Wearables 2.0: The Next Wave of Clinical-Grade Wearable Medical Devices
Oct 01, 2025
Table of Contents
Not long ago, the word wearable instantly brought to mind fitness trackers counting steps or smartwatches nudging users to stand up. While those devices sparked the early boom, the next chapter, Wearables 2.0, is unfolding at the intersection of healthcare and technology. Today, wearable medical devices are no longer just lifestyle accessories; they are evolving into validated, regulated tools capable of influencing clinical decision-making.
At the heart of this transformation is the rise of medical wearable devices designed not only to monitor activity but also to detect arrhythmias, track glucose levels continuously, or even provide early warnings through wearable medical alert devices. Unlike their consumer-grade predecessors, these devices undergo rigorous testing, FDA approvals, and integration into healthcare systems. The shift is not just technological, it’s cultural, as patients and providers alike embrace the promise of real-time health insights beyond hospital walls.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Boston Scientific Corporation Agreement to Acquire Silk Road Medical; Philips Introduced Duo Veno...
- Digital Health: Insights Into the Key Transformative Trends & Evolving Market Dynamics
- Establishment Labs Gains FDA Approval for Motiva Implants; Surmodics Receives 510(k) Clearance fo...
- Medtronic Gains FDA Clearance for Altaviva™ Device to Simplify Treatment of Urge Urinary Incontin...
- Omega’s sixth funding round; Correvio’s drug failure; and BIMA acquisition
This movement is also reshaping the wearable medical devices market. Once dominated by step counters, the sector is now projected to grow into a multi-billion-dollar powerhouse, driven by the management of chronic diseases, aging populations, and the demand for remote monitoring. In other words, Wearables 2.0 is about transforming how healthcare is delivered, with data that physicians can trust and patients can act on.
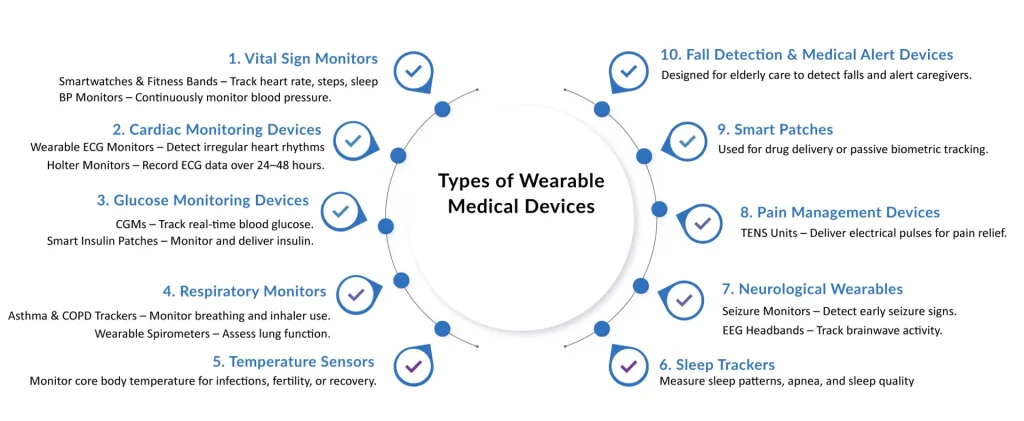
The Technology Shift: Sensors, Connectivity & AI
The leap from consumer wearables to wearable technology medical devices has been powered by rapid innovation in three core areas: sensors, connectivity, and artificial intelligence. Together, they transform raw physiological signals into actionable clinical insights, turning everyday devices into trusted wearable medical monitoring devices.
Advances in Sensor Technology
Early wearables relied heavily on accelerometers to track motion and steps. Today, new generations of sensors are dramatically expanding what types of wearable medical devices can measure.
- Optical sensors use photoplethysmography (PPG) to detect heart rate, blood oxygen saturation (SpO₂), and even blood pressure trends.
- Electrochemical sensors form the foundation of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), which accurately detect glucose levels in interstitial fluid.
