5 Upcoming Schizophrenia Drugs Competitors for Newly Approved BMS’ KarXT (COBENFY)
Oct 14, 2025
After years of little progress in the field of schizophrenia drug treatment, Bristol Myers Squibb’s USD 14 billion acquisition of Karuna Therapeutics has paid off with the approval of a groundbreaking new drug. BMS’s novel medication, KarXT—now named COBENFY—received FDA approval on 26 September 2024 for the treatment of adults with schizophrenia. COBENFY is the first muscarinic agonist approved for schizophrenia, marking the first new treatment class for the condition since the FDA approved CLOZARIL (clozapine) 35 years ago.
Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness that impacts thinking, emotions, decision-making, and social interaction. Onset typically occurs in late teens to early 20s for men and late 20s to early 30s for women. As per DelveInsight analysis, in 2024 the total diagnosed prevalent cases of schizophrenia in the 7MM were found to be 3.8 million cases out of which the US accounted for nearly 1.4 million cases. It is anticipated that these numbers will rise by 2034.
The FDA approval of COBENFY is based on findings from the EMERGENT clinical program, which includes three placebo-controlled studies assessing efficacy and safety, along with two open-label trials focused on the drug’s long-term safety and tolerability over one year. In Phase III EMERGENT-2 and EMERGENT-3 trials, COBENFY achieved its primary goal by showing statistically significant reductions in schizophrenia symptoms compared to placebo, measured by the change in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total scores from baseline to week five.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Breaking Boundaries: The Promise of LYN-005 in Schizophrenia Treatment
- Hope on the Horizon: Brilaroxazine’s Promise for Schizophrenia Patients
- An in-depth Assessment of the Top Drugs Launched by Leading Global Companies in the First Half of...
- BioXcel’s Agitation Drug Igalmi; FDA Approves Cysteine Hydrochloride Injection; Gilead’s Trodelvy...
- Navigating the Loss of Exclusivity: Big Pharma’s New Playbook
Specifically, COBENFY resulted in a 9.6-point reduction (-21.2 for COBENFY vs. -11.6 for placebo, p<0.0001) in EMERGENT-2 and an 8.4-point reduction (-20.6 for COBENFY vs. -12.2 for placebo, p<0.0001) in EMERGENT-3. Additionally, in EMERGENT-2, COBENFY showed a statistically significant improvement in illness severity from baseline to week five, as measured by the Clinical Global Impression-Severity (CGI-S) score, a secondary endpoint.
Unlike older schizophrenia drugs that focus on dopamine receptors, COBENFY’s pharmacology is distinct—it selectively affects the muscarinic receptors M1 and M4, which play roles in learning, memory, and cognition. In contrast to dopamine receptors, M1 and M4 receptor modulation addresses both the positive symptoms (hallucinations, delusions) and the negative symptoms (reduced emotional expression, speech, motivation, and pleasure) of schizophrenia.

Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) officially launched COBENFY in late October 2024, marking its entry into the schizophrenia market and intensifying competitive dynamics as peers race to defend their positions in this rapidly evolving therapeutic space. The COBENFY launch reinforces BMS’s leadership in neuropsychiatric innovation, following the successful integration of Karuna Therapeutics.
Discover the latest innovations and updates in the schizophrenia treatment space
Several schizophrenia drugs targeting the positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia through the muscarinic pathway, as well as other mechanisms, are trailing KarXT in the development pipeline. Let’s take an in-depth review of 5 of these upcoming schizophrenia drugs.
Reviva Pharmaceuticals’ Brilaroxazine
Brilaroxazine (RP5063) is a novel compound with strong affinity and selectivity for important serotonin and dopamine receptors involved in schizophrenia and other psychiatric conditions. It acts as a multimodal modulator for several serotonin receptors (5-HT1A, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT7) and dopamine receptors (D2, D3, and D4).
Reviva Pharmaceuticals showcased the results of the RECOVER Phase III clinical trial for brilaroxazine in schizophrenia at the 2024 annual meeting of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (ASCPT) in Colorado, USA. The findings indicated that brilaroxazine successfully met all primary and secondary endpoints, demonstrating significant reductions in major symptoms associated with schizophrenia. In September 2024, Reviva Pharmaceuticals unveiled new vocal biomarker data from the Phase III RECOVER trial of brilaroxazine during a virtual event featuring key opinion leaders hosted by the company.
