Cystinosis Treatment: Transforming a Life-Limiting Disorder into a Manageable Chronic Condition
Feb 02, 2026
Table of Contents
Summary
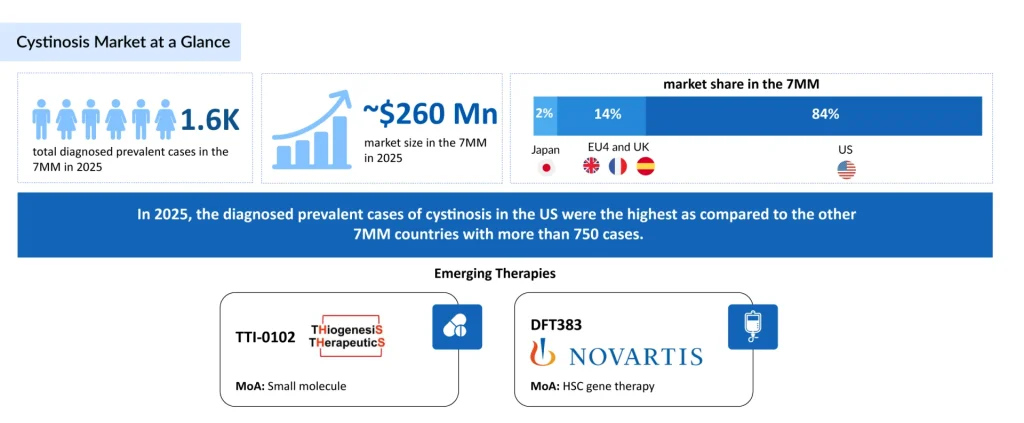
- Approximately 1,600 prevalent cases were diagnosed across the 7MM in 2025, underscoring the condition’s rarity and the concentration of patients at specialized metabolic and nephrology centers.
- Treatment is limited to long-standing cysteamine products, PROCYSBI, CYSTAGON/NICYSTAGON (cysteamine bitartrate), and CYSTADROPS/CYSTARAN (cysteamine hydrochloride). Persistent tolerability issues, high dosing burden, and adherence challenges create a clear unmet need for better therapeutic options.
- Development is progressing with emerging therapies, including TTI-0102, DFT383, and others. This focused pipeline reflects gradual yet meaningful innovation beyond cysteamine-based treatments, signaling momentum toward improved care for a rare multisystem disease with high unmet need.
- The cystinosis market across the 7MM is valued at ~USD 260 million, driven by the lifelong burden of disease, need for continuous long-term therapy, and improved survival, expanding the treated population.
Cystinosis represents one of rare disease medicine’s most transformative success stories. Once a fatal pediatric condition with limited therapeutic options, advances in cystine-depleting therapy have fundamentally altered its trajectory, converting what was historically a severe childhood disease into a manageable chronic condition extending well into adulthood. Despite these significant therapeutic gains, cystinosis continues to pose formidable clinical challenges that require a comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach to care.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
Disease Overview and Burden
Cystinosis is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by pathogenic variants in the CTNS gene, which encodes cystinosin, a critical lysosomal cystine transporter. The defective function of this protein results in progressive intracellular accumulation of cystine, triggering cascading multisystem damage. While renal involvement predominates in the initial clinical presentation, cystinosis ultimately becomes a lifelong condition affecting virtually every organ system, including the kidneys, eyes, muscles, endocrine system, and nervous system.
In 2025, the total number of diagnosed prevalent cases of cystinosis was nearly 1,600 across the 7MM. In 2025, the diagnosed prevalent cases of cystinosis in the US were the highest as compared to the other 7MM countries, with more than 750 cases. These cases are projected to increase by 2036. This expanding patient pool reflects improved diagnostic capabilities, heightened disease awareness among healthcare providers, and, importantly, better survival rates due to effective therapeutic interventions. Earlier diagnosis through advanced genetic testing and increased implementation of newborn screening programs have further contributed to rising case identification.
