Artificial intelligence and robotics are two technologies that have demonstrated the potential to address and provide solutions to numerous contemporary issues. The manufacturing sector has been using robotics for quite a long time. However, over the past three to four decades, robots have been in use in other sectors as well, such as laboratory research, earth and space exploration, transport, and many more. The use of robots has lowered production costs and increased productivity, while simultaneously leading to the creation of many new jobs in the tech sector, contributing to economic growth. Robots are mainly employed where the tasks require repetitive and monotonous work; however, with Artificial Intelligence (AI), the scope is widening. They are replacing the human workers and providing efficient results. As per the International Federation of Robotics, the automation of production is accelerating around the world: 74 robot units per 10,000 employees is the new average of global robot density in the manufacturing industries (2015: 66 units).
As the application and capabilities are improving day by day, sectors such as healthcare and its allied fields are also adopting robots to accomplish different tasks. Today, robots are used for complicated surgeries, clinical training, medicine dispensing, personal care, and many other tasks. According to the latest data from the International Federation of Robotics, global sales of medical robots reached approximately 6,100 units in 2023, marking a 36% increase compared to the previous year. This reflects a significant growth from 2017, when 2,931 units were sold. Among sub-categories, rehabilitation and non-invasive therapy robots experienced the highest growth at 128%, followed by diagnostic robots at 25% and surgical robots at 14%. Medical robots now account for an increasingly larger share of the over 205,000 professional service robots sold globally in 2023. According to DelveInsight, the global surgical robotic systems market was valued at USD 11 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 13.21% from 2025 to 2032, reaching approximately USD 29 billion by 2032. Robot-assisted surgery or therapy is the most critical application of robots in healthcare. However, the demand for other services is also increasing significantly.
Top Applications of Robots in Healthcare: Transforming Surgery, Care, and Beyond
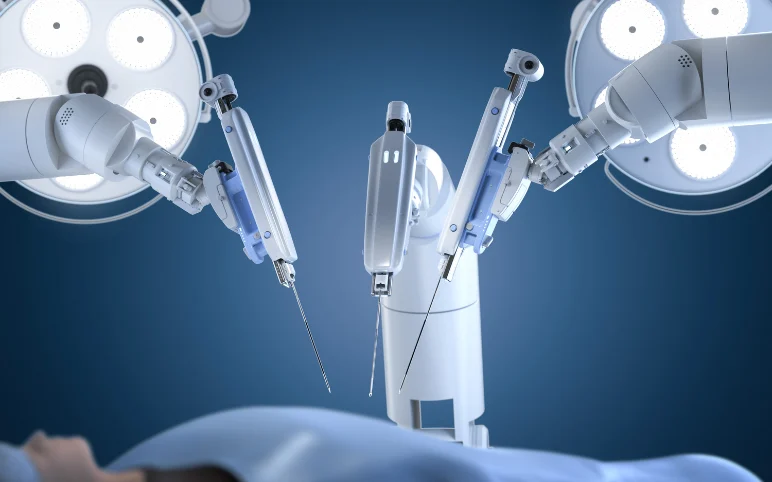
Surgeries – Surgery has emerged as one of the critical applications of robots in the past few decades and is getting much wider attention. The surgical robots offer a 3-D view along with high-definition and magnification capabilities. Robot-assisted surgeries are “minimally invasive” than traditional surgical procedures and are more precise and flexible.
In 2000, the da Vinci Surgical System was the first robotic surgical platform for general laparoscopic surgery approved by the FDA for commercial use in the United States. With advancements in technology, much progress has been achieved in 3D high-definition and magnification; it is possible to perform surgery through one or a few small incisions. Today, robots in combination with AI use the data from past operations to perform new surgeries and are yielding much better results.
To the patients, robots mean reduced hospital stays and fewer complications. Robots are being extensively used for surgical procedures such as orthopedic, urological, bariatric, gynecological, and many others. The surgical robots hold substantial future growth potential. To gain a competitive advantage, some of the key companies at the global level, such as Intuitive Surgical Inc, Stryker, JOHNSON & JOHNSON MEDICAL DEVICES COMPANIES, Medtronic, avateramedical GmbH, CMR Surgical Ltd., Medicaroid Corporation, Medrobotics Corp, Asensus Surgical US, Inc, Globus Medical, Microport Scientific Corporation, Smith & Nephew PLC., Accuray Incorporated, THINK Surgical., Renishaw plc, Zimmer Biomet, Corindus, Inc (Siemens Healthineers), Preceyes BV., MicroSure, Memic Innovative Surgery Ltd., are involved in developing surgical robots.
