How Will New Discoveries of Deep Brain Stimulation Devices Transform the Pharma Domain?
Mar 26, 2021
Table of Contents
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure that requires the implantation of a device capable of sending electrical impulses to the brain areas responsible for body movement. A DBS system is composed of the neuro-stimulator, leads, and extension. The electrodes are placed deep inside the brain and are linked to a stimulator. They can be placed on both the left and right areas of the skull, depending on the targeted type of symptoms. The neurostimulator is placed under the chest area’s skin and is connected to the electrodes via a long-wired extension, which runs across the scalp, behind the ear, below the neck to the chest.
The origin of the deep brain stimulation technique is associated with the effects of electrical stimulation of the deeper regions of the brain, performed during the stereotactic lesional functional neurosurgery to find the correct positioning of the coagulant electrodes for the treatment of dyskinetic disorders and the treatment of tremors in case of patients suffering from the Parkinson’s disease
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
DBS Procedure
Brain surgery and chest surgery is performed for the installation of the deep brain stimulation system. The brain surgery involves a prior MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan for mapping the exact areas in the brain where the electrodes are placed. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. The surgeon implants a thin wired-lead along with electrodes in specific areas of the brain. A wire runs below the skin to the neuro-stimulator that will be embedded in the chest area. In the second part of the surgery, the surgeon implants the neuro-stimulator under the chest area’s skin. General anesthesia is used again for this procedure, and the wires from the brain electrodes are brought down to the battery-operated pulse generator. The generator is programmed in such a way that it can be used to sending continuous electric pulses to the targeted brain region. The generator is controlled by an external remote control which is handled by the patient.
Applications of DBS
In earlier days, patients dealing with Parkinson’s and other forms of the disease were often overburdened with certain treatment options because not only the management of these medication regimens became immensely difficult, but also the levels of complexity kept on increasing with the progression of the disease. Often the prescription drugs had to be taken more than six times a day, making the management highly suboptimal to patients and adding to an adverse clinical impact. Another form of treatment option for patients comprised of surgery. Surgical options are not that well presumed by patients considering they are invasive forms of treatment and often involves the destruction of targeted areas of the brain (lesioning) that can contribute to the already occurring symptoms. Also, the surgical procedures used required longer recovery periods and were irreversible. The surgical options are rarely used now for patients suffering from neurological disorders and have been replaced by Deep Brain Stimulation for a number of disorders, owing to the fact that it is a minimally invasive procedure that can be used in the palliation of chronic neurological disorders.
Some of them are listed below:
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
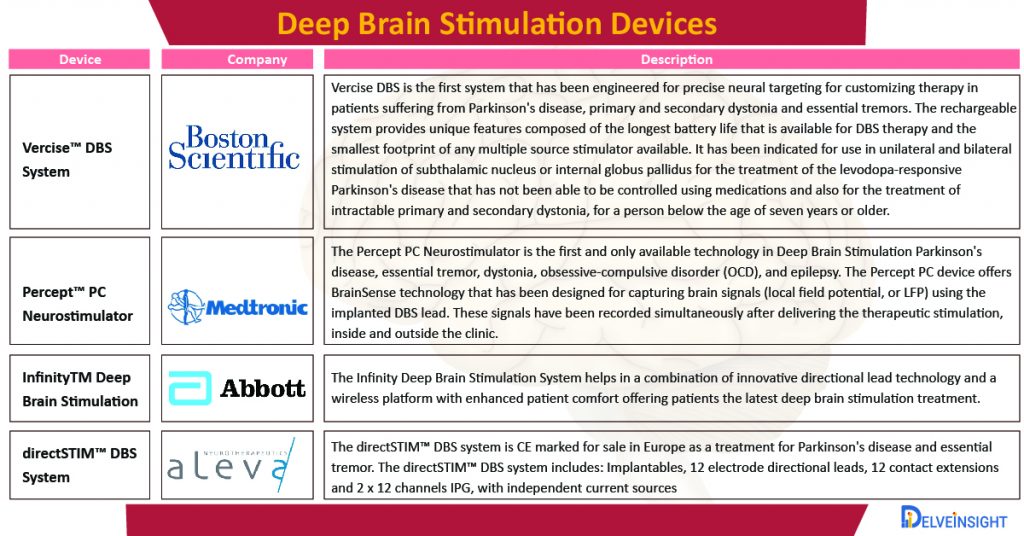
According to 2016 statistical data by Parkinson’s Foundation, an estimated seven to ten million people worldwide have Parkinson’s disease. The prevalence of the disease ranges from 41 people per 100,000 in the fourth decade of life to more than 1,900 people per 100,000 among those who are 80 and older. People affected with Parkinson’s disease generally range from seven to ten million people worldwide. Various cardinal symptoms of Parkinson’s disease including tremor, bradykinesia, and postural instability, are experienced by patients suffering from Parkinson’s disease. The pathophysiologic mechanism of Parkinson’s disease would involve the over-activity of Globus pallidus internus (GPi) and the subthalamic nucleus (STN). In 1994, the research performed by Benabid et al. showed successful treatment of Parkinson’s disease in patients who had undergone DBS of GPi and STN. The Vercise DBS System by Boston Scientific Corporation is used for moderate to advanced symptoms of levodopa-responsive Parkinson’s disease treatment.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
