Cancer Cachexia Drug Landscape Heats Up with Multiple Assets Advancing—7 Therapies to Watch Out
Jan 16, 2026
Table of Contents
Summary
- Cancer cachexia is a severe, multifactorial wasting syndrome affecting most advanced cancer patients, with no approved therapies in the US or Europe and only ADLUMIZ approved in Japan, underscoring a major unmet need.
- Despite the historical treatment gap, the cancer cachexia pipeline is now rapidly expanding, with multiple novel agents in clinical and preclinical development targeting diverse biological pathways.
- Ponsegromab (Pfizer) is the leading late-stage candidate, a monoclonal antibody that neutralizes GDF-15–GFRAL signaling to shift metabolism from catabolic to anabolic, and has shown positive Phase II results on body weight and related outcomes in cancer cachexia.
- Actimed is advancing S-pindolol benzoate into an IMPACT Phase 2b/3 program, with analysts projecting meaningful market uptake where functional outcomes and appetite gains are key treatment priorities.
- TCMCB07 (Endevica Bio) is a first-in-class peptide melanocortin-3/4 receptor antagonist that crosses the blood–brain barrier to modulate hypothalamic control of appetite and metabolism.
Cancer cachexia stands as one of oncology’s most formidable treatment challenges, a multifactorial wasting syndrome that affects up to 80% of advanced cancer patients, yet remains largely untreated. The treatment landscape for cancer cachexia remains notably underdeveloped. There are no FDA-approved cancer cachexia drugs in the US or Europe, despite an estimated cancer cachexia patient population of 1.4 million across the leading markets in 2024. Regulatory approval is currently limited to Japan’s ADLUMIZ, while the EMA issued a negative opinion due to marginal lean body mass efficacy, lack of functional or quality-of-life benefit, and insufficient safety data. This scarcity of effective, disease-modifying options underscores a critical unmet need for therapies that maintain muscle mass, restore function, and improve survival.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
However, this treatment vacuum is rapidly being filled. A robust and expanding pipeline of investigational drugs is emerging across diverse mechanistic platforms, each promising to address the fundamental pathophysiology of cachexia in ways that traditional supportive care cannot achieve.
Expanding Cancer Cachexia Drug Treatment Landscape
The cancer cachexia treatment pipeline is strong and continues to broaden, with multiple therapies advancing through various stages of development. Notable investigational candidates include ponsegromab (Pfizer), S-pindolol benzoate (Actimed Therapeutics), TCMCB07 (Endevica Bio), Rilogrotug (AVEO Oncology), FDY-8801 (Faraday Pharmaceuticals), GFS202A (GenFleet Therapeutics), EXT418 (Extend Biosciences), and others. Let’s dive deep into the detailed assessment of these 7 emerging cancer cachexia drugs.
Pfizer’s Ponsegromab (PF-06946860)
Among the emerging drug candidates, ponsegromab stands out as the frontrunner. This investigational monoclonal antibody represents a paradigm shift in cachexia treatment by targeting growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15), a pro-inflammatory cytokine that has emerged as a central driver of cancer-induced wasting.
Ponsegromab works by neutralizing circulating GDF-15, effectively blocking its binding to GFRAL (GDNF-family receptor α-like) receptors on neurons in the hypothalamus. By interrupting this signaling pathway, the drug shifts cellular metabolism from a catabolic (tissue-breaking) state to an anabolic (tissue-building) state. This represents a fundamental departure from appetite stimulants used historically.
Pfizer announced positive Phase II results in September 2024 for ponsegromab in cancer cachexia. The trial, which evaluated the drug in patients with non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, or colorectal cancer, met its primary endpoint of change in baseline body weight compared to placebo.
The company anticipates market entry by 2029, with the US representing the primary commercial opportunity given the complete absence of approved therapies in this indication. Market analyses project ponsegromab could capture significant market share, with revenue projections reaching USD 426 million by 2034 in the seven major markets.
Actimed Therapeutics’ S-pindolol Benzoate (ACM-001.1)
While ponsegromab focuses narrowly on GDF-15 inhibition, S-pindolol benzoate (commercially designated as ACM-001.1 or MT-102) represents a fundamentally different therapeutic strategy through simultaneous targeting of multiple cachexia-driving pathways. S-pindolol benzoate is classified as an Anabolic-Catabolic Transforming Agent (ACTA), a first-in-class drug category. Its multimodal pharmacology addresses cachexia through three distinct mechanisms:
- Anti-catabolic effects: Nonselective β-blockade reduces protein breakdown and tissue catabolism
- Pro-anabolic effects: Partial β2 receptor agonism promotes anabolic processes and muscle protein synthesis
- Appetite and fatigue improvement: Central 5-hydroxytryptamine 1a (5-HT1a) antagonism enhances appetite and reduces cancer-related fatigue
This multifaceted approach theoretically addresses the complete pathophysiologic cascade of cachexia rather than targeting a single cytokine.
