Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Growing Epidemic
Sep 04, 2024
Table of Contents
Obesity and diabetes are a global epidemic contributing to an increasing prevalence of related systemic disorders, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis is a subtype of NAFLD (Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver disease) that is characterized by an accumulation of an abnormal amount of fat in the liver. This excessive buildup of fat in the liver leads to hepatocyte injury, liver inflammation, and progression of fibrosis. NASH is becoming increasingly common with the alarming epidemic of obesity and carries the risk for more aggressive liver diseases such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, liver failure, and in some rare instances, hepatocellular cancer. The exact cause of the NASH has not been illuminated because, generally, it is different for each patient. NASH occurs in people who don’t abuse alcohol; however, its symptoms, though none or very few, are similar to those of the liver disease that occurs in people due to long-term, heavy consumption of alcohol. The presence of certain metabolic syndromes like type II diabetes., obesity, and insulin resistance are symptoms of NASH.
In 2023, prominent liver disease organizations, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), officially redefined Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), aligning the name more closely with its metabolic roots. For the most up-to-date insights, explore our comprehensive MASH Market Report.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Valeant’s asset-sale; Sanofi coughs up $19.8M; Sanofi’s Genzyme; India’s Alkem;...
- Merck’s WINREVAIR™ EU Approval; BALVERSA for Urothelial Carcinoma; Novartis and Versant’s Boreali...
- Empowering Change: REZDIFFRA’s Trailblazing Journey in NASH Treatment
- Interstitial Cystitis : Promising Scope for Research
- Vitiligo – High Unmet Need Indeed!
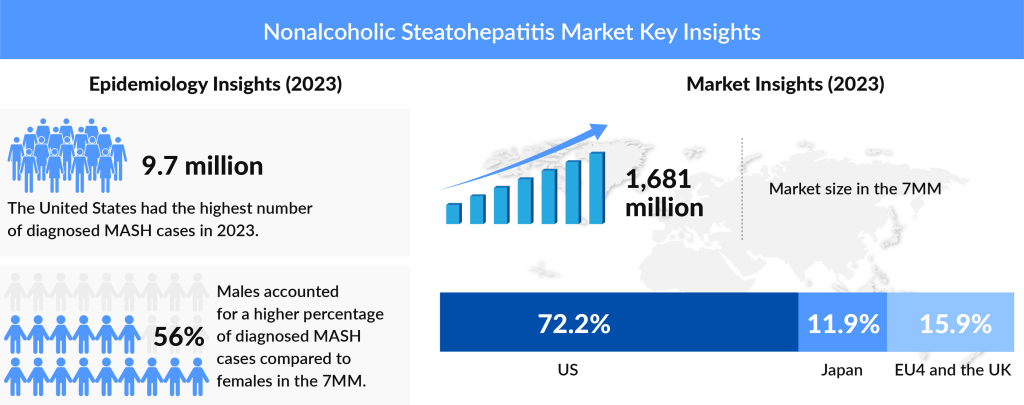
A large population-based study conducted in the United States recently, utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 2009-2010 (NHANES), reported obesity rates of 35.5% among men and 35.8% among women. According to DelveInsight’s analysis, the United States held the largest share of the obesity market in 2023, with a market size exceeding USD 2,000 million. The prevalence of NASH is believed to have increased at a similar rate over the same period. The American Liver Foundation notes that while the exact cause of NAFLD is not fully understood, it is often linked to factors such as being overweight or obese, having type 2 diabetes or pre-diabetes, and abnormal blood fat levels, among other risk factors. DelveInsight believes that the number of prevalent cases of NASH in 7MM will grow significantly during the forecasted period 2020-2034.
Why is NASH Highly Epidemic?
NASH has reached epidemic levels due to a combination of lifestyle and metabolic factors that significantly increase its prevalence.
Rising Obesity Rates
One of the primary drivers of NASH’s epidemic status is the rising prevalence of obesity. As reported by DelveInsight, around 196 million people across the seven major markets were living with obesity in 2023, with this figure projected to increase by 2034. In the United States alone, approximately 15 million individuals with obesity are under the age of 19. Nearly 90% of those with obesity do not seek treatment due to factors such as stigma, lack of awareness, and high medication costs.
Metabolic Syndrome
NASH is closely linked to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that includes hypertension, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. The prevalence of metabolic syndrome has surged in parallel with obesity rates, contributing to the growing incidence of NASH. It is estimated that approximately 20-30% of individuals with metabolic syndrome will develop NASH.
Sedentary Lifestyle and Poor Diet
The modern lifestyle, characterized by sedentary behavior and poor dietary choices, further exacerbates the NASH epidemic. High-calorie diets rich in sugars and unhealthy fats, combined with a lack of physical activity, contribute to the development of fatty liver disease. As more individuals adopt these lifestyle habits, the risk of developing NASH continues to rise.
