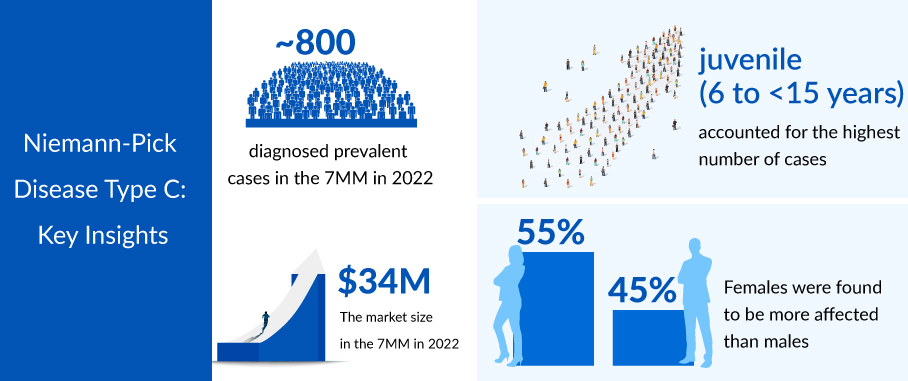
As per the assessment done by DelveInsight, there were 787 diagnosed prevalent cases of Niemann–Pick Disease Type C estimated to have occurred in the 7MM in 2022, of which 335 of the accounted cases were estimated to be from the US alone, and these cases are anticipated to increase during the forecast period. The diagnosed prevalent Niemann–Pick Disease Type C (NPC) cases were divided into gender-specific cases. The Gender-specific diagnosed prevalent cases of NPC are categorized into Males and Females, with 354 and 433 cases, respectively, in the 7MM in 2022, which will increase by 2032.
Managing NPC involves a multidisciplinary approach. A team of specialists, including pediatricians, neurologists, ophthalmologists, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists, and other healthcare experts, collaborates to develop a comprehensive treatment plan for affected children. It’s also vital to provide psychosocial support to the entire family. Genetic counseling can provide valuable insights for both patients and their families. While there is no cure for NPC, palliative treatments can significantly improve the quality of life. Occupational therapy aids in addressing issues related to posture, speech, and movement, and physical therapy plays a crucial role in maintaining mobility for as long as possible.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
ZAVESCA/BRAZAVES: The Only Approved Therapy for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Treatment
In Europe and Japan, ZAVESCA/BRAZAVES (miglustat) manufactured by Actelion Pharmaceuticals stands as the primary approved therapy for addressing NPC, a rare genetic disorder. Despite its approval in these regions, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) declined its approval for NPC treatment, citing inadequate supporting data. The FDA requested additional information, a process that could potentially take years due to limitations in patient recruitment for trials, making it challenging to meet the rigorous standards set by the FDA.
While the FDA hasn’t granted specific approval for NPC, ZAVESCA/BRAZAVES is approved for managing Gaucher’s disease in the US. Consequently, healthcare practitioners sometimes prescribe this drug off-label to NPC patients. Miglustat operates by impeding the synthesis of glycosphingolipids, a substance that accumulates in the brains of those with NPC. It’s known to decelerate the progression of neurological symptoms associated with the condition. However, it’s important to note that this treatment might not be suitable for every individual affected by NPC.
As per specialists, ZAVESCA is being administered to approximately 50% of individuals affected by Niemann-Pick Disease Type C. Miglustat has provided a beacon of hope in addressing the absence of specific therapies for the condition for an extended period.
Pipeline Therapies for Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Treatment
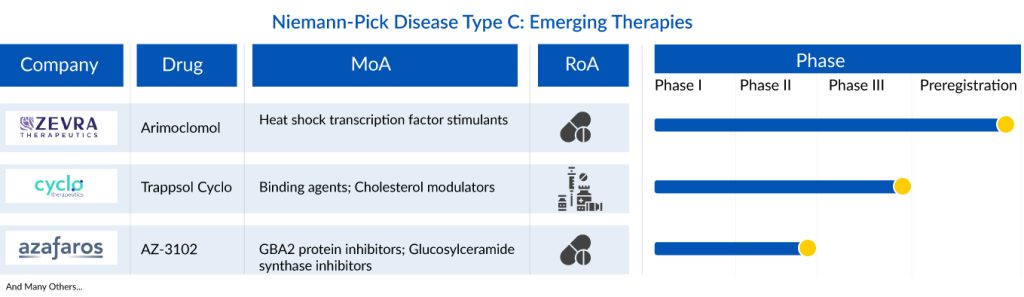
Currently, four promising therapies are in the Niemann-Pick Disease Type C pipeline: Arimoclomol by Zevra Therapeutics, AZ-3102 by Azafaros A.G., Trappsol(R) Cyclo or Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin by Cyclo Therapeutics, Inc., and IB1001 by IntraBio. These innovative therapies hold the potential to bring much-needed relief to patients and may have a substantial impact on the Niemann-Pick Disease Type C treatment market landscape in the seven major markets over the forecast period from 2023 to 2032, given the absence of approved treatments.