The worldwide lifetime prevalence rates of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) for the year 2020, have been estimated at 1.5% for women and 1.0% for men. The estimated lifetime prevalence among adults in the United States is slightly higher, recorded at 2.3 %. It is a psychiatric disorder whose symptoms can be witnessed in the form of thoughts and impulses that lead to anxiety, and patients perform repeated rituals. The precise pathophysiologic mechanism of OCD is not that known, however, it is assumed that the defective functioning of the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuitry plays a significant role in this. Medtronic plc. has received FDA approval for its Percept PC Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) system for patients suffering from neurological disorders like Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, epilepsy, or OCD in the year 2020. The DBS neurostimulation system is well equipped with BrainSense technology making it a more patient-personalized and data-driven neurostimulation system.
Epilepsy
As per World Health Organization 2019, around 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, making it one of the most common neurological diseases globally. Nearly 80% of people with epilepsy live in low- and middle-income countries. It is a disabling disorder seen across all age groups. Most researchers try using cerebellar electrical stimulation for controlling seizures by placing the electrodes via a burr hole approach. The anterior nucleus of the thalamus is a probable target for DBS treatment of seizures. An example of DBS for the treatment of epilepsy involves the Medtronic DBS System for Epilepsy.
Tremor
Essential tremor is the most common cause of action tremor. It was recorded that tremor has an estimated prevalence of one percent overall and approximately five percent in adults over the age of 60 years worldwide in the year 2013. Essential tremors were the first movement disorder for which DBS was approved in the year 1997, and after its efficacy was proved in several research studies, it became a routine form of treatment for tremors. Essential tremor is one of the most common forms of pathologic tremor that affects not only the hands but also the head, tongue, voice and lower extremities of the body. The prevalence of Essential tremor is supposed to increase with age. Thalamic DBS has replaced stereotactic thalamotomy as the patient’s treatment of choice. An example of DBS for the treatment of tremor involves Cala Health’s Cala Trio for tremors. Cala Trio is a wrist-worn device that provides neuromodulation therapy through the skin to provide symptomatic relief of hand tremors. The device stimulates the nerves responsible for the tremor gently, interrupting nerve circuits to enable movement to be better controlled.
Dystonia
The clinical development of DBS in dystonia had a gap of about a year after its use in PD. The medical treatment of dystonia does not always result in symptom control and often leads to severe side effects. Initially, ablative procedures performed at either the thalamus or the GPI resulted in symptomatic improvements. An early study of 2019 in the United States estimated the prevalence for primary dystonia to be 329 per million population. Several studies of DBS of intractable dystonia have focused on the ventral intermedius nucleus of the thalamus and the GPI. Medtronic’s Activa dystonia treatment is recommended to help in the control of chronic, intractable (drug refractory) primary dystonia, including general and/or segmental dystonia.
Depression
It’s estimated that 16.2 million adults in the United States, or 6.7 percent of American adults, have had at least one major depressive episode in 2016. Depression is one of the most common psychiatric disorders around the world. In 2005, Mayberg et al. had reported their experience with six patients who had undergone bilateral DBS of the subgenus in the corpus callsoum. After a six month follow up, four of the six patients had a prominent improvement after measuring depression using the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale. The Fisher Wallace Stimulator is cleared by the FDA to treat depression, anxiety and insomnia when used for 20 minutes, once or twice a day.
DBS is being studied and investigated as a potential treatment for various disorders, including addiction, chronic pain, cluster headache, dementia, depression, Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, stroke recovery, Tourette syndrome and traumatic brain injury. Therefore the Deep brain stimulation devices market for DBS devices will grow in the near future if they get approval for these indications.
Advantages of DBS
There are several clinical advantages offered by DBS over various other forms of surgical approaches for neuromodulation. These can be categorized as follows:
- DBS has a non-lesional nature (minimally-invasive).
