Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Market: Treatments and Market Forecast
Nov 29, 2024
Table of Contents
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), in 2022, there were approximately 2.5 million new cases of lung cancer globally, which accounted for 12.4% of all newly diagnosed cancer cases. Lung cancer continues to be one of the most common and deadly malignancies worldwide, with significant contributions to global cancer morbidity and mortality rates.
The global burden of cancer is projected to increase significantly, with more than 35 million new cases anticipated by 2050. Lung cancer remains the most common cancer worldwide, being the leading cancer in men and the second most common in women. Recent estimates indicate that approximately 53.5 million people were alive within five years of being diagnosed with cancer. Globally, about 1 in 5 individuals develop cancer during their lifetime, with 1 in 9 men and 1 in 12 women succumbing to the disease.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- IMFINZI’s AEGEAN Phase III Trial Data for Treating Resectable NSCLC; Ipsen and Day One’s Exclusiv...
- Most Promising Oncological Drugs Expected to Launch in 2022
- Unveiling the Potential of TROP-2 Inhibitors: A New Frontier in Cancer Treatment
- Roche’s TECENTRIQ HYBREZA: Setting New Standards as the First Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Drug
- Assessment of Key Products that Got FDA Approval in Second Half (H2) of 2021
According to the Global Cancer Observatory (IARC), ten types of cancer accounted for around two-thirds of new cases and deaths globally in 2022, covering data from 185 countries across 36 cancer types.
How Common is Lung cancer?
According to Cancer.org, Lung cancer (both small cell and non-small cell) is the most commonly diagnosed and second most common cancer in both men and women. About 13% of all new cancers are lung cancers.
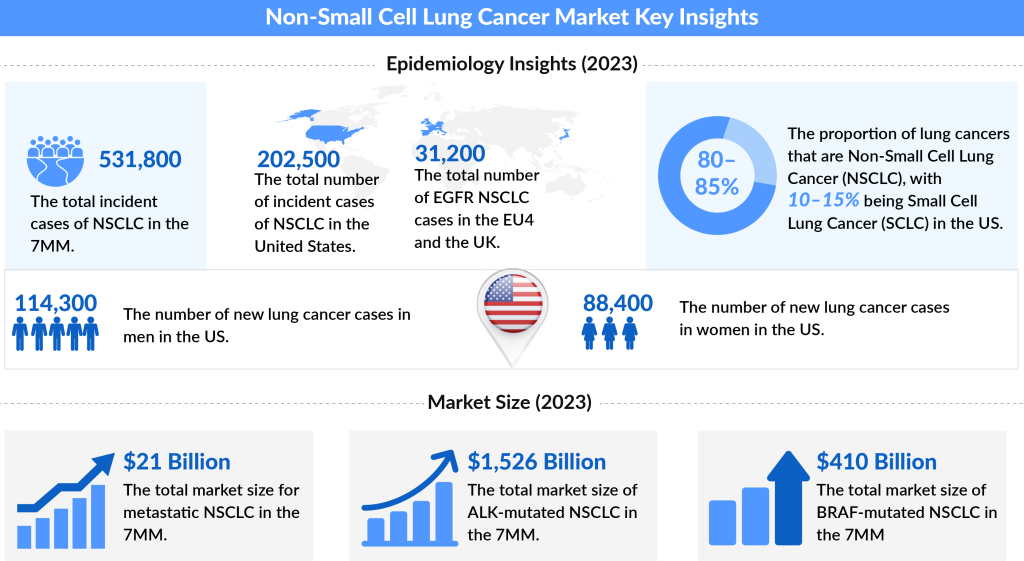
Around 80-85% of all cancers are Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The main subtypes of the NSCLC are adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
The age-adjusted Non-small cell lung cancer incidence is 47.2 per 100,000 individuals and is most frequently diagnosed among people between 65 and 74 years old (SEER), in the US.
According to the American Cancer Society estimates, the incidence of NSCLC in the United States in 2018 was about 234,030 new cases, of which 121,680 were men and 112,350 were women.
According to the WHO, if we talk about the incidence of the subtypes of NSCLC, squamous cell carcinoma accounts for 25–30% of cases of lung cancers, adenocarcinoma accounts for 40% of cases whereas large cell carcinoma accounts for 10–15%.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapeutics landscape
The Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment trends have shifted from molecular histologic subtype-based towards targeted therapies. The current treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, or some combination of these, depending on the type of cancer, stage of the disease, and overall health as well as the age of the patient.
