Top 7 Breakthrough Drugs for Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
May 08, 2025
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease of unknown origin that targets the lining of the colon. Symptoms typically include diarrhea, abdominal pain, discomfort, and the presence of blood in the stool. The severity of the condition can vary, with inflammation affecting just the rectum, extending to the splenic flexure on the left side of the colon, or involving the entire rectum and colon.
As per DelveInsight analysis, the total ulcerative colitis diagnosed prevalent cases in the 7MM comprised 3.2 million cases in 2024 and are projected to increase by 2034. As per the estimates, in 2024, approximately 60% of cases accounted for the moderate to severe cases of ulcerative colitis among the 7MM.
The treatment options for ulcerative colitis vary based on the disease’s severity and can be categorized into six main types: conventional therapies, biologics, S1P-receptor modulators, and JAK inhibitors. New mechanisms of action, such as LANCL2 protein stimulators, miR-124 enhancers, TNF-like ligand 1A inhibitors, and toll-like receptor 9 agonists, among others, are expected to broaden the range of ulcerative colitis medications.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Cogent Biosciences’ Bezuclastinib Phase 3 PEAK Trial Positive Results for GIST; Domain Therapeuti...
- FDA’s Ok to Roche’s Oral SMA Therapy; Roche’s Etrolizumab Mixed Results in Ulce...
- Eli Lilly strengthening its Gastroenterology portfolio post Acquisition of Morphic. Tracking comp...
- Sandoz’s Generic Revlimid; Agios’ Pyrukynd; Organon Announces 4Q & Full-year Earnings ...
- Pfizer to acquire Arena Pharma; Takeda’s ‘Wave 2’ multiple myeloma med data; No...
Over the years, there have been substantial improvements in the treatment of ulcerative colitis. Despite this, safety continues to be a significant concern. The absence of safer and curative UC meds greatly affects patients’ quality of life and everyday functioning. Although drugs for UC benefit some individuals with ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease, many require multiple lines of therapy, highlighting the need for alternative treatments to manage the disease effectively. Several major pharmaceutical companies are working together to develop new drug for colitis to tackle these challenges.
Several FDA-approved drugs for ulcerative colitis are SIMPONI (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), ENTYVIO (Takeda Pharmaceuticals), XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR (Pfizer), STELARA (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), CAROGRA (EA Pharma/Kissei Pharma), JYSELECA (Gilead Sciences and Galapagos NV), RINVOQ (AbbVie), ZEPOSIA (Bristol-Myers Squibb), REMICADE (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), HUMIRA (AbbVie), OMVOH (Eli Lilly), and SKYRIZI (AbbVie).
SIMPONI is a human monoclonal antibody designed to target and neutralize excess tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, a protein linked to inflammation and tissue damage in chronic inflammatory diseases. As a drug for ulcerative colitis, it holds the distinction of being the first subcutaneous anti-TNF-alpha ulcerative colitis medication administered every four weeks as maintenance therapy. Approved for treating moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults, SIMPONI is also being evaluated in ongoing trials for pediatric patients with the same condition, expanding its potential role among medications for UC.
Vedolizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets and blocks the alpha 4 beta 7 integrin, preventing it from binding to the intestinal mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1 (MAdCAM-1). This integrin is present in a specific group of circulating white blood cells involved in the inflammatory processes of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. By inhibiting this pathway, vedolizumab reduces the infiltration of these immune cells into gut tissues, thereby mitigating inflammation. It is currently approved as a colitis treatment for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis in adults who have not responded to, have lost response to, or cannot tolerate conventional therapy or a TNF-alpha blocker. As one of the new ulcerative colitis medications, it offers a targeted approach among today’s advanced UC medications.
Etrasimod (APD334) is a novel oral ulcerative colitis medication taken once daily, designed to selectively modulate the sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor. Developed by Arena Pharmaceuticals, it is engineered to interact optimally with S1P receptors 1, 4, and 5, potentially offering improved effectiveness and safety. Etrasimod targets specific immune cells both systemically and locally, making it a promising medicine for ulcerative colitis and other immune-mediated inflammatory conditions like Crohn’s disease.
Now approved by both the FDA and EMA, Etrasimod is indicated for adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who have had inadequate response, loss of response, or intolerance to conventional or advanced UC medications.
