Bleeding Disorders: How Key Companies Are Shaping The Bleeding Disorders Therapeutics Market?
Mar 17, 2021
Bleeding disorders, also known as coagulopathy, are a group of conditions in which the blood cannot clot properly due to the missing or defective protein. Bleeding Disorder can affect a person irrespective of his genders, ages and race and the person is likely to bleed more than the average person. A minor cut or scrape may result in intense bleeding.
The coagulation factors are proteins in the blood that works with platelets and plays a vital role in the blood clot. Platelets, bound together to form the fibrin clot, and any defect in the clotting factors or platelets can lead to excessive or prolonged bleeding. Excessive bleeding during or after surgery and injury, nosebleeds, bleeding of the gums, bleeding into joints, heavy menstrual bleeding are common symptoms of bleeding disorders. It is observed that most Bleeding disorders are inherited. Still, some of the diseases may develop over time due to certain medical conditions such as deficiency of vitamin K, medications side effects, low red blood cell count, and specific liver disease.
What are the most common Bleeding Disorder and their therapeutics options?
Bleeding disorders are classified based on the types of defects (or deficiencies) such as coagulation factor deficiencies, platelet disorders, vascular disorders or fibrinolytic defects. Hemophilia A and B and Von Willebrand’s disease are common bleeding disorders due to Coagulation factor Deficiencies. As the month of March is celebrated as Bleeding disorder awareness month, we have covered some of the common bleedings disorders with key companies operating in the market to address the therapeutics challenges in their management.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- von Willebrand disease (VWD) – Misdiagnosis Still Prevalent!
- Hemophilia: A Lifelong Genetic Disorder
- Novo Nordisk’s Concizumab for Hemophilia; AbbVie Ends its Alliance with Alector; ADC Therapeutics...
- RNA Interference: New Class of Drugs In The Fight Against Disease
- Sanofi’s Qfitlia Enters the Hemophilia Market—What Sets It Apart?
Hemophilia A – Haemophilia is classified based on the missing clotting factor in the blood. Hemophilia A is one of the most common genetic bleeding disorders caused by missing or defective factor VIII, a clotting protein, due to which it is also called factor VIII (FVIII) deficiency.
Haemophilia A consists of nearly 80% of the total patient pool of Hemophilia. Hemophilia A cases are categorised as mild, moderate and severe cases based on the severity of the diseases. Further, is it observed that moderate and severe cases consist of around 75% of the patient pools of Hemophilia A. As per the Delveinisght, the total Hemophilia A prevalent population in the 7MM was 43,243 in 2020, which is expected to rise during the study period.
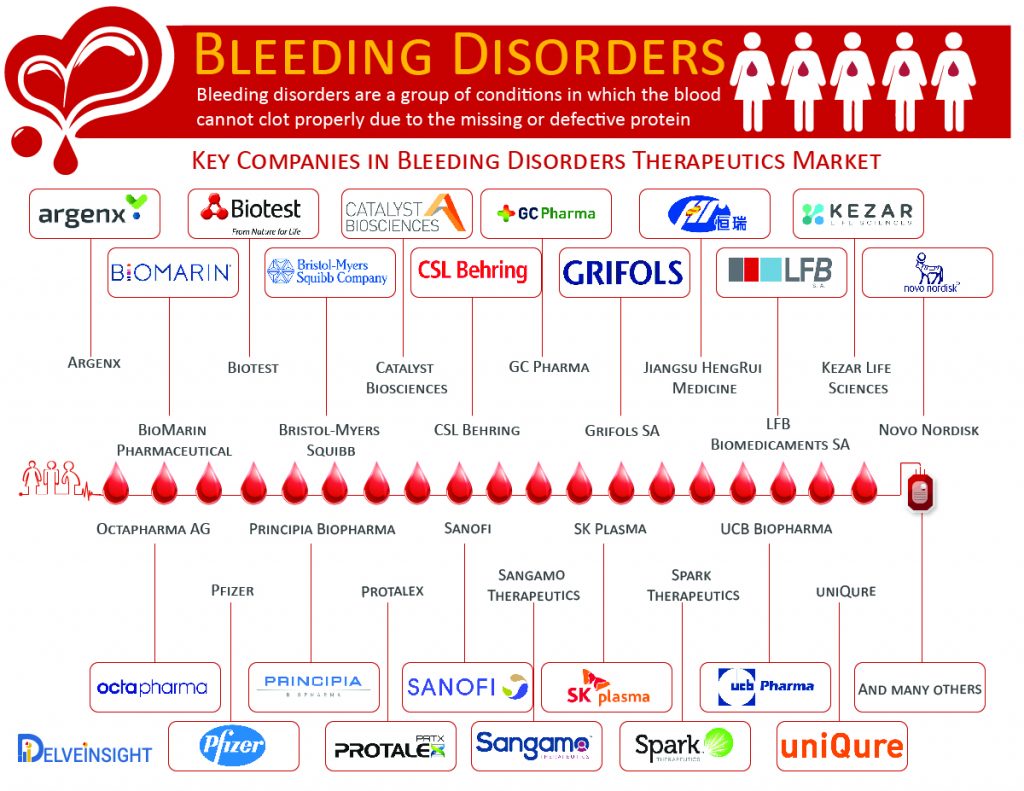
As of now, there is no cure for Hemophilia A. Factor Replacement Concentrates, and Bypassing agents are the major treatment option for Hemophilia A. However, at present, some of the key pharma and biotech players are exploring the potential of gene therapy for Hemophilia A. Companies such as BioMarin Pharmaceutical, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Pfizer, Sangamo Therapeutics, Spark Therapeutics and many others are working on novel therapeutic approaches for Hemophilia A which is expected to change the outcome for the patients affected with it. Along with the launch of the upcoming therapies, the rise in healthcare spending is expected to provide stimulus to the Hemophilia A market growth.