Lack of Awareness
Despite its increasing prevalence, NASH often goes undiagnosed. Many individuals with NASH do not exhibit symptoms until the disease has progressed to advanced stages, such as fibrosis or cirrhosis. This lack of awareness among both patients and healthcare providers can delay diagnosis and treatment, allowing the disease to progress unchecked.
Implications of NASH
NASH carries significant health implications, as it can lead to severe liver complications, including cirrhosis, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. The progression from simple fatty liver to NASH and eventually to more severe liver damage poses a substantial burden on healthcare systems. Additionally, NASH is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, further complicating patient management.
Economic Impact
The economic burden of NASH is considerable, with rising healthcare costs associated with managing complications and advanced liver disease. As the prevalence of NASH continues to grow, the financial implications for both healthcare systems and patients will become increasingly significant.
Emerging Therapies
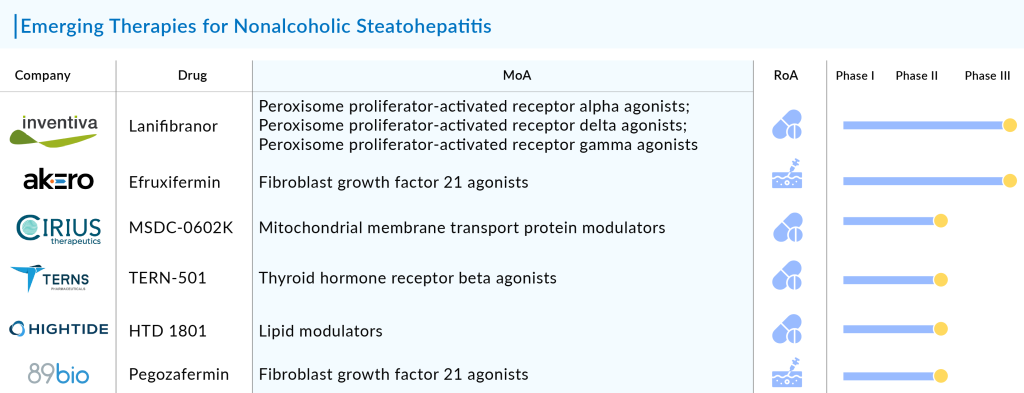
Several promising therapies are in the pipeline for NASH treatment. Notable candidates include:
- Lanifibranor (Inventiva Pharma): An orally available small molecule that acts as a PPAR agonist, targeting all three PPAR isoforms (PPARα, PPARδ, and PPARγ). Lanifibranor has received Breakthrough Therapy and Fast Track designations from the FDA and is currently in Phase III trials.
- MSDC-0602K (Cirius Therapeutics): A second-generation oral insulin sensitizer designed to modulate the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) selectively. It is currently in Phase III trials and aims to improve insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism.
- TERN-501 (Terns Pharmaceuticals): A THR-β agonist that enhances fatty acid metabolism and reduces hepatic steatosis. Currently, in Phase II trials, TERN-501 has shown promise in improving serum lipid parameters and reducing liver fat.
- HTD 1801 (HighTide Biopharma): A first-in-class ionic salt of berberine and ursodeoxycholic acid, HTD 1801 has demonstrated significant reductions in liver fat and improvements in glycemic control in patients with NASH and type 2 diabetes. It is currently in Phase II trials.
- Efruxifermin (Akero Therapeutics): A fusion protein designed to mimic the metabolic benefits of FGF21. Efruxifermin has shown significant improvements in liver fat content and markers of fibrosis in Phase II trials and is currently being evaluated in Phase IIb studies.
- Thiazolidinediones (TZD): Including pioglitazone and rosiglitazone, these PPARγ agonists have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and lipid metabolism. They are already used off-label for NASH management.
In conclusion, the battle against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis hinges on a dual approach: advancing medical treatments and enhancing public awareness. As this silent yet pervasive liver disease continues to escalate, driven by rising obesity and metabolic disorders, the need for early diagnosis and intervention has never been more urgent. By educating patients on the risks and ensuring regular screenings for those at high risk, healthcare providers can play a pivotal role in curbing the spread of NASH.
The road ahead is promising, with innovative therapies on the horizon and an increasing emphasis on prevention. Through concerted efforts to raise awareness and promote proactive health measures, we can mitigate the impact of NASH, fostering a future where fewer individuals are burdened by this serious condition. Together, we can turn the tide against NASH and pave the way for healthier communities.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Biogen’s SPINRAZA Phase II/III Trial Results; Travere’s FILSPARI FDA Approval; GSK’s ...
- Roche, Sarepta collaborates; FDA approval for Merck’s Ervebo, and Allergan’s Ubrelvy
- Valeant’s $50M; Sanofi vows; Top pharmas team up; PhRMA expels
- AZ announces positive results for durvalumab and tremelimumab; FDA nods to extend LILETTA’s use t...
- NMDA Receptor Antagonist: Emerging therapies in CNS



