Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Market: What’s More Beyond Exon-Skipping Therapies?
Aug 20, 2024
Table of Contents
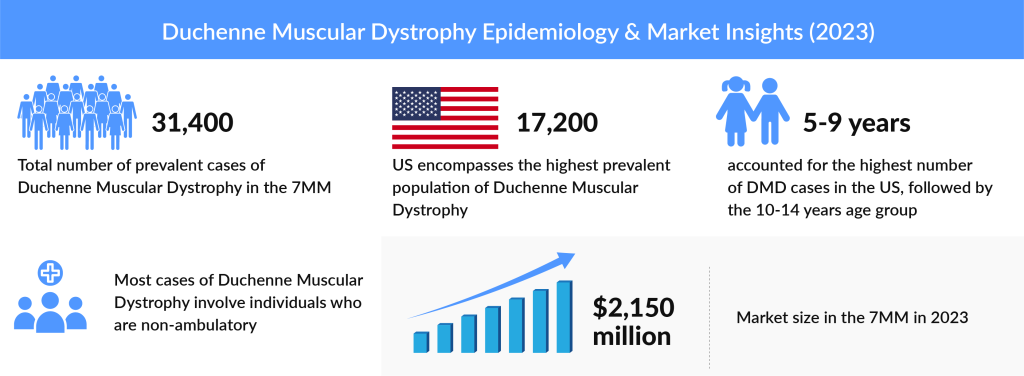
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a rare genetic disorder usually diagnosed in young boys, gradually weakening muscles across the body until the heart or lungs fail. Symptoms often show up by the age of 5; as the disease progresses, patients tend to lose the ability to walk around the age of 12. As per a recent analysis by DelveInsight, DMD market was USD 2,150 million in 2023 in the 7MM (The United States, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, UK, and Japan) and is expected to grow during the forecast period 2024–2034. The market is expected to see significant revenue growth due to the launch of recent exon-skipping therapies and anticipated approvals of emerging treatments.
What are the Current Available Treatment Options for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patients?
Currently, Sarepta is leading the DMD market with a strong, extensive pipeline and four approved antisense oligonucleotide products, namely EXONDYS 51 (eteplirsen) approved in September 2016, VYONDYS 53 (golodirsen), AMONDYS 45 (casimersen), and recently approved ELEVIDYS in June 2023. These products target patients with a mutation to exon 51, exon 53, exon 45, and exon 8 and/or exon 9, respectively. All approved in the past few years in combination can treat ~30% of all DMD cases. In June 2024, Sarepta Therapeutics received FDA approval to expand ELEVIDYS for use in ambulatory DMD patients aged 4 and older, along with accelerated approval for non-ambulatory patients. This approval marked a significant victory, with Sarepta’s stock rising by 40% on the announcement.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- What Does the Future Hold for Gene Therapy in the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Treatment Mar...
- Sarepta’s ELEVIDYS: First Gene Therapy for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) Treatment
- Zealand Pharma’s Phase III Results of Glepaglutide; FDA Approves Amylyx’s ALS Drug Relyvrio; Novo...
- FDA Fast Track Status to Kyverna’s KYV-101; Annovis’s Phase III Study for Buntanetap; Gilteritini...
- Sarepta Therapeutics Pauses ELEVIDYS Shipments in U.S. After FDA Intervention Over Patient Deaths...
Viltepso is being developed and marketed by NS Pharma. The company further plans for EU approval of the drug; however, the Phase III trial for the EU locations is still recruiting, and the approval might depend on the further data readouts. Even though both the drugs offer the intravenous mode of administration, the former offered a mean dystrophin level with an increase of 0.88%, while the latter offered an increase of 1.9% in their respective clinical trials. While the former was evaluated on a patient pool of 58 DMD patients, the latter was investigated in a trial size of eight DMD patients. Moreover, Viltepso is the only drug approved in Japan for DMD patients. Thus, it is expected to dominate the Japanese market. However, Viltepso recently failed its confirmatory Phase III RACER53 trial, showing no significant improvement in motor function over placebo. Despite a trend toward increased velocity in standing, results were not statistically significant. Safety data indicated mild to moderate adverse events, with no patient dropouts due to side effects. NS Pharma plans further analysis of the trial and will work with regulatory authorities on future steps. Viltepso remains the only approved DMD drug in Japan but faces challenges alongside other DMD therapies, including recent setbacks by Pfizer and concerns over Sarepta’s Elevidys.
