Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry: Revolutionizing Patient Care
Jun 06, 2025
Table of Contents
The healthcare industry is witnessing immense growth and transformation owing to the ongoing development and adoption of new and innovative technologies and trends. Electronic Health Records (EHR), telemedicine, telehealth, medical research, and analytics are some of the key technologies playing a crucial role in the healthcare market and delivering optimum results. These technologies are greatly streamlining the healthcare delivery process and treatment outcomes. However, the major factor behind the growing adoption and smooth functioning of these innovative applications is Cloud Computing. Over a short period of time, Cloud Computing has shifted the healthcare industry outcomes.
Cloud computing in healthcare is a rapidly evolving trend that delivers computing services via the Internet, enabling on-demand access to a shared pool of resources. The types of cloud computing in healthcare available today cater to diverse organizational needs, offering scalable and secure storage solutions crucial for managing the enormous volume of data generated, such as electronic health records, medical imaging, and patient monitoring.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- AI Hospitals of the Future–Where Robotics, Predictive Analytics, and Compassion Converge
- Utilization of Artificial Intelligence for Drug Commercialization
- From Lab to Bedside: The Rise of AI-Enabled Digital Pathology
- Breakthrough Device Designation granted to the AI Software for CTEPH
- AI in Cancer Diagnostics: Paving the Way for Early Detection and Precision Treatment
With cloud computing for healthcare, providers no longer rely on on-premises infrastructure, benefiting from efficient data storage and seamless access. The growing demand for collaboration and information sharing among healthcare professionals has driven the integration of cloud services in the healthcare sector. This facilitates real-time communication and data exchange, enhancing care coordination, accelerating decision-making, and improving patient outcomes. Numerous healthcare cloud computing companies and medical cloud service providers continue to innovate, expanding healthcare cloud enablement solutions that address both the advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing in healthcare. Cloud technology in healthcare is transforming how medical data is managed and services are delivered, shaping the future of the healthcare cloud computing market.
How is Cloud Computing Used in Healthcare?
As technology and demand grow, the role of cloud technology in healthcare is increasingly vital in facilitating healthcare delivery through electronic medical records, mobile apps, patient portals, IoT-enabled devices, and big data analytics. Cloud computing in healthcare offers the scalability and flexibility needed to enhance data management and ultimately improve the decision-making process.
Some of the key applications of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Market include:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Cloud-based Electronic Health Records (EHR) are aimed at providing the right information at the right time and right place needed. Cloud-based EHR systems allow healthcare providers to securely store, access, and share patient data in real-time. It facilitates a seamless collaboration among medical providers, clinicians, and facility management and enhances the overall continuity of care. Moreover, it enables the data mining capabilities of the administrators and assists in examining work processes and delving into patient data to identify behavior patterns, potential drug interactions, and health risk factors. The cloud-based EHR is a more scalable, flexible, intuitive, and cost-effective solution. Healthcare data stored in the cloud can be collected and reported as quality indicators of healthcare quality.
- Telemedicine and Remote Patient Monitoring: Telemedicine and Remote patient monitoring is another key segment getting significant assistance with the Cloud Computing technique. Cloud computing greatly enhances the remote patient monitoring, telemedicine consultations, and virtual healthcare services experience of the user. With Cloud Computing in place, healthcare services providers can securely transmit medical data, such as vital signs and diagnostic images, for real-time analysis and consultation.
- Data Storage and Backup: Cloud Computing, sometimes referred to as online backup or remote backup, as it provides a secure and scalable environment for storing large volumes of medical data. When a company or organization backs up the data to the cloud, it stores a copy of that data on one or more remote cloud-based servers, which are owned and managed by a third-party cloud service provider. Cloud computing can reduce reliance on physical infrastructure, improves data accessibility, and ensures data redundancy through automated backups.
- Medical Research and Analytics: Cloud computing offers computational power and storage capabilities to healthcare researchers and data scientists. They can analyze vast amounts of clinical and genomic data, accelerate drug discovery, and gain valuable insights into disease patterns and treatment effectiveness.
Similarly, healthcare providers are building an integrated ecosystem by leveraging the capabilities of cloud computing in the healthcare industry across segments like IoT, Artificial Intelligence (AI), and machine learning. By combining these technologies with cloud computing for healthcare, medical personnel can enhance patient engagement, identify care gaps, achieve improved outcomes, and pinpoint opportunities for further medical research and development.
What are the Key Features That Need to be Evaluated Before Implementing Cloud Computing in Healthcare Businesses?
When it comes to choosing a cloud computing solution for healthcare, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. The type of system and cloud computing healthcare solution varies greatly depending on the organization’s size, scale of utilization, customer needs, and budget, among other factors. Various cloud solutions for the healthcare industry are available in the market today to meet the diverse needs of healthcare organizations. However, while selecting cloud computing systems and applications in healthcare, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal implementation and performance.
- Security and Compliance: Robust security measures, data encryption, and strict access controls are essential to protect sensitive patient information. Countries worldwide follow different compliance standards and data storage and usage regulations. Healthcare organizations must prioritize solutions that adhere to industry regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States. Cloud Solutions that abide by industry rules like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) must be given top priority by healthcare organizations. To protect sensitive patient information, rigorous access limits, data encryption, and robust security measures are necessary.
