Table of Contents
Neurological disorders are one of the major causes of death and disability across the globe. As per the figures published in The Lancet journal for the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2016, neurological disorders accounted for DALYs, which were 276 million. The mortality and morbidity rates due to neurological disorders are increasing at a swift rate throughout the world. Furthermore, neuropsychiatric disorders also form a large subset of the population who require effective treatment as many times, treatment for these indications is also palliative or is followed by relapses.
Even with the mounting prevalence, there lies a huge gap between the medical needs of the patients and available treatment with no cure at hand. The neurological disorders market has witnessed several late-stage clinical trial failures with an increasing number of pharma and biotech companies opting out and disinvesting in their brain disorders therapeutic trials.
However, not all the companies are opting out, some are taking a different route to reach the destination. Leveraging the use of technology, MedTech players are exploring several non-invasive and invasive technologies to modulate the neurons renewing the focused area in the treatment of the neurological disorder. Neuromodulation allows a convenient alteration of disease symptoms without adding the risks of side effects. Decades of research have found that neuromodulation has managed to outweigh the benefits provided by the medications, heralding it as the potential future treatment for Neurological disorders. It has long been investigated to treat neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, and dystonia; however, recent years witnessed its use to target other neurological disorders including epilepsy.
Brain stimulation has two major approaches: deep brain stimulation and transcranial stimulation. In deep brain stimulation, stimulation electrodes are placed in deep brain structures via a surgical procedure that is aimed at treating various neurological conditions such as Tourette syndrome or Morbus Parkinson. Deep brain stimulation can be compared to the working of a heart pacemaker. It is an invasive technique.
The other type of brain stimulation is transcranial stimulation. It is a non-invasive technique and makes use of weak electric currents (1 mA or 2 mA). Being noninvasive, the stimulation electrodes are placed on the skull and the activity of cortical neurons is modulated by influencing membrane excitability. Transcranial stimulation is further bifurcated into two subtypes- transcranial electric stimulation and transcranial magnetic stimulation. The focus of the article is on transcranial stimulation.
Transcranial Stimulation
Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique in which electric current is passed through the brain cortex to alter brain function. The application of the electric current on an individual’s scalp is done by the placement of two or more electrodes through which the current flows and penetrates the scalp and enters the brain where it causes changes in neuronal excitability. Researchers are actively studying the relationship between transcranial electrical stimulation and behavioral changes. tES can be carried out via a number of different techniques, namely transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS), transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), and transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS). Even though these techniques share a common pattern of electrode placement on the scalp, they differ in the generation of electrical stimulation patterns, hence differing in neuronal and behavioral outcomes.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS)
tDCS is a wearable, portable simulation technique, which is used for the delivery of electric current of low intensity to the scalp. Weak direct currents in the range of (0.5-2.0 mA) are delivered through the saline-soaked electrodes to the targeted cortical area of the brain. tDCS has two polarities- anodal and cathodal. Anodal tDCS aids in cortical excitability while the cathodal tDCS inhibits it, thereby indicating the capability of tDCS in either upregulation or downregulation of cortical excitability as per need. tDCS is a neuromodulation technique where lasting and immediate changes in brain function are observed.
The current used in tDCS is not strong enough to initiate an action potential of a neuron but is considered a sub-threshold where it brings about changes in the pattern of the already active neurons. The technique causes changes in the neuronal firing and helps in improving the cellular basis of learning by strengthening synaptic transmission between neurons by boosting synaptic plasticity. tDCS sessions are accompanied by training in which synergistic effects of the tDCS session and active learning further enhances synaptic plasticity.
