Therapeutic Innovation in Sarcopenia Treatment: From TNF-alpha Inhibitors to GLP-1 Agonists
Jul 28, 2025
Table of Contents
Sarcopenia, often dubbed the “silent muscle thief,” is a progressive loss of skeletal muscle mass and strength that typically begins after the age of 30, accelerating after 60. Affecting up to 50% of adults over 80, sarcopenia isn’t just about frailty—it’s linked to increased risks of falls, fractures, loss of independence, and even mortality. With global populations aging rapidly, sarcopenia has emerged as a major yet underrecognized public health challenge.
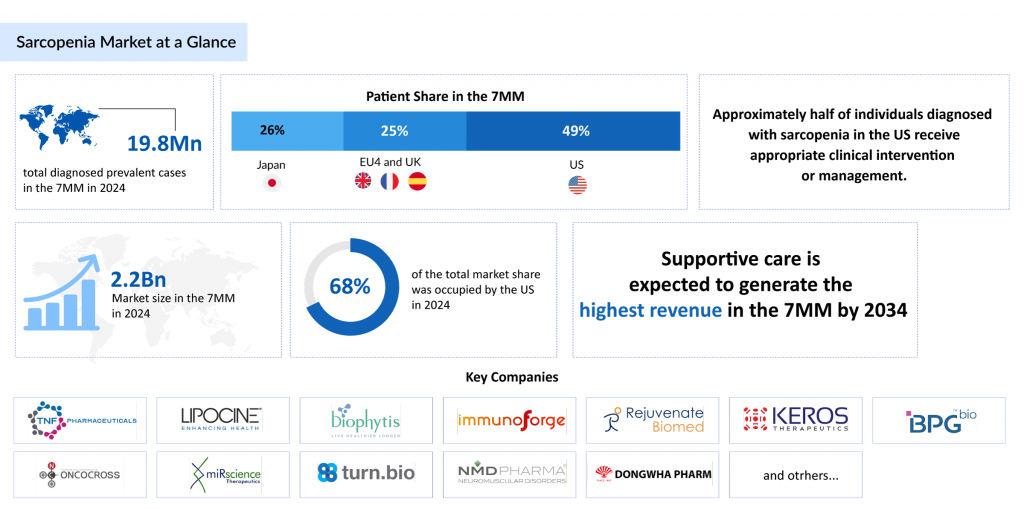
The sarcopenia prevalence ranges from 18% in diabetic patients to 66% in patients with unresectable esophageal cancer. Additionally, sarcopenia is highly prevalent in patients with liver cirrhosis and is associated with adverse clinical outcomes, affecting approximately 40% of individuals with the condition. According to DelveInsight analysis, the total diagnosed prevalent cases of sarcopenia in the 7MM were 19.8 million cases in 2024, and this number is forecasted to climb at a significant CAGR in the study period (2020–2034). Based on severity, sarcopenia cases are classified as mild to moderate and severe, with mild to moderate cases accounting for the highest number of patients in the US in 2024.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- The Next Wave in Sarcopenia Drug Development: 5 Therapies to Look Out
- FDA Grants Priority Review for Zolbetuximab BLA; FDA Traditional Approval for LEQEMBI for Alzheim...
- FDA Expands SOLIRIS for Pediatric Myasthenia Gravis; vTv’s Cadisegliatin Program Resumes as FDA L...
- Sarcopenia: “Aging-Associated Strength Loss Condition”
These cases are expected to increase during the forecast period (2025−2034) due to rising populations, improved diagnostic methods, changes in lifestyle and environmental factors, and advancements in medical technology, which enable better treatment. Despite its prevalence, awareness and diagnosis remain low, making it a pressing target for preventive and therapeutic innovation.
Current Landscape of Sarcopenia Treatment: Gaps and Opportunities
The primary aim of sarcopenia treatment is to improve muscle strength, increase muscle mass, and enhance physical function, thereby improving quality of life and reducing the likelihood of falls and related injuries. Current approaches mainly involve resistance training, dietary strategies emphasizing adequate protein and vitamin D intake, and encouraging regular physical activity while limiting sedentary behavior.
Since the underlying causes of sarcopenia are not yet fully understood and no universally effective treatment exists, ongoing research is focused on uncovering its mechanisms and developing more effective therapeutic options. Presently, prevention and sarcopenia treatment strategies largely rely on lifestyle modifications, which highlights a substantial gap in medical therapies and the urgent need for safe and effective treatment solutions.
To support musculoskeletal health, healthcare providers may recommend appropriate protein-rich diets, nutritional support, vitamin D supplementation, and in certain cases, hormone replacement therapy to correct hormonal imbalances. Although steroid hormones like dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), testosterone, and anabolic steroids have shown some benefits, their use is restricted due to potential side effects.
