Robotics in Surgery: Has the Revolution Arrived?
Mar 24, 2023
Table of Contents
With the onset of the fourth industrial revolution in the twenty-first century, a new branch emerged: Robotics. Robotics is the amalgam of computer science and engineering to make programmable machines that aim to assist humans in their tasks and produce results with minimum error. From space science to healthcare to hospitality, the usage of robots is being explored in every industry. Recent disruptive technologies such as 5G and artificial intelligence only fuel the healthcare market. With the following article, we will try to understand the use of robotics in surgeries and ponder upon the progress made in this respect.
Introduction of Robots
Robots first came into existence to be used in industrial applications. In the US, a hydraulic arm called Unimate was used to lift heavy loads. Advanced robots emerged between the 1960s and 1970s with the incorporation of cameras and sensors. Nowadays, with artificial intelligence, the robotics research field has picked up its pace.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Össur Launches POWER KNEE; DePuy Synthes Acquires CrossRoads Extremity Systems; Myomo’s MyoPro; A...
- Most Promising Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Healthcare Segment
- Penumbra’s Indigo System; Axonics’s F15 Recharge-free SNS; Stimwave’s FREEDOM-1 Clinical Trial; V...
- How Robots Are Introducing A New Dimension To Healthcare Service Delivery
- Guard Medical Announced FDA 510(k) Clearance; PROCEPT BioRobotics Announced FDA Clearance; GE Hea...
Speaking of healthcare, medical robots are deployed in various tasks such as assisting in surgeries, streamlining clinical workflow and hospital logistics, and enhancing patient care and workplace safety. Emerging first in the 1980s, medical robots provided surgical assistance via robotic arm technologies. Over decades, artificial intelligence-enabled computer vision and data analytics have transformed medical robots, expanding their capabilities into many other areas of healthcare. Let us briefly look at robots in healthcare.
Robots in Healthcare
Some of the most advanced technology is used in the medical sector to achieve the best health science. Robots are a good fit for the healthcare industry as they are equipped with advanced technologies. These days, robots used in the healthcare industry can be broadly split into two general categories, medical robots, and surgical robots. While surgical robots are used during operations and procedures by surgeons, medical robots are used across various applications, from administrative tasks in clinical settings to outpatient care.
Types of Robots in Healthcare
Different types of robots are used in healthcare based on the type of task they perform.
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Major Advantages and Disadvantages of Medical Robots
Robots are gaining momentum as automated machines have many advantages over humans. Some of the major advantages of robots are:
- Shows increased efficiency than humans.
- Can work for longer hours and on repetitive cycles.
- Robots are suitable for working in hazardous environments like the chemical and nuclear industries.
- Creates very few to minimize errors.
- Robots are more precise and consistent in their work than humans.
- Humans require breaks; however, a robot can work longer hours with less maintenance, thus saving the company time and creating profits.
- With the incorporation of artificial intelligence, smart robots can also make decisions.
- Robots can be incorporated into any industry or field, such as entertainment, manufacturing, or domestic workplace.
Similarly, robots are changing how surgeries are performed in the medical field, streamlining supply delivery and disinfection and freeing up time for providers to interact with patients. Robotic surgery has grown in popularity in recent years due to its advantages over traditional open and laparoscopic surgery. One of the significant advantages of robotic surgery is that it is minimally invasive, which means that the patient experiences less pain and recovers faster. Aside from that, the chances of infection and bleeding are significantly reduced. Another significant advantage of medical robots is that they work precisely within the parameters of time and work assigned to them.