Clinical applications of tDCS are being investigated for the treatment of various neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia, depression, addiction as well as neurological disorders such as epilepsy, aphasia, motor rehabilitation, and attention. tDCS is also being used for daily wellness purposes as well, such as relaxation, memory sharpening, and accelerated learning.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Devices Market
The tDCS devices market is in a nascent stage at present. A few products available in the market are listed below:
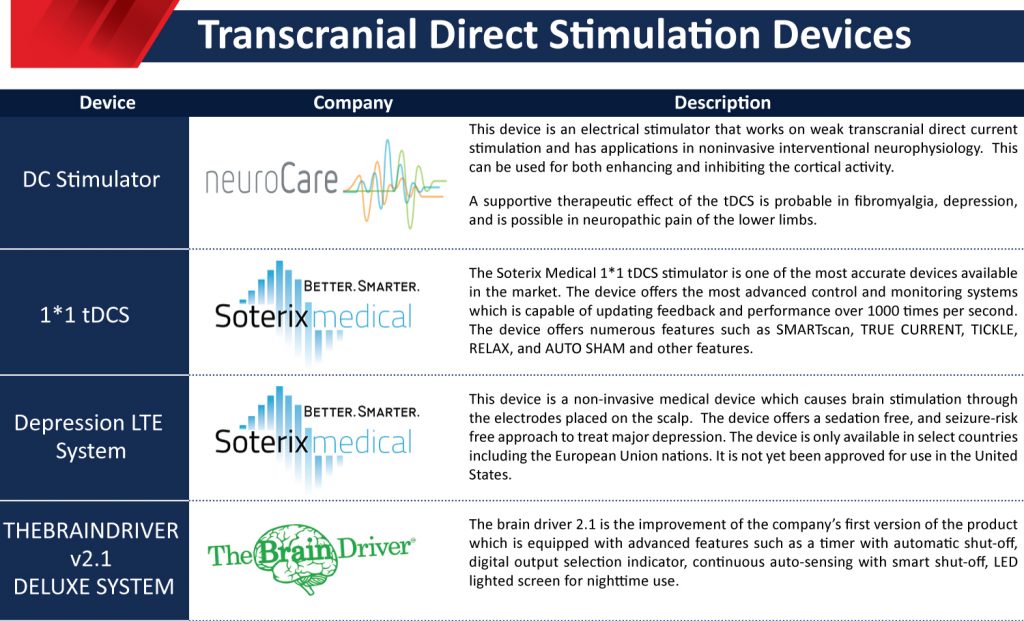
- DC Stimulator: neuroCare Group GmBH
This device is an electrical stimulator that works on weak transcranial direct current stimulation and has applications in noninvasive interventional neurophysiology. This can be used for both enhancing and inhibiting cortical activity. A supportive therapeutic effect of the tDCS is probable in fibromyalgia, depression, and is possible in neuropathic pain of the lower limbs.
- 1*1 tDCS Platform: Soterix Medical
The Soterix Medical 1*1 tDCS stimulator is one of the most accurate devices available in the market. The device offers the most advanced control and monitoring systems, which are capable of updating feedback and performance over 1000 times per second. The device offers numerous features such as SMARTscan, TRUE CURRENT, TICKLE, RELAX, and AUTO SHAM, and other features.
- Depression LTE System: Soterix Medical
This device is a non-invasive medical device that causes brain stimulation through the electrodes placed on the scalp. The device offers a sedation-free, and seizure-risk-free approach to treat major depression. The device is only available in select countries including the European Union nations. It is not yet been approved for use in the United States.
- THEBRAINDRIVER v2.1 DELUXE SYSTEM: TheBrainDriver, LLC
The brain driver 2.1 is the improvement of the company’s first version of the product which is equipped with advanced features such as a timer with automatic shut-off, digital output selection indicator, continuous auto-sensing with smart shut-off, LED lighted screen for nighttime use.
Recent Developments in the tDCS Market
The US FDA granted the Soterix Medical’s Depression LTE System an Investigational Device Exemption (IDE) in July 2020 thereby enabling the company to launch a transcranial Direct Current Stimulation-Limited Total Energy (tDCS-LTE) neuromodulation-at-home trial for patients suffering from a major depressive disorder.