Clinical Training – Clinical Training Robots are realistic simulation devices that can enhance the healthcare provider’s skills and knowledge. One of the latest and most advanced examples of a training robot is Pediatric Hal. Pediatric Hal is an artificial intelligence robot manufactured by Gaumard Scientific. Pediatric Hal can mimic a five-year-old child and exhibit symptoms of cardiac arrest and arrhythmia. It can also perform a dozen facial expressions, mimic crying, and imitate rapid breathing, providing a real “working under pressure” condition to the healthcare trainees.
Prescription Dispensing / sensitive materials – Dispensing robots are used to distribute medication and handle sensitive materials in hospital settings. Dispensing robots are quite beneficial as they can dispense medicine at a very high speed and accuracy. Similarly, they can also handle sensitive liquids or viscous materials.
Care/Services – The demand for robots in the care segment is also increasing significantly. The challenges faced by the elderly population and the people affected by dementia and other mental diseases are the main drivers for care robot demand. Care robots help patients perform some necessary day-to-day activities such as providing mobility and transportation support, performing routine body check-ups (like temperature, blood pressure, sugar levels), fetching food and water, reminding medication, and many others. The care robots are quite handy and ease the daily burden on healthcare professionals. With the increase in capabilities and a growing aging population, the demand for care robots is likely to increase in the coming years.
Disinfection and Sanitation – Lack of hygiene and poor sanitation can lead to many diseases, and to carry out the disinfection and sanitation process, hospitals are deploying robots. These specialized robots scan the hospital environment and carry out the air-circulating and surface disinfection process. UV sterilization robots, in particular, kill bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms that can cause infections. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the disinfection and sanitation robots segment observed a significant demand. Blue Ocean Robotics, Intellibot Robotics LLC, IRobot Corporation, Skytron, Bioquell, Ecovacs Robotics, Lumalier Corp, and Siemens are some of the key companies involved in developing disinfection and sanitation robots at the global level.
Telepresence – Telepresence, also known as Telemedicine Robots, makes it accessible for the doctor to connect with the patient from remote locations.
Surgical Robots – Robots are now employed to perform surgery. Surgical Robots are capable of performing sophisticated surgical procedures through small incisions with minimal scarring. These robots are equipped with high-definition 3-D cameras, mechanical arms, and several other small tools.
Logistics/Delivery – To perform hospitals’ logistics tasks, a new type of robot called logistics robots is available in the market today. The logistics robots are equipped with navigation systems that help them to perform basic tasks such as moving food and water, lab samples, beddings, and medications within the hospital premises.
Rehabilitation Robots, Receptionist Robots, Nursing Robots, Ambulance Robots, and Physical Therapy Robots are also generating significant demand.
What are the Major Benefits of Robotics in Healthcare?
In recent years, the integration of robotics in healthcare has transformed the way medical services are delivered. From performing intricate surgeries to streamlining hospital logistics and disinfection tasks, medical robots are redefining operational efficiency in healthcare systems. Robots are no longer confined to the operating room; they now assist clinicians in patient care, medication management, and support services throughout clinical settings.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the use of robotics in healthcare expanded significantly as hospitals sought ways to reduce pathogen exposure. Robots began handling cleaning, disinfection, and supply transport, reinforcing their value in maintaining hygiene and improving workflow. For instance, cleaning robots used in hospitals can autonomously disinfect rooms and reduce human contact in infectious zones. These innovations highlight the growing benefits of robots in healthcare, including faster task execution, reduced infection risks, and increased safety for both patients and medical staff.
Additionally, the implementation of AI and robotics in healthcare, such as AI-powered medication identification systems, has accelerated processes like medicine dispensing and patient matching, further improving care accuracy. The impact of robotics in healthcare is particularly evident in robotic surgery, where minimally invasive procedures lead to smaller incisions, less blood loss, faster recovery, and reduced hospital stays.
Despite the many advantages of robots in the medical field, there are ongoing discussions about the disadvantages of robotics in healthcare. High implementation costs, limited access in low-resource settings, and the need for technical training are notable challenges. Furthermore, some concerns revolve around the robotic surgery disadvantages, such as the potential for mechanical failure or high procedural costs. These pros and cons of robots in healthcare underscore the importance of balanced adoption strategies.
Nonetheless, the continued development of healthcare robotics is expected to reshape the future of medicine. From robotic nurses that assist with monitoring and routine checks to autonomous delivery robots supporting hospital logistics, the industry is steadily embracing robotic solutions. With a clear shift toward robotics automation in healthcare, both healthcare providers and patients stand to benefit, provided that concerns around cost, accessibility, and safety are addressed effectively.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Medical Robots?
