From Lab to Bedside: The Rise of AI-Enabled Digital Pathology
Sep 10, 2025
Table of Contents
Pathology—the discipline of diagnosing disease through tissue analysis, has long depended on glass slides and microscopes. Today, digital pathology is undergoing a remarkable shift, as whole-slide imaging (WSI) and artificial intelligence (AI) come together to streamline lab workflows, accelerate diagnoses, and enhance the quality of patient care.
This shift isn’t just about converting images to pixels. It’s about reimagining the pathologist’s day. Tasks like scanning, case-sharing, and annotation are being automated. AI aids in detecting subtle patterns, triaging urgent cases, and flagging anomalies, making diagnosis faster, more standardized, and more collaborative. One study illustrated this impact clearly: labs using digital pathology workflows saw diagnosis times drop by nearly 28% between 2018 and 2020, alongside a reduction in pathologist overtime.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Chemotherapy-Induced Nausea and Vomiting Side effects
- Is Gene Therapy the Next Cancer Treatment Revolution?
- FemTech Market: With 100+ Startups in the domain, Women Healthcare is Witnessing a Huge Upliftment
- Laborie’s Enhanced Gastrointestinal Diagnostics; Carestream’s Image Suite MR 10 Software Launch; ...
- Cilta-Cel’s Prolonged Impact: Deep Responses and Safety Insights from Earlier Lines of Ther...
Few technologies in healthcare are delivering such a seamless blend of digital innovation and stick-the-landing clinical utility. Let’s explore how AI-enabled digital pathology is moving from the lab to the bedside, transforming workflows, undergoing validation, and navigating regulatory milestones along the way.
What Is AI-Enabled Digital Pathology?
Digital pathology refers to the process of scanning glass slides into high-resolution digital images, also known as whole-slide images (WSIs), that can be stored, shared, and analyzed using specialized software. The integration of AI brings advanced image analysis into the equation, allowing algorithms to perform tasks like:
- Detecting suspicious or abnormal regions
- Scoring immunohistochemical markers (e.g., Ki-67, ER, PR)
- Triaging slides based on urgency or suspected disease
- Quantifying cellular and tissue features with high precision
A meta-analysis covering over 152,000 WSIs found that AI systems in pathology demonstrated a mean diagnostic sensitivity of 96.3% and specificity of 93.3%, impressive figures that underline the potential of these tools when properly validated.
Why It Matters in Modern Diagnostics
- Enhanced accuracy and consistency: Even experienced pathologists benefit from AI’s precision, especially in detecting rare or subtle features.
- Greater throughput and scalability: Combined with digital platforms, AI enables labs to handle higher volumes more rapidly, with data-driven triaging that reduces bottlenecks.
- Remote collaboration and coverage: Especially in underserved regions, digitized slides mean that expert pathologists can consult and provide diagnoses remotely, enabling more equitable access to care.
These improvements are being realized in real-world labs. Pathologists describe AI-enhanced digital systems as “liberating,” with AI taking on routine tasks like counting mitotic figures or identifying tumor-positive areas, freeing clinicians to focus on cases that require deeper interpretation.
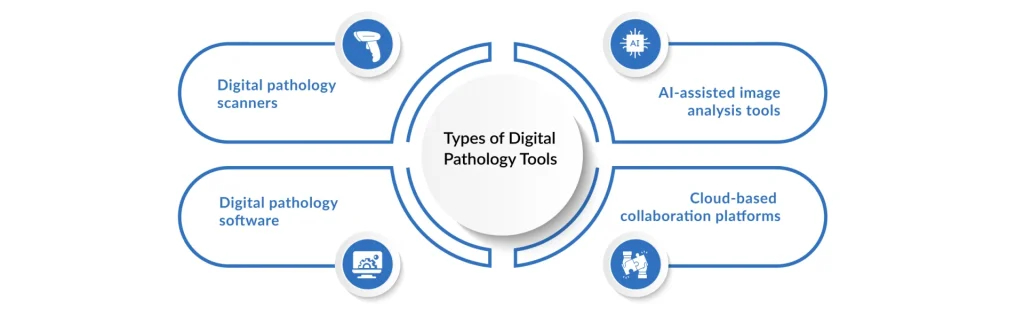
Reimagining the Pathology Workflow
The shift from glass slides and microscopes to digital pathology represents a reinvention of how pathology fits into modern healthcare. By combining digital pathology scanners, advanced software, and AI-driven interpretation, the workflow has been reimagined to prioritize speed, precision, and collaboration at scale.
