Revolutionizing Psoriasis Treatment: Advancements in the US Market
Apr 19, 2024
Table of Contents
Psoriasis is one of the most frequent chronic inflammatory dermatoses in the world, with variable prevalence globally. Important factors in the variation of the prevalence of psoriasis include age, gender, geography, and ethnicity, probably due to genetic and environmental factors. Higher prevalence rates have been reported at higher latitudes and in Caucasians compared with other ethnic groups.
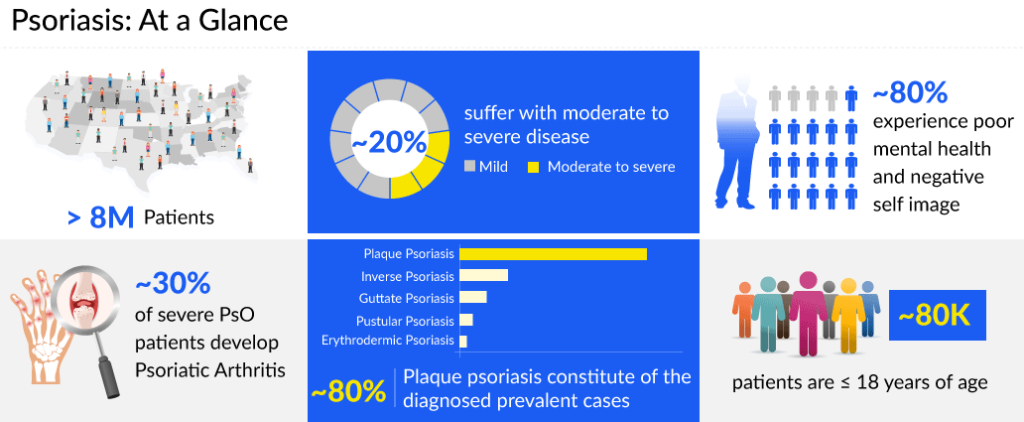
The US accounted for around 8 million diagnosed prevalent cases of psoriasis in 2022. Among the prevalent cases, nearly 99% of cases were found in adults, while only 1% of the cases were contributed by the pediatric population. ~80% of people experience poor mental health and negative self-image.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- December 7 Business Cocktail
- Sarepta Therapeutics Pauses ELEVIDYS Shipments in U.S. After FDA Intervention Over Patient Deaths...
- Thumbs down to NKTR-181, Lilly expands its insulin armamentarium
- Prolong’s PP-007 Fast-Tracked for Stroke; FDA Expands JYLAMVO Pediatric Approval; Corcept’s Cushi...
- Biogen-Eisai’s Aduhelm; Quidel acquires Ortho Clinical Diagnostics; Accutar Biotechnology’s...
According to DelveInsight estimates, the most common type of psoriasis is plaque psoriasis, followed by inverse psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis. Plaque psoriasis constitutes ~80% of the diagnosed prevalent cases of psoriasis. Based on the location of psoriasis, genital psoriasis has the highest cases contributing almost 67% of the cases, while palmoplantar psoriasis accounted for the least cases representing only 14%.
As psoriasis prevalence continues to rise globally, affecting millions, adopting effective coping strategies is crucial. Embracing a holistic approach including medical treatments, lifestyle modifications such as stress management, a balanced diet, and regular exercise, alongside seeking support from healthcare professionals and peer groups can significantly alleviate the physical and emotional burden of psoriasis.
Exploring the Current Landscape of Psoriasis Treatment: What Progress Have We Made?
Current psoriasis treatment comprises a variety of options including topical agents, phototherapy, oral agents, and biologics. Topical agents are recommended as the first line of treatment whereas oral & biologics are for the second and third-line treatment. Major topical agents include corticosteroids, retinoids such as tazarotene, and calcineurin inhibitors such as tacrolimus, vitamin D analogs such as calcipotriene or calcitriol, and combinations such as calcipotriol plus betamethasone dipropionate.
Among the patients with moderate to severe psoriasis seeking psoriasis treatment, about 35% are on biologic therapy. Biological treatments have transformed the way moderate to severe psoriasis is managed, emerging as highly effective options for patients who do not respond sufficiently to traditional systemic therapies, cannot tolerate their side effects, or have conditions that make these therapies unsuitable. The introduction of the first biologic agent for psoriasis treatment, the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) antagonist ENBREL (etanercept; Amgen), marked a significant milestone in 2004. Following this, two more TNF inhibitors, infliximab (REMICADE; Merck & Co./Janssen Biotech) in 2006 and HUMIRA (adalimumab; AbbVie) in 2008, further expanded the available psoriasis treatment options.
