CAR-T Cell Therapy aka Miraculous Technology: Mapping the Market, Approved Therapies, Competitive Landscape and Impact of COVID-19
Dec 13, 2021
Table of Contents
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T) therapies are shown to have transformative potential as a new type of cancer treatment that utilizes the immune system to fight the disease. It involves the process where genetically engineered T cells (patient/donor) express a chimeric antigen receptor to target a specific tumor antigen. Although a major groundbreaking invention in the field of cancer treatment, CAR-T Cell Therapy’s application is limited to treating patients with select liquid tumors only in the refractory and relapsed stage and these combine only for 5% of the total cancer patients today. There are necessary areas where research & development are still lacking such as optimizing autologous CAR-Ts for liquid tumors, expanding the number of healthcare settings that administer CAR-T, shortening the innovation cycle time to enable success in solid tumors, and innovating in the manufacturing of next-generation CAR T-cell therapies. There are a total of 5 approved CAR T-cell therapies by the FDA and among those, 3 have also been approved by the EMA. Due to a lack of therapies, investment is required in the above-mentioned categories in order to unlock the potentiality of CAR T-cell therapies.
The pipeline of investigative CAR T-cell therapies has rapidly expanded with almost a thousand clinical trials underway in 2021. The earliest CAR T-cell therapy studies targeted the CD19 antigen whereas the ongoing clinical programs now target a wider range of molecules/antigens and include various tumor types. The tide that is carrying the market of the growing industry such as the CAR T-cell therapy is the availability of immense clinical data, for instance, pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed or refractory ALL achieved an overall remission rate of 90 percent at 12 months with treatment with an anti-CD19 autologous CAR T therapy.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Cancer Diagnostic Market: Evaluating the Major Growth Factors and the Key Developments in the Domain
- Abeona Secures FDA Nod for ZEVASKYN, the First Gene Therapy for RDEB; AbbVie Gains FDA Approval f...
- Evaluating Key Advancements and Emerging Therapies in EGFR-Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment M...
- The Business Cocktail
- Colorectal Cancer Awareness Month
CAR-T Cell Therapy Market & Driving Factors
Among the total market share of the overall T-cell therapy market, the CAR T-cell therapy market accounts for the maximum market share. The cause of the rising market for CAR T-cell therapy lies on the factors including an increasing prevalence of cancer which is expected to drive the production of CAR T-cells for use in therapeutic areas. Also, the possibility of artificial T-cell receptors application for the treatment of a wide variety of cancers has been widely acknowledged. This process also increases the usage of chimeric immunoreceptors as they assist T-cells in finding and killing cancer cells that have the specific protein to which receptors can bind.
Continuous growth is observed in research & development in the life science and biotechnology sectors for the treatment of cancer using chimeric antigen receptors. There are extensive studies going on to validate the CAR T-cell therapy effectiveness and efficiency, mechanism of action, compliance in patients suffering from leukemia and lymphoma to CAR T-cell therapy in several countries.
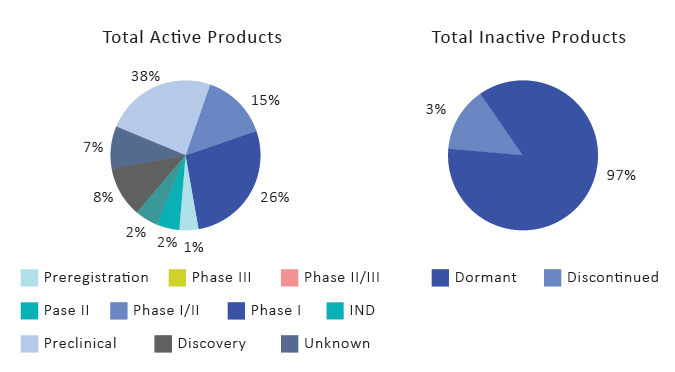
Increased Revenue and Opportunities for Market Players in CAR T-Cell Therapy Domain
CAR T-cell therapy is a treatment process where T-cells are taken from the blood of the patient and then modified by adding a gene for a man-made receptor (chimeric antigen receptor). This helps in the recognition of some specific cancer cell antigens in a better way. Afterward, those CAR T-cells are given back to the patient. Different types of cancers have different types of antigens, and that is the main reason why each CAR T-cell is prepared in a different way for specific cancer antigens. The substantial and wide array of research and development gives significant opportunities to manufacturers to generate great revenue and invest in CAR T-cell therapy for targeting cancer cells.
Increased attention on research & development therapies for the treatment of various cancers such as lung, prostate, colorectal, and others is very likely to give rise to considerable growth opportunities for CAR T-cell therapy providers. Also, mergers and acquisitions play a significant role in accelerating a manufacturer’s strategy to capitalize and capture a significant share in the market. Then there are favorable government policies and fundings for pharmaceutical, life science companies which are anticipated to boost CAR T-cell therapy demand in the near future. Many key players who are proactively working in the CAR T-cell therapy market to continuously create new therapies include names like Bluebird Bio, Gilead Sciences Inc, Celgene Corporation, Pfizer Inc, Sensei Biotherapeutics, Amgen Inc, Novartis International AG, Helix BioPharma, Bellicum Pharmaceuticals Inc, Juventas Cell Therapy, Johnson & Johnson, Sangamo Therapeutics Inc, REGENERON, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, Takeda, among many others.

The demand for novel cancer treatment options is further expected to proffer major revenue generation opportunities to participants in the chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy market.