From Slide Digitization to AI-Assisted Interpretation
For decades, pathology meant a pathologist peering through a microscope, one slide at a time. Today, digital pathology scanners capture whole-slide images in stunning detail, instantly converting tissue samples into digital files. These images are then processed by digital pathology software that uses AI to detect patterns, highlight areas of concern, and even quantify features like tumor margins or biomarker levels. This shift doesn’t replace human expertise, instead, it amplifies it, allowing pathologists to work with sharper, AI-assisted insights.
Efficiency, Collaboration, and Faster Turnaround
The benefits extend well beyond diagnostics. With slides digitized, the bottlenecks of physical transfer vanish, cutting reporting times significantly. Hospitals that have adopted pathology digital workflows report faster turnaround, in some cases, reducing diagnostic time by nearly a third. Collaboration is also effortless: a single slide can be shared across institutions or countries in seconds, enabling multidisciplinary tumor boards to access the same AI-enhanced images. For overburdened labs, automation of repetitive tasks ensures scalability, while pathologists can focus on complex cases, addressing the global shortage of diagnostic professionals.
FDA Milestones Shaping the Digital Pathology Market
Regulatory progress has been the true catalyst for digital pathology, transforming it from a research concept into a trusted part of clinical practice. FDA approvals and guidance documents not only validate the science but also build confidence for hospitals, labs, and digital pathology companies to invest in these solutions.
- Early approvals set the foundation
- In 2017, the FDA cleared Philips’ IntelliSite Pathology Solution, the first digital pathology scanner approved for primary diagnosis in the U.S., marking a historic shift from glass slides to digital workflows.
- Leica Biosystems followed in 2019 with clearance for the Aperio AT2 DX system, reinforcing regulatory acceptance and signaling to the market that scalable adoption was possible.
- AI-enabled software gains recognition
- In 2021, Paige.AI secured FDA approval for Paige Prostate, one of the first AI-driven digital pathology software tools, supporting cancer detection and strengthening trust in AI-assisted diagnosis.
- This momentum advanced significantly in 2025:
- April 2025: Paige received FDA Breakthrough Device designation for PanCancer Detect, the first AI tool designed to identify both common and rare cancer variants across multiple tissue types.
- January 2025: Modella AI’s PathChat DX, a generative AI co-pilot for diagnostic workflows, also earned Breakthrough Device designation, underscoring the role of AI assistants in shaping next-generation pathology.
- Guidance creates pathways for adoption
- Between January and March 2025, the FDA released draft and final guidance on AI-enabled medical devices, including lifecycle management and marketing submission requirements.
- These regulatory frameworks are critical for advancing AI/ML-based digital pathology software, providing companies with clearer routes from clinical validation to market entry.
Each milestone expands confidence for healthcare providers to integrate digital pathology scanners and AI tools into routine workflows. For the digital pathology market, FDA actions are accelerating adoption, creating competitive pressure for laggards, and reshaping expectations of diagnostic precision.
Market Adoption Drivers and Barriers
While digital pathology is gaining strong momentum, its adoption is influenced by both compelling drivers and persistent barriers. The table below highlights the key forces shaping the landscape:
| Drivers of Adoption | Barriers to Adoption |
| Rising cancer incidence and shortage of pathologists push demand for scalable digital pathology software and AI tools. | High upfront costs of digital pathology scanners, IT infrastructure, and software licenses. |
| Faster collaboration and telepathology enable seamless image sharing and remote second opinions. | Data management challenges due to massive whole-slide image storage and retrieval needs. |
| Integration with precision medicine, combining pathology, genomics, and clinical data for targeted therapies. | Uncertain regulatory pathways and inconsistent reimbursement for digital workflows. |
| Long-term cost savings by reducing slide storage, shipping expenses, and turnaround delays. | Resistance to change and retraining needs among pathologists and lab staff. |
From Lab to Bedside
The digital pathology landscape is rapidly evolving, transitioning from traditional microscopy to AI-driven diagnostics. This shift is not just technological but also a strategic move towards precision medicine. The integration of AI with digital pathology software enables pathologists to analyze complex tissue samples with unprecedented speed and accuracy, facilitating earlier detection and personalized treatment plans.