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS)
Like tDCS, tACS is also a non-invasive technique that is based on the application of a low-intensity sinusoidal electric current which is applied to the brain through the scalp. It is carried out in the same way as tDCS by the placement of stimulation electrodes on the scalp. tACS differ by tDCS in the type of electrical current applied. tACS uses a sinusoidal current at a chosen frequency for the interaction with the brain’s natural cortical oscillations. This is done by the placement of a large electrode over the area of interest where stimulation is needed and a reference electrode is placed at a neutral location. On the application of a single, low frequency of less than 100 hertz, the synchronization between the exogenous oscillation and the brain’s endogenous frequency takes place.
The exact mechanism of how tACS effects are brought about is currently not understood, but it has been thought to impact brain oscillations that are involved in the cognition processes. Effects of tACS are dependent on amplitude, frequency, and phase applied. When tACS is applied in the EEG frequency range (0.1-80 Hz), it is observed to enhance neural oscillations. Cortical excitability has been suggested when higher ranges (1-5 kHz) are applied.
The technique has been tested both to improve brain function as well in brain disease treatment. tACs are being investigated in the treatment of Parkison’s disease, depression, Schizophrenia, cognitive enhancement, and motor performance.
Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation (tACS) Market
The Transcranial Alternating Current Stimulation market is highly consolidated in terms of the availability of tACS-specific products. A few of the products that are accessible in the market are listed below:
- 1*1 tACS: Soterix Medical
This device is the only electrical stimulator that is designed for transcranial alternating current stimulation. 1*1 tACS device guarantees clean sinusoidal output even when conditions are not ideal, thereby offering unmatched precision.
- Bioelectric memory patch: humm
Based on transcranial alternating current stimulation, this device is used for boosting theta waves. These waves are responsible for communicating between different parts of the brain, restoring information flow and enhancing the recalling process. It is a memory sharpening device.
Transcranial Random Noise Stimulation (tRNS)
tRNS is a relatively new technique when compared to two other two tES techniques. tRNS is similar to tACs in the way that it also employs alternating current but instead of working at a fixed frequency, tRNS switches between random frequencies and amplitude in a specified range. The mechanism behind how tRNS works in humans are not yet fully understood, studies conducted in rats presented that repetitive high-frequency stimulation led to the inward sodium currents in the neurons and weak depolarization. This was then used by other groups of researchers in a separate study that excitability enhancing effects of tRNS were reduced with the blockage of voltage-gated sodium channels.
The standalone devices for this technology are not yet available in the market. The technology is being offered as a part of the consolidated systems known as transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) devices.
Transcranial Electrical Stimulation (tES)
Transcranial electrical stimulation (tES) is a noninvasive brain stimulation technique that comprises different techniques such as tDCS, tACS, and tRNS. The market scenario for these devices is that these techniques are mostly offered as a consolidated system wherein a single device is capable of offering the three different types of electrical stimulation. tDCS is the most popular technique among the three, and many companies sell devices based only on just this technique. The market scenario for tEs devices is moderately competitive as a sizeable number of companies are active in this domain and offer a diverse product portfolio. A few of the products available in the market are described below.
- Nurostym tES: Brainbox Ltd
This device is sold by Brainbox Ltd., is a complete tES solution that offers tDCS, tACS, tRNS along with other modifications of these techniques such as AM-tACS, pulsated tDCS, and Analogue Input stimulation modes. The device offers numerous ‘state-of-the-art’ features that enable the smooth conduction of procedures.
- 1*1 tES Device: Soterix Medical
This device by Soterix Medical is specifically made for research purposes and helps in the non-invasive electrical stimulation of the brain. This system offers the reproduction of tACS, tDCS, tRNS, and tPNS protocols used in clinical trials. This device is extremely useful for research labs interested in studying tES waveforms.
