Epilepsy Market
- The Epilepsy Market is set for steady growth, with a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 7% anticipated from 2024 to 2034. This expansion in the 7MM is driven by the introduction of innovative therapies such as LIBERVANT (diazepam buccal film), XEN1101, COMFYDE (carisbamate), Lorcaserin (E2023), Soticlestat (TAK-935), among others.
- The Epilepsy Therapeutics Market is becoming increasingly competitive, driven by the development of new therapies and innovative treatment approaches. Moreover, the epilepsy surgery market has witnessed a good number of recent approvals, targeting specific segments of patients like acute repetitive seizures, partial onset seizures, Lennox-Gastaut syndrome (LGS), etc.
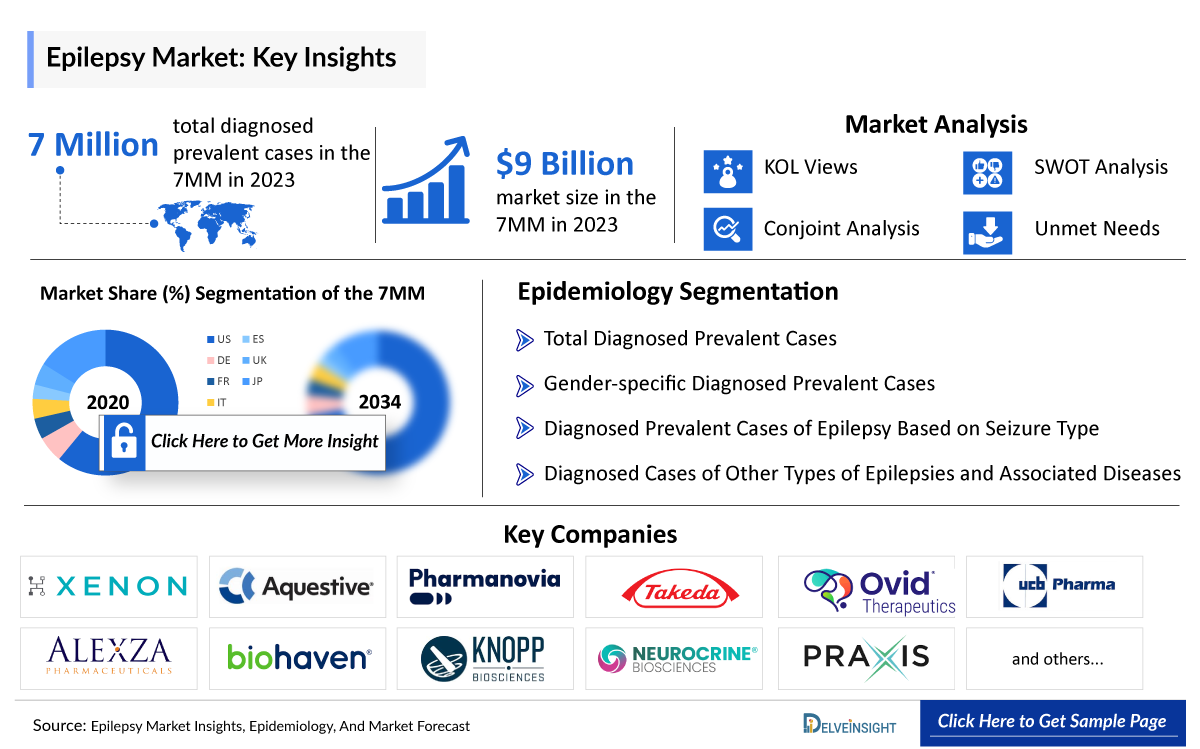
- According to DelveInsight’s estimates, in 2023, there were approximately 7 million total Epilepsy diagnosed prevalent cases in the 7MM. Of these, the US accounted for 48% of the cases, the EU4 and the UK represented 39% of the cases, while Japan reported 13% respectively.
- Most current antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) primarily focus on controlling seizures rather than curing epilepsy and often come with cardiovascular and respiratory side effects. For patients with Refractory Epilepsy, these drugs offer limited effectiveness, leaving many still experiencing seizures despite multiple drug combinations, highlighting a significant therapeutic gap.
- A robust drug development pipeline that might target certain ion channels, receptors, or neurotransmitters involved in the production, transmission, or modulation of seizures might change the Epilepsy market dynamics during the forecast period.
Request for unlocking the sample page of the "Epilepsy Diagnosis & Treatment Market"
DelveInsight’s “Epilepsy Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast – 2034” report delivers an in-depth understanding of Epilepsy, historical and forecasted epidemiology, as well as the Epilepsy market trends in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan.