TNF-alpha inhibitors such as etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab (accounted for the largest share (~30%) owing to payer and prescriber convenience for these drugs. Also, the rising approval of anti-TNF biosimilars and their cost-effectiveness increase patient access to the drug class through greater adoption of biosimilars. IL-12/23 inhibitors (ustekinumab) and IL-17 inhibitors (Secukinumab, brodalumab, and Ixekizumab) also accounted for a significant share in the current psoriasis treatment market due to the higher efficacy of interleukins compared with TNF-α inhibitors and non-biologic therapies
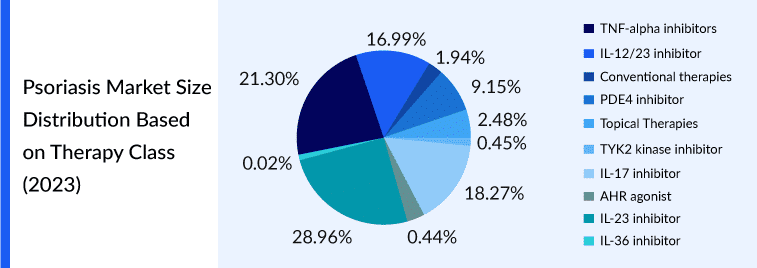
PDE4 inhibitors (apremilast) are capturing a prominent share due to their easy route of administration compared to biologics and higher efficacy compared to conventional oral therapies. TYK2 Kinase inhibitors (deucravacitinib) approved in 2022, is the new drug class for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in adults. It is a targeted therapy modulating multiple cytokine pathways implicated in psoriasis, including IL-23.
There are plenty of treatment options available for psoriasis patients; however, each of them has some potential shortcomings such as side effects and high costs. To combat these issues, many psoriasis therapies are currently under different stages of clinical development, which will fuel the psoriasis treatment market and drive its growth in the coming years.
Challenges in the Current Psoriasis Treatment Market
The landscape of psoriasis treatment is marked by a series of challenges, reflecting the diverse needs of patients across varying demographics. One pressing concern lies in the unmet needs of a significant portion of the patient population. Despite advancements, many individuals continue to struggle with ineffective treatments, emphasizing the urgency for novel therapeutic approaches. This includes patients who do not respond adequately to existing medications, necessitating a more tailored and diversified range of options to address the diverse nature of the disease.
Another critical area requiring attention is the limited scope of clinical studies focused on pediatric psoriasis. Few pipeline drugs for mild to moderate psoriasis along with limited clinical studies for pediatric patients are some of the unmet needs in the current psoriasis treatment market landscape. Children and adolescents grappling with this chronic condition often face a scarcity of treatment options tailored to their unique physiological and psychological needs.
The lack of comprehensive research on this demographic leaves healthcare providers with few evidence-based guidelines, presenting a considerable challenge in ensuring optimal care and outcomes for younger patients. Pharmaceutical companies are redirecting their efforts to address unmet needs by pursuing approval for drugs designed for pediatric patients. For example, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Arcutis Biotherapeutics, Novartis, Boehringer Ingelheim, and various others have introduced treatments tailored for pediatric use.

Furthermore, the current psoriasis treatment market often overlooks individuals with mild to moderate forms of psoriasis, as well as those with rare types of the condition. While severe cases have garnered substantial research and therapeutic options, those with milder manifestations or rarer variants often find themselves with limited choices. This underscores the necessity for increased clinical research efforts aimed at developing effective, targeted treatments for these overlooked segments of the psoriasis patient population. Addressing these challenges is crucial to achieving a more inclusive, effective, and patient-centered approach to psoriasis care and treatment.
Unlocking Potential: Expanding Psoriasis Market Horizons with Emerging Opportunities
Psoriasis treatment market dynamics are anticipated to change in the coming years due to the rising awareness of the disease and better approaches to therapy development across the world. Companies including AnaptysBio (Imsidolimab), Eli Lilly (DC-806), Protagonist Therapeutics/Janssen Pharmaceuticals (JNJ 2113), Nimbus Lakshmi/Takeda (TAK-279), Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS-986322), UNION Therapeutics (Orismilast), Pfizer (PF-07038124), Evelo Biosciences (EDP2939), are some of the key players involved in developing therapies for psoriasis treatment.
