A New Era for Multiple Myeloma Treatment: Bispecific Antibodies Enter the Fray
Jun 10, 2025
Table of Contents
Step aside, CAR-Ts; with three FDA approvals, the class of bispecific antibodies has begun to take on the relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treatment segment.
Currently, the FDA has authorized 10 bispecific antibodies and one bispecific molecule, the majority of which are approved for oncology indications, primarily hematological malignancies, including multiple myeloma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Only two bispecific antibodies, HEMLIBRA and VABYSMO, are authorized for non-oncology indications such as hemophilia A, neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration, and diabetic macular edema, respectively. The FDA authorized three bispecific antibodies (VABYSMO, TECVAYLI, and LUNSUMIO) and one bispecific molecule (KIMMTRAK) in 2022.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Syndax Pharmaceuticals Receives FDA Approval for REVUFORJ; FDA Approves BLENREP for Adults with R...
- BeiGene’s BRUKINSA Gets FDA Accelerated Approval; GSK’s Positive Results in DREAMM-8 ...
- Amgen’s Olpasiran Candidate; GSK’s Novel Antibiotic for Urinary Tract Infections; AstraZeneca and...
- Eli Lilly’s Jaypirca Approval; Novartis’ Adakveo EMA Review; Janssen’s CARTITUDE-4 Study of CARVY...
- Transforming Multiple Myeloma Treatment: The Promise of Novel Drug Classes
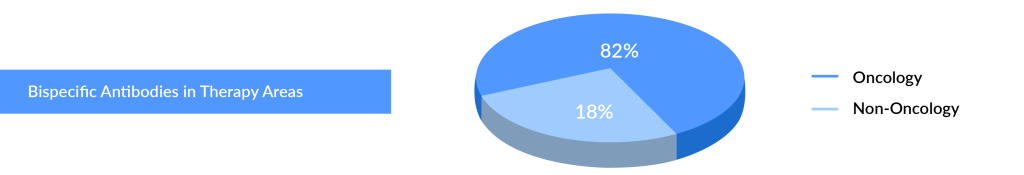
The multiple myeloma treatment market is rapidly evolving, and current and emerging key players face significant risk due to this high degree of innovation. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), CAR-T cell treatments, and bispecific antibodies are just a few of the novel modes of action that have recently entered the market for later lines of therapy. The bispecific antibodies market, in particular, is anticipated to evolve in the coming years, with multiple companies entering the multiple myeloma treatment space with their products. Johnson & Johnson (J&J) dominates this field by adding two bispecific antibodies approved in the bispecific antibodies market. TECVAYLI (teclistamab) became the first bispecific antibody to receive regulatory approval for treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) in 2022 in the United States and Europe. Later in 2023, TALVEY (talquetamab) and ELREXFIO (elranatamab) were approved for RRMM.
What is new in the field of bispecific antibodies for multiple myeloma treatment in 2023?
Several multispecific antibodies under development are also making progress. Bispecific antibodies have seen significant progress for hematological oncology indications in the last few years, especially in 2022 and 2023. In August 2023, the FDA approved four bispecific antibodies for indications like DLBCL and Multiple Myeloma. Some recent developments in the field of bispecific antibodies for multiple myeloma are:
- In November 2024, Nanjing Leads Biolabs Co., Ltd. announced that LBL-034, a humanized bispecific T-cell engaging antibody targeting GPRC5D and CD3 for multiple myeloma, has received Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) from the FDA.
- At the EHA Congress in Madrid held in June 2024, Regeneron showcased linvoseltamab’s promising Phase I/II results for multiple myeloma. This BCMA and CD3-targeting bispecific antibody, developed with VelociGene and VelocImmune, demonstrated potential in treating the disease.
- On 10 August 2023, J&J received FDA approval for its second bispecific antibody TALVEY (talquetamab), for treating RRMM, who have received at least four prior lines of therapy.
- In August 2023, the US FDA approved a third bispecific antibody ELREXFIO (elranatamab), for treating RRMM who have received at least four prior lines of therapy.
- In August 2023, J&J received approval from the European Commission (EC) for TECVAYLI, providing the option for a reduced dosing frequency of 1.5mg/kg every two weeks in patients who have achieved a complete response (CR) or better for a minimum of six months.