Early diagnosis of the cancer is necessary as most stage I/II NSCLC can be surgically removed. Earlier, the NSCLC therapy market revolved around chemotherapy regimens.
The therapeutic efficacy of Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has significantly improved with the introduction of targeted therapies. In case of mutations, targeted therapies are the best option.
The targeted therapies include anti-angiogenesis therapy, epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitors, ALK inhibitors, an immune checkpoint inhibitor, and drugs that target other genetic changes.
Moreover, the cancerous cells are tested for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which, in excess, facilitates the faster growth of the cells. Drugs like Afatinib (Gilotrif), Gefitinib (Iressa), Erlotinib (Tarceva), Osimertinib (Tagrisso), Dacomitinib (Vizimpro), etc. block the EGFR signalling pathway helping in treating cancer.
Another cause of Non-small cell lung cancer is a rearrangement in a gene called ALK (Anaplastic lymphoma kinase). Drugs such as Crizotinib (Xalkori), Ceritinib (Zykadia), Alectinib (Alecensa), Brigatinib (Alunbrig), Lorlatinib (Lorbrena), and others target the mutated ALK protein, hampering cell division in excess.
If the mutation in the BRAF gene causes NSCLC, drugs such as Dabrafenib (Tafinlar) and Trametinib (Mekinist) are used to treat metastatic NSCLC.
Programmed cell death to beat cancer has brought a revolutionary transformation in the cancer treatment landscape. Immune checkpoint inhibitors, fundamentally those that act by blocking the programmed cell death receptor-1 (PD-1) and its ligand the programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1), have emerged as novel NSCLC treatment option, demonstrating undoubted superiority over chemotherapy in terms of efficacy. Several regulatory organizations globally have recognized immunotherapy as one of the viable options for Non-small cell lung cancer treatment. The available approved immune checkpoint modulators such as Pembrolizumab (Keytruda), Nivolumab (Opdivo), and Atezolizumab (Tecentriq) are recommended in first-line and second-line metastatic NSCLC.
IMFINZI (durvalumab) is approved for unresectable Stage III NSCLC and as maintenance after chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced disease.
To explore the full list of approved drugs in the NSCLC treatment market, click here.
Breakthroughs in NSCLC: Advancing Targeted Therapies and Precision Medicine
Recent advancements in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treatment emphasize significant progress in targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and precision medicine. Highlights from 2024 include breakthroughs in clinical trials such as osimertinib (LAURA study), demonstrating remarkable progression-free survival in EGFR-mutant NSCLC, and lorlatinib (CROWN trial), showing superior efficacy for ALK-positive cases, particularly in managing brain metastases. Novel approaches like datopotamab deruxtecan, ivonescimab, and tumor-targeting fields (TTFields) therapy gained momentum with promising clinical results and regulatory approvals. Emerging therapies targeting biomarkers such as PD-L1, EGFR, and KRAS have reshaped treatment paradigms, while advances in artificial intelligence and big data analytics promise enhanced diagnostics and personalized care. With a robust pipeline of innovative treatments and collaborations, the NSCLC treatment landscape is poised for significant growth and improved patient outcomes.
Key Advancements in EGFR-Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment
EGFR-Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer mutations are one of the most common genetic alterations. These mutations are critical in determining treatment approaches, as EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) have been a standard therapy. However, resistance to these treatments, particularly from mutations like T790M and exon 20 insertions, poses significant challenges. Emerging therapies, including third-generation TKIs, antibody-drug conjugates, and novel agents like Telisotuzumab Vedotin, are showing promise in overcoming resistance mechanisms. Companies like AstraZeneca, AbbVie, and Dizal Pharmaceuticals are at the forefront of this therapeutic evolution, aiming to address unmet needs and improve survival rates for EGFR-mutant NSCLC patients.
For a deeper dive into the EGFR-Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Market, click on our latest blog curated specifically for this topic!