Imsidolimab, a fully humanized IgG4 antibody, works by blocking the activity of the interleukin-36 receptor (IL-36R). It is being developed as a treatment for generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP). On October 9, 2023, AnaptysBio, Inc. reported positive initial findings from its global Phase III GEMINI-1 trial of imsidolimab (IL-36R mAb) in patients experiencing GPP flares. The investigational imsidolimab successfully achieved its main goal in the study, which was the rapid improvement of pustules, redness, and scaling by Week 4 following a single 750mg IV dose. Additionally, the early data indicate a positive safety and tolerance profile.
JNJ-2113, an investigational drug, represents a groundbreaking advancement as the first oral peptide specifically designed to inhibit the IL-23 receptor. This receptor is crucial in triggering inflammatory responses seen in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis and other diseases influenced by IL-23. The development of JNJ-2113 is a collaborative effort between Protagonist Therapeutics and Johnson & Johnson, with Johnson & Johnson holding sole global rights for its advancement through Phase II clinical trials and beyond. Additionally, they have the exclusive rights to commercialize any compounds resulting from the research conducted as per the agreement, covering a wide array of medical conditions.
Johnson & Johnson recently shared new findings in March from its Phase IIb FRONTIER 2 trial regarding the effectiveness of its experimental peptide therapy, JNJ-2113, for patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. The company presented these results at the American Academy of Dermatology’s Annual Meeting during a special session. After one year, 76.2% of patients on the highest dosage—100 mg, twice daily—maintained significant skin improvement, as measured by a 75% enhancement in Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores. By the 16-week mark, this treatment plan resulted in a 78.6% PASI-75 response.
The anticipated launch of these emerging therapies for psoriasis treatment are poised to transform the psoriasis market landscape in the coming years.
Highlights from the AAD Conference: Insights on Psoriasis Treatment
At the recent American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Conference, groundbreaking insights into psoriasis treatment took center stage. Among the highlights, new biologic therapies showcased promising results in managing moderate to severe cases, offering hope for improved symptom control and quality of life. Additionally, advancements in personalized medicine approaches, including biomarker studies, hinted at a future where tailored treatments could revolutionize psoriasis care, marking a significant step forward in addressing this challenging dermatological condition. Some of the highlights from AAD conference include:
Future Outlook of Psoriasis Treatment
The future outlook of the psoriasis treatment market holds promise as advancements in medical research and technology continue to pave the way for more effective and personalized therapies. With an increasing understanding of the complex immune mechanisms underlying psoriasis, pharmaceutical companies are developing targeted biologics and small molecules that offer better disease management with fewer side effects. These innovative treatments, often tailored to individual patient needs, are anticipated to drive substantial growth in the psoriasis treatment market.
As per DelveInsight, in 2023 the US Psoriasis market was valued at ~$17billion and the estimates suggested that the market for psoriasis treatment in the US is likely to grow at a CAGR of ~3.0% due to an increase in drug approvals and improving patient access.
Moreover, the rise of digital health technologies is transforming how psoriasis is monitored and treated. Wearable devices, mobile apps, and telemedicine services are enabling patients to track their symptoms, medication adherence, and overall health more conveniently. This trend not only enhances patient engagement but also provides healthcare providers with real-time data for more informed decision-making, leading to improved outcomes and potentially reducing healthcare costs.
Additionally, the increasing prevalence of psoriasis worldwide, coupled with a growing awareness of the disease and its impact on patient’s quality of life, is creating a demand for more accessible and affordable treatment options. As a result, market players are focusing on expanding their global reach, developing biosimilars to existing biologics, and investing in patient support programs. This concerted effort towards innovation, accessibility, and patient-centricity paints a promising picture for the future of the psoriasis treatment market, where effective therapies and improved quality of life for patients are at the forefront.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Sarepta Therapeutics Pauses ELEVIDYS Shipments in U.S. After FDA Intervention Over Patient Deaths...
- AstraZeneca’s Imfinzi for Biliary Tract Cancer; FDA Clears Boehringer’s Spesolimab; Novo Nordisk ...
- Amgen to Acquire Horizon Therapeutics; Sanofi and Teva Announce Collaboration; Boehringer Obesity...
- IMFINZI’s AEGEAN Phase III Trial Data for Treating Resectable NSCLC; Ipsen and Day One’s Exclusiv...
- Could Hidradenitis Suppurativa Be Another Psoriasis?