- Based on the Phase II results of linvoseltamab, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals plans to submit a Biologics License Application (BLA) to the FDA in the second half of 2023 in RRMM.

What is the main target of bispecific and CAR-T cell therapies?
According to DelveInsight’s pipeline analysis of multiple myeloma, B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) is the primary target for bispecific and CAR-T cell therapies. Most approved and investigational medicines of the above-mentioned technologies target a protein known as BCMA. With several FDA-approved therapies, BCMA has emerged as a hot target in multiple myeloma. BCMA is frequently expressed on the surface of the malignant plasma cells that characterize this cancer type, which is key to its potential in multiple myeloma therapy.
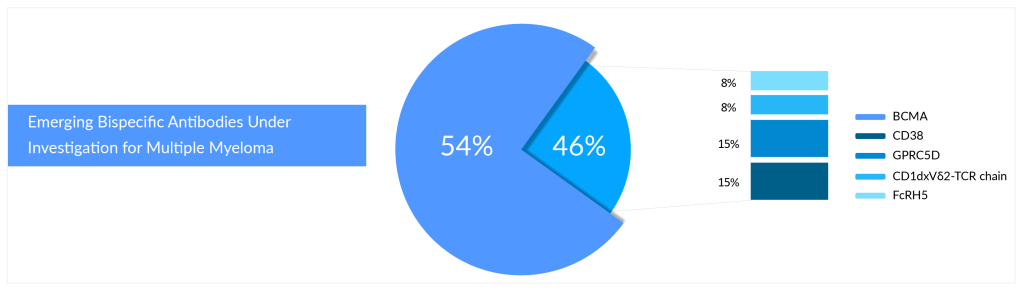
Who Will Win the Battle of Bispecifics in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma?
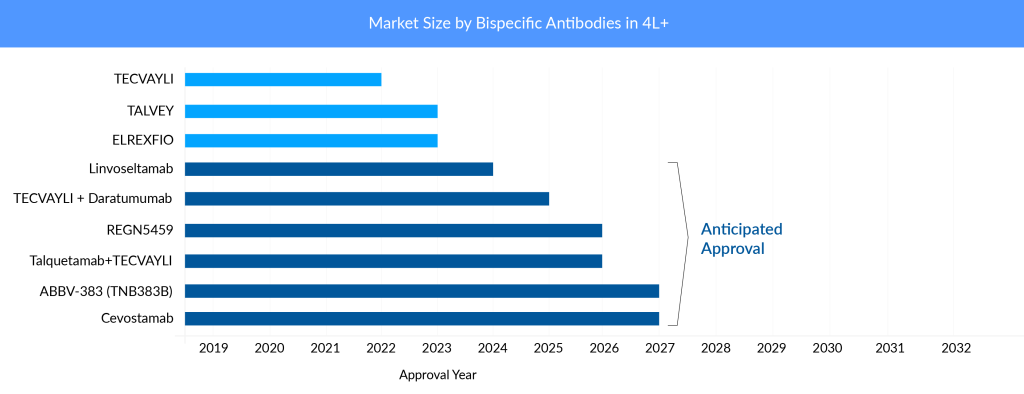
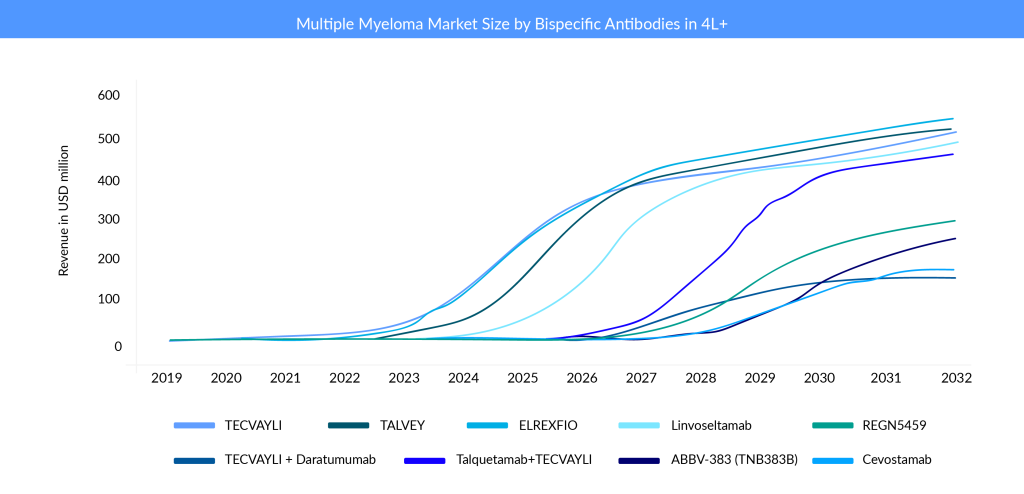
Johnson & Johnson’s (J&J) TECVAYLI (BCMA × CD3) is the first bispecific antibody to be approved for multiple myeloma treatment. It targets BCMA, a protein that is highly expressed in myeloma cells, and CD3, a protein that is essential for T-cell activation. TECVAYLI is J&J’s fourth approved therapy for multiple myeloma treatment, adding to the company’s industry-leading oncology portfolio. TECVAYLI is a ready-to-use therapy that does not require customization for each patient. In a Phase II trial involving 110 patients who had received a median of five prior lines of therapy, TECVAYLI achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 61.8%, with 28.2% of patients reaching a complete response (CR) or better.