Current Cystinosis Treatment Landscape
Cysteamine: The Cornerstone of Therapy
For nearly four decades, cysteamine has been the primary pharmacological approach to the management of cystinosis. This small-molecule compound works through a thiol-disulfide interchange reaction within the lysosome: cysteamine reacts with accumulated cystine to form cysteine and cysteamine-cysteine mixed disulfides, both of which can exit the lysosome. By reducing intracellular cystine concentrations, cysteamine slows disease progression, delays renal decline, and mitigates extra-renal complications.
The pharmacokinetics of cysteamine are characterized by rapid absorption following oral administration, with maximum plasma concentration achieved within approximately 1.4 hours. The drug undergoes significant first-pass metabolism and has a relatively short half-life of approximately 3.7 hours, necessitating frequent dosing to maintain therapeutic cystine-depleting effects. Cysteamine is predominantly protein-bound (approximately 52%) and distributed throughout the body, reaching therapeutic concentrations in all affected tissues.
Approved Systemic Formulations
PROCYSBI (cysteamine bitartrate delayed-release capsules) represents a major therapeutic advance. Approved by the FDA in December 2020 and by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2013, PROCYSBI features a delayed-release formulation designed to minimize gastrointestinal irritation while providing sustained drug delivery. The formulation allows twice-daily (every 12-hour) dosing, compared with the four-times-daily regimen required for earlier immediate-release formulations, thereby significantly reducing treatment burden.
Clinical efficacy data from the pivotal Phase III trial (RP103-03) demonstrated noninferiority of PROCYSBI compared with the immediate-release standard, CYSTAGON. The cystinosis clinical trial showed that PROCYSBI maintained white blood cell (WBC) cystine levels at a mean of 0.80 nmol cystine/mg protein at 12 months and 0.74 nmol cystine/mg protein at 18 months, thereby controlling cystine accumulation. Long-term extension studies confirmed that PROCYSBI maintains stable renal function and sustained cystine control for up to four years of therapy.
Beyond the primary endpoint of cystine reduction, PROCYSBI demonstrated significant improvements in quality of life. A comparative analysis with immediate-release cysteamine showed that patients switching to PROCYSBI experienced improvements in social function, school function, and overall function scores that were maintained over two years of continued therapy. The reduced dosing frequency resulted in superior tolerability, with significantly lower rates of gastrointestinal adverse effects, a critical advantage in a patient population requiring lifelong adherence.
CYSTAGON/Nicystagon (cysteamine bitartrate immediate-release capsules) by Viatris remains widely used, particularly in regions where PROCYSBI has not yet achieved market penetration or where cost considerations predominate. The immediate-release formulation requires four-times-daily administration at six-hour intervals, which substantially increases treatment burden and contributes to adherence challenges.
Ocular Formulations
The management of corneal cystine crystal accumulation, a manifestation affecting all cystinosis patients, has evolved significantly. Corneal cystine crystals can cause photophobia (light sensitivity), a foreign body sensation, and progressive visual impairment if left untreated.
CYSTARAN (cysteamine hydrochloride 0.44% ophthalmic solution) was the first FDA-approved topical cysteamine formulation (2012) and originally required hourly application during waking hours. This substantial treatment burden led to limited real-world utilization and variable patient compliance.
CYSTADROPS (cysteamine ophthalmic solution 0.37%) by Recordati and Viatris represents a meaningful clinical improvement, reducing the required application frequency to four times daily. FDA approval came in August 2020, followed by EMA approval in 2021. A significant milestone was reached in April 2025, when the EMA expanded the indication for CYSTADROPS to include infants as young as 6 months of age, recognizing that early intervention in ocular disease provides long-term benefits. CYSTADROPS was also launched in Japan in March 2024, marking the first approved treatment for corneal cystine crystal deposits in that market.
Emerging Cystinosis Therapeutic Approaches
The cystinosis clinical trial landscape reflects recognition of both cysteamine’s limitations and the disease’s fundamental complexity. Emerging therapies target diverse pathogenic mechanisms, with a particular focus on disease modification and reduction of treatment burden.