- Scalability and Performance: Scalability and Performance are other key factors in Cloud Computing adoption. Scalability is the ability of a system to handle and meet the changing demand without impacting the application’s performance or availability. The organization or the healthcare facility needs to assess the cloud platforms that can handle increasing data volumes, accommodate fluctuating demand, and deliver high-performance services. Scalable infrastructure and robust network capabilities are crucial for seamless operations.
- Interoperability: Interoperability plays an important role in any digital system, as it facilitates the exchange of information. Cloud solutions need to be capable of moving an application from one cloud service to another, or between a client’s environment and a cloud service. Cloud solutions that offer seamless integration with existing healthcare systems, such as EHRs and medical devices, are vital. This ensures efficient data exchange and interoperability across different healthcare providers and systems.
- Vendor Reliability and Support: Reliability in cloud computing systems encompasses different criteria such as downtime, cost-efficiency, performance, and security. Healthcare organizations or facilities need to adopt a reputable cloud service provider with a strong track record. Reliable customer support, service-level agreements (SLAs), and compliance with regulatory requirements are important factors to consider.
What are the Key Benefits of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry?
In recent years, the healthcare industry has undergone a significant digital transformation, driven largely by the rapid adoption of cloud computing in healthcare. With each passing day, the scale of cloud computing in the healthcare industry adoption continues to grow. Organizations of all sizes, from small clinics to large hospital networks, are implementing cloud computing healthcare solutions to gain a competitive edge and unlock new revenue potential. When it comes to selecting a cloud computing solution for healthcare, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. These solutions are used in diverse ways across various healthcare verticals to revolutionize patient care, enhance operational efficiency, and support the broader digital evolution of healthcare services.
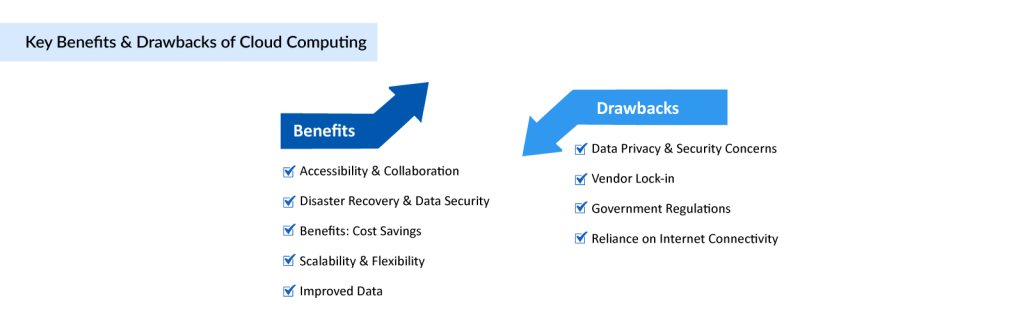
Some of the major benefits of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry are as follows:
- Cost Savings: Cloud computing is cost-effective because costs usually directed at purchasing hardware and software are immediately eliminated. Cloud-based solutions also reduce the need for large capital investments in maintenance and upgrades. Moreover, various lucrative options are available in the market. Healthcare organizations can opt for a pay-as-you-go model, reducing upfront costs and enabling budget flexibility.
- Enhanced Data Accessibility and Collaboration: One of the key factors for the high demand for Data Cloud-based systems in the healthcare market is the accessibility and collaboration opportunities. Cloud-based systems provide secure, real-time access to patient records, allowing healthcare professionals to access critical information from anywhere, anytime. It significantly improves the collaboration among care teams, leading to enhanced patient outcomes and reduced medical errors.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud infrastructure allows healthcare organizations to scale their computing resources based on demand. This flexibility enables them to handle peak workloads efficiently, accommodate new applications, and easily adapt to changing organizational needs.
- Disaster Recovery and Data Security: Cloud-based backups and disaster recovery mechanisms ensure data redundancy and business continuity. In the event of a physical disaster or system failure, healthcare organizations can quickly recover critical data and resume operations.
What are the Major Drawbacks of Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry?
While cloud computing offers numerous benefits, some drawbacks need to be evaluated before making any final decision, some of which include:
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: Data privacy and security have always been a big concern with the digital sharing and exchange of information all over the world. In industries like healthcare, it becomes even more difficult and sophisticated to handle large amounts of private data related to patients’ health. Similarly, with cloud technology, there are some concerns in the healthcare industry. Storing sensitive patient data in the cloud raises concerns about data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance with privacy regulations. Healthcare organizations need to carefully evaluate the security measures implemented by cloud service providers.
- Reliance on Internet Connectivity: Internet connection is a must for Cloud Computing to operate. Cloud-based systems heavily rely on robust and uninterrupted internet connectivity. Any disruptions or network outages can hinder access to critical patient data and disrupt healthcare operations.
