Cushing’s Disease Treatment: A New Era of Therapeutic Possibilities
Dec 15, 2025
Table of Contents
Cushing’s disease is a rare but serious endocrine disorder caused by a pituitary adenoma that leads to excessive secretion of ACTH. This condition results in abnormally high cortisol levels in the body, causing a cascade of serious health complications. Cushing’s syndrome, the clinical manifestation of this disorder, accounts for 80-85% of all hypercortisolism cases, with Cushing’s disease responsible for 75-80% of these cases. The clinical significance of this condition cannot be overstated, as the estimated 5-year survival rate for untreated Cushing’s disease is only 50%, highlighting the critical need for effective treatments.
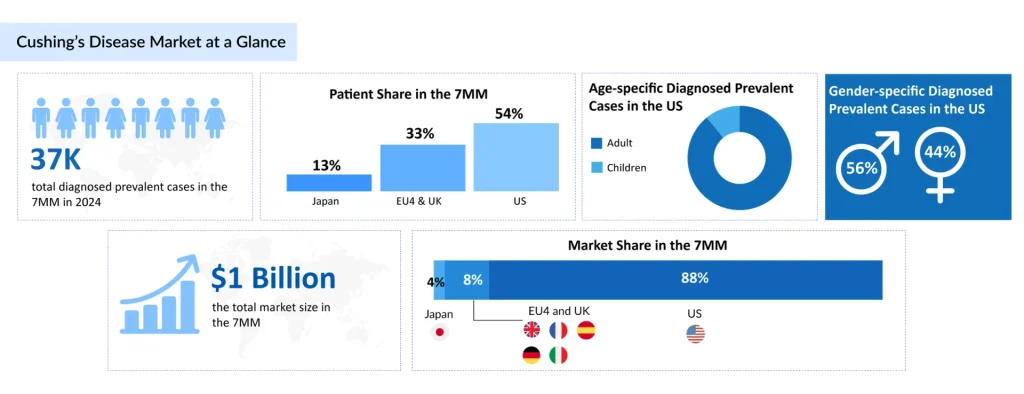
Based on DelveInsight’s 2024 assessment, the 7MM had approximately 37K prevalent cases of Cushing’s disease. These cases are expected to rise due to advancements in diagnostic capabilities and increased awareness about the disease during the forecast period (2025–2034). Only 2.7% of diagnosed cases of Cushing’s disease in Japan in 2024 occurred in children, compared to 97.3% in adults. This reflects a well-established trend, as ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas are significantly rarer in pediatric populations. The adult predominance highlights the disease’s age-related pathophysiology, with hormonal dysregulation and adenoma development most commonly occurring in middle-aged individuals.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
Current Cushing’s Disease Treatment Landscape
Transsphenoidal surgery remains the gold-standard first-line treatment for Cushing’s disease. This minimally invasive surgical approach to remove the pituitary adenoma has achieved high success rates in achieving remission. However, the reality of clinical practice is more complex: some patients experience relapse over time, and surgery may not be feasible or successful for all patients. When surgical intervention is unsuccessful or cannot be performed, medical therapies become essential for managing cortisol levels and improving patient outcomes.
Medical Cushing’s Disease Therapies
When surgery is not viable or effective, several FDA-approved pharmaceutical options are available to manage hypercortisolism.
SIGNIFOR and SIGNIFOR LAR (Recordati)
SIGNIFOR, developed by Recordati, is the first therapy for Cushing’s disease. The drug received FDA approval in 2012, along with concurrent EU approval. This somatostatin analog inhibits ACTH secretion at the pituitary level.
SIGNIFOR LAR represents an advance in the same drug class, offering a long-acting intramuscular formulation that maintains the exact mechanism of action as SIGNIFOR while providing superior convenience. Approved by both the FDA and PMDA in 2018, SIGNIFOR LAR is administered intramuscularly once every 4 weeks, improving patient compliance compared to multiple daily dosing schedules.
ISTURISA (Recordati)
ISTURISA, another product by Recordati, represents an important innovation as the first FDA-approved medicine that blocks the enzyme responsible for cortisol synthesis. Specifically, it inhibits 11β-hydroxylase (CYP11B1)—the enzyme responsible for the final step of cortisol biosynthesis in the adrenal gland.
The oral route of administration of ISTURISA makes it one of the most patient-compliant products, offering greater convenience and ease of use compared to injectable treatments. Clinical efficacy has been substantial: in the Phase III LINC-4 pivotal trial, 86% of ISTURISA-treated patients achieved a complete response (normal mean urinary free cortisol at week 34) compared to only 29% in the placebo group. In the Phase III LINC-3 study, 77% of patients achieved normal UFC levels at week 12, and 81% maintained their response at week 36.
Notably, ISTURISA is the only currently marketed drug expanding its therapeutic scope, with a Phase II trial (NCT03708900) underway to evaluate its use in children and adolescents.
RECORLEV (Xeris Pharmaceuticals)
RECORLEV, developed by Strongbridge Biopharma and subsequently acquired by Xeris Pharmaceuticals, represents one of the latest additions to the approved armamentarium. This drug received FDA approval in 2021 for the treatment of endogenous hypercortisolemia in adult patients with Cushing’s syndrome for whom surgery is not an option or has not been curative.
RECORLEV works uniquely by inhibiting cortisol synthesis at multiple stages of the steroidogenesis pathway, reducing cortisol production in the adrenal glands. This multi-target mechanism distinguishes it from ISTURISA’s single-enzyme inhibition approach.