Companies investing in advancing Non-small cell lung cancer Market
Key pharma companies involved in propelling the Non-small cell lung cancer therapy market and trying to dominate the significant major NSCLC market share are:

Advancing Treatments for Rare Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
The evolving landscape of rare biomarkers in NSCLC, including METex14 skipping alterations, ALK rearrangements, and HER-2 mutations, has ushered in transformative advancements in diagnostics and therapies. FDA-approved drugs like TEPMETKO (Tepotinib) and Capmatinib (Tabrecta) now provide targeted treatments for METex14 skipping, significantly improving response rates and survival outcomes in previously under-served patient populations. Emerging therapies such as APL-101 and vebreltinib further promise innovative options, addressing treatment resistance and enhancing clinical efficacy. Despite challenges in cost-effectiveness, these advancements highlight the critical role of personalized medicine in offering better quality of life and survival outcomes for patients with rare genetic alterations in NSCLC.
To learn more about the advancements in rare biomarkers for NSCLC and how they are transforming treatment options, check out our latest blog prepared exclusively on this topic. Click here!
Non-small cell lung cancer Pipeline
The current research is looking toward the employment of effective therapies, such as targeted therapies, personalized therapies, and Immunotherapy. Targets currently being used or investigated in the treatment of NSCLC include the human epidermal growth factor (HER) family of receptors, EGFR, KRAS, ALK, PI3K/AKT/mTOR, IGF-1R, MET, ROS, Monoclonal antibodies, T-cell therapies, immune checkpoint inhibitors, etc.
Drugs, such as Zipalertinib, YK-029A, TAS3351, NVL-330, JS-113, JANX-008, IN-119873, and others are being developed as the highly effective Non-small cell lung cancer therapies.
The launch of these emerging NSCLC therapies is expected to significantly impact Non-small Cell Lung Cancer treatment scenario in the coming years, 2020-2034.
Advancing NSCLC Care: Tackling the Global Healthcare Burden Through Precision Medicine and Early Detection
NSCLC remains a significant global health burden due to its late-stage diagnoses, high treatment costs, and limited access to advanced therapies in many regions.
Despite substantial advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies, disparities in care and affordability hinder widespread benefits. Addressing this burden requires a multifaceted approach, including the expansion of healthcare infrastructure, greater awareness campaigns, and a stronger emphasis on early detection through improved screening programs.
Personalized medicine and the development of cost-effective treatment options are pivotal in reducing mortality rates and enhancing the quality of life for NSCLC patients worldwide.
To learn more about how innovative therapies are reshaping the fight against the global burden of NSCLC, click here.
Non-small cell lung cancer Market forecast
The Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer market has undergone a transformative shift over the past decade, driven by several key factors. The rise in the number of NSCLC cases, combined with the increasing adoption of approved therapies, especially immune checkpoint inhibitors, has significantly contributed to market expansion.
Furthermore, the growing awareness of genetic mutations such as KRAS, BRAF, and c-Met, along with advancements in mutation analysis, has played a pivotal role in guiding treatment decisions and facilitating the development of molecularly targeted therapies.
The market is also expected to benefit from the anticipated entry of emerging, premium-priced therapies. For EGFR-positive NSCLC, third-generation EGFR inhibitors, such as AstraZeneca’s TAGRISSO, are projected to dominate. Other promising therapies include AbbVie’s Telisotuzumab Vedotin and the joint collaboration between AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo, which has led to the development of Datopotamab Deruxtecan—both of which have the potential to create a substantial impact on the market.
By the end of 2024, the Non-small cell lung cancer market size in the United States is projected to reach approximately USD 12,600 million, with key therapeutic areas, including PD-L1, EGFR, ALK, and KRAS, contributing significantly to market growth. These advances, along with the launch of new therapies, are expected to drive continued growth in the NSCLC market throughout the forecast period of 2020-2034.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Reblozyl under FDA review; Audentes buyout & Tecentriq’s new approval
- Boston Scientific Pushes Forward Despite $200M Tariff Challenge; Northstrive Biosciences Gets FDA...
- Roche’s TECENTRIQ HYBREZA: Setting New Standards as the First Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Drug
- X4 Pharmaceuticals’ XOLREMDI FDA Approval; ONO to Acquire Deciphera Pharmaceuticals; Johnson &...
- CDK 4/6 Inhibitors- The Changing Paradigm for Breast Cancer Treatment