Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Market Trends and Future Prospects
Dec 24, 2024
Table of Contents
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects movement control. It occurs when dopamine-producing neurons in the brain are damaged or die. The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease is still unknown, but symptoms include tremors, stiffness, and difficulty with coordination. Parkinson’s disease progresses through various stages, with symptoms worsening over time, affecting an individual’s quality of life. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing Parkinson’s and slowing its progression.
The Parkinson’s disease therapeutic market plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms and progression of the condition. With no cure currently available, the Parkinson’s disease market focuses on providing treatments that help alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression. Medications, such as dopaminergic therapies, and advanced treatments like deep brain stimulation, are essential components of the Parkinson’s disease therapeutic market. As the prevalence of Parkinson’s continues to rise, advancements in research and drug development are vital to expanding treatment options, offering hope to patients and caregivers.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Parkinson’s Disease: How Close are we to a Cure?
- Evolving Landscape of Multiple System Atrophy Treatment: Recent Developments and Future Directions
- Navigating the Healthcare Horizon: Odyssey of Mergers, Funding, and Acquisitions in 2024
- Aurinia’s Lupkynis for Lupus; FDA Fast Track Designation for Toripalimab; Wren Therapeutics...
- Business Cocktail
Parkinson’s Disease Market Overview
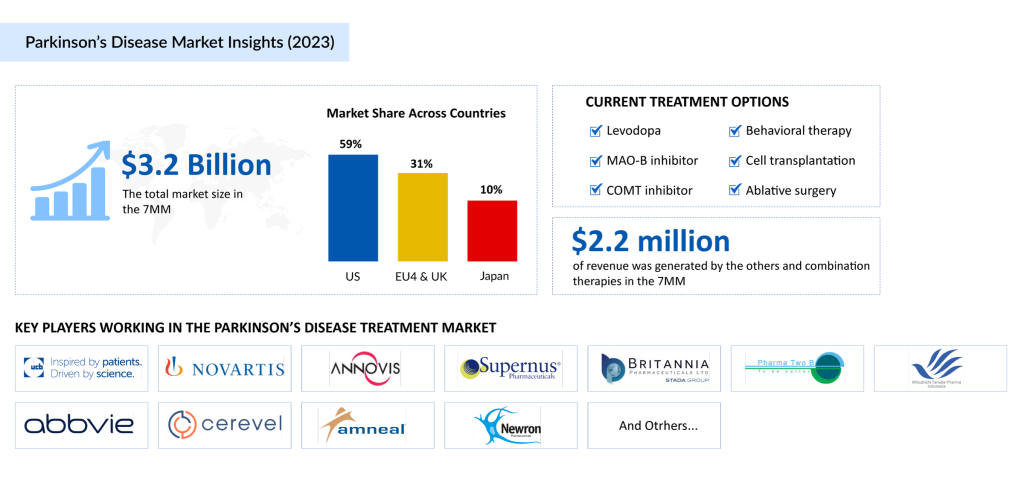
The Parkinson’s disease market is experiencing substantial growth, driven by aging populations and heightened disease awareness. In 2023, the US market size for Parkinson’s disease treatment reached USD 1.8 billion. With the anticipated launch of novel Parkinson’s disease drugs such as SPN-830, Tavapadon, P2B001, and ND0612, alongside advancements in diagnostics and care, the market is poised for significant expansion during the forecast period which is from 2024 to 2034.
Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Segmentation
The Parkinson’s disease treatment landscape is evolving to address unmet needs. Current therapeutic approaches include:
- Drug Therapy:
The mainstay of treatment is carbidopa/levodopa, with innovative formulations like CREXONT, RYTARY, XADAGO/EQUFINA, and DUOPA enhancing symptom control. Dopamine agonists, MAO-B inhibitors, and transdermal options like HARUROPI TAPE provide additional avenues for symptom management. - Advanced Therapies:
Techniques like deep brain stimulation (DBS) and infusion therapies, such as levodopa/carbidopa enteral suspension, are offering advanced solutions for patients with severe motor symptoms. - Emerging Treatment Approaches:
Promising drugs targeting a-synuclein pathology, gene therapies, and stem cell-based regenerative strategies signal the arrival of potential disease-modifying Parkinson’s disease therapies. Late-stage candidates such as ND0612 and SPN-830 could reshape the Parkinson’s disease drug market.