The Epilepsy Diagnosis & Treatment Market report provides current treatment practices, emerging drugs, market share of individual therapies, and current and forecasted 7MM Epilepsy market size from 2020 to 2034. The report also covers Epilepsy diagnosis & treatment market practices/algorithms and unmet medical needs to curate the best opportunities and assess the market’s potential.
|
Study Period |
2020–2034 |
|
Forecast Period |
2024–2034 |
|
Geographies Covered |
|
|
Epilepsy Epidemiology |
|
|
Epilepsy Surgery Market |
|
|
Epilepsy Market Analysis |
|
|
Epilepsy Companies |
|
|
Future opportunity |
The epilepsy surgery market holds future opportunities with the development of novel therapies targeting refractory and drug-resistant epilepsy. Advances in precision medicine, gene therapy, and neuromodulation promise more personalized treatments, while innovations in digital health and wearable technologies could enhance seizure monitoring and patient adherence. A focus on addressing the underlying causes of epilepsy, beyond symptomatic relief, may lead to groundbreaking therapies and expanded market potential. |
Epilepsy Diagnosis & Treatment Market
The World Health Organization (WHO) describes epilepsy as a chronic, non-communicable brain disorder that affects individuals of all ages and contributes to a burden worldwide. It is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. A seizure is a sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbance in the brain that can manifest in various ways, such as convulsions, altered consciousness, unusual sensations, or behaviors. Characteristics of seizures vary and depend on where in the brain the disturbance first starts and how far it spreads. There are transient symptoms that manifest as awareness or consciousness loss, as well as disruptions in movement, emotion, taste, hearing, vision, and other cognitive functions.
In epilepsy, the normal pattern of neuronal activity becomes disturbed due to a series of physiological changes and events such as impaired Na+/K+ ATPase activity, reduced GABA releases from interneurons, calcium overload, loss of hyperpolarization that leads to strange sensations, emotions, and behavior or sometimes convulsions, muscle spasms, and loss of consciousness. Moreover, in the majority of instances worldwide, the pathogenesis is still unknown, which is why the condition is referred to as idiopathic epilepsy.
As per the International League against Epilepsy (ILAE) Classification 2017, seizures are classified as focal onset seizure that originates in a localized area of the brain and includes (simple focal seizure, complex focal seizure), and generalized onset seizures that involve both hemispheres of the brain from the onset (tonic-clonic seizure, myoclonic seizure, atonic seizure, and absence seizure). Based on etiology, seizures are further classified as cryptogenic (unknown cause) and symptomatic seizures that result from an identifiable cause, such as a brain injury or infection.
Furthermore, certain combinations of clinical features and epilepsy types are associated with specific syndromes such as Lennox–Gastaut Syndrome (LGS), Dravet Syndrome, juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, and others. Certain factors, including age, family history, head injury, dementia, brain infections, seizures in childhood, and stroke, may increase the risk of epilepsy
Epilepsy Diagnosis
Epilepsy diagnosis involves a comprehensive evaluation that includes a detailed medical history, neurological examination, and an Electroencephalography (EEG) to detect abnormal brain activity. Imaging tests, such as MRI or CT scans, are used to identify any structural brain abnormalities. Blood tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions, and in some cases, video EEG monitoring or functional imaging is used for more precise analysis. This thorough approach helps determine the presence, type, and potential causes of epilepsy.
Epilepsy Treatment
The management of epilepsy involves a comprehensive approach aimed at controlling seizures, improving the individual’s quality of life, and addressing any associated issues, but none of them is curative. It includes the pharmacological, nonpharmacological (ketogenic diet), and medical device approaches (vagus nerve stimulation [VNS], deep brain stimulation). Medications are the early treatment choice for almost all patients with multiple seizures.
Some patients who only have a single seizure and whose tests do not indicate a high likelihood of seizure recurrence may not need medications. The medications treat the symptoms of epilepsy (seizures) rather than curing the underlying condition. They are highly effective and completely control seizures in most patients (approximately 70%). The drugs prevent seizures from starting by reducing the tendency of brain cells to send excessive and confused electrical signals. The choice of medication depends on a variety of factors, some of which include the type of seizure and type of epilepsy, the likely side effects of the medication, other medical conditions the patient may have, potential interactions with the patient’s other medications, age, gender and cost of the medication.
In principle, anticonvulsant therapy in adults is usually considered after two unprovoked epileptic seizures. Since most patients can be treated successfully with one agent, there is a broad consensus that therapy should be started by choosing a single anti-epileptic drug of the first choice. The advantages of monotherapy are obvious – ease of concordance with a treatment plan, fewer interactions, and fewer side effects. The choice of the first agent is determined by seizure type, tolerability, efficacy, and patient characteristics like age, gender, contraception, or family planning issues. Several anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) have been approved for the treatment of epileptic patients; generics of most of these therapies are already available in the market, including lamotrigine, sodium valproate, carbamazepine, levetiracetam, topiramate, and others. Certain recently approved epilepsy therapies include XCOPRI, FYCOMPA MOA, NAYZILAM, EPIDIOLEX, BRIVIACT, SYMPAZAN, and others.
Currently, the first-line monotherapy of AEDs can be classified as sodium channel modulators (phenytoin, lacosamide, BRIVIACT), gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptor modulator (XCOPRI, clobazam, and others), calcium channel blockers, synaptic vesicle protein SV2A modulator, Na+/Ca2+ channel modulators, other mono or combo therapies. While the second line of therapies includes mono or combo AEDs. Furthermore, brain surgery for epilepsy may be considered when other pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment options have failed to provide adequate seizure control, impacting the person’s quality of life.
