Need of the Hour: Enhanced Strategies for PD-LID Treatment and Management
Dec 30, 2022
Table of Contents
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative neurological condition primarily affecting middle-aged and older adults and is characterized by tremors, muscular rigidity, and slow, clumsy movement. It is connected to the brain’s basal ganglia atrophy and a lack of the neurotransmitter dopamine. Levodopa is considered a linchpin despite the availability of other agents for reducing the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. However, prolonged levodopa usage can lead to levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID).
As per a study by Jose (2000), Parkinson’s disease is an age-related neurodegenerative disorder with an average onset age of 60. In the United States, approximately 1 million people suffer from Parkinson’s disease, and there are 60,000 newly diagnosed cases every year. After 5 years of PD-LID treatment, >50% of patients experience motor fluctuations and dyskinesias.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Navigating the Healthcare Horizon: Odyssey of Mergers, Funding, and Acquisitions in 2024
- Parkinson’s Disease: How Close are we to a Cure?
- Reprogrammed cells relieve Parkinson’s symptoms in trials
- Bayer Phase III NSCLC Trial; D&D Pharmatech Gets FDA Nod for GLP-1R Agonist in Multiple Sclet...
- Dengvaxia study; Opdivo racks up; FDA issues plant; Teva’s Rimsa fraud; Mission bags Fox grant
According to the latest published “Parkinson’s disease Levodopa-induced dyskinesia Epidemiology” report, Parkinson’s disease levodopa-induced dyskinesia (PD-LID) affected around 290,000 people in the US, 250,000 people in EU4 and the UK, and 45,000 in Japan in 2021.
Are the shortcomings answered for PD-LID treatment?
Although levodopa is the gold standard for treating Parkinson’s disease patients, its prolonged usage can cause levodopa-induced dyskinesia, as there are no validated diagnostic techniques to determine the emergence and progression of levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Patients’ self-assessments are considered to establish the different aspects of dyskinesia and the effects of drugs. Despite all the advances, the pathogenesis of dyskinesia induced by levodopa remains unclear. It requires research to illuminate the pathomechanism and assist the pharma players in establishing new Parkinson’s disease levodopa-induced dyskinesia treatment options and related symptoms.
Due to the unclear pathomechanism, PD-LID management remains a matter of concern as the current strategies revolve around dopamine stimulation, levodopa-sparing strategies, and nondopaminergic add-ons. Though therapies like GOCOVRI (PD-LID) and NOURIANZ (wearing off) are available for PD-LID management, none improve daily living activities, enhance the quality of life, or decrease caregiver burden. Furthermore, the appearance of levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease patients creates an additional economic burden. Compared to patients without levodopa-induced dyskinesia, those with levodopa-induced dyskinesia have a 78% increase in PD-related treatment expenses and a 29% increase in overall treatment costs. Hence, advancements are required for PD-LID treatment that pave the way for potential therapies to enter the PD-LID treatment market.
Reflecting on the upcoming PD-LID treatment options
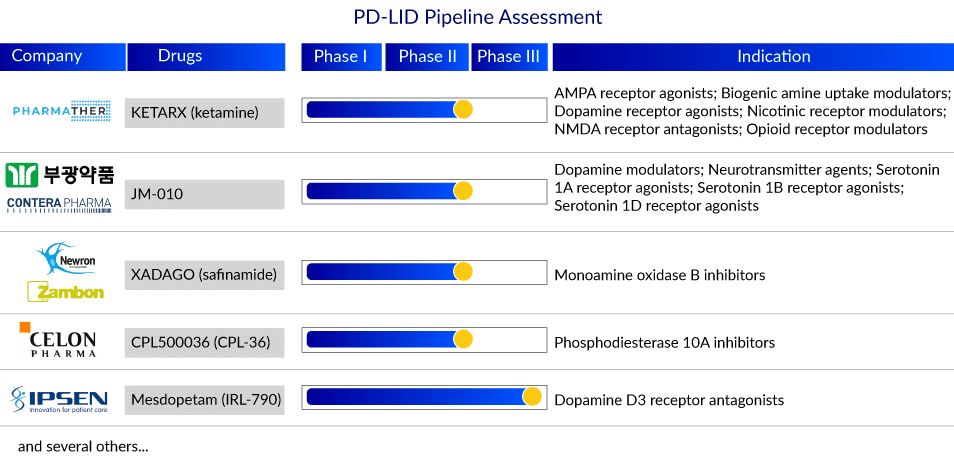
The PD-LID market was valued at around USD 1,400 million in 2019 and is expected to reach USD 2,300 million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 3.6% during the study period. KETARX (PharmaTher), NLX-112 (Neurolixis SAS/Gala laboratories), JM-010 (Bukwang Pharmaceutical/Contera Pharma), AV-101 (Vistagen), Mesdopetam (Ipsen Pharma), XADAGO (Newron Pharmaceuticals/Zambon Pharmaceuticals) and CPL500036 (Celon Pharma SA) are investigating their respective candidates for PD-LID treatment and management in the 7MM. Several late-stage assets with distinct MoA are being developed to treat PD-LID patients and are expected to enter the 7MM PD-LID treatment market in the next few years.