On June 18, 2024, the FDA approved SKYRIZI for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis. This milestone expands the drug’s accessibility to approximately 1 million patients in the United States. SKYRIZI becomes the first IL-23 inhibitor approved for both ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease—the two primary forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Following a 12-week induction period, patients can self-administer this ulcerative colitis medication at home using an on-body injector device, which AbbVie describes as user-friendly. The device adheres to the body and delivers the medication for ulcerative colitis in about five minutes.
Since its initial approval for Crohn’s disease in 2022, SKYRIZI has emerged as a strong competitor to Johnson & Johnson’s STELARA in the IBD market. AbbVie’s UC medication has already captured a significant portion of STELARA’s market share. The market for ulcerative colitis drugs remains highly competitive, with companies like Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Roche, Eli Lilly, Abivax, Landos Biopharma, NImmune, Merck, Takeda, and Mesoblast Ltd. actively conducting clinical trials to develop new treatments for ulcerative colitis.
Several promising drugs for UC are currently in various stages of development and are expected to further enrich the ulcerative colitis treatment landscape. Now, let’s explore the 7 best ulcerative colitis medications currently under investigation.
TREMFYA (guselkumab): Janssen Pharmaceuticals
Registration
TREMFYA (guselkumab) is a human monoclonal antibody targeting the p19 subunit of interleukin (IL)-23, developed by Janssen. IL-23 plays a key role in the development of inflammatory diseases like ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. As an interleukin-23 inhibitor, TREMFYA is a human immunoglobulin G1 lambda (IgG1λ) monoclonal antibody produced in a mammalian cell line through recombinant DNA technology. It specifically binds to the p19 subunit of IL-23, preventing its interaction with the IL-23 receptor.
Recently, in May 2025, Johnson & Johnson revealed new findings from the Phase III QUASAR long-term extension (LTE) study of TREMFYA in adults with moderately-to-severely active ulcerative colitis (UC). These findings are part of 24 abstracts showcasing the company’s research at Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2025. The QUASAR LTE study data show that patients treated with TREMFYA maintained both clinical and endoscopic effectiveness at Week 92:
- 72% of patients were in clinical remission, with 99% of them remaining corticosteroid-free for 8 weeks or more through Week 92.
- 43% of patients achieved endoscopic remission.
- Among patients who showed endoscopic improvement at Week 44, 84% maintained this improvement through Week 92.
Patients treated with TREMFYA consistently sustained clinical and endoscopic remission, regardless of their prior biologic or JAK inhibitor treatment history.
ABX464 (Obefazimod): Abivax
Phase III
ABX464 is a first-in-class, orally administered small molecule that selectively increases the expression of miR-124 in immune cells. This molecule has shown a strong safety profile and significant anti-inflammatory effects across preclinical studies and Phase IIa and IIb induction trials for ulcerative colitis. ABX464’s mechanism of action, marked by the substantial upregulation of miR-124, a novel RNA splicing product with anti-inflammatory properties, sets it apart from other treatments. Clinical trials have indicated its potential to induce remission and heal inflammatory lesions in ulcerative colitis patients.
The pivotal Phase III ABTECT program is underway, with the first patient in the U.S. enrolled in October 2022. Final patient enrollment for the induction trials is expected in early Q1 2025. Top-line results from the 8-week induction study are anticipated in early Q2 2025, followed by data from the 44-week maintenance trial in Q1 2026. A New Drug Application (NDA) submission is targeted for the latter half of the first half of 2026.
BT-11 (Omilancor): Landos Biopharma/NImmune
Phase III
Omilancor is an innovative, gut-restricted therapeutic in Phase III readiness, intended to overcome the drawbacks of existing treatments for ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. It offers once-daily oral dosing, minimal systemic exposure, and enhanced tolerability without significant toxicity concerns.
Omilancor operates by targeting LANCL2, a membrane receptor that regulates immunological processes linked to ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. This targeting stimulates the production of regulatory CD4+ cells (Tregs), which act locally at the inflammation site in the gastrointestinal tract. This mechanism aims to restore and sustain immune tolerance.
