Navigating the Most Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare
Aug 28, 2025
Table of Contents
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in healthcare involves utilizing software bots to automate routine and repetitive tasks, such as data entry, billing, scheduling, and claims processing. These bots mimic human actions on digital systems, aiming to enhance efficiency, minimize manual errors, and enable healthcare workers to devote more attention to patient care.
Initially, before 2010, automation in healthcare was limited to basic tools like macros, which lacked flexibility and required complex coding. RPA began gaining traction around 2010, first in finance, and then in healthcare, with use cases like patient data entry and claims handling, although adoption was slow due to integration and security challenges.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Understanding How Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology are Upgrading the Healthcare Delivery?
- Interoperability Solutions in Healthcare – Evolving Market Dynamics and Improving Health Ou...
- Where Women Healthcare Stands
- Emerging Role of Digital Health in the Field of Oncology
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) Applications Driving Healthcare Innovation
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, RPA adoption has accelerated. Recently, it has been widely used for managing electronic health records (EHRs), automating regulatory reporting, streamlining inventory, and improving patient engagement through reminders and digital assistants. Bots operate continuously, saving time and costs while enhancing accuracy. In the future, RPA is expected to evolve through integration with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and natural language processing (NLP), enabling bots to handle complex tasks such as clinical decision-making, real-time monitoring, and predictive analytics. This advanced form of cognitive RPA will help manage public health crises, improve telehealth, and enhance system interoperability.
Key Applications of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare
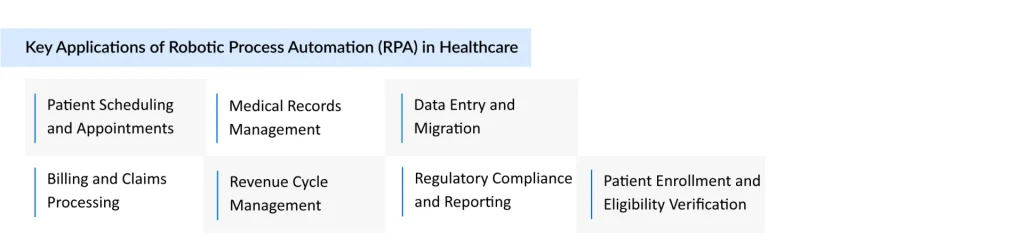
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is transforming the healthcare industry by streamlining administrative and operational tasks through software bots. These bots can replicate human actions in digital systems, enabling organizations to perform routine, rule-based tasks more efficiently, accurately, and at scale.
- Patient Scheduling and Registration:
Patient scheduling and registration are critical, yet time-consuming, administrative processes in healthcare. By leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA), healthcare providers can automate these tasks, leading to reduced administrative workload, fewer no-shows, and a better patient experience.
Automated Data Collection: RPA bots can automatically extract patient information from various sources, including online forms, emails, and existing patient records, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Real-Time Eligibility Verification: The bots can instantly validate insurance coverage and eligibility in real time, catching any issues before the appointment and preventing future billing headaches.
Intelligent Appointment Scheduling: Based on factors like physician availability, patient preferences, and the type of visit, RPA can intelligently schedule appointments, ensuring a more efficient use of clinic time.
Automated Patient Communication: The bots automatically send appointment reminders and confirmations to patients via their preferred method (e.g., email, SMS), which significantly reduces the rate of no-shows.
For Instance, in March 2024, according to the East Lancashire NHS Trust (UK), East Lancashire NHS Trust in the UK automated appointment scheduling for around 15,000 patient referrals per month using RPA bots. The system handled referrals, checked physician availability, booked appointments in the EHR, and sent confirmations automatically. This saved about 83,600 sheets of paper monthly and reduced the workload equal to 2.5 full-time staff, improving efficiency and patient satisfaction.
- Automated Healthcare Billing and Claims with RPA:
Billing and insurance claims are a complex, multi-step process, including data collection, claim creation, validation, submission, and follow-up, that can be a major headache for healthcare organizations. Fortunately, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can streamline this entire workflow, from data collection to payment reconciliation. Errors at any stage can result in delays or denials. Instead of manual data entry, RPA bots can pull relevant information, like billing codes and patient demographics, directly from Electronic Health Records (EHRs). They can then automatically create claims, ensuring the data is accurate and complete from the start.
RPA bots are programmed to follow payer-specific rules, instantly validating claims to catch errors that would otherwise lead to delays or denials. Once a claim is validated, the bot automatically submits it to the correct insurance company or government program. After submission, the RPA bot continuously tracks the claim’s status. If a claim is denied or requires more information, the bot can automatically handle the resubmission, ensuring a faster turnaround and fewer lost claims.