Hemophilia B – Hemophilia B, also called factor IX (FIX) deficiency (or Christmas disease), is caused by missing or defective factor IX, a clotting protein. Haemophilia B is the second most common type of haemophilia. Being male and family history are the two main risk factors for Hemophilia B, however, in some cases, females may also show some signs of bleeding. It is genetically passed down in the family, and it may also occur by spontaneous mutation. It is found to be more prevalent in the royal families of Spain, Germany, and Russia, due to which it is also known as the “Royal disease. Like other bleeding disorders, the Hemophilia B affected person may bleed longer than other people and internal bleeding into joints and muscles and external bleeding may also occur.
According to the Delveinsight analysis, in 2020, the total Hemophilia B prevalent population in the 7MM in 2020 was 10,739 and expected to rise by 2030. The prevalent population of Hemophilia B in the United States was observed to be 4,134 cases in 2020.
Hemophilia B lacks a permanent cure; however, treatment options such as Recombinant Factor IX Concentrates, Plasma-Derived Factor IX Concentrates, and Fresh Frozen Plasma are available in the market. At present companies such as Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Pfizer, Sangamo Therapeutics, Catalyst Biosciences, uniQure, and others are working on different therapeutic approaches for Hemophilia B.
Von Willebrand disease – Von Willebrand disease is the most common bleeding disorder that equally affects men and women; however, women are likely to show more symptoms than men. As per the CDC, in the United States, around 1% of the population which is roughly around 3.2 million, is found to be affected by Von Willebrand disease. VWD is inherited from one or both parents and caused by the absence or defect in the von Willebrand factor, a protein that helps in blood clotting. The signs and symptoms of Von Willebrand disease may vary from person to person according to the severity and types. The disease largely remains unnoticed for years until the episode of severe bleeding occurs after surgery or other such procedures.
Over the past few years, increased awareness and improved diagnostics tools have played a significant role in accessing Von Willebrand disease’s burden. According to Delveinsight, in 2017, the total diagnosed Von Willebrand disease prevalent population in seven major markets (i.e the United States, Italy, Spain, Germany, the United Kingdom and Japan) was observed to be 33,758. Among the 7MM, the United States accounted for the highest diagnosed prevalence.
As per the CDC, “between 2012 and 2016, more than 14,600 men, women, and children were seen at haemophilia treatment centres for the treatment of VWD, and about 2/3 were women and girls. The current VWD treatment option is categorised into three parts based on drugs administered, which includes Non-replacement Therapy (using desmopressin (DDAVP)), Replacement Therapy (using plasma-derived coagulation factor concentrates) and Adjunct Therapy (using primarily antifibrinolytics). To minimise the burden of the VWD, some of the key market players, such as Shire Plc. (earlier Baxalta), CSL Behring, LFB Biomedicaments SA, Octapharma AG, Grifols SA and many others are working on developing Von Willebrand disease therapies. The entry of the promising expanded recombinant therapies and regulatory approvals is expected to fuel the VWD market growth during the forecasted period.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) – Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is another blood disorder that results in an abnormal decrease in the number of platelets (or thrombocytes) in the blood which can lead to bleeding gums, internal bleeding and excessive bruising. Occurring in both children and adults, ITP can cause purple bruises. Blood in the vomit, urine or stool, nosebleeds, bruising, uncontrolled bleeding during surgery or due to cut and gum bleeding are some of the most common symptoms of ITP. Apart from bleeding, diabetes, osteoporosis, cataracts are some of the most common complications of ITP. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) is diagnosed based on the medical and medication history, physical exam and complete blood count (CBC), the blood and urine tests.
As per the Delveinsight estimations, the total Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) prevalent population in the seven major markets was found to be 180,498 in 2017. The current ITP therapeutics market is marked with several first- and second-line therapies. The therapeutics approach for ITP aims to provide a platelet count that prevents major bleeding rather than correcting the platelet count to normal levels. Some of the pharma giants such as Biotest, UCB Biopharma, Argenx BVBA, GC Pharma, SK Plasma, Jiangsu HengRui Medicine, Argenx, Kezar Life Sciences, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Principia Biopharma, and Protalex hold the potential to improve the dynamics of Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) market with the launch of potential therapies during the forecast period.
Worldwide a significant proportion of the population is living with different bleeding disorders and creates a significant challenge in term of diagnosis and treatment. It affects the quality of life of the patients and their life expectancy. However, to address the unmet need in the treatment market companies at the global level are conducting various clinical trials to provide safe and effective therapeutic options. Similarly, some of the companies are exploring the potential of gene therapy as a treatment option for haemophilia A. Overall, in the coming years, the launch of emerging therapies, rising awareness, increasing healthcare spending, and regulatory approval is expected to address several prevailing challenges in bleeding disorder treatment and management.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- NeuroNOS’ BA-101 Granted FDA Orphan Drug Status for Glioblastoma; Takeda’s VONVENDI Approval Expa...
- Global Hemophilia Market
- Hemophilia B Market: How Pipeline Therapies are Transforming the Treatment Hemisphere?
- Sanofi’s Qfitlia Becomes First FDA-Approved Therapy for Hemophilia A or B; FDA Approves AstraZene...
- von Willebrand disease (VWD) – Misdiagnosis Still Prevalent!