Epilepsy Epidemiology
As the Epilepsy diagnosis & treatment market is derived using a patient-based model, the Epilepsy epidemiology chapter in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by total diagnosed prevalent cases of epilepsy, gender-specific diagnosed prevalent cases of epilepsy, diagnosed prevalent cases of epilepsy based on seizure type, diagnosed cases of other types of epilepsies and associated diseases in the 7MM covering the United States, EU4 countries (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) and the United Kingdom, and Japan from 2020 to 2034.
- In the 7MM, the total Epilepsy diagnosed prevalent cases were nearly 7 million in 2023, which is expected to increase at a CAGR of 0.4% by 2034.
- In the US, the total diagnosed epilepsy prevalence cases were approximately 3.3 million in 2023, of which nearly 14% of cases were diagnosed in children and 86% in adults; the total cases of epilepsy are expected to increase by 2034.
- In 2023, the diagnosed prevalent cases in the EU4 and the UK comprised nearly 1.3 million male cases and 1.5 million female cases. These numbers are expected to rise throughout the study period.
- In 2023, among EU4 and the UK, Germany had the highest number of cases of epilepsy, i.e., 735 thousand, of which nearly 74% of the cases were focal epileptic seizures, 18% were generalized epileptic seizures, while 8% of the cases were other determined or undetermined epileptic seizures.
- Among the 7MM, in 2023, Japan accounted for the second highest diagnosed prevalent cases of epilepsy, i.e., 890 thousand cases, these cases are expected to change during the study period.
- In Japan, among the other types of epilepsies and associated diseases, the highest cases were found in drug-resistant epilepsy/refractory cases, i.e., 82 thousand followed by photosensitivity and childhood absence epilepsy with equal cases, i.e., 44 thousand, in 2023. These cases are expected to change by 2034.
Epilepsy Recent Developments
- In March 2025, EpiWatch, Inc., a commercial-stage company spun out from Johns Hopkins University, announced that it received FDA 510(k) clearance to market EpiWatch in the U.S. EpiWatch® is a Continuous Seizure Monitor (CSM™) platform that works with Apple Watch to detect and alert for tonic-clonic seizures in people with epilepsy.
- In January 2025, the FDA granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to Capsida Biotherapeutics for CAP-002, a first-in-class gene therapy for STXBP1 disorder, developed in collaboration with Dr. Mingshan Xue at Texas Children’s Duncan Neurological Research Institute.
- In January 2025, Alembic received FDA approval for its generic version of AbbVie’s Depakote Sprinkle, divalproex sodium delayed-release capsules (125 mg). Divalproex sodium is an anti-epileptic drug used to treat epilepsy, specifically for complex partial seizures, simple and complex absence seizures, and as adjunctive therapy for multiple seizure types.
- In December 2024, Aquestive Therapeutics, Inc. (NASDAQ: AQST) announced that the FDA has granted seven years of orphan drug exclusivity (ODE) to Libervant® (diazepam) Buccal Film. This treatment is indicated for managing acute episodes of seizure clusters or acute repetitive seizures in epilepsy patients aged 2 to 5 years, offering a novel solution for these critical situations.
Epilepsy Marketed Drugs
- LIBERVANT (diazepam buccal film): Aquestive Therapeutics/Atnahs Pharma (Pharmanovia)
LIBERVANT is a buccally, or inside of the cheek, administered film formulation of diazepam, a benzodiazepine intended for the acute treatment of intermittent, stereotypic episodes of frequent seizure activity (i.e., seizure clusters) that are distinct from a patient’s usual seizure pattern in patients with epilepsy 12 years of age and older. The drug has been developed as an alternative to the device-based products currently available for patients with refractory epilepsy, including rectal gel and nasal spray products. The company has utilized PharmFilm technology to develop a diazepam formulation that is absorbed directly through the buccal mucosa. The buccal mucosa’s wide, relatively immobile, and highly permeable surface area provided the stable and controlled microenvironment needed to optimize adhesion, absorption, and onset of action.
In April 2024, the US FDA approved LIBERVANT (diazepam buccal film) for the acute treatment of intermittent, stereotypic episodes of frequent seizure activity (i.e., seizure clusters, acute repetitive seizures) that are distinct from a patient’s usual seizure pattern in patients with epilepsy between 2 to 5 years of age.
- EPIDIOLEX/EPIDYOLEX (cannabidiol): Jazz Pharmaceuticals
EPIDIOLEX/EPIDYOLEX (cannabidiol), an oral solution, is a clear, colorless-to-yellow liquid containing cannabidiol at 100 mg/mL concentration. Cannabidiol, the active ingredient in EPIDIOLEX, is a cannabinoid that naturally occurs in the Cannabis sativa L. plant. Inactive ingredients include dehydrated alcohol, sesame seed oil, strawberry flavor, and sucralose. EPIDIOLEX contains no ingredient made from a gluten-containing grain (wheat, barley, or rye). The precise mechanisms by which EPIDIOLEX exerts its anticonvulsant effect in humans are unknown.