- Vendor Lock-in: Vendor lock-in occurs when the organization relies solely on one cloud provider for a particular service (or a number of them) when using public cloud services. Some of the key concerns, such as excessive costs, legal restrictions, or technical incompatibilities, may force the organization to switch vendors. But it becomes extremely difficult in the case of Cloud technologies. Moving data and applications to the cloud may result in vendor lock-in, making it challenging to switch to alternative platforms or providers in the future. Healthcare organizations must consider exit strategies and ensure data portability. A careful evaluation is needed before implementing Cloud Computing.
What are the Key Challenges in Utilizing Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry?
Despite several benefits, there are several challenges associated with the implementation of cloud technology in the healthcare market. Some of the key challenges and drawbacks of implementing cloud computing in the healthcare industry include:
- Legacy System Integration: Many healthcare organizations have legacy systems that are not easily compatible with cloud platforms. Migrating data and integrating existing systems with cloud solutions can be complex and time-consuming.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Ensuring interoperability and data exchange between various healthcare systems, EHRs, and devices remains a significant challenge. The lack of standardized formats and protocols complicates data integration and hampers seamless collaboration.
- Change Management and Training: Transitioning to cloud-based solutions requires healthcare professionals to adapt to new workflows and processes. Adequate training and change management strategies must be implemented to ensure the successful adoption and utilization of cloud computing technologies.
- Government Regulations: Countries worldwide follow different rules and regulations to govern the different IT products and services. Countries in North America and European regions follow strict regulations to deal with data storage and exchanges. Contrary to it, in most of the developing countries, there is no overarching or specific regulation at present on providing cloud services.
Major Companies in Cloud Computing in the Healthcare Industry
Currently, several major tech giants and HealthTech companies are at the forefront of cloud computing in the healthcare industry. These healthcare cloud providers and medical cloud service providers are actively working to expand their market share by offering innovative cloud computing healthcare solutions and services. Some of these companies have a strong global presence and dominate specific segments of the cloud computing in healthcare market. At the same time, local and national healthcare cloud computing companies are also competing vigorously to capture market share and address the evolving needs of healthcare organizations.
Some of the key companies with a strong global presence in the Cloud Computing market include:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS offers a range of cloud services tailored for healthcare, including secure data storage, analytics, and machine learning tools. Their HIPAA-compliant infrastructure has gained traction among healthcare organizations.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure provides a comprehensive cloud platform with services specifically designed for healthcare organizations. It offers scalable infrastructure, advanced analytics, and AI capabilities to support healthcare workflows and research.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): GCP offers a robust cloud infrastructure along with specialized healthcare solutions, including secure data storage, machine learning tools, and interoperability capabilities.
- IBM Cloud: IBM Cloud provides healthcare-specific cloud solutions, such as Watson Health, which combines AI and analytics to support clinical decision-making, drug discovery, and population health management.

SAS, Athenahealth, Oracle, Dell Technologies, Amazon Web Services, Azure, NTT DATA, GE Healthcare Cloud, Salesforce Health Cloud, DXC Healthcare Cloud, Cerner, Allscripts, and Progress Health Cloud, are among other major players actively working to provide various Cloud Computing solutions in the healthcare industry. Similarly, several new startups are anticipated to enter the market with more innovative and advanced technologies in the upcoming years, thereby elevating the competitiveness in the domain.
The Future of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Over the past few years, cloud computing has gained significant attention among various stakeholders and organizations operating in the healthcare domain. The cloud computing in the healthcare industry is evolving at an immense pace, driven by scalable, secure, and collaborative cloud solutions for the healthcare industry. The applications of cloud computing in healthcare are expanding rapidly across diverse functions. While advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing in healthcare exist, particularly for some small entities, the availability of affordable and advanced medical cloud services tailored to different business needs makes it a technology healthcare providers cannot afford to ignore.
In the coming years, cloud computing in healthcare is expected to further fuel innovation in healthcare analytics and AI-driven applications. Predictive analytics, precision medicine, and personalized patient care will become more accessible and efficient through healthcare cloud services. Likewise, cloud computing in medicine will accelerate the adoption of Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices and wearables, enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and seamless integration of cloud services in the healthcare sector. This will greatly enhance remote patient monitoring and preventive care. Blockchain, combined with cloud computing healthcare solutions, also holds the potential to revolutionize data privacy, interoperability, and secure patient consent management. Additionally, cloud computing and healthcare services will play a critical role in advancing population health management, disease surveillance, and public health interventions through enhanced analytics capabilities.
Despite some challenges, the benefits of cloud computing in healthcare far outweigh the drawbacks. To fully harness its potential and improve patient care in the digital era, healthcare organizations must carefully assess their needs and collaborate with credible healthcare cloud computing companies and healthcare cloud providers. Overall, the future of cloud computing in the healthcare market looks exceptionally promising, with wide-ranging applications and significant advantages for service delivery.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Artificial Intelligence in Remote Patient Monitoring: Enabling Continuous, Predictive, and Person...
- Breakthrough Device Designation granted to the AI Software for CTEPH
- From Paper to Pixels: The Advantages and Challenges of Electronic Health Record
- Top Artificial Intelligence-Based Healthcare Mobile Apps and Their Use Cases
- Healthcare Mobility Solutions: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Operational Efficiency