Promising Nephrotic Syndrome Treatments: A Look into the Future
Mar 18, 2024
Table of Contents
Nephrotic syndrome is a clinical condition characterized by significant protein in the urine (exceeding 40 mg/m2/h), leading to low levels of albumin (below 30 g/L), which in turn causes high levels of lipids, swelling, and a range of associated complications.
The epidemiological assessment of nephrotic syndrome plays a pivotal role in understanding the prevalence, distribution, and impact of this renal disorder. To comprehensively evaluate the landscape of nephrotic syndrome, assumptions, and rationales are employed to delineate the primary and secondary glomeruli nephropathies contributing to the overall burden of the syndrome.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- B. Braun’s Introcan Safety 2 IV Catheter; Everly Health’s At-Home Collection Kidney Health Test; ...
- FDA Approves Genentech’s GAZYVA for Lupus Nephritis; Glaukos’ EPIOXA Wins FDA Approval for Kerato...
- Bayer’s New Cardiology Drug Acoramidis; Two Datopotamab Deruxtecan Applications Validated in the ...
- Aurinia’s Lupkynis for Lupus; FDA Fast Track Designation for Toripalimab; Wren Therapeutics...
- Aktis’s Novel Targeted Alpha Radiopharmaceuticals; Koye Partners with Sonde Health; Novartis to S...
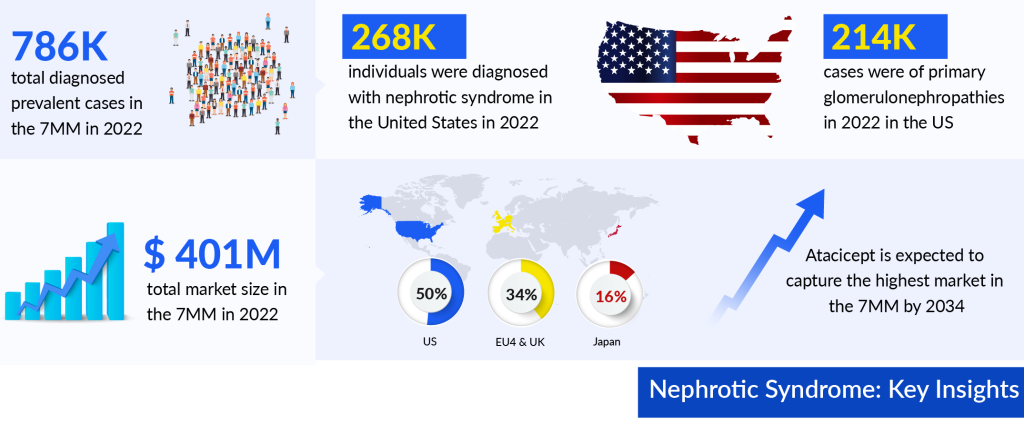
As per DelveInsight’s estimations, the total nephrotic syndrome diagnosed prevalent cases in the 7MM were approximately 786K in 2022 and are projected to increase by 2034. DelveInsight’s analyst projects that among the total diagnosed prevalent cases of Nephrotic Syndrome in 7MM approximately 34% of cases were from the US. As per our estimations, in 2022, the EU4 and the UK accounted for nearly 367K diagnosed prevalent cases of nephrotic syndrome.
The nephrotic syndrome treatment involves dealing with the root medical issues that lead to its development. Medical practitioners might recommend medications and dietary adjustments to manage symptoms and tackle the complications linked with nephrotic syndrome.
Traditional Approaches for Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment: Steroids and Immunosuppressants
At present, there are no approved treatments specifically tailored for managing nephrotic syndrome, so the main nephrotic syndrome treatment methods typically involve using medications off-label. Drugs such as prednisone, cyclophosphamide, and cyclosporine are used to bring about remission in nephrotic syndrome. Diuretics are also used to reduce swelling while angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers are used to decrease proteinuria.