EPIDIOLEX is approved for the treatment of seizures associated with Lennox-Gastaut syndrome, Dravet syndrome, or tuberous sclerosis complex. Jazz Pharmaceuticals had initiated a Phase III trial to treat children and adolescents living with developmental and epileptic encephalopathy, however, the trial was terminated due to a business decision. The Japanese unit of Jazz Pharmaceuticals has started a trial of the drug for epilepsy in Japan.
- XCOPRI/ONTOZRY (cenobamate): SK Biopharmaceutical/Angelini Pharma/Ono Pharmaceutical
Cenobamate is a novel antiseizure medication discovered and developed by SK Biopharmaceuticals and SK Life Science. While the precise mechanism by which cenobamate moa exerts its therapeutic effect is unknown, it is believed to reduce repetitive neuronal firing by inhibiting voltage-gated sodium currents. It is also a positive allosteric modulator of the ion channel ?-aminobutyric acid (GABA-A). Cenobamate is approved in the US for the treatment of partial-onset seizures in adults and is available under the brand name XCOPRI (cenobamate tablets). It can be combined with other ASMs or used alone
Cenobamate moa is also approved in the EU and the UK for the adjunctive treatment of focal-onset (partial-onset) seizures with or without secondary generalization in adult patients with seizures that have not been adequately controlled despite a history of treatment with at least two anti-epileptic medicinal products and is marketed by Angelini Pharma under the brand name ONTOZRY. Additionally, cenobamate moa is in clinical development in Asia, and Ono Pharmaceutical has the rights to develop and commercialize cenobamate moa in Japan. ONO-2017 is being developed in Japan for the treatment of primary-generalized tonic-clonic seizures and partial-onset seizures. Further, cenobamate moa is being investigated for primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures.
- AFINITOR DISPERZ/VOTUBIA (everolimus): Novartis
AFINITOR DISPERZ/VOTUBIA is an oral inhibitor of the mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. AFINITOR DISPERZ is the first adjunctive treatment approved in the US, specifically for adult and pediatric patients aged 2 years and older with TSC-associated partial-onset seizures. The product is also approved in more than 30 countries, including EU member states, for treating TSC-associated seizures. AFINITOR works by inhibiting the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a protein that regulates multiple cellular functions. Treatment with an mTOR inhibitor in animal models of mTOR dysregulation in the brain resulted in prolonged survival, seizure suppression, prevention of the development of new-onset seizures, and prevention of premature death. Additionally, the drug is approved for other indications, including TSC with subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEGA). The recommended starting dosage of AFINITOR DISPERZ (everolimus tablets for oral suspension) is 5 mg/m2 orally once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
|
Drug |
MoA |
RoA |
Company |
Phase |
|
XEN1101/ Azetukalner |
Kv7 potassium channel agonist |
Oral |
Xenon Pharmaceuticals |
III |
|
Soticlestat (TAK-935) |
Cholesterol 24-hydroxylase inhibitor |
Oral |
Takeda/ Ovid Therapeutics |
III |
|
BHV-7000 (KB-3061) |
Kv7.2/7.3 potassium channels activator |
Oral |
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals/Knopp Biosciences |
II/III |
|
XX |
XX |
XX |
XXX |
X |
Note: Further marketed drugs and their details will be provided in the report...
Epilepsy Emerging Drugs
- XEN1101/Azetukalner: Xenon Pharmaceuticals
XEN1101 is a novel, orally administered, potent, selective KCNQ2/3 (Kv7.2/7.3) potassium channel opener being developed to treat focal onset seizures and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (PGTCS). It acts as a neuronal Kv7 voltage-gated potassium channel opener and has been developed to stabilize nerve cells, control action potential burst firing, and reduce brain hyperexcitability as a seizure treatment. The Kv7 potassium channel mechanism has been clinically validated with ezogabine. The FDA approved this earlier generation Kv7 modulator as an adjunctive treatment for adults with focal seizures with or without secondary generalization. XEN1101’s unique composition is chemically designed to improve the potency, selectivity, and pharmacokinetics of ezogabine and is not expected to have ezogabine’s composition-specific tissue pigmentation effects.
The drug is currently being investigated in multiple Phase III clinical trials to treat patients with focal-onset and primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures with topline data anticipated in the second half of 2025. Moreover, the drug is also being developed for major depressive disorder and is undergoing Phase II clinical trials.
- Soticlestat (TAK-935): Takeda/Ovid Therapeutics
Soticlestat (TAK-935), formerly known as OV935, is a potent, highly selective, first-in-class inhibitor of the enzyme cholesterol 24-hydroxylase (CH24H). CH24H is predominantly expressed in the brain and plays a central role in cholesterol homeostasis. CH24H converts cholesterol to 24-S-hydroxycholesterol (24HC), exiting the brain into the blood plasma circulation. It is believed that CH24H is involved in the over-activation of the glutamatergic pathway, which has been shown to play a role in the initiation and spread of seizure activity. TAK-935 is the only molecule with this mechanism of action in clinical development.