Approved CAR T-cell Therapies by the USFDA
Till date the FDA has approved the following five CAR T-cell therapies:
Abecma (idecabtagene vicleucel)
Abecma by Celgene Corporation, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company is a CAR T-cell therapy used to target refractory/relapsed Multiple Myeloma (MM) in adult patients who have earlier dealt with at least four more lines of therapy including an immunomodulatory agent, a proteasome inhibitor, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody. It is based on a therapy namely – B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed genetically modified autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
In every IV administered dose, a new gene is introduced specifically to target and kill Myeloma cells into the patient’s own genetically modified T-cells (WBCs). The safety and efficacy for the drug were reported in clinical trials of around 127 patients with refractory/relapsed Myeloma, where around 72% of people responded to the treatment either completely or partially. In March 2021, Abecma was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of multiple myeloma.
Breyanzi (lisocabtagene maraleucel)
Breyanzi– a CAR T-cell therapy manufactured by Juno Therapeutics, Inc., a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company isanother drug manufactured by the same parent company for the treatment of relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma in adult patients. The patients must have earlier gone through two or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), high-grade B-cell lymphoma, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, and follicular lymphoma grade 3B. The safety and efficacy of the drug were reported in clinical trials of around 250 adult patients with refractory/relapsed large B-cell lymphoma.After treatment, it was observed that the complete remission rate was 54%. An IV administered dosage of lisocabtagene maraleucel is targeted to induce selective toxicity in CD19-expressing tumor cells. It has become the 3rd gene therapy to be approved by the FDA for specific types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. It came under medicinal use in February 2021.
Yescarta (axicabtagene ciloleucel)
Yescarta is another CAR T-cell therapy by Kite Pharma Inc. for treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma after two or more lines of systemic therapy, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) not otherwise specified, primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma, high-grade B-cell lymphoma, and DLBCL arising from follicular lymphoma. Axicabtagene ciloleucel is not indicated for the treatment of patients with primary central nervous system lymphoma. On March 5, 2021, Yescarta was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Tecartus (brexucabtagene autoleucel)
Tecartus manufactured by Kite Pharma, Inc. is a CAR T-cell therapy which is used in adult patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). Following FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation and a priority review, Tecartus is the first chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy approved for adults (18 years and older) with ALL. Tecartus is an autologous, anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy that uses the XLP™ manufacturing process that includes T cell enrichment, a necessary step in certain B-cell malignancies in which circulating lymphoblasts are a common feature. On July 24, 2020, Tecartus was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Kymriah (tisagenlecleucel)
Kymirah by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation is a CAR T-cell therapy used for the treatment of pediatric and young adult patients (age 3-25 years) with B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) that is refractory or in second or later relapse. On August 30, 2017, Kymriah was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Kymriah was also the first CAR-T cell therapy ever approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
EMA has approved three therapies among the above-mentioned – Kymriah, Tecartus, Yescarta. By cancer type, they are approved to treat Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), B-cell lymphoma, Follicular lymphoma (FL), Mantle cell lymphoma and Multiple myeloma.
Competitive Landscape of CAR T-cell Therapies
Companies providing CAR T-cell therapy are vigorously seeking to strengthen their position through collaborations, approvals, acquisitions, and agreements with established as well as emerging market players. It can be seen that the business scenario of the market is dynamic and major companies are competing with each other to increase their market share in the major geographies of the US and Europe.
Along with opening new centers and acquiring necessary government approvals, landmark approval by regulatory bodies worldwide, the companies are also focusing on partnerships, acquisitions, and mergers within the CAR-T industry. There is an increasingly competitive IP environment and unprecedented investment flowing into CAR-T cell research and development which can prove to be immensely beneficial for CAR T-cell therapy market players.
- Celgene acquired Juno Therapeutics in November 2018 and further Bristol-Myers Squibb completed acquired Celgene in November 2019.
- A Japanese government panel in May 2019, approved Novartis to sell Kymriah in Japan in order to treat the young population with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and adult population with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
- Gilead Science acquired Kite Pharma Inc. In August 2017, Kite had developed 2 FDA-approved CAR T-cell therapies, both the companies were considered pioneers in their respective fields.
- Gilead Science also acquired Cell Design Labs Inc in December 2017. This acquisition was done to benefit Gilead for attaining new technology platforms that can enhance research & development efforts in cellular therapy.
Impact of COVID-19 and the Future of CAR T-cell Therapies
The COVID-19 pandemic has brought up with it the lockdown restrictions that caused obstruction in the supply chain and left business operations discontinued due to which many biopharma and life science companies are waiting for the availability of new batches of raw material for CAR T-cell production. The lockdown impact has hampered biopharmaceutical production activities as there was a shortage of manpower, restraining the growth of the end-user segment market.

But fortunately, the impact of lockdown is short-term, and very stable & steady growth is expected as per DelveInsight analysis in the upcoming years as soon as the situation gets back to normal. The field of immuno-oncology is one of a kind booming with millions of dollars of investment. CAR T-cell therapy has the ability to rewire the immune system and make it fight cancer, which is why this therapy is proven to be very hopeful and has created huge expectations. With over 500 current clinical trials, many key pharmaceuticals are keen on developing various CAR T-cell therapies for the treatment of cancer.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- HPK1 Inhibitors: A Promising Frontier in Immuno-Oncology Therapeutics
- Oncolytic Viruses: Can Be The Next Frontier in Cancer Immunotherapy?
- Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 Market Forecast & Insights
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Software as a Medical Device (SaMD)
- AI-Driven Diagnostics: Why are They the Next Big Thing in Healthcare?