Finally, RPA automates the task of posting payments and reconciling accounts. This minimizes human intervention, drastically reducing the potential for error and freeing up staff to focus on more complex tasks.
For Instance, in October 2024, UiPath, a leading enterprise automation and AI software company, announced that it had transformed operations for Omega Healthcare through AI-powered automation. Omega Healthcare was named a UiPath AI25 Award Winner at UiPath FORWARD, recognized as one of the 25 most innovative customers using AI and automation to drive strategic change and achieve significant outcomes.
- How RPA Streamlines Electronic Health Record (EHR) Management:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can significantly reduce the manual effort involved in maintaining and updating Electronic Health Records (EHRs). By automating repetitive, data-heavy tasks, RPA bots ensure greater accuracy, save time for clinical staff, and improve data accessibility.
Data Extraction and Updating: RPA bots can extract clinical data from various external sources, such as labs, imaging centers, and physician notes. They then use this information to automatically update patient records with diagnostic reports, treatment plans, and medication lists.
Data Transfer and Verification: When patients are transitioned to a different care setting, RPA can seamlessly transfer their records between different systems. The bots can also verify and standardize data as it moves, which helps eliminate inconsistencies and reduces the chance of errors.
Improved Accuracy and Accessibility: Automating EHR management with RPA ensures accuracy by reducing the risk of human error in data entry. This not only maintains the integrity of patient records but also improves data accessibility, allowing clinical staff to make faster, more informed decisions based on reliable information.
By handling these time-consuming administrative tasks, RPA allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care and less on paperwork.
For Instance, in 2025, a featured article highlighted how AI‑driven RPA is enabling large health systems to overcome barriers caused by limited API access to EHR platforms. By emulating human interaction at the user interface, modern RPA enhanced with NLP and computer vision automates workflows like clinical intake, prior authorization, and EHR updates at scale. This hybrid strategy enabled healthcare organizations to deploy automation quickly, reduce labor costs by up to 80%, and improve claims verification speed nearly ninefold.
- Automating the Healthcare Revenue Cycle with RPA:
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can automate the entire healthcare revenue cycle, ensuring financial operations run smoothly from patient intake to payment collection. This end-to-end automation helps healthcare institutions maintain steady revenue and reduces the administrative burden on staff.
Pre-Service and Patient Intake: RPA bots can verify patient insurance details and check for prior authorization before an appointment even takes place. This proactive step helps prevent claim denials down the line.
Claim Management: Once a service is rendered, RPA bots can automatically generate invoices and process payments. They can also follow up on unpaid claims or denied requests, handling the resubmission process with speed and accuracy.
Payment and Reconciliation: Bots help to automate the posting of payments and reconciling accounts, ensuring that the financial records are accurate and up-to-date.
By automating these financial tasks, RPA not only improves cash flow for healthcare providers but also allows administrative staff to focus on more complex, patient-facing activities.
For Instance, in March 2025, Coronis Health partnered with UiPath to enhance its revenue cycle management (RCM) operations using advanced automation. The implementation included RPA, process mining, and AI-driven decision support to streamline tasks such as claim submission, denial detection, and reimbursement optimization. As a result, the company reduced claim denials by identifying discrepancies before submission and improved cash flow and overall financial operations through predictive automation, and increased productivity.
- Ensuring Healthcare Compliance with RPA:
Healthcare providers must adhere to strict regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the U.S. and GDPR in Europe. Manual compliance tracking is often a tedious and error-prone process. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can significantly simplify this by automating key compliance tasks, ensuring continuous adherence to regulations, and reducing the risk of costly penalties.
Automated Auditing and Reporting: RPA can automatically create audit logs and access records. It can also compile compliance reports for both internal reviews and external audits, saving countless hours of manual work.
Proactive Monitoring: RPA bots are programmed to monitor data access and user activities in real time. They can detect violations of security protocols, such as irregular access to sensitive patient data.
Instant Alerts: If a bot detects a potential security breach or policy violation, it can immediately send alerts to the appropriate personnel, allowing for a swift and effective response.