In December 2024, Actimed Therapeutics published comprehensive pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data from its Phase I bridging study of ACM-001.1 in The Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle. This study compared the pure S-enantiomer (ACM-001.1) with racemic pindolol to support clinical trial advancement.
The company is preparing for a Phase 2b/3 clinical development program designated the IMPACT Programme (Improving Muscle Preserving Function and Cachexia Treatment). The improved stability characteristics of the benzoate salt formulation make ACM-001.1 a practical choice for clinical development, with the established safety profile of the parent racemic pindolol providing additional confidence in tolerability.
DelveInsight’s market analysts project S-pindolol benzoate could capture approximately USD 112 million in the seven major markets by 2034, with particular strength in markets where appetite improvement and functional outcomes are prioritized therapeutic goals.
Endevica Bio’s TCMCB07
TCMCB07 represents an innovative approach to cachexia treatment, bringing peptide-based therapeutics into a space traditionally dominated by small molecules and monoclonal antibodies. TCMCB07 is a melanocortin-3/4 receptor antagonist peptide designed as a first-in-class agent with a remarkable capability: the ability to cross the blood-brain barrier and target central nervous system receptors previously considered inaccessible to therapeutic intervention. By blocking melanocortin-3/4 signaling in the hypothalamus, TCMCB07 modulates both behavioral (appetite) and metabolic responses to chronic disease.
In April 2025, Endevica Bio announced first-patient dosing in a Phase 2 trial designated B07 for cancer cachexia treatment. This represents a bold innovation in trial design, rather than conducting traditional post-diagnosis treatment trials, the B07 trial is prophylactic in nature, enrolling 100 patients with stage IV metastatic colorectal cancer as they initiate chemotherapy.
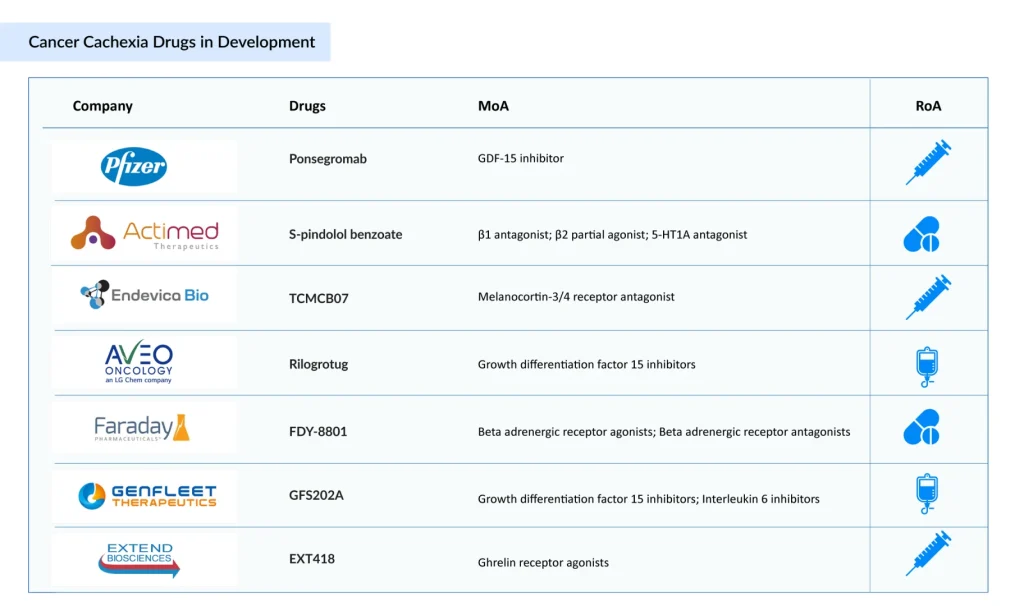
AVEO Oncology’s Rilogrotug (AV-380)
While ponsegromab led the anti-GDF-15 movement, rilogrotug (also known as AV-380), developed by AVEO Oncology (an LG Chem company), represents another potent GDF-15 targeting approach with unique characteristics. Rilogrotug is a humanized inhibitory IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds GDF-15 with exceptionally high affinity and a slow off-rate, resulting in sustained sequestration and elimination of GDF-15 from circulation.
AVEO initiated a Phase 1b ascending-dose study of rilogrotug in cancer patients with cachexia and elevated GDF-15 levels. The Phase 1b trial evaluates rilogrotug in combination with standard-of-care chemotherapy, with dose cohorts ranging from 50 mg to 800 mg administered intravenously.