he MajesTEC-1 study revealed that, with a median follow-up of 30.4 months, patients treated with TECVAYLI at the recommended Phase II dose (RP2D) showed an overall response rate (ORR) of 63%. Notably, 46% of these patients achieved a complete response (CR) or better, with responses continuing to improve.
“Over the past two years, TECVAYLI has treated over 10,000 patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma,” said Rachel Kobos, M.D., VP of Oncology R&D at Johnson & Johnson. “With strong clinical and real-world data, we’re committed to meeting unmet needs in myeloma and advancing new treatments, including for frontline use.”
In February 2024, the FDA approved a supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for TECVAYLI, allowing a reduced dose of 1.5 mg/kg every two weeks for relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients in sustained complete response (CR) for at least six months.
Pfizer’s ELREXFIO is currently a main competitor of J&J’s TECVAYLI. ELREXFIO (elranatamab) is the second BCMA × CD3 bispecific antibody approved for RRMM in 2023. ELREXFIO is similar to TECVAYLI in its mechanism of action, but it has a different structure and dosing regimen. In the Phase I/II trial involving 149 patients who had received a median of six prior lines of therapy, ELREXFIO achieved an ORR of 61%, with 19% of patients reaching a CR or better. ELREXFIO faces direct competition from TECVAYLI as well as from other bispecific antibodies in development that target BCMA and CD3, such as Linvoseltamab and REGN5459 by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, and ABBV-383 (TNB383B) by AbbVie.
In June 2024, the MagnetisMM-3 trial data showed that after over two years of follow-up, patients receiving ELREXFIO achieved an overall response rate (ORR) of 61.0%, with 37.4% reaching a complete response (CR). Responses continued to improve over time, and the median duration of response (DOR) was not yet reached. At two years, the estimated DOR rate was 66.9% for all responders and 87.9% for those with a CR or better. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 17.2 months, with a PFS rate of 90.6% at two years for patients with a CR or better response.
So far, findings from BCMA × CD3-directed bispecific antibodies are comparable, although ELREXFIO appears to have a convenience advantage. The ability of ELREXFIO to be dosed every other week after 24 weeks of weekly therapy has given it an advantage over TECVAYLI. J&J’s TECVAYLI is currently being administered weekly throughout the maintenance period. However, J&J has filed additional data to make TECVAYLI a biweekly therapy as well.
TALVEY (GPRC5D × CD3) is another bispecific antibody from J&J’s portfolio that was approved for RRMM. It targets G protein-coupled receptor family C group 5 member D (GPRC5D), a new protein that is also highly expressed in myeloma cells, and CD3. TALVEY became J&J’s fifth novel medicine and second bispecific antibody authorized for treating multiple myeloma. In Phase I/II trial involving 184 patients who had received a median of six prior lines of therapy, TALVEY achieved an ORR of 73%, with 25% of patients reaching a CR or better. J&J is also testing a combination of TALVEY and TECVAYLI in RRMM patients. The combination showed early signs of efficacy and safety in a Phase I trial. The launch price of BCMA × CD3-directed bispecific antibodies are comparable. However, TALVEY’s per-month charge of USD 45,000 is greater than TECVAYLI’s price of USD 39,500.