By automating these processes, RPA provides a robust, round-the-clock solution for compliance management, ensuring data security and regulatory adherence with minimal human intervention.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) further enhances healthcare operations by streamlining inventory and supply chain management through real-time tracking, automatic reordering, invoice verification, and procurement oversight, ensuring optimal stock levels and reduced shortages. It also strengthens patient engagement by automating reminders, personalized messages, feedback collection, and portal navigation, thereby improving communication and continuity of care. In research, RPA assists by extracting, cleaning, and transferring clinical data, which eases researchers’ workloads and accelerates insights. For prior authorization, it expedites approvals by accessing payer portals, submitting documentation, and verifying coverage details. Additionally, RPA streamlines HR and payroll functions by automating onboarding, payroll processing, compliance monitoring, and staff scheduling, significantly boosting overall operational efficiency.
RPA Use Cases in the Pharmaceutical Industry
| Use Case | Description | Key Benefits |
| Regulatory Compliance & Reporting | Automates regulatory documentation, submissions, and audit trails | Ensures compliance, minimizes errors, and reduces manual workload |
| Pharmacovigilance & Adverse Event Reporting | Extracts and submits adverse event data to safety databases and authorities. | Faster detection, better compliance, enhanced patient safety |
| Clinical Trial Management | Automates recruitment, data entry, consent tracking, and data transfer | Speeds up trials, improves accuracy, supports faster approvals |
| Manufacturing & Supply Chain Optimization | Monitors stock, automates reordering, and matches purchase orders/invoices | Enhances production efficiency, ensures product traceability |
| Sales & Marketing Automation | Generates reports, automates CRM data handling, and campaign targeting | Improves decision-making, reduces manual tasks |
RPA Use Cases in Health Insurance
| Use Case | Description | Key Benefits |
| Claims Processing | Automates intake, validation, adjudication, and fraud detection | Faster claims handling, fewer errors, increased productivity |
| Member Enrollment & Policy Admin | Automates enrollment, document updates, and policy management | Speeds up onboarding, improves data accuracy |
| Eligibility Verification & Authorization | Submits and tracks prior auth requests, verifies coverage in real time | Accelerates care delivery, reduces provider wait times |
| Fraud Detection & Risk Management | Identifies anomalies using patterns and flags suspicious activities | Prevents financial losses, improves oversight |
| Customer Service Automation | Automates responses, sends documents, and escalates complex issues | Enhances user experience, reduces support costs |
Top Robotic Process Automation (RPA) Solutions in Healthcare
- UiPath
- Recognized as the leading RPA platform in 2025, UiPath features a user-friendly drag-and-drop IDE (Studio), cloud and on-prem deployments via Orchestrator, and tight integration with healthcare systems.
- Widely used for automating claims processing, insurance eligibility, patient scheduling, clinical documentation, EHR updates, and patient onboarding.
- Automation Anywhere
- A cloud-native, AI-integrated platform noted for its enterprise scalability. It includes pre-built healthcare bots for claims, billing, inventory, and patient scheduling.
- Strong in AI/ML automation, user experience, and analytics.
- Blue Prism (SS&C Blue Prism)
- Known for secure, scalable, enterprise-grade RPA ideal for large healthcare systems. Offers robust governance, compliance controls, and deep integration capabilities.
- Claims automation, eligibility verification, compliance reporting, and contact center workflows.
- Pega Systems (Pegasystems)
- Combines RPA with business process management (BPM), offering end-to-end automation across clinical and administrative workflows.
- Patient onboarding, prior authorization, claims automation, compliance reporting, and workforce management.
- WorkFusion
- An intelligent automation platform with RPA + ML/NLP analytics, specializing in document-heavy healthcare workflows.
- Clinical documentation, claims reconciliation, coding, and research data ingestion.
- Kofax (now Tungsten Automation)
- Offers cognitive document capture, process orchestration, analytics, and workflow intelligence tailored to healthcare needs.
- Particularly strong in automating document processing, inventory tasks, onboarding, and regulatory reporting.
Emerging Trends in Healthcare RPA
- Integration with AI agents and GenAI
The most significant trend is the fusion of RPA with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). This “intelligent automation” allows RPA bots to handle more complex, cognitive tasks that were previously beyond their capabilities.
Handling Unstructured Data: Traditional RPA struggles with unstructured data like clinical notes, physician dictations, or patient emails. By integrating with AI, specifically Natural Language Processing (NLP), bots can now understand and process this information. This enables them to extract key data, summarize documents, and even respond to patient inquiries with human-like understanding.
Predictive Analytics: AI-powered RPA can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns and predict health outcomes. This enables proactive care, risk management, and the creation of personalized treatment plans.
Enhanced Decision-Making: With AI, bots can move beyond rule-based actions to make more informed decisions, such as identifying potential fraud in claims processing or flagging inconsistencies in medical records that a human might miss.