Inhibition of CH24H by soticlestat reduces the neuronal levels of 24HC and may improve the excitatory/inhibitory balance in the brain, thereby reducing seizure susceptibility and improving seizure control. Recently the company posted topline results for soticlestat (TAK-935) in patients with dravet syndrome and lennox-gastaut syndrome. Soticlestat showed a consistent and favorable safety and tolerability profile in the studies. Furthermore the company will move forward to discuss the totality of the data with regulatory authorities.
- BHV-7000 (KB-3061): Biohaven Pharmaceuticals/Knopp Biosciences
BHV-7000 is a potent, selective activator of Kv7.2/7.3 potassium channels, a clinically validated target to regulate the hyperexcitable state in epilepsy. BHV-7000 is structurally and pharmacologically distinct from other potassium channel activators and demonstrates minimal GABAA receptor activation, potentially providing better tolerability. BHV-7000 was potent in the maximal electroshock (MES) preclinical epilepsy model without adverse effects on neurobehavior and was well-tolerated in a Phase I SAD/MAD clinical study without CNS adverse events typical of antiseizure medications.
Currently, Phase II/III studies in focal epilepsy are ongoing. Moreover, the company is also enrolling participants in ongoing pivotal clinical trials with the Kv7 activator, BHV-7000, targeting generalized epilepsy, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder.
Note: Further emerging therapies and their detailed assessment will be provided in the final report...
Epilepsy Drugs Market Insights
Epilepsy treatment involves various drug classes to control seizures, including sodium channel blockers (e.g., phenytoin, lamotrigine), which stabilize neuronal activity by inhibiting abnormal electrical impulses. Calcium channel blockers (e.g., ethosuximide) are effective for absence seizures, while GABAergic agents (e.g., valproate, benzodiazepines) enhance inhibitory neurotransmission to reduce seizure frequency. Newer-generation AEDs like levetiracetam and topiramate offer broader efficacy with fewer side effects, addressing both generalized and focal seizures. Non-pharmacological options such as vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) and the ketogenic diet are also utilized, particularly in drug-resistant cases, providing additional therapeutic avenues.
Epilepsy Market Outlook
The Epilepsy treatment paradigm or its management strategies involves three main categories, i.e., pharmacotherapy, surgery, and alternative treatment strategies, including neurostimulation, ketogenic diet, and lifestyle changes. Medical professionals decide the treatment line according to the patient’s condition and the severity of the case.
The commonly used treatment therapy for epilepsy is anti-epileptic medications (AEDs). The early treatment choice for almost all patients with multiple seizures is AEDs. The medications treat the symptoms of epilepsy (seizures), are highly effective, and completely control seizures in the majority (70%) of cases. The drugs prevent seizures from starting by reducing brain cells’ tendency to send excessive and confused electrical signals.
The choice of medication depends on a variety of factors, some of which include the type of seizure and type of epilepsy, epilepsies syndromes, the likely side effects of the medication, other medical conditions the patient may have, potential interactions with the patient’s other medications, age, gender and cost of the medication. Anticonvulsant therapy is also considered after two unprovoked epileptic seizures. The medication prescribed by the medical practitioner could be monotherapy or a combinational therapy, including two or more products as a medication.
AEDs that have been tested in rigorous scientific trials and got approval from regulatory authorities, including carbamazepine, cannabidiol, cenobamate moa, brivaracetam, divalproex sodium, clobazam, felbamate, fenfluramine, clonazepam, eslicarbazepine, everolimus, ethosuximide, gabapentin, ganaxolone, lacosamide, lamotrigine, midazolam, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, perampanel, phenobarbital, phenytoin, pregabalin, primidone, rufinamide, sodium valproate, stiripentol, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin, valproic acid market, and zonisamide are the mainstay of epilepsy treatment.
However, several drugs have their generic version in the market due to the loss of patent exclusivity. There is a variety of mechanisms of action, and some AEDs possess multiple mechanisms of action. Although precise mechanisms of some drugs remain elusive, antiseizure medications tend to be grouped by their principal mode of action. Some AEDs act on the sodium channels by either blocking their repetitive activation (phenytoin, carbamazepine). Others work on calcium channels by blocking either T-type calcium channels (ethosuximide, valproic acid market) or the N- and L-type calcium channels (zonisamide). Lamotrigine works by blocking sodium channels, N- and L-type calcium channels, and modulating H-current. Topiramate works by blocking sodium channels, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors, and by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase.
Other mechanisms through which AEDs act are by enhancing gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-A receptors (phenobarbital, benzodiazepines), blocking N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors (felbamate), and opening neuronal potassium channels (ezogabine). More detailed descriptions of some of these drugs are provided in the following paragraphs.
Epilepsy treatment is prescribed based on several factors, including rare and severe forms of epilepsy, epileptic syndromes (Dravet syndrome, infantile spasms, tuberous sclerosis complex, Lennox–Gastaut syndrome, etc.), and types of epileptic seizures, focal (simple, complex, and secondary) and generalized (absence seizures, tonic-clonic, myoclonic, tonic, and atonic seizures).