In a recent MonumenTAL-1 study, Talvey showed an ORR of over 71% in RRMM patients, many of whom were refractory to five previous treatments. While response duration is still being assessed, Talvey is noted for enhancing patients’ quality of life.
In September 2024, the RedirecTT-1 Phase Ib study (NCT04586426) reported that TALVEY combined with TECVAYLI achieved durable responses in patients with triple-class-exposed relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Findings were presented at the 21st Annual International Myeloma Society Meeting.
Another bispecific antibody from Regeneron Pharmaceuticals is set to join the multiple myeloma foray. Regeneron’ Linvoseltamab could become the third bispecific antibody to receive FDA approval that targets BCMA and CD3. In a Phase II trial involving 121 patients who had received a median of five prior lines of therapy, linvoseltamab achieved an ORR of 64% in the 200 mg dose group and 50% in the 50 mg dose group. Linvoseltamab is being studied in a broad clinical program as both monotherapy and in combination across various treatment lines in multiple myeloma, including earlier-stage disease and plasma cell precursor disorders. Ongoing trials include the Phase Ib LINKER-MM2 study evaluating combination regimens in relapsed/refractory MM and the Phase III LINKER-MM3 confirmatory trial assessing linvoseltamab as monotherapy in the same setting.
In February 2025, Regeneron announced that the FDA accepted the resubmitted Biologics License Application (BLA) for linvoseltamab to treat adults with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (MM) who have undergone at least four prior therapies or three prior therapies and are refractory to the last. The FDA’s target action date is July 10, 2025.
The resubmission follows the resolution of third-party manufacturing issues, the only approvability concern in the previous submission. Supported by data from the pivotal LINKER-MM1 trial, linvoseltamab is also under review by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) for the same indication.
REGN5459 is another bispecific antibody by Regeneron Pharmaceuticals that targets BCMA and CD3. It is still in Phase I/II development and has shown impressive results in efficacy and safety. In a study involving 43 patients who had received a median of seven prior lines of therapy, REGN5459 achieved an ORR of 65.1%, with 61.9% of patients reaching a CR or better among the 21 patients treated at the higher doses (480 mg and 900 mg). However, the primary completion date of the trial is by November 2025, and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals seems to focus more on linvoseltamab.
ABBV-383 (TNB383B) is another bispecific antibody that targets BCMA and CD3. AbbVie is developing it in collaboration with Teneobio. In June 2024, AbbVie announced the first patient dosing in the Phase III CERVINO study of ABBV-383, a bispecific BCMA-CD3 T-cell engager with high BCMA avidity and low-affinity CD3 binding. The trial evaluates ABBV-383 against standard therapies in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients who have received at least two prior treatments. Dr. Peter Voorhees, clinical professor of medicine and director of plasma cell disorders at Atrium Health Levine Cancer Institute, stated, “The CERVINO Phase III trial is designed to evaluate the efficacy of ABBV-383 with monthly dosing, and we look forward to seeing the data as it emerges.”
Cevostamab is a bispecific antibody that targets FcRH5, a protein related to BCMA but with lower expression on normal B cells and CD3. Developed by Roche, cevostamab is still in Phase I/II development and is being evaluated for its potential in treating relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM).
The CAMMA-2 Phase I/II study (NCT05535244) is assessing the efficacy and safety of cevostamab in patients with RRMM who are triple-class refractory and have previously received a BCMA-targeted therapy. Initial results from Cohort A1 of the trial were presented at EHA 2024.
At the data cut-off, with a median follow-up of 11 months, 6 out of 14 responders remained in response. The overall response rate (ORR) was 67%, with the prior ADC group achieving an ORR of 60% and a very good partial response or better (≥VGPR) in 20% of patients. In the prior CAR T-cell group, the ORR reached 73%, with 55% achieving ≥VGPR. These promising results highlight cevostamab’s potential as a novel therapy for patients previously treated with BCMA-targeted approaches.
Cevostamab has the lowest ORR among all the bispecific antibodies, and Roche has not announced any anticipated BLA filing plans for this multiple myeloma therapy.
