CAR-T Beyond Cancer: Resetting Immunity in Autoimmune Diseases
Dec 22, 2025
Table of Contents
Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy has established itself as one of the most disruptive innovations in modern medicine. Since the first approval in 2017, CAR-T therapies have transformed outcomes in hematologic malignancies, achieving deep, durable remissions in patient populations previously resistant to standard therapies. This clinical success has fueled interest in leveraging CAR-T’s precision and potency beyond oncology. Among emerging frontiers, autoimmune diseases represent a particularly compelling opportunity, where CAR-T offers the prospect of an immune system reset rather than symptomatic suppression.
From Oncology to Autoimmunity: A Platform Evolution
The oncology field provided the foundation for CAR-T’s credibility. Tisagenlecleucel (KYMRIAH) was the first to gain FDA approval for B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in children and young adults, and later for large B-cell lymphoma. Axicabtagene ciloleucel (YESCARTA) was approved for large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma, while brexucabtagene autoleucel (TECARTUS) was approved for mantle cell lymphoma and adult B-cell ALL. Lisocabtagene maraleucel (BREYANZI) is available for large B-cell and follicular lymphomas, and in some regions for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). In multiple myeloma, two BCMA-targeting CAR-T therapies, idecabtagene vicleucel (ABECMA) and ciltacabtagene autoleucel (CARVYKTI), have provided new hope for patients with advanced disease after multiple prior treatments. More recently, Obecabtagene autoleucel (AUCATZYL) was approved for adult B-cell precursor ALL, adding to the growing list.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Novo Nordisk Seeks FDA Approval for CagriSema; EU Approves Subcutaneous Self-administration of SA...
- 7 Late-Stage SLE Drugs Expected to Enter Therapeutic Domain
- Aelis Farma pockets $30M; Alcyone unveils $23M for AAV gene therapies; Progentec and GSK collabor...
- Is Gene Therapy the Next Cancer Treatment Revolution?
- Evaluating the Upcoming Drugs in Pipeline for Major Autoimmune Diseases
While oncology CAR-T faces challenges of safety, durability, and cost, its trajectory from experimental therapy to a diverse, FDA-approved platform has validated its transformative clinical potential. Building on this foundation, CAR-T development is shifting toward non-malignant conditions with autoimmune diseases at the forefront.
Scientific Rationale of CAR-T Use for Autoimmune Diseases
Traditional treatments for autoimmune diseases rely on broad immunosuppressants or biologic agents targeting cytokines or receptors. While effective for symptom management, these approaches rarely achieve durable remission and carry long-term safety risks, including infection and malignancy.
CAR-T offers a different paradigm
- Immune reset through targeted B-cell depletion (CD19-directed CAR-T)
- Dual-targeting constructs (CD19/BCMA, BAFF-R) to extend depletion to long-lived plasma cells.
- CAR-T approaches for selective elimination of pathogenic B-cell clones.
- CAR-Tregs to restore immune tolerance by reprogramming, not depleting.
- Next-generation innovations: transient CAR expression, safety switches, logic-gated constructs, and allogeneic “off-the-shelf” products to improve accessibility.
This mechanistic versatility positions CAR-T as a potential disease-modifying therapy in autoimmunity.
Clinical Pathways: Progress and Pipelines in CAR-T
Among autoimmune diseases, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis represent the most advanced indications under investigation for CAR-T cell therapies. Early studies with CD19-directed CAR-Ts have demonstrated the potential to achieve sustained, drug-free remission in these patients. Beyond lupus, high-priority areas of research include multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, and rheumatoid arthritis, where CAR-T approaches are being evaluated for their ability to deplete pathogenic immune cells and re-establish immune tolerance selectively. While no CAR-T therapy has yet been approved for autoimmune diseases, SLE and lupus nephritis are currently at the forefront of development.
To contextualize the evolving competitive landscape, the “below table” outlines ongoing CAR-T programs across autoimmune indications, detailing their targets, therapeutic areas, and clinical stages.