- Low-Code/No-Code Platforms and Citizen Developers
RPA is becoming more accessible to non-technical staff. Low-code and no-code platforms allow healthcare professionals with little or no programming experience to build and deploy their own automation solutions.
Empowering Clinicians: This trend empowers “citizen developers” like doctors and nurses to automate simple, repetitive tasks within their departments. This further streamlines workflows and allows them to focus more on direct patient care.
Increased Adoption: As the barrier to entry for automation drops, the adoption of RPA across healthcare institutions is expected to accelerate.
- Hyperautomation and Process Mining
Hyperautomation is the end-to-end automation of an entire business process. It’s not just about automating a single task but connecting multiple automated steps to create a seamless workflow. Process Mining, a key part of this trend, uses data analytics to map out and understand business processes.
Holistic Optimization: Process mining helps healthcare organizations identify the most impactful processes to automate. This ensures that automation efforts are focused on areas that will yield the greatest return on investment and improve overall efficiency.
End-to-End Solutions: This allows RPA to support the entire patient journey, from initial scheduling and intake to billing, claims, and follow-up.
- Cloud-Based RPA Solutions
The shift to cloud computing is also impacting RPA. Cloud-based RPA solutions offer greater flexibility, scalability, and security compared to on-premise setups.
Scalability on Demand: Cloud solutions allow healthcare organizations to easily scale their automation efforts up or down as needed without significant upfront infrastructure investments.
Enhanced Interoperability: Cloud-based platforms can more easily integrate with existing healthcare systems and applications, facilitating seamless data exchange and workflow automation.
- Focus on Patient Experience
While RPA has traditionally focused on back-office and administrative tasks, a growing trend is using it to directly improve the patient experience.
Personalized Engagement: RPA can power conversational AI chatbots that provide 24/7 support for patients, answer frequently asked questions, send medication reminders, and offer personalized health advice.
Simplified Patient Journeys: Automating tasks like appointment scheduling, registration, and billing inquiries reduces patient wait times and administrative hassle, leading to higher satisfaction.
- Increased focus on RPA in revenue cycle management (RCM)
Platforms like Waystar, FinThrive, and NextGen are leading in claim automation, denial prevention, and interoperability with EHRs.
Emerging startups like AgentAI, ConnectivityWise, Ease My Med, iEHR.ai, Sinewave AI, and anamedi are delivering focused automation capabilities from RCM to interoperable EHR platforms and speech-to-text clinical workflows.
These emerging trends show that RPA is evolving from a simple tool for task automation into a core component of a healthcare organization’s digital transformation strategy, playing a central role in improving efficiency, patient care, and overall operational performance.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Healthcare: Market Overview and Dynamics
The global Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in healthcare market was valued at USD 2,280.57 million in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 20.37% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2032 to reach a value of USD 10,013.16 million by 2032. Key drivers of this growth include the rising need for operational efficiency, labor shortages, increased digitization of healthcare services, and demand for cost reduction in administrative tasks.
In 2024, North America led the market due to high adoption of digital health infrastructure, a mature regulatory environment, and the presence of major RPA vendors like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Blue Prism. Healthcare providers in the U.S. and Canada are leveraging RPA to streamline billing, claims processing, and patient registration.
Europe and the Asia-Pacific are emerging as high-growth markets. In the Asia-Pacific, rapid digitization of hospitals, rising investment in AI and automation, and government initiatives to modernize healthcare systems are fueling demand. In Europe, emphasis on reducing healthcare costs, an aging population, and strong data privacy regulations (like GDPR) are encouraging providers to implement secure RPA solutions.
From a solution standpoint, the market includes front-office automation (patient registration, appointment scheduling), mid-office functions (EHR updates, coding, lab report management), and back-office processes (billing, claims, payroll, HR, and compliance documentation). Integration with AI, process mining, and machine learning is transforming basic task automation into intelligent, adaptive workflows.
Driving a Healthier Bottom Line: The Accelerating Growth of Healthcare RPA
Why Healthcare is Choosing Bots: The Forces Behind RPA Growth
- Administrative Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Hospitals and clinics are burdened with time-consuming administrative tasks such as data entry, claims processing, and billing. RPA reduces manual workloads, cuts operational costs, and improves accuracy.
- Integration with EHRs and Health IT: Modern RPA solutions integrate with EHR platforms (like Epic, Cerner) to auto-update patient records, manage scheduling, and synchronize data across systems, ensuring seamless digital operations.
- Labor Shortages and Burnout: Staffing shortages, especially post-pandemic, have driven demand for digital assistants (bots) to handle repetitive processes, allowing human workers to focus on patient care.