At present, there are no approved pharmacological treatments for sarcopenia, but active research continues to explore promising drug candidates.
Advancements in Sarcopenia Therapeutics: A Diverse Pipeline of Novel Mechanisms
Leading pharma companies developing sarcopenia therapies to improve the treatment landscape include TNF Pharmaceuticals (MYMD-1/Isomyosamine) (TNF-alpha inhibitors), Biophytis (Sarconeos) (Proto-oncogene protein c-MAS-1 agonists), and Lipocine (LPCN 1148) (androgen receptor agonist). Additionally, companies working on early-phase sarcopenia treatment drugs include ImmunoForge (Froniglutide) (Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist), Keros Therapeutics (KER-065) (Target ActRIIB-Fc), BPGbio (BPM 31510) (Targets aerobic glycolytic pathway), and others with their candidates in different stages of clinical development.
TNF-alpha inhibitors may offer therapeutic benefits for sarcopenia by addressing key drivers of muscle loss. These agents primarily work by suppressing inflammation, as TNF-alpha is a key pro-inflammatory cytokine known to accelerate muscle degradation. By blocking TNF-alpha activity, the inhibitors can help reduce inflammation and thereby slow muscle wasting. Furthermore, they can mitigate muscle atrophy by interfering with the catabolic effects of TNF-alpha and may also prevent pyroptosis, an inflammation-induced form of cell death that damages muscle tissue. Overall, TNF-alpha inhibitors hold potential in slowing sarcopenia progression, particularly in cases where inflammation is a major contributing factor.
Androgen receptor agonists help combat sarcopenia by stimulating androgen receptors in muscle tissue, which are essential for promoting muscle mass and strength. These drugs mimic the effects of natural androgens like testosterone, enhancing muscle protein synthesis and supporting the maintenance and growth of muscle. By activating these receptors, they can help improve muscle strength, reduce further muscle degradation, and enhance functional capacity, especially in older adults experiencing age-related declines in testosterone. This makes androgen receptor agonists a promising strategy for treating muscle loss associated with sarcopenia.
As awareness rises and new therapies emerge, the sarcopenia treatment market is set for expansion, with innovative treatments and combination therapies advancing in clinical development to address unmet needs.
Recent Developments in Sarcopenia Treatment Space
- In January 2025, TNF Pharmaceuticals announced that it had achieved a key safety data milestone supporting expanded and longer-term clinical studies of isomyosamine in multiple indications.
- In December 2024, the US FDA granted Fast Track Designation (FTD) to LPCN 1148 as a treatment for sarcopenia in patients with decompensated cirrhosis.
- In December 2024, TNF Pharmaceuticals presented positive top-line results from a Phase IIa study of its lead drug candidate MYMD-1 at a prestigious international congress of global experts in sarcopenia.
Future of Sarcopenia Treatment Market Looks Promising
The future of the sarcopenia treatment market looks promising, driven by a growing aging population, increased awareness, and advancements in therapeutic research. Sarcopenia, characterized by progressive loss of muscle mass and strength, is becoming a critical public health concern as the global elderly population rises. With no FDA-approved treatments currently available, the unmet need presents a significant opportunity for pharmaceutical and biotech companies. As understanding of the disease’s molecular mechanisms improves, novel therapeutic targets, such as myostatin inhibitors, selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs), and TNF-alpha inhibitors, are under active clinical investigation, promising potential breakthroughs in disease management.
The sarcopenia market size shall grow from USD 2.2 billion in 2024 at a CAGR of 8.1% by 2034 due to the launch of upcoming therapies and the increasing cases of sarcopenia. This market is expected to increase at a significant rate due to the development of emerging drugs in different patient segments, including liver cirrhosis, obesity, chronic inflammation, and others.
Additionally, the integration of digital health tools and diagnostics, such as AI-powered muscle mass assessment and wearable technologies, is expected to complement pharmacological interventions by enabling early detection, continuous monitoring, and personalized treatment approaches. Governments and regulatory agencies are also supporting research through funding and fast-track designations for promising therapies. As clinical pipelines mature and health systems recognize sarcopenia as a distinct condition, the market is poised for robust growth over the next decade, with potential to shift from supportive care to disease-modifying therapies.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- The Next Wave in Sarcopenia Drug Development: 5 Therapies to Look Out
- Sarcopenia: “Aging-Associated Strength Loss Condition”
- FDA Grants Priority Review for Zolbetuximab BLA; FDA Traditional Approval for LEQEMBI for Alzheim...
- FDA Expands SOLIRIS for Pediatric Myasthenia Gravis; vTv’s Cadisegliatin Program Resumes as FDA L...