The treatment chosen for nephrotic syndrome should depend on the specific kidney disease causing the syndrome. Corticosteroids show a very positive response in cases of minimal change disease. However, only about 20% of patients with focal glomerulosclerosis respond well to corticosteroids. In treating focal glomerulosclerosis, doctors often use prednisone, cyclosporine, and cyclophosphamide. For idiopathic membranous nephropathy, an important part of the treatment involves using prednisone along with chlorambucil or cyclophosphamide. When nephrotic syndrome relapses after prednisone treatment or when it doesn’t respond to prednisone, Rituximab has been found effective. This drug, which is a mix of mouse and human antibodies targeting the CD20 antigen of B cells, is thought to work by reducing antibody production.
In addition to the treatment methods mentioned earlier, some nephrotic syndrome medications have been approved to target specific causes of nephrotic syndrome. For example, for lupus nephritis, regulatory approval has been granted to BENLYSTA (belimumab), which is a human monoclonal antibody, and LUPKYNIS (voclosporin), a potent immunosuppressive calcineurin inhibitor. In the case of IgA nephropathy, there are FDA-approved nephrotic syndrome drugs such as FILSPARI (Sparsentan), which acts as a dual endothelin angiotensin receptor antagonist (DEARA), and TARPEYO (Nefecon), classified as a corticosteroid. Both of these are small molecules indicated for treating IgA nephropathy. Additionally, INVOKANA (Canagliflozin), an FDA-approved medication, is used to address diabetic nephropathy and functions as a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor.
Understanding treatment patterns in nephrotic syndrome is crucial for improving the practical dimension and gaining insights into the evolving healthcare landscape.
Nephrotic Syndrome Pipeline Therapies: Hope on the Horizon
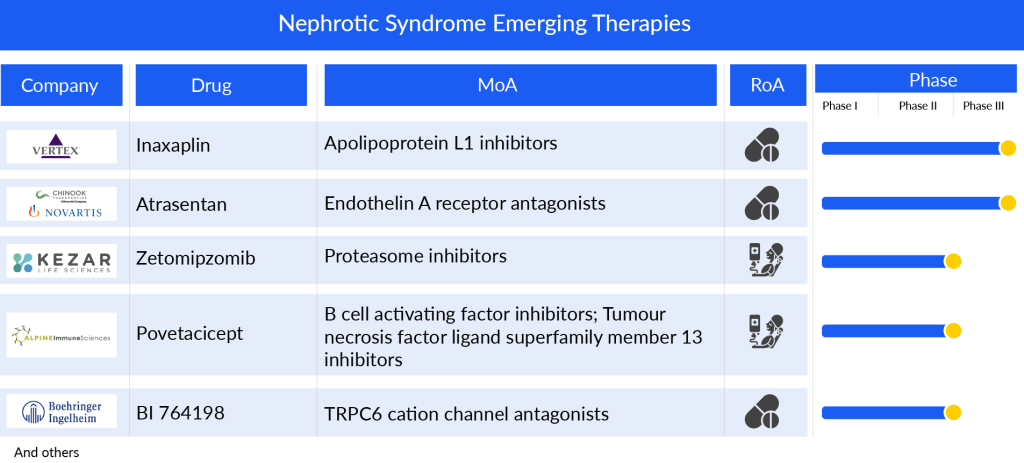
Companies across the globe are diligently working toward the development of novel treatment nephrotic syndrome therapies. To date, there are several emerging market players, Vertex Pharmaceuticals (Inaxaplin), Novartis/Chinook Therapeutics (Atrasentan), Kezar Life Sciences (Zetomipzomib), Alpine Immune Sciences (Povetacicept), and others that are developing drugs for the treatment of nephrotic syndrome.
Inaxaplin (VX-147), previously identified as VX-147, is an oral, small molecule inhibitor of Apolipoprotein L1 (APOL1), developed by Vertex Pharmaceuticals to address APOL1-mediated FSGS and various other kidney diseases characterized by proteinuria. It stands as the pioneering investigational therapy designed to tackle the root cause of APOL1-mediated kidney disease (AMKD). Vertex Pharmaceuticals is currently in the process of conducting a Phase II/III clinical study for the treatment of APOL1-mediated kidney disease. Furthermore, a Phase I trial is underway involving patients with renal impairment.