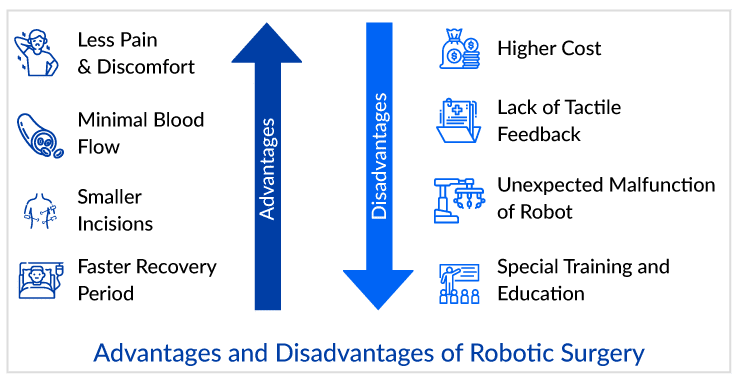
However, there are two sides to every coin. While there are numerous advantages to using robots to run errands in healthcare, there is a risk of errors and failures. With these advanced robots, human error or mechanical failure is always possible. A single mechanical failure can result in the loss of life. Small risks of infection and bleeding cannot be ignored in the case of surgical robots. There are numerous disadvantages of medical robots in healthcare. The most significant disadvantage of medical robots is their high cost. Surgical robots are only used in developed countries, research facilities, and advanced hospitals. Similarly to patients, in some cases, robotic surgeries are out of reach. Furthermore, the healthcare provider must invest a significant amount of money and time in training the workforce to operate robots; additionally, the cost of their lifetime maintenance is a concern.
The Number of Surgeries and Burden on the Healthcare Workforce
- The growing cases of cancer result in an increase in the number of cancer treatment surgeries worldwide. According to the Lancet study, the number of cancer cases globally with an indication for surgery will increase by 5 million procedures (52%) between 2018 (9 million) and 2040 (13.8 million). The greatest relative increase in surgical demand will occur in 34 low-income countries with a workforce shortage.
- As per a 2021 research article based in Japan, the number of laparoscopic surgeries has increased.
- According to the American Society of Plastic Surgeons, there were 6.8 million reconstructive procedures done in 2020, which is a 3% increase from 2019.
- As per another study, more than 6 billion (6.4 billion) people live in low to middle-income countries and have insufficient access to cardiac surgery.
- According to a study based in the US, the average orthopedic surgical volume has increased to 38.04% from January to December 2016–2019. While the US population grew by 18% between 2000 and 2020, overall surgery volume increased by 31.5%.
- A study estimated that in 2019, the world had 104.0 million health workers, including 12.8 million physicians, 29.8 million nurses and midwives, 4.6 million dentistry personnel, and 5.2 million pharmaceutical personnel. In total, the 2019 national health workforce fell short of 6.4 million physicians, 30.6 million nurses and midwives, 3.3 million dentistry personnel, and 2.9 million pharmaceutical personnel.
Therefore, as per the above statistics, it is clear that there is a trend of increase in surgeries as per the treatment algorithms. However, with an increase in surgeries worldwide for different indications, the workforce of surgeons and caregivers has not increased much over time. Thus, the current healthcare workforce is overburdened by the number of surgeries. If deployed fully, surgical robots will remove this burden from the healthcare workforce and help patients waiting for their surgeries to be done on time.
Application of Robotics in Healthcare
Robots have been used in minimally-invasive surgery, allowing surgeons to perform various operations with greater precision and faster patient recovery times. The range of existing systems is continuously expanding, accounting for over USD 5 billion in 2019, per the International Federation of Robotics. As per DelveInsight analysis, the global surgical robotic systems market was valued at USD 5.58 billion in 2022 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 11.49% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2028 to reach USD 10.76 billion by 2028. Let us look at some recent developments and major players which will eventually give rise to an increase in surgical robots in the future.
Intuitive Surgical: Headquartered in California, the US
The da Vinci platform is an intuitive, minimally invasive surgery robot. Equipped with advanced vision technologies and energy systems, the da Vinci platform has been used in millions of surgeries since the late 1990s. The company reported a 28% increase in surgical procedures through its da Vinci Surgical Systems from 2020 to 2021. According to the 2022 report from Intuitive, da Vinci Surgical Systems have been used in over 12 million surgeries worldwide.
Stryker Corporation: Headquartered in Michigan, the US
Stryker’s Mako Smart Robotics is an innovative solution for arthritis of the knee or hip. Mako uses a 3D CT-based planning software to get insights into a patient’s anatomy, which helps in personalized joint replacement surgical plans. Furthermore, Mako’s AccuStop technology allows the surgeon to cut less by cutting precisely what’s planned.