Brilaroxazine continues to emerge as a differentiated late-stage asset in schizophrenia, with new one-year open-label extension (OLE) data reaffirming its durable efficacy and favorable tolerability profile. The once-daily oral drug demonstrated robust, broad-spectrum symptom control across all major domains—including positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms—sustained over 12 months (mean PANSS reduction –18.1; negative symptoms –4.4).
Following the successful completion of both its pivotal Phase III RECOVER trial and long-term OLE study, Reviva now considers all core clinical requirements for registration met. The company plans to meet with the FDA in Q4 2025 to discuss the path to approval and targets a New Drug Application (NDA) submission in Q2 2026. A potential second Phase III registrational trial (RECOVER-2) remains under consideration pending FDA feedback.
Beyond schizophrenia, Reviva is broadening brilaroxazine’s reach into additional neuropsychiatric and inflammatory indications, supported by patent protection extending to 2045 and beyond.
With consistent efficacy, strong adherence, and clean safety data, brilaroxazine stands out as a potential next-generation standard of care in schizophrenia—positioning Reviva as an increasingly visible contender in the CNS therapeutics landscape.
Minerva Neurosciences/Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma’ Roluperidone (MIN-101/MT-210)
Minerva Neurosciences is developing roluperidone (MIN-101) to treat negative symptoms of schizophrenia that persist chronically for a lifetime and can contribute to poor quality of life and functional outcomes. The drug can block serotonin and sigma receptors, two receptors in the brain that are involved in regulating mood, cognition, sleep, and anxiety. The company holds the license to roluperidone from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation with the rights to develop, sell, and import roluperidone (MT-210) globally. The drug candidate has completed Phase III (US) for negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
In February 2024, Minerva Neurosciences received a Complete Response Letter (CRL) from the US FDA for its New Drug Application (NDA) seeking approval of roluperidone for the treatment of negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. The FDA concluded that the current data package was insufficient and requested at least one additional positive, adequate, and well-controlled clinical trial to demonstrate the drug’s safety and efficacy.
Minerva has continued active dialogue with the FDA following the February 2024 CRL for roluperidone’s NDA. The agency has now confirmed that approval hinges on an additional confirmatory trial in schizophrenia patients with stable positive and impairing negative symptoms—mirroring prior C03 and C07 designs. The study will test once-daily 64 mg roluperidone monotherapy versus placebo, using change in PANSS Marder negative symptom score at 12 weeks as the primary endpoint, and PSP as the key secondary measure. Importantly, the FDA requires a 52-week observational phase to assess relapse and long-term safety in monotherapy. If successful, this single, well-controlled trial could support NDA resubmission without the need for adjunctive antipsychotic data.
In light of the FDA’s requirement for an additional confirmatory trial and its current cash constraints, Minerva is implementing cost-cutting measures and has launched a strategic review to explore potential value-maximizing options for shareholders. The company cautioned that this process may not lead to any specific transaction or timeline and plans to withhold further updates unless a definitive course of action is approved or disclosure becomes legally necessary.
Alto Neuroscience’s ALTO-101
ALTO-101 is an innovative small molecule PDE4 inhibitor being developed to address cognitive impairment linked to schizophrenia, a condition characterized by negative and cognitive symptoms that currently lack targeted treatment options. Utilizing a unique transdermal delivery system, ALTO-101 aims to maintain consistent drug concentrations, enhancing safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics. This specialized delivery system was developed in collaboration with MEDRx.
In June 2024, Alto Neuroscience announced the start of a Phase II double-blind, placebo-controlled trial for its transdermal formulation of ALTO-101. The company anticipates releasing top-line results from this Phase II study in the second half of 2025. Recently, Alto completed a Phase I trial of ALTO-101 involving healthy adults, which showed promising effects on cognitive performance and electroencephalography (EEG) metrics associated with cognitive function. Additionally, Alto’s innovative transdermal formulation of ALTO-101 provided higher systemic drug exposure compared to the oral version, while also resulting in fewer typical class-related side effects.