In healthcare facilities, robots are used in a variety of settings. They have an indirect or direct impact on the patients’ lives. They even take care of elderly and disabled patients and engage them in conversation so that they do not suffer from pain or boredom. Along with that, there are numerous advantages of medical robots. The major advantages of medical robots are that the surgeries carried out with the help of robots are smoother and without errors. Even the success rate of the surgery is higher. Furthermore, robots work precisely within the parameters of time and work assigned to them, which is another key advantage of medical robots. Other benefits of medical robots include proper monitoring services of patients, flawless performance, reduced risk of infection, does not waste time, and many more.
Every coin has two sides. While there are innumerable benefits of employing robots to run errands in healthcare, there are chances of errors and failures. There is always some scope for human error or mechanical failure with these advanced robots. A single mechanical malfunction can cost human lives. In the case of surgical robots, small risks of infection and bleeding can’t be neglected. There are many disadvantages of robotics in healthcare.
The major disadvantage of medical robots is the cost. The use of surgical robots is limited to developed countries, research centers, and advanced hospitals. Similarly to patients, in some cases, it is out of their reach to afford robotic surgeries. Also, the healthcare provider needs to invest a lot of money and time to train the workforce to handle robots; besides, their lifetime maintenance cost is another problematic factor. Another disadvantage of robots in healthcare is that they may take the place of people and lead to unemployment.
What is the Future of Robotics in Healthcare?
With the integration of new applications and advanced features, healthcare robots are poised to significantly enhance the quality, accuracy, safety, and operational efficiency of modern healthcare delivery. The advancement of artificial intelligence and medical robotics technology is opening new dimensions in robotics in medical science, making clinical procedures faster, more precise, and safer. This evolution in automation and robotics in healthcare is not limited to surgery alone; it is expanding into diagnostics, rehabilitation, and even hospital logistics.
Coupled with data analytics and improvements in both hardware and software systems, robotics healthcare solutions are increasingly being adopted across various medical domains. The growing collaboration between robotic technology companies and healthcare providers is expected to drive further innovation and accelerate the growth of the healthcare robots market.
However, despite the many positive things about robots, certain challenges persist, particularly the high cost of implementation and limited affordability for the average patient. These factors continue to raise discussions around the advantages and disadvantages of robotic surgery and highlight broader concerns related to the disadvantages of automation in healthcare. Addressing these concerns will be crucial to ensuring that the future of robotics in healthcare is both inclusive and sustainable.
FAQs
Do patients actually trust robots more than human doctors in certain cases? Yes, in situations like medication dispensing or disinfection, patients often perceive robots as more reliable because they eliminate human error. However, in emotionally sensitive care (like counseling or end-of-life support), trust still heavily leans toward humans.
Why are robots in healthcare often designed to look less humanlike than expected? Many medical robots are intentionally designed to look functional rather than humanoid. This avoids the “uncanny valley” effect, reduces patient anxiety, and emphasizes reliability over personality — especially in surgical and logistics roles.
Which companies are currently active in the surgical robot market? Some of the key companies at the global level, such as Intuitive Surgical Inc., Stryker, JOHNSON & JOHNSON MEDICAL DEVICES COMPANIES, Medtronic, avateramedical GmbH, CMR Surgical Ltd., Medicaroid Corporation, Medrobotics Corp, Asensus Surgical US, Inc., Globus Medical, Microport Scientific Corporation, Smith & Nephew PLC., Accuray Incorporated, THINK Surgical., Renishaw plc, Zimmer Biomet, Corindus, Inc (Siemens Healthineers), Preceyes BV., MicroSure, Memic Innovative Surgery Ltd., are involved in developing surgical robots.
Could robots eventually prescribe medicines on their own without doctors? While current robots mostly dispense medications, advancements in AI are moving toward robots that analyze diagnostic data and recommend prescriptions. However, ethical, regulatory, and liability barriers mean full autonomy is still years away.
How do surgical robots “learn” from past surgeries? AI-enabled robots store anonymized surgical data — every movement, outcome, and complication. Over time, they use machine learning to refine precision, anticipate surgeon errors, and suggest best approaches, almost like a digital “memory bank of surgeries.”
What happens if a robot malfunctions during a critical surgery? Most surgical robots are built with redundancy — multiple safety backups and a quick manual override, allowing surgeons to instantly take over. But downtime costs and rare malfunctions remain a genuine concern in adoption.
Could healthcare robots unintentionally widen the gap between rich and poor patients? Yes. Since robotic surgeries and services are expensive, access is currently limited to advanced hospitals in wealthier regions. Without policy interventions or cost-reducing innovations, robotics might deepen healthcare inequality.
Do robots in elderly care reduce loneliness, or can they make it worse? It depends. Robots like companion care bots can remind patients to take medicine and even simulate conversation, which helps some seniors feel less isolated. But over-reliance may reduce human interaction, making social isolation a hidden risk.