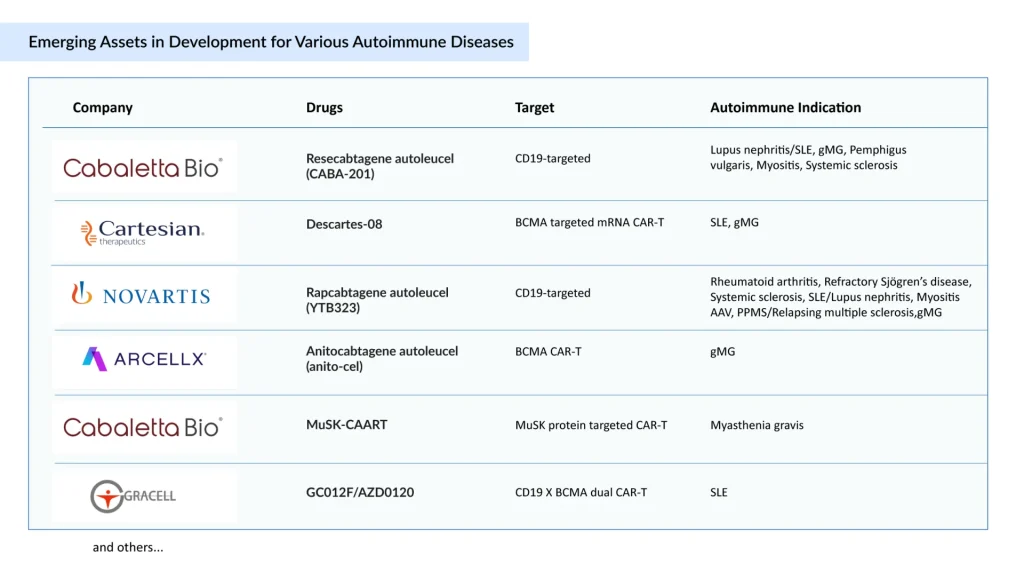
Leading developers and CAR-T
- Cabaletta Bio (Resecabtagene autoleucel, CABA-201) – Broadest autoimmune pipeline; FDA Fast Track and RMAT designations in SLE, systemic sclerosis, MS, and myositis.
- Cartesian Therapeutics (Descartes-08) – First-in-class mRNA CAR-T against BCMA; differentiated by outpatient administration and RMAT (Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy), ODD (Orphan Drug Designation), and RPDD (Rare Pediatric Disease Designation) designations.
- Novartis (Rapcabtagene autoleucel, YTB323) – next-generation, autologous CD19-directed CAR-T developed using its proprietary T-charge platform, designed to preserve T-cell stemness and significantly shorten manufacturing time.
- AstraZeneca (GC012F/AZD0120) – dual CD19 X BCMA strategy.
- Bristol Myers Squibb (CD19 NEX-T) – Leveraging its NEX-T platform, Bristol-Myers Squibb is advancing a broad CD19 CAR-T portfolio across autoimmune diseases, including SLE, gMG, and MS, positioning itself as a key contender in next-generation, off-the-shelf immunotherapies.
- Abbvie (CPTX2309) – CPTX2309 could emerge as a first-in-class CAR-mRNA therapy with its in vivo targeted Lipid Nanoparticle (tLNP) delivery, offering a more precise and potentially simpler approach than competitors using alternative methods.
Smaller players such as AbelZeta (C-CAR168) and Kyverna (KYV-101) are also advancing programs in lupus nephritis, myositis, and stiff person syndrome.
CAR-T in 2025: Emerging Data Redefining the Autoimmune Frontier
Several CAR-T programs reported encouraging results across autoimmune diseases.
Cabaletta Bio – RESET-SLE Phase I/II (CABA-201; NCT06121297): At EULAR 2025, the RESET-SLE Phase I/II trial showed that a single infusion following lymphodepletion was generally well tolerated, with only low-grade CRS in two patients and one reversible ICANS event. All four treated patients (three SLE, one lupus nephritis) demonstrated early clinical improvement, discontinued immunosuppressives, and two tapered off steroids, supported by rapid B-cell depletion and re-emergence of naïve B cells.
Cartesian Therapeutics – Descartes-08: In April 2025, Cartesian Therapeutics reported Phase IIb data in myasthenia gravis showing Descartes-08 induced durable responses, with an average 4.8-point MG-ADL score reduction at 12 months, deep sustained benefit in biologic-naive patients (7.1-point reduction; 57% at minimal symptom expression), and a favorable outpatient safety profile; preliminary SLE data from its ongoing Phase II trial are expected in 2H 2025.
AbelZeta – C-CAR168 Phase I (NCT06249438): At LUPUS 2025, AbelZeta C-CAR168 Phase I trial (NCT06249438) demonstrated robust CAR-T expansion, rapid depletion of B cells and plasma cells, and promising efficacy: all four lupus nephritis patients at 6 months met SRI (4), with two complete and one partial renal responses, most steroid-free, and one flare; a secondary progressive multiple sclerosis patient showed marked neurological and biomarker improvement. Across 10 treated patients (7 with lupus nephritis, 1 with Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (SPMS), 1 with Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD), and 1 with Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy (IMNM)), safety was favorable, with only low-grade CRS and no ICANS or severe infections.
“Emerging data support CAR-T therapy’s potential to reset immune homeostasis and provide durable disease control across multiple severe autoimmune indications.”