The announced Phase II study is a cross-over, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that involves dose escalation of ALTO-101 and placebo in patients with Cognitive Impairment Associated with Schizophrenia. Alto aims to enroll about 70 adult participants aged 21 to 55 who have schizophrenia and exhibit a noticeable degree of cognitive impairment. The study will assess the impact of ALTO-101 on EEG markers related to cognitive function and will also investigate its effects on cognitive performance. The primary outcome measure is the influence of ALTO-101 on theta band activity, which will be evaluated using EEG after each dosing period.
Alto shared data at the Society of Biological Psychiatry (SOBP) Annual Meeting showing that theta band activity correlates most strongly with cognitive function in schizophrenia patients, compared to a wide range of EEG measures, and also exhibits the highest case-control sensitivity. These results, which were confirmed through prospective replication, validate the primary outcome measure being assessed in the current study, providing strong proof-of-concept for ALTO-101 as a potential treatment for CIAS.In October 2025, Alto Neuroscience received FDA Fast Track Designation for ALTO-101 in CIAS. The prior month, the company independently validated its EEG biomarker, theta-band inter-trial coherence (ITC), which showed strong correlation with cognitive performance and outperformed traditional EEG markers—supporting its role as the primary endpoint in the Phase II ALTO-101 trial.
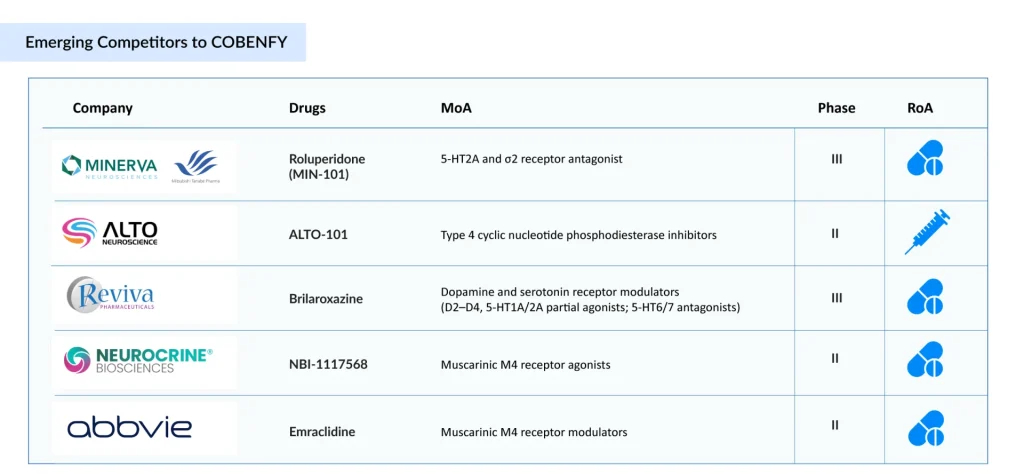
Neurocrine Bioscience’ NBI-1117568/direclidine/NBI-‘568
NBI-’568 is the first and only M4 selective orthosteric agonist currently in clinical development. Five muscarinic acetylcholine receptors play a role in neurotransmission. These muscarinic receptors are crucial for brain function and have been established as valid targets for drugs treating psychosis and cognitive disorders. As an M4 selective orthosteric agonist, NBI-’568 presents the potential for a new mechanism with an enhanced safety profile, eliminating the need for combination therapy to reduce off-target pharmacological side effects, and it does not rely on the presence of acetylcholine to be effective.
In August 2024, Neurocrine Biosciences reported encouraging top-line results from its Phase II clinical trial of NBI-1117568 (NBI-’568) in adults with schizophrenia. The NBI-’568-SCZ2028 dose-finding study achieved its primary objective with the once-daily 20 mg dose, showing a clinically meaningful and statistically significant decrease from baseline in the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score at Week 6. This resulted in a placebo-adjusted mean reduction of 7.5 points (p=0.011, effect size of 0.61) and an overall reduction of 18.2 points from baseline. Additionally, the 20 mg dose exhibited significant improvements in other measures, such as the Clinical Global Impression of Severity (CGI-S) scale, Marder Factor Score for Positive Symptom Change, and Marder Factor Score for Negative Symptom Change.