Chinook Therapeutics/Novartis has developed Atrasentan, an orally administered, potent, and selective blocker of the endothelin A (ETA) receptor. This drug operates by preventing the ETA receptor from activating various cell types within the kidney, ultimately decreasing kidney inflammation and fibrosis. This mechanism leads to a reduction in proteinuria among patients suffering from chronic kidney disease. Recently, the company shared preliminary findings from the Phase III registration trial (ALIGN), focusing on IgA nephropathy. Furthermore, ongoing trials include a Phase II open-label basket trial (AFFINITY) studying proteinuria-related glomerular diseases such as IgA nephropathy, FSGS, Alport syndrome, and diabetic kidney disease. Additionally, a Phase II crossover trial (ASSIST) is underway, targeting individuals with IgA nephropathy who are on stable doses of a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi) and an SGLT2 inhibitor (SGLT2i).
Kezar Life Sciences’ Zetomipzomib (KZR-616) is an innovative immunoproteasome inhibitor designed for various autoimmune conditions. This unique drug selectively targets immunoproteasomes, which are crucial in maintaining the immune system’s normal functions. By inhibiting these proteasomes, Zetomipzomib affects multiple pathways linked to the production of inflammatory cytokines and the activity of immune cells like macrophages, B cells, and T cells. These pathways are central to the development of numerous autoimmune diseases.
Presently, the company is progressing with a Phase IIb PALIZADE trial following promising outcomes from the Phase IIa segment of the MISSION trial, which evaluated Zetomipzomib in patients with lupus nephritis and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Alpine Immune Sciences’ Povetacicept (ALPN-303) is a compound that targets both the B-cell activating factor (BAFF) and APRIL, two cytokines crucial for B-cell activation, development, and survival. These cytokines, BAFF and APRIL, have complementary yet partially overlapping roles in the lifecycle of B cells. Early in development, BAFF predominates due to its influence on BAFF-R expression, while later stages rely on APRIL and/or BAFF, linked to the expression of TACI and BCMA.
Povetacicept, therefore, is an Fc fusion designed with an engineered variant TACI domain, structurally different from the natural TACI-Ig, with the aim of more effectively blocking the diverse B-cell cytokines BAFF, BLyS, and APRIL.
Alpine Immune Sciences is currently engaged in a Phase Ib/IIa clinical trial (RUBY 3) involving adults with glomerulonephritis, including conditions such as IgA nephropathy, primary membranous neuropathy, and lupus nephritis. Furthermore, Povetacicept is being developed for various diseases associated with B cells and/or autoantibodies, such as SLE, glomerulonephritis, and autoimmune cytopenias.
The anticipated launch of these emerging nephrotic syndrome therapies are poised to transform the market landscape in the coming years. As these cutting-edge therapies continue to mature and gain regulatory approval, they are expected to reshape the nephrotic syndrome treatment market landscape, offering new standards of care and unlocking opportunities for medical innovation and economic growth.
Precision Medicine: Tailoring Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment to Individuals
Precision medicine has revolutionized the approach to treating conditions like nephrotic syndrome, offering a tailored and personalized path to recovery for individuals. By analyzing a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle factors, and specific disease characteristics, healthcare providers can design treatment plans that are uniquely suited to the patient’s needs. For nephrotic syndrome, this means identifying the underlying cause of the condition, whether it be a genetic predisposition, autoimmune response, or another factor, and targeting treatments accordingly. Through advanced diagnostics, such as genetic testing and biomarker analysis, doctors can pinpoint the most effective medications and therapies, minimizing side effects and maximizing outcomes.
This individualized approach not only enhances the effectiveness of treatment but also reduces the trial-and-error often associated with standard therapies. By understanding the nuances of each patient’s condition, doctors can prescribe medications at the right dosages and intervals, adjust nephrotic syndrome treatment regimens as needed, and provide comprehensive support for managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Precision medicine empowers both patients and healthcare providers in the battle against nephrotic syndrome, offering hope for better outcomes and a path toward long-term wellness tailored to the unique needs of each individual.
Challenges and Future Directions in Nephrotic Syndrome Treatment
One of the foremost hurdles lies in the variability of response to treatments among patients. While corticosteroids remain the initial line of defense, a substantial portion of patients either do not respond adequately or develop steroid dependence or resistance over time. This necessitates the exploration of alternative therapies, such as immunosuppressive agents like cyclosporine and tacrolimus. However, the long-term use of these medications poses risks of infection, hypertension, and nephrotoxicity, thereby underscoring the delicate balance between managing the disease and the potential adverse effects of nephrotic syndrome treatment.