- Motion and biomechanical sensors enable fall detection, gait analysis, and activity tracking crucial for elderly care and rehabilitation.
These advancements not only expand capability but also improve reliability. A CGM today, for example, can maintain accuracy within ±9% of a lab blood glucose test, making it a true wearable medical device rather than a wellness gadget.
Connectivity and AI: Powering Real-Time Health
Equally transformative has been the evolution of connectivity. The rise of IoT-enabled medical devices and 5G networks ensures data from medical wearable devices can be transmitted instantly to cloud platforms, physicians, or emergency services. This real-time data flow underpins the value of wearable medical alert devices, where seconds can make a difference.
Artificial intelligence then elevates this data into insight. Algorithms trained on millions of health records now power arrhythmia detection in ECG patches, predict hypoglycemic episodes in diabetes care, and even flag anomalies in hydration and respiratory status. By integrating AI, wearable medical devices are shifting from passive recorders to proactive health companions.
The synergy between advanced sensors, seamless connectivity, and AI-driven analytics is what makes Wearables 2.0 revolutionary. It’s the bridge that allows wearable medical device design support teams to innovate faster while ensuring clinical-grade accuracy and compliance.
Wearable Medical Devices Key Sensors and Clinical Applications
The true value of wearable medical devices emerges when advanced sensors translate raw data into meaningful clinical applications. From chronic disease management to emergency response, the latest generation of wearable medical monitoring devices is redefining patient care.
Glucose Monitoring: CGMs and Implantables
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) have become a cornerstone of diabetes management. Devices like DexCom G7 and Senseonics Eversense 365 provide real-time glucose readings via wearable medical devices, helping patients avoid hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia episodes. Implantable CGMs extend this capability, offering up to 12 months of continuous monitoring without frequent finger sticks. The global CGM Market is projected to exceed USD 18.89 billion by 2032, highlighting the enormous market opportunity for wearable technology medical devices.
ECG and Arrhythmia Detection
Cardiac health is another critical focus area. Wearable medical devices equipped with ECG sensors, such as patches and smartwatches, can detect arrhythmias like atrial fibrillation with clinical-grade accuracy. AI algorithms process continuous ECG data, alerting patients and providers to irregularities early, often before symptoms appear, enabling timely interventions that can prevent strokes or other complications.
SpO₂, Hydration, Blood Pressure, and Fall Detection
Modern types of wearable medical devices extend beyond heart and glucose monitoring.
- SpO₂ sensors track oxygen saturation trends, which are crucial for monitoring COPD or COVID-19.
- Hydration and fluid balance sensors assist in managing renal disorders and heart failure.
- Continuous blood pressure monitors provide early detection of hypertension.
- Fall detection sensors, often combined with wearable medical alert devices, protect elderly or high-risk patients by automatically notifying caregivers or emergency services when a fall occurs.
Integration into Chronic Disease Management and Telehealth
The convergence of these sensors with telehealth platforms and remote patient monitoring (RPM) programs is reshaping healthcare delivery. Patients with diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, or chronic respiratory conditions can now share real-time data with providers, reducing hospital visits and enabling proactive care. This integration fuels the growing wearable medical devices market, demonstrating the potential for scalable, personalized healthcare solutions.
Barriers and Challenges in Adoption
Despite the remarkable advancements in wearable medical devices, the road to widespread adoption is not without obstacles. From technical limitations to regulatory hurdles, several factors influence how quickly these innovations move from prototype to standard-of-care. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developers, healthcare providers, and investors navigating the wearable medical devices market.
Data Accuracy and Clinical Validation
At the heart of adoption lies trust. For a wearable medical device to be clinically useful, it must produce reliable, reproducible, and validated data. Variability due to skin tone, motion artifacts, or sensor placement can compromise readings for metrics like SpO₂, ECG, or glucose levels. Rigorous clinical trials and validation studies are essential to ensure devices meet regulatory standards and deliver actionable insights. Without robust validation, even the most sophisticated medical wearable devices risk skepticism from both clinicians and patients.