- Compliance and Audit Readiness: RPA ensures consistent documentation, maintains audit trails, and supports compliance with HIPAA, GDPR, and other regulatory frameworks crucial for healthcare data integrity.
When Bots Can’t Break Through: The Bottlenecks of Automation
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: Healthcare RPA bots handle sensitive PHI (Protected Health Information). Risks of breaches, non-compliance with data regulations, and ethical concerns around automation slow adoption in some areas.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many hospitals still rely on outdated IT systems that lack APIs or interoperability, making integration of RPA solutions more complex and costly.
- Change Management and Workforce Resistance: Transitioning from manual to automated processes requires cultural change, staff training, and process redesign, which can delay RPA adoption in conservative healthcare environments.
- High Implementation and Maintenance Costs: The initial investment for RPA can be a major barrier, especially for smaller healthcare providers. These costs include software licenses, development, customization, and integration with existing systems.
Investment and Funding Trends in RPA Healthcare
Investors are increasingly recognizing the potential of digital tools that support medication adherence, chronic disease management, and connected healthcare ecosystems. Recent funding rounds signal strong interest in AI-driven, user-friendly platforms.
January–March 2025
- UiPath and Omega Healthcare: In early 2025, Omega Healthcare expanded its partnership with UiPath to automate over 100 million annual transactions in revenue cycle management (RCM). Results included a 50% reduction in processing time and 99.5% data accuracy.
- Coronis Health and UiPath (March 2025): Launched a multi-region automation project using RPA, AI, and process mining for RCM tasks like denial management and claims submission, boosting cash flow and financial efficiency.
- Blue Prism in UK NHS Trusts: Several NHS hospitals adopted Blue Prism bots to manage patient registration and backlog scheduling, reducing administrative delays and eliminating 100,000+ paperwork hours annually.
- Waystar + Baylor Scott & White Health: Implemented AI-powered RPA for patient financial estimation, automating 70% of cost estimates and increasing point-of-service collections by 60–100%.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation in the healthcare sector is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of digital transformation in the industry. From scheduling and EHR management to billing, insurance verification, inventory, and compliance tracking, RPA enables healthcare organizations to operate more efficiently, reduce errors, and save costs.
Top platforms like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, Blue Prism, Pega, and Kofax are leading the way with scalable, AI-integrated automation solutions. Hospitals benefit from increased staff productivity, real-time data processing, faster billing cycles, and better patient satisfaction. Meanwhile, patients indirectly benefit from shorter wait times, fewer administrative errors, and smoother care journeys.
As the healthcare ecosystem evolves, RPA is expected to converge with technologies like artificial intelligence, NLP, and process intelligence to create “hyperautomation” systems capable of handling both structured and unstructured data in real time. This makes RPA not just a back-office tool, but a strategic asset for sustainable, high-quality healthcare delivery in the future.

Frequently Asked Questions
RPA in healthcare refers to the use of software bots to automate repetitive, rule-based administrative and clinical tasks, such as patient registration, billing, claims processing, data entry, and scheduling. These bots mimic human interactions with digital systems to complete tasks faster and more accurately, allowing staff to focus on patient care.
RPA reduces manual workloads, minimizes human errors, and accelerates routine processes. For example, automating insurance claims can cut processing time from hours to minutes. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances staff productivity and patient satisfaction.
Yes, when implemented correctly. RPA platforms can be configured to comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA (U.S.) and GDPR (Europe). Bots maintain audit trails and access controls, and organizations must ensure data encryption, access restrictions, and secure integration with health IT systems.
RPA is rule-based and focuses on automating structured, repetitive tasks. AI (Artificial Intelligence), on the other hand, handles complex decision-making tasks and can analyze unstructured data. When combined (e.g., cognitive RPA), bots can make intelligent decisions and learn over time.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a game-changer for the healthcare industry, offering a wide range of benefits that go beyond simple cost savings. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA improves efficiency, accuracy, and compliance, ultimately allowing healthcare professionals to focus on what matters most: patient care.
The future includes the integration of RPA with AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, a trend known as hyperautomation. This will enable bots to handle more complex tasks like predictive analytics, real-time clinical alerts, and personalized care coordination.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- How is Technology Addressing the Sleeping Disorders?
- Interoperability Solutions in Healthcare – Evolving Market Dynamics and Improving Health Ou...
- Biochips: An Evolving Technology Driving the Future of Healthcare Market
- Understanding How Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology are Upgrading the Healthcare Delivery?
- Navigating the Emerging Trends and Technologies in the Spinal Cord Injury Rehabilitation Segment