Contrasting Pathways: How CAR-T Differs in Autoimmune Diseases and Cancer
While CAR-T therapy originated in oncology to eliminate malignant cells, its application in autoimmune diseases represents a fundamental shift in therapeutic intent and mechanism. In cancer, CAR-Ts are engineered to seek and destroy tumor cells expressing a target antigen, aiming for cytotoxic eradication. In contrast, autoimmune-directed CAR-Ts focus on transiently depleting autoreactive B cells or immune drivers to “reset” immune tolerance rather than sustain long-term cell killing. CAR-T therapies play fundamentally different roles in cancer versus autoimmune diseases. Key contrasts are outlined in the “table below”.
| Key Differences Between CAR-T Applications in Autoimmunity vs. Cancer | ||
| Aspect | Cancer indications | Autoimmune Indications |
| Target and Goal | Tumor cells (eradication, long-term surveillance) | Autoreactive immune cells (immune reset, remission) |
| CAR-T Persistence | Desired long-term survival of CAR-T cells | Prefer controlled or transient activity |
| Safety Profile | High risk of CRS, neurotoxicity, off-target effects | Milder CRS, lower off-target risk (but still needs precision) |
| Clinical Evidence | Established with several FDA approvals | Early, promising results; ongoing trials |
| Manufacturing | Complex, autologous, expensive | Same constraints, but off-the-shelf and in vivo approaches are being explored |
This comparison underscores that, unlike oncology CAR-Ts, where long-term persistence is desirable, autoimmune CAR-Ts often benefit from controlled or transient activity to minimize off-target effects while achieving immune reset.
Momentum Shift: How Industry is Powering the Next CAR-T Revolution
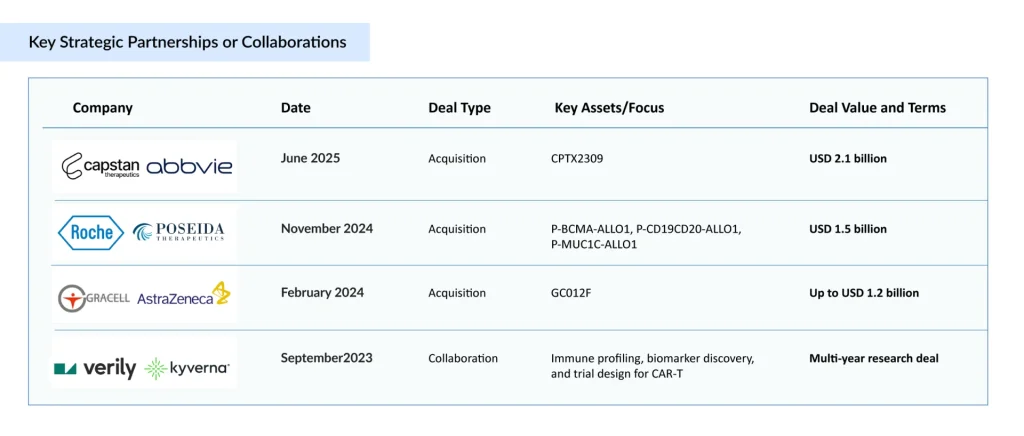
Alongside clinical development, major pharmaceutical companies are actively shaping the CAR-T landscape for autoimmune diseases through acquisitions and strategic collaborations. The “below table” highlights the key partnerships and deals driving innovation and expansion in this emerging field.
Conclusion
The trajectory of CAR-T in autoimmune diseases mirrors oncology’s early path: Rapid innovation, strong clinical signals, and accelerating investment. Unlike oncology, however, the goal is not indefinite surveillance but immune reset and drug-free remission. Early data from lupus, gMG, and MS trials validate this concept, suggesting CAR-T could deliver disease modification where traditional immunosuppressants fall short.If forthcoming mid- and late-stage trials confirm durability and safety, CAR-T therapies may emerge as the first curative-like interventions in autoimmunity, reshaping treatment paradigms and creating multi-billion-dollar opportunities across multiple indications. With Cabaletta and Cartesian spearheading the first wave and big pharma ensuring scalability and diversification, autoimmune CAR-T is poised to become one of the most significant breakthroughs in the next decade. For patients, this represents a shift from chronic symptom management to the possibility of true immune reset and lasting remission.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- 66 Year Ohio Woman Becomes Cancer Free, Thanks to CAR T Cell Therapy
- DelveInsight launches Indication Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Reports
- CAR-T cell therapy market for Non-Hodgkin lymphoma: Future prospects, and untapped opportunities
- New Lupus Nephritis Drugs on the Horizon: 6 Promising Therapies Eyeing Newly Approved GAZYVA’s Ma...
- KaliVir, Astellas licensing deal; AbCellera’s IPO; Bayer CAR-T Cell therapy collab with Ata...