Asensus Surgical: Headquartered in North Carolina, the US
Asensus Surgical’s Senhance Surgical System is used in laparoscopic procedures, which has fully reusable instruments and can integrate with existing technology.
Vicarious Surgical: Headquartered in Massachusetts, the US
Vicarious Surgical’s Robotic System is designed to aid surgeons with invasive abdominal procedures. The technology is attached with a 360-degree-view camera and two flexible robotic arms, able to be inserted with a 1.5-centimeter incision and controlled remotely by the surgeon at hand.
Vicarious Surgical received Breakthrough Device Designation from the FDA in 2019 and has undergone a pre-submission process with the FDA for 510(k) approval on its Robotic System as of 2021.
Medtronic: Headquartered in Minnesota, the US
In October 2021, Medtronic received the CE Mark for their Hugo™ robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) system, thereby enabling Medtronic to access the European market for this device. The device received approval for gynecologic and urological procedures.
Johnson & Johnson: Headquartered in New Jersey, the US
One of the surgical robotic sphere leaders, Johnson and Johnson, has two surgical robots named Ottava and Velys. Ottava is a next-generation surgical robotic platform that has the potential to revolutionize surgery and provide optimal outcomes. Velys is a robotic-assisted solution that helps simplify surgeons’ existing workflow during total knee replacement surgery.
Another robotic surgery system, Monarch by Johnson and Johnson, has recently earned FDA clearance in 2022 for the first and only multispecialty, flexible robotic solution for use in both bronchoscopy and urology. Apart from these major companies, there are many players to watch out for, such as MicroPort, Medrobotics, CMR Surgical, and Accuray, among others.
The Road Ahead: Has the Revolution Arrived?
In the past decades, there has been a steep growth in the development and adoption of robotic-assisted surgeries in healthcare. As the number of players, their products, and regulatory approvals increase, we expect to see increased adoption of robots. The procedure volume of robotic surgical procedures within the healthcare industry is growing rapidly, which can be attributed to increased adoption rates of robotic surgical systems globally. Intuitive Surgical is the market leader, and its global procedures increased by 32% from 2017 to 2018.
With advancements in motion control technologies, surgical-assistance robots have become more precise. These robots help surgeons achieve new levels of speed and accuracy while performing complex operations with artificial intelligence-enabled computer vision technologies. Some surgical robots may even complete tasks autonomously, allowing surgeons to oversee procedures from a console. This ability to share video feeds of the operating room from a distance will allow patients for a better surgical experience as the best surgeons of the globe could be present from a far distance and will assist in surgery remotely.
Not only this, but surgical robots also play a key role in surgeon education. Simulation platforms use AI and virtual reality to provide surgical robotics training. Within the virtual environment, surgeons can practice procedures and hone skills using robotics controls.
The field of surgical robotics is evolving to make greater use of AI. Computer vision enables surgical robots to differentiate between types of tissue within their field of view. For example, surgical robots can now help surgeons avoid nerves and muscles during procedures. High-definition 3D computer vision can provide surgeons with detailed information and enhanced performance during procedures. Eventually, robots will be able to take over small sub-procedures, such as suturing or other defined tasks, under the watchful gaze of the surgeon.
Therefore, it is not incorrect to say that the revolution in robotically assisted surgery has arrived. However, the road ahead is long, and much progress needs to be made, as this is just the beginning. The key to market domination will be product proliferation.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Guard Medical Announced FDA 510(k) Clearance; PROCEPT BioRobotics Announced FDA Clearance; GE Hea...
- FDA Grants Approval to Caris Life Sciences for MI Cancer Seek; Johnson & Johnson MedTech Secu...
- The Future Of Medicinal Care – Medical Robots
- Most Promising Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Healthcare Segment
- Insulet’s Omnipod 5 Automated Insulin Delivery System; Alivecor’s KardiaMobile Card; BD Boa...