- ZTALMY (ganaxolone), approved in March 2022 in the US, became the first medication approved to treat seizures associated with CDD in patients 2 years of age and older. It was also approved in Europe in July 2023; however, it was for children from 2 to 17 years of age. Its anticonvulsant effects are thought to result from positive allosteric modulation of the GABAA receptor in the CNS; however, the precise mechanism of action is unknown.
- EPIDIOLEX, a cannabidiol medication, was approved in the US by the FDA in 2018 and later by EMA in 2019 for patients =2 years of age with Dravet syndrome or LGS. While the mechanism of action of CBD underlying the reduction of seizures in humans is unknown, CBD possesses an affinity for multiple targets, including transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1), the orphan G protein-coupled receptor-55 (GPR55), and the equilibration nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT-1), across a range of target classes, resulting in functional modulation of neuronal excitability, relevant to the pathophysiology of many disease types, including epilepsy.
- BRIVIACT (brivaracetam [BRV]), an analog of levetiracetam (LEV), was initially approved in 2016 by the US FDA and EMA as an add-on treatment to other medications to treat partial onset seizures in patients aged 16 years and older with epilepsy. However, over time, it received several supplemental, and recently, in 2023, its oral formulation was approved for pediatric epilepsy patients of four years and older. The drug is available for oral and intravenous administration.
Key Epilepsy Drug Companies such as Xenon Pharmaceuticals, Eisai, Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, Knopp Biosciences, and others are evaluating their lead candidates in different stages of clinical development. They aim to investigate their products to treat Epilepsy.
- The total Epilepsy Treatment Drugs Market Size in the 7MM was approximately USD 9 billion in 2023 and is projected to increase during the forecast period (2024–2034), with a CAGR of approximately 7%.
- The total Epilepsy Treatment Drugs Market Size in the US was approximately USD 4.3 billion in 2023, accounting for approximately 48% of the total market revenue for the 7MM.
- The total Epilepsy Treatment Market Size in EU4 and the UK accounted for nearly 29% market share in 2023. Among the EU4 and the UK, Germany accounted for the highest market share followed by France and the UK. These numbers are expected to change during the forecast period.
- The total Epilepsy Treatment Drugs Market Size in Japan was approximately USD 2.1 billion in 2023.
Epilepsy Drugs Uptake
This section focuses on the uptake rate of potential Epilepsy drugs expected to be launched in the market during 2020–2034. For example, BHV-7000 (KB-3061) is expected to enter the US market in 2026 and is projected to have a medium uptake during the forecast period.
Epilepsy Pipeline Development Activities
The Epilepsy therapeutics market report provides insights into Epilepsy clincial trials Phase III, Phase II, and Phase I. It also analyzes key Epilepsy Companies involved in developing targeted therapeutics.
Pipeline development activities
The Epilepsy therapeutics market report covers information on collaborations, acquisitions and mergers, licensing, and patent details for emerging therapies for Epilepsy.
KOL Views on Epilepsy
To keep up with current Epilepsy market trends, we take KOLs and SMEs’ opinions working in the domain through primary research to fill the data gaps and validate our secondary research. Industry Experts contacted for insights on Epilepsy evolving treatment landscape, patient reliance on conventional therapies, patient therapy switching acceptability, and drug uptake, along with challenges related to accessibility, including Medical/scientific writers, Medical Professionals, Professors, Directors, and Others.
DelveInsight’s analysts connected with 50+ KOLs to gather insights; however, interviews were conducted with 15+ KOLs in the 7MM. Centers like the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, University of Miami, University Hospital of Giessen and Marburg, Charité University Medicine Berlin, University of Leicester, and St. Marianna University School of Medicine, among others, were contacted. Their opinion helps understand and validate current and emerging therapy treatment patterns or Epilepsy surgery market trends. This will support the clients in potential upcoming novel treatments by identifying the overall scenario of the market and the unmet needs.
Physician’s View
As per the KOLs from the US, about 3 million people in the US and approximately 50 million worldwide are affected due to this chronic non-communicable disease. In addition, men are significantly more likely to experience epilepsy than women. As per the KOLs from the UK, our lack of knowledge, or perhaps lack of suitable diagnostic tools, has made epilepsy economic implications. Moreover, the healthcare expenses and social stigma associated with the disease place a significant financial strain on households. As per the KOLs from Japan, for patients, who are drug-resistant, sometimes the key is figuring out the right medicine combination and that's always exciting. Not everyone is going to be a candidate for epilepsy surgery. We should not give up on finding and developing these breakthroughs in medical management.
Qualitative Analysis
We perform Qualitative and Epilepsy treatment market Intelligence analysis using various approaches, such as SWOT and Conjoint Analysis. In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in terms of disease diagnosis, patient awareness, patient burden, competitive landscape, cost-effectiveness, and geographical accessibility of therapies are provided. These pointers are based on the Analyst’s discretion and assessment of the patient burden, cost analysis, and existing and evolving Epilepsy treatment drugs market landscape.
Conjoint Analysis analyzes multiple emerging therapies based on relevant attributes such as safety, efficacy, frequency of administration, route of administration, and order of entry. Scoring is given based on these parameters to analyze the effectiveness of therapy. To analyze the effectiveness of these therapies, have calculated their attributed analysis by giving them scores based on their ability to improve atrial and ventricular dimension/function and ability to regulate heart rate.