The Digital Pathology Market: A Surge in Growth
According to DelveInsight, the digital pathology market is experiencing significant expansion. Valued at approximately USD 1.2 billion in 2024, it is projected to reach USD 2.6 billion by 2032, reflecting a robust CAGR of 10.51%. Several factors drive this growth:
- Increased Cancer Incidence: The rising global burden of cancer necessitates more efficient and accurate diagnostic tools.
- Advancements in AI and Imaging Technologies: Innovations in AI algorithms and imaging systems enhance the capabilities of digital pathology platforms.
Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Seamless integration facilitates better data management and accessibility. - Telepathology and Remote Diagnostics: The adoption of telepathology enables pathologists to consult and diagnose remotely, expanding access to quality care.
The Role of AI in Precision Medicine
AI is at the forefront of this transformation, acting as a catalyst for precision medicine. By analyzing vast amounts of pathological data, AI algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that the human eye may overlook. This capability leads to:
- Early Detection of Diseases: AI can identify subtle changes in tissue samples, leading to earlier diagnosis and better patient outcomes.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By integrating genetic and molecular data, AI assists in developing tailored treatment strategies.
- Enhanced Workflow Efficiency: Automation of routine tasks allows pathologists to focus on complex cases, improving overall productivity.
What’s Next for the Digital Pathology Ecosystem?
The digital pathology ecosystem is evolving rapidly, moving beyond simple slide scanning toward fully integrated, AI-powered diagnostic networks. Hospitals and laboratories are increasingly adopting cloud-based digital pathology software, enabling remote consultations, real-time collaboration, and faster second opinions. AI tools are being trained on larger, multi-institutional datasets, enhancing their ability to detect rare and complex cancer patterns. When combined with predictive analytics, these tools are starting to guide treatment decisions, not just diagnoses.
Moreover, integration with genomics and other clinical data is creating a more comprehensive view of patient health, supporting precision medicine and personalized care. This dynamic landscape is being shaped by both startups and established digital pathology companies, including Philips Healthcare, Leica Biosystems, Roche Diagnostics, Agilent Technologies, Hamamatsu Photonics, 3DHISTECH, Inspirata, Proscia, Ibex Medical Analytics, Huron Digital Pathology, Sectra, Visiopharm, Indica Labs, PathAI, ContextVision, Koninklijke Philips N.V., Danaher Corporation, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Paige AI, Sectra AB, and others.
As these players continue to innovate, the digital pathology market is set to transform diagnostic workflows, enhance patient outcomes, and redefine the future of pathology from lab to bedside.
Conclusion
AI-enabled digital pathology is reshaping the landscape of diagnostics, moving the field from traditional slide-based workflows to a connected, data-driven ecosystem. Digital pathology scanners and software are improving accuracy, reducing turnaround times, and enabling seamless collaboration among pathologists. Breakthrough FDA approvals and real-world hospital adoption highlight the practical impact of these technologies.
At the same time, innovations in AI-driven image analysis and predictive diagnostics continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible. As the ecosystem evolves, the integration of AI with precision medicine and multi-omics insights promises to transform patient care, making diagnoses faster, treatment decisions smarter, and healthcare delivery more personalized than ever before.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- PAVmed-Novosound’s Partnership; J&J Acquires Abiomed; Approval to Sysmex’s Assay Kit t...
- Pioneering Progress: ZYNLONTA and Rituximab Combo Delivers Striking 96% Overall Response in Relap...
- Byondis’s HER2-targeting ADC trastuzumab duocarmazine; AbbVie Migraine Drug Atogepant; Grünenthal...
- Notizia
- Amber Implants Wins FDA 510(k) Clearance for VCFix® Spinal System; Merit Medical’s Embosphere Mic...