Dr. Richter presented data from the ongoing CAMMA-2 trial at EHA 2024, focusing on relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma patients who have progressed despite BCMA-based therapies. These patients may have previously received treatments like teclistamab (Tecvayli), belantamab-mafodotin (Blenrep), or CAR T-cell therapies such as ide-cel (Abecma) and cilta-cel (Carvykti).
The trial is still recruiting, but if successful, cevostamab could be approved as a monotherapy for BCMA-exposed myeloma patients, offering a new treatment option.
Companies are trying to get to early lines of treatment settings now that the FDA has approved bispecific antibodies in later lines. However, it is too early to predict patient outcomes and performance. The bispecific antibody market is projected to grow overcrowded as a result of many approvals and intensive pipeline activity. The competition between drugs with similar targets will be fierce. For example, there are many BCMA-targeting drugs on the market, two CAR-T cell therapies, and two bispecific antibodies, and some are expected to receive regulatory approval by next year in a later line. Moving into the early lines of setup would be the ideal plan for key pharma players. J&J and Pfizer are working extensively to broaden the label of their respective bispecific antibodies since both companies are conducting clinical trials in an array of settings with and without combination.
Are bispecific antibodies better than CAR-Ts?
Both CAR T-cell therapy and bispecific treatment are gaining popularity. Both drugs have induced profound and long-lasting responses in R/R patients, which has never been seen previously. The question is, which is better for patients, CAR T-cell therapy or bispecific therapy? Both therapies have advantages and disadvantages. CAR T-cell therapy is a “one-and-done” therapy, whereas bispecific therapies are not. Bispecific antibodies require ongoing treatment. CAR-T therapies have shown remarkable efficacy in multiple myeloma, but they also have some drawbacks, such as the risk of cytokine release syndrome (CRS), a potentially life-threatening inflammatory reaction. CRS can also occur with bispecific antibodies but is usually less severe than CAR-T therapies.
Regarding safety, none of the bispecific antibodies exhibit unusual neurotoxicity, which is a major advantage for bispecific antibodies over CAR-T cell therapies for multiple myeloma. In terms of safety, bispecific antibodies are a clear winner, and owing to the high-grade CRS, high-grade neurotoxicity, and Grade 3 or higher of BCMA-directed CAR T-cell therapies, bispecific antibodies are likely to be preferred by oncology experts. Another challenge for CAR-T therapies is the cost, convenience, and time required to produce them, as each patient needs a personalized product. Bispecific antibodies, on the other hand, are ready-made (off-the-shelf) and can be administered more easily, which is a major advantage. Another key issue with CAR-T is market access. The cost and access aspects are where bispecific antibodies can truly make a difference. Bispecific antibodies may also be more suitable for older patients or those with other health problems who cannot receive CAR-T therapies. Like CAR-T cell therapies, bispecific antibodies are increasingly making their way to the front lines.
It may be possible to combine CAR-T therapies and bispecific antibodies to target different proteins in myeloma cells and achieve a cure for this disease.
Summary
To summarize, bispecific antibodies are emerging as a new class of therapies, and J&J is leading the multiple myeloma treatment market with two approved bispecific antibodies, TECVAYLI and TALVEY, which target BCMA and CD3, and GPRC5D and CD3, respectively. Pfizer has also entered the multiple myeloma treatment market with ELREXFIO, another bispecific antibody that targets BCMA and CD3. J&J has better experience and a competitive advantage in the multiple myeloma treatment space. DARZALEX from J&J is the top CD38 antibody with regulatory approval across all therapy lines. To cut a long story short, following the success of monoclonal antibodies and CAR-T, many researchers believe bispecific antibodies can change the treatment landscape of multiple myeloma and will represent a new dimension of precision treatment.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Novartis’ Canakinumab for NSCLC; Novartis’s Zolgensma Updates; Trodelvy Prospects in New Breast C...
- BMS Vs. Janssen: Which Company Will Dominate The Multiple Myeloma Treatment Market This Decade?
- FDA Approves BMS’s Reblozyl for MDS; FDA Awards Orphan Drug Designation to NXC-201; Janssen Submi...
- AZ offloads; Pfizer’s deal; Takeda’s work on plant; Germany’s doc payment
- Bispecific and Trispecific Antibodies: Are They Better Than CAR-Ts?