Nevertheless, the future of nephrotic syndrome treatment holds promise through advancements in precision medicine. As per DelveInsight analysis, the nephrotic syndrome market size in the 7MM reached approximately USD 401 million in 2022. Projections indicate substantial growth during the forecast period of 2023 to 2034. As per the estimates, out of the 7MM, the United States dominated the nephrotic syndrome treatment market in 2022, representing the largest share at nearly 50%.
Moreover, understanding the intricate molecular mechanisms underlying the disease will enable the development of targeted therapies that could revolutionize patient care. Research into novel immunomodulatory agents, including monoclonal antibodies and biologics, offers hope for more effective and safer treatment options. Moreover, the integration of genetic profiling may allow for personalized therapeutic approaches, optimizing outcomes while minimizing adverse events. Collaborative efforts among clinicians, researchers, and pharmaceutical companies will be crucial in navigating these challenges and ushering in a new era of tailored, effective treatments for individuals grappling with nephrotic syndrome.

Frequently Asked Questions
Currently, there is no therapy specifically approved for all forms of nephrotic syndrome, so clinicians rely heavily on off-label use of corticosteroids (e.g. prednisone), immunosuppressants (such as cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine), diuretics, and agents targeting proteinuria (ACE inhibitors or ARBs). In many disease subtypes, these treatments either fail to induce remission or lead to significant side effects, especially with long-term use. In steroid-resistant or frequently relapsing cases, options are limited, highlighting a strong unmet need for more targeted and safer therapies.
Researchers are developing novel agents with more precise mechanisms of action to address unmet needs in nephrotic syndrome. Some pipeline candidates include Inaxaplin (by Vertex), Atrasentan (Novartis/Chinook), Zetomipzomib (Kezar Life Sciences), and Povetacicept (Alpine Immune Sciences) as experimental drugs for various nephrotic etiologies. In focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (a common cause of nephrotic syndrome), advances such as sparsentan (a dual endothelin-angiotensin receptor antagonist) are already showing promise. These novel therapies aim to reduce proteinuria, preserve kidney function, and minimize systemic side effects.
The future of nephrotic syndrome treatment is leaning toward precision medicine, where therapies would be tailored based on the underlying subtype, genetic markers, response patterns, and risk factors. Tools and resources like NURTuRE, a biobank/database initiative, are being built to support research that links patient phenotypes, biomarkers, and treatment outcomes, thereby enabling more effective personalized approaches. By classifying patients more accurately, clinicians hope to match emerging therapies to those who will benefit most, reducing overtreatment and side effects.
Several hurdles remain in the development and adoption of new nephrotic syndrome therapies. First, the heterogeneity of disease causes (e.g. minimal change disease, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy) makes it difficult to design one-size-fits-all drugs. Second, demonstrating both safety and durable efficacy (especially in terms of sustained remission and kidney protection) in clinical trials is challenging. Regulatory approval pathways may be complex given the rarity and severity of many nephrotic syndromes. Finally, real-world translation requires cost-effectiveness, long-term monitoring, and ensuring access across populations.
While timelines vary by agent and disease subtype, some drugs are already in advanced clinical stages. For example, sparsentan has progressed toward regulatory consideration in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Others such as Inaxaplin, Atrasentan, and Zetomipzomib are in earlier development stages and may take several years to clear regulatory hurdles. Realistically, widespread availability of more novel, targeted therapies might emerge over the next 5–10 years, though for particular subtypes progress could be faster.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Biogen terminates ALS Pact with Karyopharm; AbbVie’s Immunological Drug Skyrizi; NICE Backs Astel...
- AUCATZYL Approved for R/R B-ALL; FDA Accepts NDA for Unicycive’s Oxylanthanum Carbonate; AstraZen...
- Aktis’s Novel Targeted Alpha Radiopharmaceuticals; Koye Partners with Sonde Health; Novartis to S...
- Roche’s GAZYVA Extends Indications Into Lupus, Strengthening Immunology Pipeline
- Baird Medical’s Microwave Ablation System; BrainSpec’s AI-Backed Solution for Non-Invasive Brain ...