Regional Market Insights of Parkinson’s Disease
The Parkinson’s disease market exhibits regional variability in revenue and growth potential:
- United States: The largest market, valued at ~USD 2 billion in 2023, is expected to grow significantly with increasing awareness and therapeutic advancements.
- EU4 and the UK: Germany dominated this region, contributing ~USD 400 million, followed by France and the UK. The EU4 and the UK collectively accounted for 31% of the total market revenue in 2023, with projected growth through 2034.
- Japan: The Parkinson’s disease treatment market in Japan stood at USD 348 million in 2023 and is expected to expand further during the forecast period.
Parkinson’s Disease Key Players and Competitive Landscape
The Parkinson’s disease market is highly competitive, with a mix of established pharmaceutical companies and emerging biotech firms driving innovation in therapies and treatments. Key players include Amneal Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, Newron Pharmaceuticals, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Britannia Pharmaceuticals, Pharma Two B, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma (NeuroDerm), UCB Biopharma SRL, Novartis, Annovis Bio, Cerevel Therapeutics, LLC, and many others.
AbbVie remains a frontrunner in the market, introducing groundbreaking therapies such as Tavapadon, a promising oral dopamine D1/D5 receptor partial agonist, and DUOPA, a carbidopa/levodopa enteral suspension providing advanced options for patients with severe disease progression. AbbVie’s innovative pipeline highlights its commitment to addressing unmet needs in Parkinson’s disease treatment.
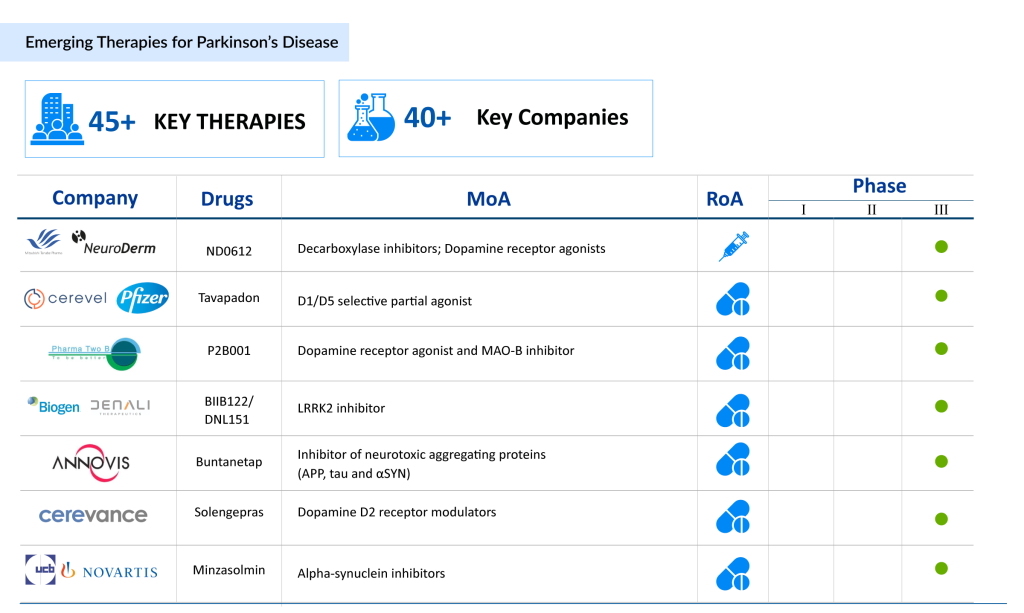
Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. and Britannia Pharmaceuticals are spearheading advancements with late-stage candidates like SPN-830, an apomorphine infusion pump designed to deliver continuous dopaminergic stimulation, reducing “off” episodes for patients requiring consistent symptom management.
Pharma Two B is making strides with P2B001, a novel combination therapy that integrates extended-release pramipexole and rasagiline to optimize motor symptom control while minimizing side effects. Similarly, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma (NeuroDerm) is advancing ND0612, a levodopa/carbidopa infusion therapy, offering potential breakthroughs in continuous motor symptom management.