KORLYM (Corcept Therapeutics)
KORLYM, marketed by Corcept Therapeutics, offers a different therapeutic approach. It is indicated to control hyperglycemia secondary to hypercortisolism in adult patients with endogenous Cushing’s syndrome who have Type 2 diabetes mellitus or glucose intolerance and have failed surgery or are not candidates for surgery. This selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist addresses the metabolic complications of excess cortisol.
Off-Label Medical Cushing’s Disease Therapies
In clinical practice, several off-label treatments continue to play important roles, particularly in the United States. These include ketoconazole, metyrapone, cabergoline, mitotane, and etomidate. While these agents have not received specific FDA approval for Cushing’s disease, they are employed when approved therapies are unavailable or ineffective. In Europe, HRA Pharma markets some of these drugs, providing additional treatment options.
Emerging Cushing’s Disease Therapeutic Options
The treatment landscape for Cushing’s disease is undergoing a significant transformation, with a robust pipeline of emerging Cushing’s disease therapies addressing unmet medical needs.
Corcept Therapeutics’ Relacorilant (CORT125134)
Relacorilant, developed by Corcept Therapeutics, is a selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonist with an unprecedented mechanism of action. Rather than lowering cortisol levels, this novel approach binds selectively to glucocorticoid receptors while avoiding other hormone receptors, effectively blocking cortisol’s harmful effects at the tissue level.
In June 2024, Corcept Therapeutics announced positive results from the Phase III GRACE trial, which demonstrated significant improvements in cortisol-related clinical outcomes, supporting relacorilant’s potential as a nonsurgical treatment option. The FDA has assigned a PDUFA target action date of December 30, 2025, suggesting imminent regulatory approval. Relacorilant received Orphan Drug Designation in May 2019, acknowledging its potential to address this rare disease.

Sparrow Pharmaceuticals’ Clofutriben (SPI-62)
Clofutriben, developed by Sparrow Pharmaceuticals, represents a novel approach to HSD-1 inhibition. This proprietary oral small molecule reduces intracellular cortisol levels and alleviates their harmful effects. The company anticipates initiating a Phase III trial in 2025 for endogenous Cushing’s syndrome. Notably, clofutriben was granted Orphan Drug Designation by the US FDA in October 2024 for the treatment of endogenous Cushing’s syndrome.
Crinetics Pharmaceuticals’ Atumelnant (CRN04894)
Atumelnant, developed by Crinetics Pharmaceuticals, is a potent, once-daily, oral, nonpeptide, selective MC2R antagonist—a first-in-class competitive antagonist that blocks ACTH-mediated signaling at the adrenal cortex. This approach directly addresses the ACTH overproduction driving Cushing’s disease.
In September 2024, Crinetics Pharmaceuticals entered into a Clinical Trial Agreement with the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) to collaborate on a company-sponsored clinical trial in ACTH-Dependent Cushing’s Syndrome. The company anticipates beginning enrollment for Phase Ib/IIa trials in late 2025 or early 2026.
Other Emerging Therapies
Lu AG13909, developed by H. Lundbeck, represents yet another innovative approach as an ACTH-blocking antibody therapy. ST-002, a glucocorticoid receptor antagonist from Stero Therapeutics, is currently in Phase II trials, with the company announcing that the first patient was successfully dosed in June 2025.
Recent Developments in the Cushing’s Disease Treatment Space
- In June 2025, Stero Therapeutics announced that the first patient had been successfully dosed in its ongoing Phase II clinical trial evaluating ST-002 for the treatment of Cushing’s Syndrome.
- In March 2025, Corcept Therapeutics announced that the FDA had assigned a PDUFA target action date of December 30, 2025, for relacorilant to treat patients with endogenous hypercortisolism.
- In February 2025, Crinetics Pharmaceuticals stated that it anticipates beginning enrollment in Phase Ib/IIa trials of Atumelnant (CRN04894) for Cushing’s disease in late 2025 or early 2026.
Cushing’s Disease Market Landscape and Future Directions
The total market size for Cushing’s disease in the 7MM was approximately USD 1 billion in 2024. This market is expected to grow substantially by 2034, driven by extensive market penetration of approved therapies, label expansions, and the entry of new emerging therapies. The US dominates the market with nearly 88% of the total market share in 2024, compared to the EU4 and the UK combined, and Japan.
Cushing’s disease treatment has evolved dramatically, transitioning from limited options to a diverse therapeutic armamentarium encompassing surgery, multiple classes of medical therapies, and promising emerging agents. While transsphenoidal surgery remains the gold standard first-line therapy, the availability of numerous medical options, including SIGNIFOR/SIGNIFOR LAR, ISTURISA, RECORLEV, and KORLYM, provides clinicians with flexibility to individualize treatment approaches based on patient characteristics and needs.
The emerging pipeline represents a paradigm shift in therapeutic strategy, moving beyond traditional cortisol-lowering agents to innovative approaches including selective glucocorticoid receptor antagonism and ACTH pathway blockade. This expanding therapeutic landscape offers hope to patients with Cushing’s disease, particularly those for whom surgery is not feasible or has not achieved remission. As these emerging therapies complete clinical development and gain regulatory approval, the treatment options available to clinicians and patients will continue to expand, further improving outcomes in this rare but serious condition.

Downloads
Article in PDF