NBI-’568 was found to be generally safe and well tolerated across all doses tested in the Phase II clinical trial. The rates of treatment discontinuation due to adverse events were comparable between NBI-’568 and the placebo group. The most commonly reported adverse events included somnolence, dizziness, and headache. Gastrointestinal issues such as nausea and constipation occurred infrequently and were similar to those in the placebo group. Cardiovascular-related events were also rare and were not considered clinically significant at any dose. NBI-’568 did not lead to a greater increase in weight compared to the placebo. Only a few instances of extrapyramidal symptoms were reported.
It is currently being studied in a Phase III registrational trial that is actively enrolling patients.
AbbVie’s Emraclidine
Similar to KarXT and NBI-1117568, emraclidine acts on the M4 receptor. AbbVie gained ownership of emraclidine through its USD 8.7 billion acquisition of Cerevel in December 2023, with the deal finalized on August 1, 2024.
Emraclidine is a positive allosteric modulator specifically designed to target the M4 muscarinic receptor subtype. Recent findings indicate that activating M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors can decrease striatal dopamine signaling and alleviate psychotic symptoms, without directly inhibiting dopamine receptors. Most current schizophrenia treatments work by directly antagonizing postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptors to reduce heightened striatal dopaminergic activity.
In December 2022, Cerevel Therapeutics announced the publication of data from its Phase Ib clinical trial of emraclidine, a novel muscarinic M4-selective positive allosteric modulator, in adults with schizophrenia, in The Lancet.
The trial evaluated two dosing regimens of emraclidine (30 mg once daily and 20 mg twice daily), both of which showed clinically significant and statistically meaningful improvements in symptom severity, as measured by the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) total score. Emraclidine was also generally well-tolerated compared to placebo over the six-week treatment period. Currently, AbbVie is evaluating emraclidine in the phase II stage of development.
The expected launch of these schizophrenia drugs in the coming years will bring stiff competition in the space. Additionally, the future of schizophrenia treatment, with ongoing research and advancements in understanding disease mechanisms, is promising. Moreover, the development of novel therapies, such as those targeting neuroplasticity and inflammation in schizophrenic patients, is expected to revolutionize the market.

FAQs
COBENFY (KarXT) by AbbVie is the first muscarinic agonist approved for schizophrenia, breaking a 35-year drought since clozapine introduced a new treatment class. Unlike dopamine-blocking drugs, COBENFY targets M1 and M4 receptors, offering benefits for both positive (hallucinations, delusions) and negative (emotional withdrawal, lack of motivation) symptoms.
In Phase III EMERGENT studies, COBENFY demonstrated statistically significant reductions in PANSS scores, with up to a 9.6-point advantage over placebo. Importantly, it also improved illness severity as measured by CGI-S scores, showing strong efficacy across core schizophrenia domains.
Iclepertin is a GlyT1 inhibitor designed to improve cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia (CIAS), an area where most drugs fall short. With FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation and ongoing Phase III trials, it is the only late-stage drug directly targeting cognition, a key unmet need.
Valued at USD 8 billion in 2024, the schizophrenia market is set for major shifts by 2034. With COBENFY and other late-stage drugs advancing, competition will intensify. Muscarinic agents like emraclidine and NBI-’568 could rival COBENFY, while brilaroxazine and cognition-focused therapies such as iclepertin target underserved needs. These entrants may capture multi-billion-dollar revenues and challenge older dopamine blockers, reshaping schizophrenia treatment standards.
ALTO-101 uses a transdermal PDE4 inhibitor formulation to tackle cognitive symptoms specifically. Early data show positive effects on EEG markers linked to cognition, and Phase II results expected in 2025 could determine if it becomes the first therapy for CIAS delivered via a skin patch.
Acquired through the $8.7B Cerevel deal, emraclidine is an M4-positive allosteric modulator designed to reduce psychotic symptoms without directly blocking dopamine receptors. Currently in Phase II, its favorable PANSS improvements and tolerability give AbbVie a strong foothold to challenge COBENFY and NBI-’568.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Exploring the Impact of AI in Mental Health: How it is Going to Revolutionize Diagnosis and Treat...
- US/AZ deal; Alkermes’ Schizophrenia drug; Innovent/Lilly’s China market expansion; Re...
- BioXcel’s Agitation Drug Igalmi; FDA Approves Cysteine Hydrochloride Injection; Gilead’s Trodelvy...
- How are Antipsychotics Transforming the Schizophrenia Treatment Space?
- Hope on the Horizon: Brilaroxazine’s Promise for Schizophrenia Patients