Further, the therapies’ safety is evaluated wherein the adverse events are majorly observed, and it sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials, which directly affects the safety of the molecule in the upcoming trials. It sets a clear understanding of the side effects posed by the drug in the trials. In addition, the scoring is also based on the route of administration, order of entry and designation, probability of success, and the addressable patient pool for each therapy. According to these parameters, the final weightage score and the ranking of the emerging therapies are decided.
Pediatric Epilepsy Market Access and Reimbursement
Reimbursement of rare disease therapies can be limited due to lack of supporting policies and funding, challenges of high prices, lack of specific approaches to evaluating rare disease drugs given limited evidence, and payers’ concerns about budget impact. The high cost of rare disease drugs usually has a limited effect on the budget due to the small number of eligible patients being prescribed the drug. The US FDA has approved several rare disease therapies in recent years. From a patient perspective, health insurance and payer coverage guidelines surrounding rare disease treatments restrict broad access to these treatments, leaving only a small number of patients who can bypass insurance and pay for products independently.
The reimbursement challenges related to medical care and treatment for individuals with Epilepsy can be significant as it often requires specialized medical attention, covering the costs of diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing care. Health insurance plans may not fully cover limited coverage of some medical treatments, therapies, and devices specific to Epilepsy. This can result in high out-of-pocket expenses for families seeking the best care for their loved ones. Moreover, it requires specialized care from healthcare providers with expertise. Finding and accessing such specialists may be challenging, and the associated costs may not always be fully reimbursed by insurance.
- EPIDIOLEX Copay Savings Program by JassCares
The program is good for up to four 15-day free supplies for a patient’s first-time prescription. The program is designed to support patients’ needs from Day 1. Hospital-to-home program: The hospital-to-home program supports access to EPIDIOLEX therapy after hospitalization. This program provides a 30-day supply of EPIDIOLEX at no cost to the patient upon discharge from an inpatient hospital. This program is intended solely for patients discharged from an inpatient hospital setting who do not have access to EPIDIOLEX upon discharge. Patients with a supply of EPIDIOLEX at home are not eligible for this program. In the US, around 97% of all US-insured patients have EPIDIOLEX coverage for LGS and DS. EPIDIOLEX is a preferred brand with the lowest brand copay, and company re-alignment of PBM clients creates commercial opportunities. Furthermore, the JazzCares Patient Assistance Program (PAP) enables help when insurance coverage is an issue. It has helped hundreds of eligible patients access free medication.
- NAYZILAM Patient Assistance Program by UCB
UCB, the maker of NAYZILAM (midazolam) nasal spray, CIV, remains committed to helping epilepsy patients access the medicines that UCB manufactures. The NAYZILAM Patient Assistance Program helps if the patients do not have health insurance or cannot afford the NAYZILAM medicine. The NAYZILAM Patient Assistance Program may also provide medication at no cost to eligible patients who cannot pay for their NAYZILAM prescription.
- BRIVIACT Patient Assistance Program
UCB, the maker of BRIVIACT, remains committed to helping epilepsy patients gain access to the medicine. The BRIVIACT Patient Assistance Program provides medication at no cost to eligible patients who cannot pay for their BRIVIACT prescription. BRIVIACT (brivaracetam) CV is a prescription medicine used to treat partial-onset seizures in people 1 month of age and older. It is not known if BRIVIACT is safe and effective in children younger than 1 month of age.
- FYCOMPA MOA Instant Savings Card Program
The program provides FYCOMPA at no or low cost to financially needy patients who meet program eligibility criteria. With the FYCOMPA MOA Instant Savings Card Program, eligible, commercially insured patients may pay as little as USD 10 per month with a maximum savings of USD 1,300 per year. For eligible cash patients, Eisai will pay up to USD 60 per prescription for a maximum of USD 720 per year.
The Pediatric Epilepsy Therapeutics Market report provides detailed insights on the country-wise accessibility and reimbursement scenarios, cost-effectiveness scenarios, programs making accessibility easier and out-of-pocket costs more affordable, insights on patients insured under federal or state government prescription drug programs, etc.
Epilepsy Treatment Market Report Scope
- The Pediatric Epilepsy Therapeutics Market report covers a segment of key events, an executive summary, and a descriptive overview explaining its causes, signs and symptoms, pathogenesis, and currently available therapies.
- Comprehensive insight into the epidemiology segments and forecasts, the future growth potential of diagnosis rate, disease progression, and treatment guidelines have been provided.
- Additionally, an all-inclusive account of the current and emerging therapies and the elaborative profiles of late-stage and prominent therapies will impact the current Epilepsy treatment drugs market landscape.
- A detailed review of the Epilepsy surgery market, historical and forecasted market size, market share by therapies, detailed assumptions, and rationale behind our approach is included in the report, covering the 7MM drug outreach.
- The Pediatric Epilepsy Therapeutics Market report provides an edge while developing business strategies by understanding trends through SWOT analysis and expert insights/KOL views, patient journey, and treatment preferences that help shape and drive the 7MM Epilepsy drugs market.