Trappsol Cyclo being developed by Cyclo Therapeutics is a proprietary formulation of hydroxypropyl betacyclodextrin and in multiple clinical studies has shown encouraging results to effectively manage the transportation of cholesterol. Taking the place of the defective NPC1 protein, Trappsol Cyclo, with its cyclic structure, captures cholesterol within the cell and transports it out of the cell. The drug is currently being evaluated in Phase III TransportNPC pivotal trial in pediatric and adult patients with NPC1. Enrollment is anticipated to be completed by year-end 2023. It is an Orphan drug-designated product in the US and Europe. It has also received Rare Pediatric Disease Designation, and Fasttrack designation by the US FDA for the treatment of NPC. Recently, the company announced the results of Phase II trial, wherein it demonstrated a favorable benefit-risk ratio, and a change in cholesterol homeostasis in peripheral organs and the brain after the initial infusion
IntraBio’s lead drug series, IB1000s, are a set of orally administered, modified amino acids, N-acetyl-leucine, categorized by a well-established safety and tolerability profile. IB1001 (N-acetyl-l-leucine) is being developed for Niemann Pick Disease Type C besides other orphan indications like Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff Disease and inherited Cerebellar Ataxias.
IB1000s have an effect on the normalization of neuronal membrane potential and intracellular ion regulation via calcium channels and have been observed to have symptomatic and neuroprotective properties and disease-modifying potential. IntraBio has been granted Orphan Drug Designations, Rare Pediatric Disease Designations by the US FDA and EC for Niemann Pick Disease Type C treatment, and Fast Track Designation for IB1001 by the FDA for NPC. Recently, IntraBio announced positive pivotal trial results of IB1001 for Niemann-Pick disease type C treatment, and the drug met the primary endpoint, demonstrating improvement in symptoms, functioning, quality of life, and cognition in both pediatric and adult patients with NPC. Based on these positive results, IntraBio plans to file for marketing authorization with IB1001 with the FDA and EMA.
Arimoclomol is being developed by Zevra Therapeutics, is an orally-delivered, first-in-class investigational product candidate for NPC. KemPharm, now known as Zevra, acquired arimoclomol from Orphazyme. It has been granted orphan drug designation, by both the US FDA and the EMA and fast track designation, and rare pediatric disease designation and breakthrough therapy designation by the US FDA. Orphazyme received a Complete Response Letter (CRL) from the US FDA in 2021, regarding NDA for arimoclomol for the treatment of NPC. Zevra plans on resubmitting of New Drug Application (NDA) to the US FDA as early as Q3 2023 and is advancing activities to bolster NDA with confirmatory evidence.
AZ-3102 is being developed by Azafaros for the treatment of NPC. It is an orally available azasugar with a unique dual mode of action, developed as a potential treatment for rare lysosomal storage disorders with neurological involvement. The drug has been granted Fast Track Designation and Orphan Drug Designations by the US FDA for Niemann-Pick disease Type C treatment. In January 2023 the company received IND approval and is currently conducting Phase II RAINBOW trial to evaluate the safety and pharmacokinetic profile in NPC patients. In June 2023, the first patient was enrolled in its RAINBOW study, to evaluate safety in patients with GM2 gangliosidosis and Niemann-Pick disease type C.
Niemann-Pick Disease Type C Treatment Market Looks Promising
Before the approval of ZAVESCA, only symptomatic therapies were used for the treatment of neurological manifestations, psychiatric manifestations, and visceral manifestations associated with NPC. There are several Niemann-Pick Disease Type C clinical trials currently taking place investigating new therapeutic options for patients with NPC. With the advancement in the development of novel drug candidates by various pharmaceutical companies, the dynamics of the Niemann-Pick Disease Type C treatment market are anticipated to change in the coming years owing to the expected launch of emerging therapies during the forecast period of 2023–2032.
As per DelveInsight analysis, the total Niemann-Pick Disease Type C market size in the 7MM was approximately USD 34 million in 2022 and is projected to increase during the forecast period (2023–2032). The Niemann–Pick Disease Type C market size in the 7MM will increase at a CAGR of about 11.79% due to the advancing treatment landscape.
Moreover, recent breakthroughs in gene therapy, enzyme replacement therapy, and small molecule drugs have opened up new avenues for potential treatments. With increased awareness, improved diagnostics, and collaborative efforts among researchers, the future Niemann-Pick Disease Type C treatment market is expected to expand. As more therapies enter clinical trials and receive regulatory approval, patients and their families can look forward to a brighter and more hopeful future in the management and treatment of this rare disease. The continued investment in research and development in this field is likely to shape a more robust and comprehensive Niemann-Pick Disease Type C treatment market.