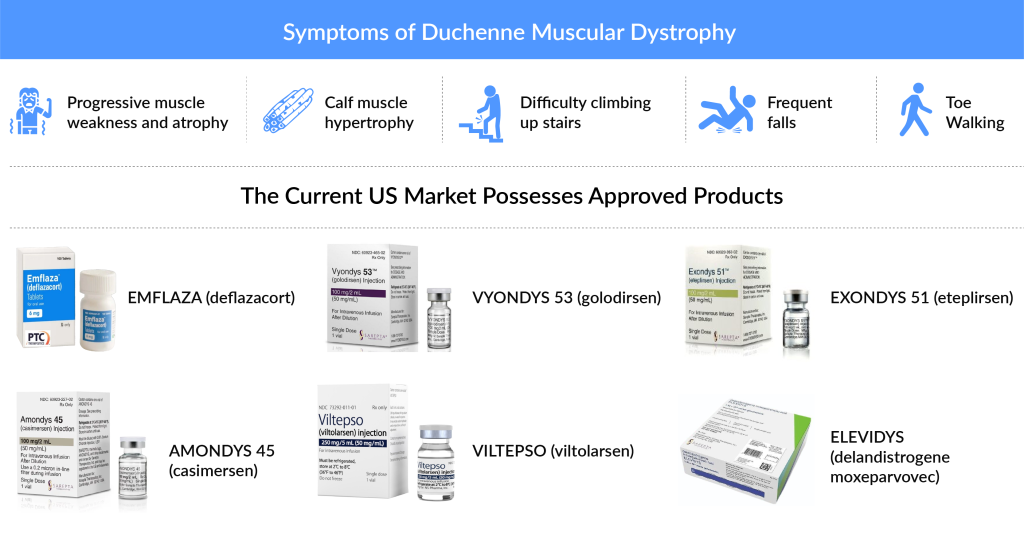
Another key player, PTC Therapeutics, has two approved products. TRANSLARNA (ataluren) was approved to treat patients aged 2 years and older with Ambulatory DMD patients by (European Economic Area) EEA in 2014, with a negative response from the US FDA in 2017 pertaining to the efficacy of the drug. As per the latest news in 2024, in March 2024, PTC Therapeutics announced plans to resubmit its NDA for Translarna later in the year, following feedback from the FDA. The NDA is a formal request to the FDA for approval to market a new drug in the U.S. The agency reviews this submission to assess the drug’s safety and efficacy, evaluate if its benefits outweigh the risks, determine if the proposed labeling is appropriate, and ensure that manufacturing standards are met. Another drug by PTC, EMFLAZA (deflazacort), targets all DMD patients aged 5 years and older. The drug was approved in 2017 in the US and is potentially superior as compared to conventional corticosteroids such as prednisone and prednisolone. Although the drug has faced major setbacks due to its extremely high cost of therapy in the United States, in the case of Europe, emflaza has been available for more than a decade at a much lower price. In June 2024, Cranbury Pharmaceuticals received FDA approval for the generic version of EMFLAZA (deflazacort) for DMD.
What are the Major Challenges Faced by the Approved Drugs?
It is worth noticing that all the approved products received accelerated approval, and further data is required for continued approval of all the drugs. Considering the historical trend in DMD, the probability of success to enter the market varies throughout 7MM. Interestingly the DMD market is quite disparate geographically in terms of regulatory approval (i.e., EMA versus FDA), with several instances of products being approved in one jurisdiction and rejected in the other based on the same clinical data. Thus, the current therapies are facing a major challenge for approval in the regions outside their respective pre-approved countries. For instance, Translarna, which is approved in EEA, met principal concerns for the US approval, whereas none of Sarepta’s exon-skipping therapies have to date received approval outside the United States. Despite previous rejections from the FDA in 2016 and 2017 and a recent regulatory setback in Europe, PTC Therapeutics plans to resubmit Translarna for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) by mid-2024. The company aims to address past concerns, including incomplete application details and insufficient clinical evidence, based on recent feedback from the FDA.

Scope of Upcoming Therapies
The current scenario is anticipated to shift toward the upcoming therapies with fair competition between the approved and emerging therapies, as some of the emerging therapies are targeting the patient pool captured by the already existing drugs. Here is a list of major key players and competitors.
| Upcoming Therapies | Emerging Key Players and Major Competitors |
| ITF2357 (Italfarmaco) | Italfarmaco is developing Givinostat (ITF2357), an orally available small molecule that acts as a histone deacetylase inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic, and antineoplastic activities. ITF2357 inhibits HDAC enzyme to increase the amount of the follistatin protein in muscle cells, which in turn increases the muscle mass and prevent muscle degeneration by opposing the effects of myostatin to reduce the symptoms of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. The drug is currently being studied in Phase III trial. The FDA has granted Givinostat Orphan Drug, Rare Pediatric Disease Designation and Fast Track Designation for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. The European Commission has granted Orphan Medicinal Product Designation for Givinostat for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. |
| Pamrevlumab (Fibrogen) | Pamrevlumab is a first-in-class antibody developed by FibroGen to inhibit the activity of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF), a common factor in fibrotic and proliferative disorders characterized by persistent and excessive scarring that can lead to organ dysfunction and failure. Pamrevlumab is advancing towards Phase III clinical development for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and pancreatic cancer and has been granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) in each of these indications, and is currently in a Phase 2 trial for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). |
| Vamorolone (Santhera) | Vamorolone is a first-in-class drug candidate that binds to the same receptors as corticosteroids but modifies the downstream activity of the receptors1,2. This has the potential to ‘dissociate’ efficacy from typical steroid safety concerns and therefore could emerge as a valuable alternative to corticosteroids, the current standard of care in children and adolescent patients with DMD. There is a clear unmet medical need in this patient group as high dose corticosteroids have significant systemic side effects that detract from patient quality of life. On September 2, 2020, Santhera exercised its option and obtained worldwide rights to vamorolone in Duchenne muscular dystrophy and all other indications. Santhera and ReveraGen expect to complete the rolling NDA submission to the U.S. FDA in June 2022. In January 2024, Santhera Pharmaceuticals announced the introduction of its AGAMREE (vamorolone) to treat Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patients aged four years and above in Germany. Santhera Pharmaceuticals has officially entered the commercial stage of its biopharma journey with the launch of this drug in Germany. In June 2024, Santhera Pharmaceuticals launched an Early Access Program for vamorolone in China for DMD patients in partnership with Sperogenix Therapeutics. |