At Digestive Disease Week 2025, new clinical research highlighted the effectiveness of daily oral omilancor in achieving clinical remission in 30.4% of patients with active ulcerative colitis (UC) and 33.3% of those with biologic-refractory UC at the Phase 3 dose of 440 mg/day. The latest findings also revealed that omilancor reverses immunometabolic dysfunction in patients with severe ulcerative colitis and triggers clinical remission, with biomarker improvements observable within just two weeks of starting treatment. Across multiple clinical trials, omilancor has consistently demonstrated an excellent safety profile, with no treatment-related adverse events reported.
This new ulcerative colitis medication was shown to restore depleted colonic regulatory T cells (Tregs) and correct mitochondrial dysfunction, hallmarks of a difficult-to-treat UC patient subgroup that appears particularly responsive to LANCL2-targeting therapies. These results support omilancor’s path toward commercialization for ulcerative colitis, reinforce plans to finalize its Phase III program, and aim for a New Drug Application (NDA) submission to the US FDA by 2027, with further NDA filings to follow.
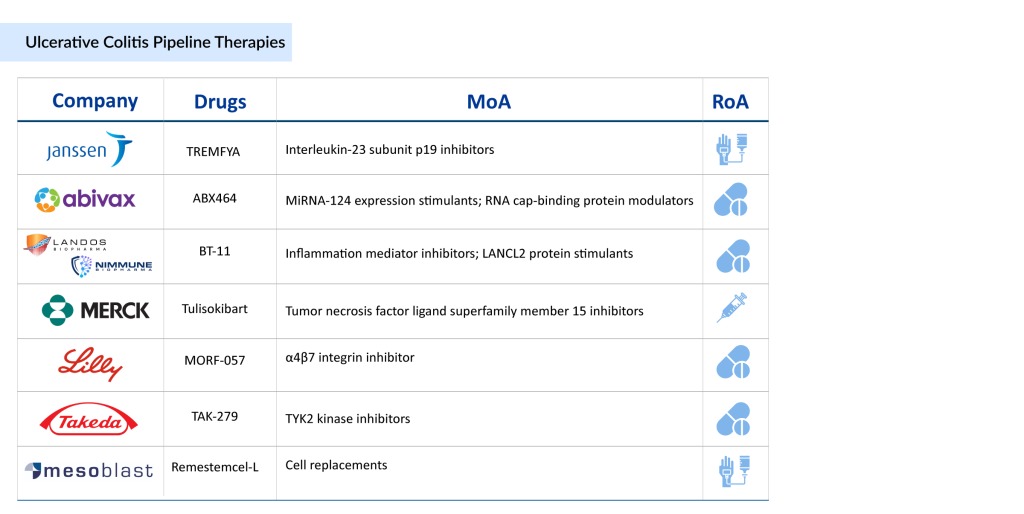
Tulisokibart (MK-7240)/PRA023: Merck
Phase III
Tulisokibart is an experimental humanized monoclonal antibody targeting the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-like ligand 1A (TL1A). It became part of the pipeline through the acquisition of Prometheus Biosciences. This ulcerative colitis drug is currently in Phase III clinical trials. In a Phase II study (NCT04996797), tulisokibart showed greater effectiveness than placebo in achieving clinical remission in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.
MORF-057: Eli Lilly
Phase II
MORF-057 is an oral, selective small molecule inhibitor targeting the α4β7 integrin, developed for treating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The α4β7 integrin is a validated therapeutic target in IBD, as demonstrated by the clinical success of vedolizumab, an approved injectable antibody. Similar to vedolizumab, MORF-057 aims to disrupt the interaction between α4β7 on lymphocytes and the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) on endothelial cells. This mechanism reduces the migration of lymphocytes into the intestinal mucosa, thereby limiting inflammation linked to IBD.
In August 2024, Eli Lilly and Company announced it had completed the acquisition of Morphic Holding, Inc., which includes MORF-057 in its portfolio. Eli Lilly is currently evaluating this ulcerative colitis drug in the phase II stage of development.
TAK-279: Takeda
Phase II
TAK-279, currently in the advanced stages of development, is a specialized oral inhibitor targeting allosteric tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2). It demonstrates exceptional selectivity, showing approximately 1.3 million times greater affinity for TYK2 compared to JAK1. TAK-279 holds promise as a significant therapeutic option for various immune-mediated inflammatory conditions.
