Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Market Garners Attention amid the Pandemic Chaos
Dec 09, 2022
Table of Contents
Smell and taste disorders affect an individual’s choice of following a safe and healthy diet. Besides, they also impact food-related behaviors, like enjoying a meal. These disorders impair the ability to sense warning odors in foods and the environment and hinder the quality of life (QoL) related to social interactions, eating, and feelings of well-being. Although they usually represent underlying diseases, they are not life-threatening and are often overlooked by the medical community.
With the onset of the pandemic, the prevalence of COVID-19-related challenges (like olfactory disorders, commonly anosmia and hyposmia) increased rapidly. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions emerged as new symptoms of COVID-19 and were observed more in European patients. Taste disturbances are common in various oral and systemic diseases and were largely reported in COVID-19 patients with varying severity and onset.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- We’re all in this together!
- HCQ/ CQ failure; AZ/ Catalent’s deal; Sinovac’s CoronaVac and Lilly’s Olumiant trial results
- Ocugen-Bharat Biotech’s Covaxin Against B.1.617 Corona Variant; uniQure Shares; J&J Covid Va...
- Pfizer & Lilly’s JAK Inhibitors Drug; FDA Approves Lilly’s Bebtelovimab; GSKR...
- Cerner, Scanwell Health and Personal Genome Diagnostics Acquisition; Zynex’s Fluid Monitori...
According to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD), nearly 1 in every 5 Americans (or 19%) over 40 has a change in their taste. The prevalence of reported changes in taste increases with age, reaching a high of 27% for people aged 80 and up. Almost 1 in every 4 Americans (23%) over the age of 40 reports a change in their sense of smell. Rates rise in older populations, reaching 32% for those over the age of 80.
According to the CDC, approximately 50 million adults in the United States have chronic daily pain, with approximately 20 million adults experiencing high-impact chronic smell and flavor loss that interferes with daily life or work activities, indicating the enormous opportunity in this area.
According to the latest published “Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Epidemiology” report by DelveInsight, there were over 86 million people in the US, approximately 105 million in the EU5, and ~23 million in Japan affected by chronic smell and flavor loss in 2021.
There are few treatments for smell disorders, and proven effective treatments are only available where nasal illnesses cause smell disorders. The emphasis is on surgical treatment (polypectomy, pansinus procedures) and corticosteroid administration. Treatments with corticoids and vitamin A are frequently attempted for the treatment of taste disorders, but there is a lack of convincing clinical studies. The same is true for acupuncture. Only data on the therapeutic effectiveness of zinc gluconate (140 mg/day for 3 months) are available.
Emerging Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Landscape: Scarce Pipeline
The pipeline for chronic smell and flavor loss treatment is relatively dry, with only Cyrano Therapeutics’ CYR-064 in mid to late-stage development. Several chronic smell and flavor loss clinical trials have been halted in the past as primary and secondary outcomes were unfavorable. With new and innovative research approaches, the intent to fill the gaps in scientific knowledge and improve research capacity could facilitate the progress toward potential therapies. The treatment of smell and taste disorders for high yield should be focused on three areas: Increasing awareness and research capacity (e.g., patient advocacy), developing and enhancing clinical measures of taste and smell, and supporting new avenues of research into cellular and therapeutic approaches.
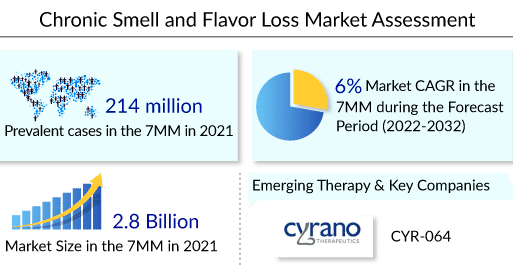
CYR-064: The Only Emerging Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Option with Potential
As per DelveInsight’s analysis, the chronic smell and flavor loss market was valued at approximately USD 2,800 million in 2021 and is expected to reach USD 4,000 million by 2032, at a CAGR of 6%. Cyrano Therapeutics is the only major player in the chronic smell and flavor loss therapeutic space.
CYR-064 compositions comprise phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors formulated for intranasal administration. The major mechanism underlying all pathologies responsible for smell and flavor loss is similar. It involves inhibition of stem cell activation, which usually occurs by the action of adenylyl cyclase III through cAMP and cGMP. It is expected to enter the US market by 2025.
Besides Cyrano, no pharmaceutical company is currently involved in developing an improved version of existing chronic smell and flavor loss treatment options or novel treatment alternatives. However, some chronic smell and flavor loss clinical trials are underway, sponsored mainly by universities and research-based organizations. Growing awareness due to the ongoing COVID-19 crisis and the speculated success of the sole pipeline candidate, in the long run, is expected to impact the chronic smell and flavor loss treatment market landscape in the upcoming years.
The Chronic Smell and Flavor Loss Treatment Market Offers Significant Patient Needs and Commercial Opportunity
The development of disease-specific therapies for chronic smell and flavor loss will auger well for the market landscape, leading to significant changes in the chronic smell and flavor loss treatment market during the forecast period (2019–2032). However, there is room for further research into current healthcare pathways for patients with olfactory disorders and a need for further clinical research to improve the chronic smell and flavor loss treatment options. The low sensitivity of self-reported olfactory impairment suggests that for the vast majority of those affected, individual suffering is insufficient motivation to seek chronic smell and flavor loss treatment.
Moreover, during the pandemic, an increase in the prevalence of COVID-19-related consequences, such as olfactory disorders, prompted a massive research effort among olfactory scientists. This would promote intervention development in the chronic smell and flavor loss treatment market and inform clinical management.

FAQs
Olfactory dysfunction is classified as either quantitative, involving changes in the strength but not the quality of odors, or qualitative, involving changes in the quality of odors. Qualitative disorders, such as parosmia, are frequently associated with negatively perceived changes in smell quality.
A doctor’s diagnosis is required to identify and treat the underlying cause of a potential smell or taste disorder. Physical examination by health care professionals using self-assessment tools, psychophysical assessments, and imaging is used to make a chronic smell and flavor loss diagnosis.
There are few treatments for smell disorders, and proven effective treatments are only available where nasal illnesses cause smell disorders. The emphasis is usually on surgical treatment (polypectomy, pansinus procedures) and corticosteroid administration.
As per the assessment done by DelveInsight, there were over 86 million people in the US, approximately 105 million in the EU5, and ~23 million in Japan affected by chronic smell and flavor loss in 2021.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- LensGen’s Juvene Intraocular Lens; Nevro announces clinical data publications; FDA Clearance to I...
- Is Hydroxychloroquine the answer to all the COVID-19 questions?
- GE and Medtronic’s Collaboration; Vivalink’s Multi-Vital Blood Pressure Patch; Foldax...
- What are Monoclonal Antibodies and How Can They Treat COVID-19?
- Pfizer & Lilly’s JAK Inhibitors Drug; FDA Approves Lilly’s Bebtelovimab; GSKR...