| TAS205(Taiho Pharma) | TAS-205 (pizuglanstat) is a selective hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase (HPGDS) inhibitor discovered by Taiho Pharmaceutical. It is under development as a DMD treatment which can be used regardless of the dystrophin gene mutation type, controlling the decline in motor function in DMD patients by inhibiting HPGDS, which exacerbates the inflammatory response in DMD patients’ muscles. Currently, It is in Phase III. |
Overcoming the Cost Burden Among DMD Patients
Patients with DMD face a severe challenge in combating the high price associated with the approved therapies. In 2017, Marathon Pharmaceuticals agreed to sell its newly approved steroidal treatment– Marathon Pharmaceuticals, to PTC, offloading the drug after backlash over initial plans to charge a list price of USD 89,000 per year. PTC cut down to around USD 35,000 per year for a child weighing 25 kg but later increased the drug’s list price by about 9%, to more than USD 65,000 annually. This high price makes this old-turned-new drug a significant cost burden for DMD patients. Through the PTC Care Assistance Program, PTC therapeutics provides financial assistance for DMD patients who are prescribed Emflaza. Moreover, PTC Cares offers a co-pay assistance program for patients with commercial insurance and out-of-pocket costs associated with EMFLAZA and who qualify for assistance. Additionally, the Bridge Program allows patients currently taking EMFLAZA to continue receiving it free of charge while waiting for insurance verification of coverage. In the first nine months of 2023, EMFLAZA generated approximately $188 million, as reported in PTC’s quarterly updates, with full-year results still pending. According to FDA records, the drug has no remaining patents, though it retains FDA exclusivity for treating DMD in patients aged 2 to 5, which expires in June 2026. EMFLAZA faced controversy after its 2017 FDA approval, when Marathon Pharma set its price at $89,000 per year, drawing criticism from lawmakers due to the high cost despite the drug’s long history.
To make the drugs (EXONDYS 51, VYONDYS 53, AMONDYS 45, and ELEVIDYS) easily available and affordable to the patients, the company (Sarepta) has a patient support program called SareptAssist, designed to help patients navigate the process of starting and staying on these drugs. The company also has a Sarepta Patient Co-Pay Assistance Program, which was created for eligible individuals with commercial health insurance in the US who are prescribed these therapies. This program may help with some out-of-pocket costs related to receiving treatment, such as co-pays, co-insurance, and deductibles. Similarly, the only DMD drug approved in Japan – Nippon Shinyaku’s Viltepso-offers services and resources to patients through the NS Support program.
Thus, it is believed that the emerging drugs may face a significant challenge to reimburse their key products for better patient compliance. Certain DMD drugs under development have received Orphan Drug status by the FDA and EMA, providing certain benefits for approvals and reimbursements over other drugs. This, in turn, might boost the accessibility of these drugs.
Increase in New Born Screening, Research, and Awareness
A significant problem faced by DMD patients is the side effect associated with Steroids – the current standard of care. DelveInsight anticipates that the upcoming therapies can combat the current unmet need and the big stink faced by DMD patients. In July 2021, CureDuchenne teamed up with Brigham and Women’s Hospital, US, to launch the first free newborn screening initiative for DMD in the US. The partnership established Brigham and Women’s Hospital as the only US birth hospital to offer parents the choice of screening their new baby for DMD. An increase in newborn screening and awareness for the disease is anticipated to drive the increasing DMD patient pool. Additionally, In April 2024, Ohio Governor Mike DeWine announced that Ohio would be the first state to screen all newborns for DMD. Also, in May 2024, PPMD awarded $250,000 to support the creation of Baby Duchenne, a research network dedicated to infants diagnosed with DMD through newborn screening.
Furthemore, early testing would allow the families to access treatments that may help delay or prevent symptom onset and improve outcomes. Moreover, correct diagnosis also can give parents and caregivers a better understanding of how a child’s disease is likely to progress. Thus, an increase in research and development, awareness and newborn screening are further expected to boost the diagnosis and treatment for this patient pool.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- 5 Promising Exosome-based Therapies Paving the Way for Personalized Medicine
- In Search for a Curative Treatment Option for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Actinium Announces SIERRA Trial Results; Santhera Seeks FDA Review for Vamorolone; Seres Announce...
- Novo Nordisk Seeks FDA Approval for Higher-Dose 7.2 mg WEGOVY Injection; Ascendis Pharma Granted ...
- Gene therapy: Following Pfizer’s Unexpected Failure, Sarepta is celebrating its much-awaite...