Regulatory Hurdles: FDA, CE, and MDR
Navigating global regulatory frameworks remains a significant barrier. Devices must comply with FDA requirements in the U.S., CE marking in Europe, and the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) for EU markets. Each pathway demands extensive documentation, clinical evidence, and quality assurance protocols. Startups and innovators often require specialized wearable medical device design support to ensure devices meet these standards without delaying time-to-market. Regulatory delays or uncertainties can slow adoption, particularly for novel sensors or AI-integrated systems.
Cybersecurity, Interoperability, and Reimbursement
As wearable medical monitoring devices increasingly connect to cloud platforms, telehealth systems, and hospital networks, data security becomes paramount. Breaches or vulnerabilities can compromise patient trust and trigger regulatory penalties. Interoperability with electronic health records (EHRs) and remote monitoring systems also remains a challenge, limiting seamless integration. On the financial side, inconsistent reimbursement policies for wearable devices can deter healthcare providers from adopting these technologies, even when clinical benefits are clear.
Patient Compliance and Engagement
Finally, the effectiveness of wearable medical devices hinges on patient engagement. Devices must be comfortable, user-friendly, and minimally intrusive to encourage regular use. Alerts and notifications must be actionable but not overwhelming. Education and behavioral support programs are critical to ensure that patients consistently wear, calibrate, and respond to their devices. Without compliance, even the most advanced medical wearables cannot deliver meaningful health outcomes.
Despite these challenges, the wearable medical devices market continues to expand rapidly, driven by technological advances, regulatory evolution, and increasing demand for remote and preventive care solutions. Overcoming these barriers requires a combination of robust design, regulatory expertise, patient-centered strategies, and secure data integration.
Wearable Medical Devices Market Growth and Recent Developments
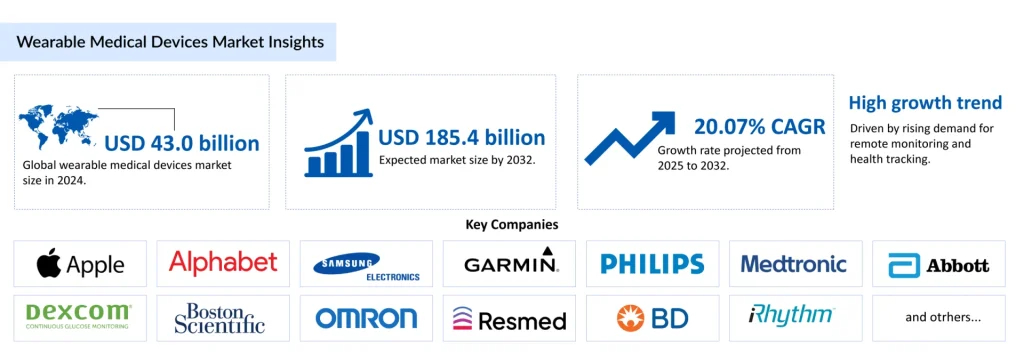
The wearable medical devices market is witnessing explosive growth, evolving from fitness-focused gadgets to essential clinical tools. The global market is projected to rise from USD 42,981.29 million in 2024 to USD 185,415.73 million by 2032, reflecting a CAGR of 20.07% from 2025 to 2032. This surge is fueled by the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, an aging population, and the increasing adoption of remote patient monitoring. Advanced sensors, AI-driven insights, and 5G connectivity are enabling wearable medical monitoring devices to deliver accurate, real-time health data directly to clinicians and patients.
Market Drivers
- Chronic Disease Management: Wearables support continuous monitoring for diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, respiratory conditions, and other chronic illnesses, enabling early detection and personalized care.
- Remote Patient Monitoring & Telehealth: Integration of wearable medical alert devices into RPM programs reduces hospital visits while improving patient engagement and outcomes.
- Technological Advancements: Miniaturized sensors, AI analytics, improved battery life, and seamless connectivity enhance usability and clinical accuracy.