- The adjustment feature for stimulation allows maximized benefits and reduction in adverse events and the convenience to a direct interface with the circuit pathology that influences visible symptoms.
- Speaking of DBS as a scientific tool, it can be used effectively to investigate the physiological concepts of brain dysfunctions that are still uncovered, further carrying out identification and alterations of these pathological neuronal signatures, thus helping the medical device pioneers excel in technological innovations promote better clinical outcomes.
- DBS’s dual benefits have been observed both in the form of a probe and as a modulator of the brain circuitry, thus vouching for its therapeutic value in a broad spectrum of disorders, affecting motor, limbs, memory, and cognitive functions.
- It can be performed on both sides of the brain, depending on the area that has to be targeted.
- The effects of DBS are reversible and can be tailored according to the clinical status of the patient.
- It is capable of providing continuous symptom control for 24 hours a day.
Recent Market Activity
- In January 2020, Abbott’s Infinity Deep Brain Stimulation system that allows the targeted stimulation of a new area of the brain associated with Parkinson’s disease symptoms had received an expanded clearance from the FDA.
- In February 2021, the Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorder Center at Henry Ford Health System became the first in the United States to offer a new FDA-approved device to help treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosurgeon Jason Schwalb, MD, surgically implanted the Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) System, which stimulates a targeted region of the brain through – implanted leads placed in the brain.
- In September 2020, Boston Scientific Corporation had announced the receipt of the CE Mark and the subsequent limited-market launch of its fourth-generation Vercise Genus Deep Brain Stimulation System in Europe for treatment of Parkinson’s disease and dystonia.
- In February 2021, Newronika, a spin-off company of two of the world’s leading neurology research centres in the field of neurology, the Fondazione IRCCS Ca’ Granda Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico and the University of Milan received CE Mark approval for its AlphaDBS System.
- In February 2021, Newronika has announced the first patient to be implanted with the AlphaDBS adaptive closed-loop deep brain stimulation (aDBS) system. It is the most notable development in the DBS area to date.
A glimpse of the current and future scenario
Over the past 25 years, DBS has become the potential standard of care that is available for indications such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia and obsessive-compulsive disorder. However, technology is also being investigated in the pipeline for other disorders, majorly depressive disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. The modern DBS systems comprise of an intracranial electrode, an extension wire and a pulse generator, and they have evolved slowly over the past two decades. Various advancements in engineering and imaging, along with a complete understanding of brain disorders, have definitely ramped up the way in which DBS has been implied in patients.
To date, use of DBS has been limited to high-income countries, although use in many developing nations is rising. Analysis of a US database of hospital discharges between 2002 and 2011 showed that more than 30,000 DBS surgeries were performed during that time. The numbers of publications on DBS have also risen steeply over the same period, with more than 7,000 manuscripts published between 1991 and 2014.
Advances in terms of electrode and battery designs, sensing technologies, closed-loop and on-demand stimulation, and sensing technologies, stimulation paradigms are expected to bring about a change in the efficacy and tolerability of DBS. The closed-loop DBS helps in simultaneously recording and stimulating the neural activity depending on the individual’s need, and the adjustment can be made according to disease-specific neural biomarkers. Stimulation, such as triggering thalamic DBS by arm movement in critical tremor or through seizure activity in epilepsy, maybe on-demand. Alternatively, closed-loop DBS can be adaptive, with continuous modulation of DBS by feedback such as the level of beta power in the subthalamic nucleus local field potential in Parkinson disease. Another major advancement is phase-controlled DBS. At the specific timings (stages) that either increase or attenuate oscillations, as needed for treatment, stimulation is delivered. In thalamic DBS for tremor, this approach has been piloted.
Various significant opportunities and unmet needs that still have to be dealt with are technological innovation that is focused on improving efficiency and tolerability, improved integration with imaging and other modalities and registering the global experience through study designs and registries. In the past few years, a trend towards a translational approach to programming based on an improved understanding of the biophysical and physiological properties of DBS parameters. This approach has helped to overcome the lack of progress in DBS development partially.
In many ways, the DBS technology has been evolving, but with a single focused goal of treating brain disorders safely and effectively.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Cost-effectiveness, Advanced Technology, Rising Demand Pushes the Insulin Delivery Devices Market
- DRUG-RESISTANT EPILEPSY
- Peloton raises $150M; BiomX raises $32M; Abbott and Novo collaborate; Blaze Bioscience nets $5M
- Notizia
- Decoding Parkinson’s Diagnosis with Gene Therapies and Prevention Insights