Faraday Pharmaceuticals’ FDY-8801
FDY-8801 represents Faraday Pharmaceuticals’ dedicated approach to addressing cancer cachexia through a mechanistically distinct therapeutic platform currently progressing through Phase II clinical development. As part of a novel class of agents specifically designed for cachexia intervention, FDY-8801 is being developed with the recognition that cancer cachexia is a debilitating disease characterized by progressive muscle wasting that significantly impairs quality of life and prognostic outcomes for affected patients. The cancer cachexia drug belongs to a category of cachexia-targeting therapeutics that work through pathways independent of single cytokine inhibition, reflecting the company’s understanding that multiple pathophysiologic mechanisms drive the wasting syndrome in cancer patients.
GenFleet Therapeutics’ GFS202A
GFS202A by GenFleet Therapeutics represents a genuinely innovative approach to cancer cachexia treatment through dual pathway targeting—the world’s first bispecific antibody simultaneously addressing both GDF-15 and interleukin-6 (IL-6). In March 2025, China’s National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) approved the clinical trial application for GFS202A, making it the first China-developed GDF-15-targeted therapy to enter cancer cachexia clinical development. This bispecific antibody approach is scientifically compelling because both GDF-15 and IL-6 are significantly overexpressed in cancer cachexia patients and contribute to the disease’s dual pathophysiology, GDF-15 directly suppresses appetite and promotes metabolic dysfunction through GFRAL receptor activation, while IL-6 drives the systemic inflammatory cascade underlying cachexia-associated muscle loss and functional decline.
The dual-targeting rationale behind GFS202A extends beyond simple cachexia treatment. Emerging preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that GDF-15 blockade may overcome immunotherapy resistance by improving T-cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment and enhancing response to checkpoint inhibitors. By simultaneously neutralizing IL-6, a master regulator of cancer-related inflammation, GFS202A aims to address the complete inflammatory milieu driving cachexia while potentially enhancing anti-tumor immunity. The Phase I trial launched in early 2025 will evaluate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of this novel bispecific approach in advanced solid tumor patients with pre-cachexia or cachexia.
Extend Biosciences’ EXT418
EXT418 by Extend Biosciences represents a radically different therapeutic strategy for cancer cachexia, a novel, long-acting constitutively active ghrelin analog enabled by the company’s proprietary D-VITylation™ platform technology. Traditional ghrelin therapy is severely limited by the remarkably short half-life of active (acylated) ghrelin, which remains functional for only approximately 11 minutes in humans, making clinical application impractical.
EXT418 solves this problem through an elegant chemical solution: covalently conjugating a ghrelin peptide to a vitamin D derivative (25-OH-vitamin D3), which associates with the abundant serum vitamin D-binding protein (VDBP) and prevents renal clearance, thereby extending the peptide’s half-life dramatically. Additionally, the compound incorporates a chemical modification that converts the reversible ester linkage of native ghrelin’s acyl group to a stable amide bond, creating a constitutively active ghrelin that resists deacylation and maintains biological activity in vivo.
Preclinical efficacy studies demonstrate that EXT418 effectively mitigates cancer cachexia through multifaceted mechanisms. In Lewis lung carcinoma mouse models, EXT418 administered daily or every other day significantly attenuated tumor-induced anorexia, preserved skeletal muscle fiber cross-sectional area across all fiber types, reduced tumor-induced inflammation (particularly IL-6 and TNF-α elevation), and suppressed pathologic mitophagy and autophagy-related protein degradation, notably achieving these benefits without affecting tumor mass.
The compound works partially independent of food intake, suggesting direct muscle-protective mechanisms beyond appetite stimulation. With efficacy studies completed and IND-ready status achieved, EXT418 represents a promising preclinical candidate poised for clinical development, offering cancer patients a potentially transformative long-acting ghrelin approach that addresses the fundamental anabolic-catabolic imbalance underlying cachexia.
Conclusion
The cancer cachexia therapeutic landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. After decades characterized by therapeutic emptiness and clinical resignation, a robust pipeline of investigational drugs targeting diverse pathophysiologic mechanisms is rapidly advancing through clinical development. Ponsegromab’s encouraging Phase II results have validated the GDF-15 target, while S-pindolol benzoate’s multimodal approach and TCMCB07’s innovative peptide platform demonstrate that multiple successful therapeutic strategies may coexist.
For the estimated 1.4 million patients suffering from cancer cachexia, and for the healthcare systems supporting their care, the emergence of these new options represents genuine therapeutic hope. As these drugs progress through development and toward commercialization, oncology practice will be redefined, from palliation to active treatment of one of cancer’s most debilitating associated conditions. The next few years will be critical as registration-enabling studies progress and late-phase trial data mature, with industry observers, healthcare professionals, and most importantly, patients awaiting these developments with considerable anticipation. For the first time in medical history, cancer cachexia appears poised to become a treatable disease rather than an inevitable companion to advanced malignancy.

Downloads
Article in PDF