Gene Therapy: Correcting the Genetic Defect
DFT383 is an experimental gene therapy for nephropathic cystinosis that aims to introduce a working CTNS gene to correct the root cause of cystine buildup in lysosomes. Previously known as AVR-RD-04 or CTNS-RD-04, the therapy originated at AVROBIO before being acquired. DFT383 is now being developed for pediatric patients in a Phase I/II trial, following earlier adult studies conducted under the AVR-RD-04 program.
In May 2023, AVROBIO signed an Asset Purchase Agreement with Novartis, transferring the cystinosis gene therapy program AVR-RD-04 and associated assets for USD 87.5 million, along with granting Novartis exclusive intellectual property rights. In March 2021, the European Commission awarded Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to AVR-RD-04 for the treatment of cystinosis. The therapy has also received ODD status in the United States from the FDA.
The potential of gene therapy lies not only in providing sustained cystine control but in fundamentally altering disease trajectory. Unlike lifelong symptomatic therapy, a successful gene therapy could potentially provide durable disease modification, reducing or eliminating the need for chronic cysteamine administration, with attendant improvements in quality of life.
Advanced Cysteamine Prodrugs
TTI-0102, developed by Thiogenesis Therapeutics, is an oral cysteamine prodrug engineered to overcome the drawbacks of conventional thiol treatments. Its development utilizes the 505(b)(2) regulatory pathway, allowing faster progress by building on existing cysteamine safety and toxicology data. Early findings indicate that TTI-0102 is well tolerated at higher doses while maintaining cysteamine’s dual actions of reducing cystine and providing antioxidant benefits.
In its December 2025 presentation, Thiogenesis announced plans to file an IND in the second half of 2026 to initiate a pivotal Phase III trial for TTI-0102 in cystinosis. Additionally, in November 2025, the company stated that it had broadened the scope of its planned Phase III program for TTI-0102 in nephropathic cystinosis, reaffirming the expectation of an IND submission in 2026 and emphasizing the drug’s aim of improving tolerability and simplifying dosing.
Investigational Small Molecules
Additional candidates at earlier stages of development include BRH101 (Birch Therapeutics) and the cysteamine hydrochloride new delivery system LB202 (Leadiant Biosciences), both in preclinical research. These compounds explore novel delivery formats and formulation approaches designed to improve cystine-depletion efficacy, enhance tolerability, reduce treatment burden, and potentially provide more consistent cystine control compared with current therapies.
Conclusion
Cystinosis treatment has undergone a remarkable transformation over the past four decades. What was once a fatal pediatric disease has become a manageable chronic condition, with many patients now reaching adulthood and beyond. This success reflects the critical importance of early diagnosis, intensive cysteamine-based therapy, multidisciplinary care, and unwavering commitment to treatment adherence.
The market size for cystinosis in the 7MM was approximately USD 260 million in 2025 and is expected to increase by 2036. In 2025, the US had the largest cystinosis market among the 7MM, with ~87% market share.
The 7MM cystinosis market is driven by increased disease recognition, improved diagnostic techniques, and a growing patient base. Demand is further supported by the approval of therapies like CYSTADROPS and the ongoing development of targeted treatments addressing the unmet need in functional improvement and disease progression
However, substantial opportunities for further improvement remain. High treatment burden, persistent extra-renal complications despite optimal cystine control, and the absence of curative therapies continue to limit real-world outcomes. The emerging pipeline, particularly gene therapy approaches such as DFT383 and next-generation cysteamine formulations such as TTI-0102, offers significant promise for addressing these remaining unmet needs.
The coming decade will likely witness a paradigm shift in cystinosis management, moving from purely symptomatic cystine depletion toward potentially curative genetic approaches. Success in these endeavors would represent a watershed moment for a disease that has affected thousands of families worldwide and would provide a template for approaching other monogenic lysosomal storage disorders.

Downloads
Article in PDF