Emerging players like UCB Biopharma SRL, Novartis, Annovis Bio, and Cerevel Therapeutics, LLC are focusing on innovative therapies targeting underlying disease mechanisms, such as a-synuclein aggregation and neuroregeneration. These efforts, along with advancements in gene therapies and regenerative medicine, contribute to a robust pipeline of potential Parkinson’s disease drugs, positioning the market for transformative breakthroughs in the near future.
Parkinson’s Disease Market Outlook
The future of the Parkinson’s disease market lies in the development of innovative treatments that extend beyond symptom management to address the underlying causes of the disease. By targeting mechanisms such as alpha-synuclein aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation, pharmaceutical companies have the potential to create therapies capable of slowing or halting neurodegeneration. These efforts are supported by advancements in drug delivery systems, including brain-penetrant small molecules and gene therapies, which aim to enhance precision and efficacy in treatment.
Additionally, the use of biomarkers for early detection and patient stratification is expected to revolutionize how Parkinson’s disease is diagnosed and treated. By identifying patients earlier and tailoring therapies to their specific needs, companies can develop disease-modifying treatments that significantly improve outcomes and establish new standards of care in Parkinson’s disease management.
Recent developments highlight the progress in addressing unmet needs. In November 2024, Sunbird Bio announced its diagnostic technology, which demonstrated 86% accuracy in classifying blood samples from Parkinson’s disease-positive patients by detecting aggregated alpha-synuclein proteins. This innovation represents a significant step forward in early and accurate diagnosis, a critical area in Parkinson’s care.
Similarly, AbbVie achieved a major milestone in October 2024 with FDA approval of VYALEV (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa), the first 24-hour continuous subcutaneous infusion of a levodopa-based therapy. This groundbreaking treatment offers improved management of motor fluctuations in adults with advanced Parkinson’s disease, addressing a significant challenge in symptom control.
Emerging therapies are also shaping the future landscape. Supernus Pharmaceuticals and Britannia Pharmaceuticals have developed SPN-830, an investigational apomorphine infusion device designed to provide continuous treatment for motor fluctuations (OFF episodes). Offering a less invasive and more convenient administration than existing therapies, SPN-830 has the potential to enhance patient compliance. Following a complete response letter from the FDA in April 2024, Supernus resubmitted its NDA in August 2024, signaling continued progress toward approval.
AbbVie, following its acquisition of Cerevel Therapeutics, is advancing Tavapadon, a once-daily oral therapy designed to selectively target dopamine D1/D5 receptor subtypes. This therapy aims to provide meaningful motor benefits while minimizing side effects such as dyskinesia and impulse control issues. Tavapadon’s Phase III TEMPO-3 trial reported positive results in April 2024, solidifying its potential as a treatment for both early- and late-stage Parkinson’s disease.
Another promising therapy, P2B001, developed by Pharma Two B, combines extended-release pramipexole and rasagiline in a once-daily formulation. This dual mechanism aims to optimize motor symptom control while minimizing side effects, offering a potentially superior alternative to current combination therapies. Phase III study results published in November 2023 highlighted its tolerability and efficacy, with an NDA submission to the FDA in progress.
Future Predictions
The Parkinson’s disease market is projected to experience significant growth during the forecast period (2024–2034), driven by these therapeutic advancements, increasing disease awareness, and improvements in diagnostic technologies. Late-stage pipeline drugs such as SPN-830, Tavapadon, and P2B001, alongside innovations like Sunbird Bio’s diagnostic technology, are expected to redefine how Parkinson’s disease is managed.
These developments position the market for transformative breakthroughs, with pharmaceutical companies focusing on curative and disease-modifying therapies that could significantly impact patient care and market dynamics.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Snippets : Parkinson
- FDA Fast Track Status to Kyverna’s KYV-101; Annovis’s Phase III Study for Buntanetap; Gilteritini...
- PTC Therapeutics’ Gene Therapy Upstaza; Sanofi and Regeneron’s Dupixent; Bayer CAR-T Collaboratio...
- Wireless Brain Sensors: Revolutionizing Neuroscience and Healthcare
- Need of the Hour: Enhanced Strategies for PD-LID Treatment and Management