- DC-STIMULATOR PLUS: neuroCare
NeuroCare offers an extensive portfolio for tES products, one of them being DC-STIMULATOR PLUS. This device is a consolidated system that offers weak currents of both alternating and direct frequencies to non-invasive interventional neurophysiology. This device is specifically constructed to be used in scientific research.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is another type of transcranial stimulation. It is also a noninvasive approach like its counterpart tES. In this, recurring magnetic energy pulses are directed at the specific brain regions which then painlessly pass through the skull. These then stimulate brain cells that then improve communication between different parts of the brain. Repetitive TMS or rTMS is the variation when TMS pulses are delivered at regular intervals. Its mode of action is still unclear but has been highly effective in boosting mood and easing depression-related symptoms. Deep TMS or dTMS is another type in which deeper and larger brain regions are stimulated. This is done by placing specialized coils about 4 centimeters beneath the skull surface.
TMS has been approved in the US only for the treatment of the major depressive disorder. This therapy can only be used when all other medication and therapy fail to make an impact in disease improvement. In European countries, TMS is approved for various indications such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, chronic pain among others. Some of the companies focusing on developing TMS devices are Magstim, Brainsway Ltd, Neuronetics Inc., TMS Neurosolutions, eNeura Therapeutics, Mag Venture, Nexstim Plc among others.
- Brainsway Deep TMS device: BrainsWay
BrainsWay’s Deep TMS device is an FDA-cleared device for the safe and effective management of the major depressive disorder. This device uses BrainsWay’s H-coil technology. Deep TMS uses a magnetic field that accesses deeper and wider regions of the brain and regulates the neural activity of regions associated with depression, specifically the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex.
- Horizon Performance: Magstim
This product of Magstim is the first FDA-cleared TMS Navigation system, which is designed to be used in clinical settings. The company offers a wide range of products offering TMS and offers a portfolio both for clinical as well as research purposes.
- SAVI: eNeura Inc.
eNeura Inc. is a medical technology company that is involved in the development of magnetic stimulation devices for migraine treatment. SAVI is an FDA-approved device that uses magnetic stimulation on the head and provides both preventive and acute treatment options for people suffering from migraines.
- MagPro R30: Mag Venture
MagPro R30 by Mag Venture is a TMS-based device that is intended to be used for both types of research as well as clinical purposes. The device performs repetitive TMS and is capable of running multiple complex protocols successively. The device has received regulatory approvals from the USFDA for major depressive disorder in adult patients. The device has also received CE mark making them accessible to European markets as well.
Recent Developments in Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Market
The Mag Venture TMS therapy received clearance from the USFDA as the adjunct treatment for obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) in August 2020.

Transcranial Stimulation Devices Market Drivers and Constraints
Even though tDCS, tACS, trNS techniques are being extensively studied and researched upon in the treatment of psychiatric disorders as well as cognitive enhancement, it has been observed that the data related to these studies have been inconsistent over the years. Some of the early studies presented positive results but recent work has failed to replicate earlier results. One of the major aspects of these devices not receiving regulatory approvals by the regulatory authorities such as the U.S. food and Drug Administration is the lack of clarity regarding the inclusion of the devices under the regulatory umbrella of the agency. Due to the inconsistency in clinical results of the efficacy of these devices, some of these devices are also available as off-label, consumer products. There are certain challenges present before the FDA if the regulatory approval of consumer devices is taken into account. In terms of establishing the safety and efficacy of consumer products, the challenge becomes enormous when that has to be established for devices improving cognitive function. However, tDCS is approved for medical treatment in European Union, Singapore, and Israel among other nations.
Conclusion
Treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders and neurological disorders has been a challenge due to the limited scope of treatment and understanding of disease pathways. Transcranial stimulation devices, being relatively new to the field of therapeutics may offer a solution for these diseases and disorders in coming years. The increasing research and development activities concerning the potential of tES in neurophysiology are indicative of the potential the technology holds in the treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases. The mechanisms of how the technique works are still being studied and multiple studies are being conducted for their characterization. Further work is required to characterize the effects of all types of stimulations on neuronal and behavioral levels. With positive results being reported across various investigatory studies and research, there are many devices that are being developed in the pipeline for their therapeutic effects. Additionally, the stance of the US FDA on regulating neuro-enhancement and treatment devices may give a major boost to the Transcranial stimulation devices market in the coming years.






-Agonist.png)