Can gene therapy be the silver lining for the PD-LID treatment landscape?
As PD-LID demands more advancements to bridge the gap between research and PD-LID treatment, more studies are being conducted to understand the disease and establish PD-LID treatment options. Research is underway to understand whether the specific calcium channel in the brain results in dyskinesia; however, it is unknown if blocking or silencing this channel can reduce dyskinesia. The experimental model of PD-LID has shown promising results using gene therapy, which enables new genetic information to reduce the number of channels. The positive results from the preliminary data have established a belief that ‘gene silencing’ could relieve the symptoms of PD-LID and potentially slows the disease progression. Given the favorable preliminary data, the gene therapy approach could be a boon for PD-LID patients.
What’s ahead in the PD-LID treatment market?
The current PD-LID treatment landscape is based on discontinuing, reducing, or adjusting the amount of dopamine given to patients. Furthermore, different approaches and strategies are personalized through trial and error. The PD-LID treatment market offers these players numerous opportunities to capitalize on the untapped PD-LID treatment market. Although the field is quite active, with numerous trials underway to treat patients with PD-LID, ongoing efforts are required to develop novel PD-LID treatment drugs that are more effective and less toxic. However, more research is needed to develop drugs to treat dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease patients taking levodopa. As there is only one approved pharmaceutical PD-LID treatment across the entire landscape, any significant advancement in this direction is expected to have a tectonic impact on the existing PD-LID treatment market scenario during our forecast period (2022–2032).

FAQs
LID is a type of dyskinesia caused by the drug levodopa (l-DOPA), which is used to treat Parkinson’s disease. It frequently includes hyperkinetic movements such as chorea, dystonia, and athetosis. There are three clinical variants of PD-LID: peak-dose dyskinesia, off-period dystonia, and diphasic dyskinesias; they commonly present as chorea or choreoathetosis, but myoclonus, akathisia, ballism, and other abnormal movements have also been described.
Parkinson’s disease signs and symptoms can vary from person to person. Early symptoms may be subtle and go unnoticed. Parkinson’s disease symptoms typically begin on one side of the body and worsen on that side, even after symptoms begin to affect limbs on both sides. Common Parkinson’s disease symptoms include tremors, slowed movement, speech changes, writing changes, rigid muscles, and others.
Levodopa is the most effective Parkinson’s disease treatment; however, long-term use is complicated by LID, which disables motor fluctuations and involuntary movements. Despite significant progress, the pathogenesis of LID remains unknown. There are currently no validated, quantitative, or qualitative diagnostic techniques to assess the emergence and progression of LID in Parkinson’s disease patients.
Key players in the global PD-LID treatment market include PharmaTher Inc., Neurolixis SAS/Gala laboratories, Bukwang Pharmaceutical/Contera Pharma, VistaGen, Ipsen Pharma, and Newron Pharmaceuticals/Zambon Pharmaceuticals. The expected entry of promising agents, including KETARX, NLX-112, JM-010, AV-101, Mesdopetam, and XADAGO, can transform the current standard of care and PD-LID treatment market during the forecast period.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Parkinson’s Disease: Impact of Emerging Therapies on the Therapeutics Market
- What Lies Ahead For Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis Treatment Market?
- Advancements in Neuromodulation
- Byondis’s HER2-targeting ADC trastuzumab duocarmazine; AbbVie Migraine Drug Atogepant; Grünenthal...
- Key Updates on Phase 1 Trial of AB-1005 Gene Therapy for Multiple System Atrophy-Parkinsonian Typ...