Epilepsy Market Report Insights
- Epilepsy Patient Population
- Epilepsy Therapeutic Approaches
- Epilepsy Pipeline Analysis
- Epilepsy Market Size and Trends
- Existing and Future Epilepsy Drugs Market Opportunity
Epilepsy Treatment Market Report Key Strengths
- 11 years Epilepsy Market Forecast
- The 7MM Coverage
- Epilepsy Epidemiology Segmentation
- Key Cross Competition
- Attribute analysis
- Epilepsy Drugs Uptake
- Key Epilepsy Market Forecast Assumptions
Epilepsy Market Report Assessment
- Current Epilepsy Treatment Market Practices
- Epilepsy Unmet Needs
- Epilepsy Pipeline Product Profiles
- Epilepsy Drugs Market Attractiveness
- Qualitative Analysis (SWOT and Attribute Analysis)
- Epilepsy Market Drivers
- Epilepsy Market Barriers
Key Questions Answered
Epilepsy Market Insights
- What was the total Epilepsy treatment market size, the Epilepsy drugs market size by therapies, and Epilepsy Therapeutics Market share (%) distribution in 2020, and what would it look like by 2034? What are the contributing factors for this growth?
- How will XEN1101 affect the treatment paradigm of Epilepsy?
- How will Jazz Pharmaceuticals’ EPIDIOLEX/EPIDYOLEX compete with the upcoming Epilepsy therapies?
- Which Epilepsy drug is going to be the largest contributor by 2034?
- What are the pricing variations among different geographies for approved and marketed Epilepsy therapies?
- How would future opportunities affect the Epilepsy market dynamics and subsequent analysis of the associated trends?
Epilepsy Epidemiology Insights
- What are the disease risks, burdens, and Epilepsy Unmet Needs? What will be the growth opportunities across the 7MM concerning the patient population about Epilepsy?
- What is the historical and forecasted Epilepsy patient pool in the United States, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan?
- Out of the countries mentioned above, which country would have the highest diagnosed prevalent Epilepsy population during the forecast period (2024–2034)?
- What factors are contributing to the growth of Epilepsy cases?
Current Epilepsy Treatment Market Market Scenario, Marketed Drugs, and Emerging Therapies
- What are the current options for the treatment of Epilepsy? What are the current clinical and treatment guidelines for treating Epilepsy?
- How many Epilepsy Drug companies are developing therapies for the treatment?
- How many emerging Epilepsy therapies are in the mid-stage and late stage of development for treating Epilepsy?
- What are the recent novel therapies, targets, Epilepsy mechanisms of action, and technologies developed to overcome the limitations of existing therapies?
- What is the Epilepsy cost burden of current treatment on the patient?
- Patient acceptability in terms of preferred treatment options as per real-world scenarios?
- What are the accessibility issues of approved Epilepsy therapy in the US?
- What is the 7MM historical and forecasted Epilepsy Drugs Market?
Reasons to Buy
- The Epilepsy market report will help develop business strategies by understanding the latest trends and changing treatment dynamics driving the Epilepsy drugs market.
- Insights on patient burden/ epilepsy prevalence, evolution in diagnosis, and factors contributing to the change in the epidemiology of the disease during the forecast years.
- Understand the existing Epilepsy drugs market opportunities in varying geographies and the growth potential over the coming years.
- The distribution of historical and current patient share is based on real-world prescription data in the US, EU4 (Germany, France, Italy, and Spain) the United Kingdom, and Japan.
- Identifying upcoming Epilepsy companies in the Epilepsy drugs market will help devise strategies to help get ahead of competitors.
- Detailed analysis and ranking of class-wise potential current and emerging therapies under the conjoint analysis section to provide visibility around leading classes.
- Highlights of Access and Reimbursement policies for Epilepsy, barriers to accessibility of approved therapy, and patient assistance programs.
- To understand Key Opinion Leaders’ perspectives around the accessibility, acceptability, and compliance-related challenges of existing treatment to overcome barriers in the future.
- Detailed insights on the unmet needs of the existing Epilepsy drugs market so that the upcoming Epilepsy companies can strengthen their development and launch strategy.
Stay Updated with us for Recent Articles
- Role of Seizures Alert and Monitoring Devices in the Management of Epilepsy
- Which Pharma Companies are Transforming the Drug-Resistant Epilepsy Market Landscape?
- 21 of the most common questions about Epilepsy
- Ever-evolving Market Dynamics of Epilepsy – a silver lining!
- DRUG-RESISTANT EPILEPSY
- World Epilepsy Day
- EPILEPSY - A Neurological Disorder
- XEN-1101: An Illuminating Prospect for Adults Afflicted by Focal Epilepsy
- LIBERVANT Buccal Film: Pioneering Pediatric Epilepsy Treatment Advancements
- Unveiling Boundless Horizons: Unlocking BHV-7000’s Potential in Epilepsy
- Soticlestat (TAK-935): A Paradigm Shift in Epilepsy Treatment Strategies
- Improving Epilepsy Care: XCOPRI’s Effectiveness and Safety
- Latest DelveInsight Blogs