Remestemcel-L: Mesoblast Ltd.
Phase I/II
Remestemcel-L, developed by Mesoblast Ltd., contains 100 million mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). In preclinical studies, it has shown immunomodulatory abilities by regulating T-cell mediated inflammatory responses, inhibiting T-cell proliferation, and reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-alpha and interferon-gamma. Importantly, MSCs can effectively down-regulate Th17 cells, lower IL-17 levels, and induce FOXP3 regulatory T cells. These inflammatory pathways are key to the pathogenesis of inflammatory conditions. Remestemcel-L is currently in Phase I/II of clinical development.
The anticipated launch of new drugs for ulcerative colitis represents a major advancement in the treatment landscape, offering the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and quality of life. Historically, managing ulcerative colitis has posed considerable challenges, with many patients facing recurrent symptoms and the risk of long-term complications. However, the emergence of these novel medicines for ulcerative colitis brings renewed hope. Many of these ulcerative colitis meds are designed to target specific pathways involved in the inflammatory process, offering more precise symptom control and better disease management.
By reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups, these medications for ulcerative colitis aim to help patients achieve sustained remission—an essential goal in improving long-term health and daily functioning. This evolution in ulcerative colitis treatment not only enhances clinical outcomes but also boosts quality of life for individuals living with this chronic condition.
Moreover, the arrival of these medicines for ulcerative colitis signals a shift toward more personalized approaches in gastroenterology. Tailoring treatment plans based on factors such as disease severity, genetic profile, and past response to colitis meds allows healthcare providers to fine-tune therapy and reduce the risk of side effects. The broader availability of drugs for UC now enables clinicians to better match therapies with patient needs, potentially lowering healthcare costs linked to flare-ups, complications, and hospital stays.
Overall, the introduction of these new ulcerative colitis treatments marks a transformative era in IBD care, delivering improved disease control, greater patient adherence, and enhanced overall outcomes for those affected.

FAQs
The treatment options for ulcerative colitis vary based on the disease’s severity and can be categorized into six main types: conventional therapies, biologics, S1P-receptor modulators, and JAK inhibitors. New mechanisms of action, such as LANCL2 protein stimulators, miR-124 enhancers, TNF-like ligand 1A inhibitors, and toll-like receptor 9 agonists, among others, are expected to broaden the range of ulcerative colitis medications.
Several FDA-approved drugs for ulcerative colitis are SIMPONI (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), ENTYVIO (Takeda Pharmaceuticals), XELJANZ/XELJANZ XR (Pfizer), STELARA (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), CAROGRA (EA Pharma/Kissei Pharma), JYSELECA (Gilead Sciences and Galapagos NV), RINVOQ (AbbVie), ZEPOSIA (Bristol-Myers Squibb), REMICADE (Janssen Pharmaceuticals), HUMIRA (AbbVie), OMVOH (Eli Lilly), and SKYRIZI (AbbVie).
Companies such as Janssen Pharmaceuticals (TREMFYA), Abivax (ABX464), Landos Biopharma/NImmune (BT-11), Merck (Tulisokibart), Eli Lilly (MORF-057), Takeda (TAK-279), Mesoblast Ltd. (Remestemcel-L), and others are currently evaluating their lead ulcerative colitis drugs in various stages of clinical trials.
Traditional treatments, such as aminosalicylates and immunomodulators, primarily focus on general inflammation. In contrast, emerging therapies target specific immune pathways or cellular mechanisms, offering more precise and potentially effective treatments with fewer side effects.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Gilead Sciences’ Sunlenca Approval; FDA Approves Roche’s CD20xCD3 Bispecific Antibody Lunsumio; E...
- Algernon’s NP-120; FDA nod to 4DMedical tool; SaNOtize’s NORSTM trial; Pole’s c...
- Cogent Biosciences’ Bezuclastinib Phase 3 PEAK Trial Positive Results for GIST; Domain Therapeuti...
- FDA’s Ok to Roche’s Oral SMA Therapy; Roche’s Etrolizumab Mixed Results in Ulce...
- Sandoz’s Generic Revlimid; Agios’ Pyrukynd; Organon Announces 4Q & Full-year Earnings ...