Key Players
The wearable medical devices market is highly competitive, with leading global companies driving innovation and adoption: Apple Inc., Alphabet Inc., Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Garmin Ltd., Koninklijke Philips N.V., Medtronic, Abbott Laboratories, Dexcom, Inc., Boston Scientific Corporation, OMRON Corporation, ResMed, Becton, Dickinson and Company, iRhythm Technologies, Inc., Withings, Vital Connect, Inc., Masimo Corporation, Insulet Corporation, Zoll Medical Corporation, Biotricity Inc., Nuvo Group, Ypsomed, and others. These players are advancing clinical-grade wearables, expanding indications, and forming strategic partnerships to accelerate adoption.
North America is expected to dominate due to advanced healthcare infrastructure, high per-capita spending, and a robust innovation ecosystem. Diagnostic and monitoring devices currently account for the largest segment of the wearable medical devices market, while consumer-grade devices with FDA clearance are bridging the gap toward clinical adoption.
Wearable Medical Devices Recent Developments
- September 2025: Biolinq received FDA De Novo Classification for Biolinq Shine™, a forearm patch wearable biosensor for non-insulin type 2 diabetes patients, tracking glucose, activity, and sleep.
- August 2025: FDA approved Nyxoah’s Genio system for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), combining bilateral hypoglossal nerve stimulation with a wearable component.
- August 2025: FDA granted a second 510(k) clearance for Respiree’s RS001, expanding its use for home care in cardio-pulmonary diseases.
- July 2025: FDA 510(k) clearance for CardioTag by Cardiosense, enabling noninvasive ECG, SCG, and PPG monitoring for cardiac timing intervals.
- June 2025: FDA approved SoundHealth’s SONU Band for pediatric nasal congestion treatment, offering a drug-free at-home solution.
- May 2025: FDA 510(k) clearance for AeviceMD, a smart wearable stethoscope for pediatric respiratory monitoring.
- May 2025: Masimo W1 watch received FDA clearance for continuous heart rate and SpO₂ monitoring.
- May 2025: FDA approved Element Science’s Jewel® Patch Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator (Patch-WCD) for patients at temporary risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
- April 2025: WHOOP obtained FDA clearance for its ECG feature, moving a consumer device into a medical-focused role.
- April 2025: Dexcom G7 15-Day CGM System received FDA clearance, offering extended wear with improved MARD of 8.0% for adults with diabetes.
- April 2025: VitalConnect’s VitalRhythm biosensor cleared by FDA for continuous ECG, heart rate, and respiratory monitoring, enhancing RPM utility.
These developments, combined with robust market growth and strategic moves by key players, underscore the rapid evolution of wearable medical devices as critical tools for connected, proactive healthcare.
Conclusion
Wearables 2.0 are more than just a step forward in technology; they are transforming the way healthcare is delivered and experienced. By seamlessly integrating into daily life, these devices empower patients to take ownership of their health while providing clinicians with continuous, actionable insights. The convergence of precision sensors, AI-driven analytics, and remote monitoring is laying the foundation for a healthcare ecosystem that is predictive, preventive, and highly personalized.
As the wearable medical devices market continues to expand, collaboration between tech innovators, healthcare providers, and regulatory bodies will be key to unlocking its full potential. Beyond clinical benefits, the proliferation of these devices has the potential to reduce healthcare costs, improve population health outcomes, and democratize access to high-quality care. In essence, Wearables 2.0 are catalysts for a healthcare paradigm shift, where real-time data, patient engagement, and intelligent monitoring converge to create smarter, more responsive healthcare systems.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Generative AI in Drug Discovery: Applications and Market Impact
- Exploring the Impact of AI in Mental Health: How it is Going to Revolutionize Diagnosis and Treat...
- WORLD CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE DAY
- Ipsen’s Cabometyx Rejected by NICE; Vertex and CRISPR Therapeutics’s Submit BLA to the FDA for ex...
- Asensus Surgical Acquired by Karl Storz; Allosource® Launched Aceconnex®; Siemens Healthineers FD...




